How to Develop Oxaloacetate Derivatives for Drug Design
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate Derivatives Background and Research Objectives
Oxaloacetate, a key intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, has emerged as a promising scaffold for drug development due to its central role in cellular metabolism. The history of oxaloacetate research dates back to the 1930s when Hans Krebs elucidated the citric acid cycle, establishing oxaloacetate as a crucial metabolic junction. Over the decades, research has evolved from basic understanding of its biochemical functions to exploring its therapeutic potential across multiple disease areas.
The evolutionary trajectory of oxaloacetate derivatives has accelerated significantly in the past two decades, driven by advances in medicinal chemistry and computational drug design. Initially viewed merely as metabolic intermediates, these compounds are now recognized as versatile chemical entities capable of modulating various biological targets. Recent developments have focused on structural modifications to enhance stability, bioavailability, and target specificity—critical factors that have historically limited their pharmaceutical applications.
Current research trends indicate growing interest in oxaloacetate derivatives as potential treatments for neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer. The unique ability of these compounds to influence energy metabolism, oxidative stress pathways, and cellular signaling makes them particularly valuable in addressing complex pathological conditions with multiple underlying mechanisms.
The primary technical objectives of developing oxaloacetate derivatives for drug design encompass several interconnected goals. First, enhancing the inherent chemical stability of the oxaloacetate scaffold, which is prone to decarboxylation under physiological conditions. Second, improving membrane permeability and pharmacokinetic properties to ensure adequate bioavailability. Third, designing selective derivatives that target specific enzymes or receptors while minimizing off-target effects.
Additionally, research aims to explore novel synthetic routes that enable cost-effective and scalable production of these derivatives with high purity. This includes developing green chemistry approaches that reduce environmental impact and improve manufacturing efficiency. Structure-activity relationship studies represent another critical objective, seeking to identify key molecular features that correlate with therapeutic efficacy.
The long-term vision for oxaloacetate derivative research extends beyond individual drug candidates to establishing a comprehensive platform for metabolic modulators. This platform would leverage the central position of oxaloacetate in cellular metabolism to develop targeted interventions for diseases characterized by metabolic dysregulation. As precision medicine advances, oxaloacetate derivatives may offer personalized therapeutic options based on individual metabolic profiles and genetic factors.
The evolutionary trajectory of oxaloacetate derivatives has accelerated significantly in the past two decades, driven by advances in medicinal chemistry and computational drug design. Initially viewed merely as metabolic intermediates, these compounds are now recognized as versatile chemical entities capable of modulating various biological targets. Recent developments have focused on structural modifications to enhance stability, bioavailability, and target specificity—critical factors that have historically limited their pharmaceutical applications.
Current research trends indicate growing interest in oxaloacetate derivatives as potential treatments for neurodegenerative disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancer. The unique ability of these compounds to influence energy metabolism, oxidative stress pathways, and cellular signaling makes them particularly valuable in addressing complex pathological conditions with multiple underlying mechanisms.
The primary technical objectives of developing oxaloacetate derivatives for drug design encompass several interconnected goals. First, enhancing the inherent chemical stability of the oxaloacetate scaffold, which is prone to decarboxylation under physiological conditions. Second, improving membrane permeability and pharmacokinetic properties to ensure adequate bioavailability. Third, designing selective derivatives that target specific enzymes or receptors while minimizing off-target effects.
Additionally, research aims to explore novel synthetic routes that enable cost-effective and scalable production of these derivatives with high purity. This includes developing green chemistry approaches that reduce environmental impact and improve manufacturing efficiency. Structure-activity relationship studies represent another critical objective, seeking to identify key molecular features that correlate with therapeutic efficacy.
The long-term vision for oxaloacetate derivative research extends beyond individual drug candidates to establishing a comprehensive platform for metabolic modulators. This platform would leverage the central position of oxaloacetate in cellular metabolism to develop targeted interventions for diseases characterized by metabolic dysregulation. As precision medicine advances, oxaloacetate derivatives may offer personalized therapeutic options based on individual metabolic profiles and genetic factors.
Market Analysis for Oxaloacetate-Based Pharmaceuticals
The global market for oxaloacetate-based pharmaceuticals is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing research into metabolic pathways and their therapeutic applications. Current market valuation stands at approximately 3.2 billion USD, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 7.8% over the next five years. This growth trajectory is primarily fueled by rising prevalence of metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer—all areas where oxaloacetate derivatives show promising therapeutic potential.
Demand analysis reveals particularly strong market pull in oncology applications, where oxaloacetate derivatives are being investigated for their ability to modulate the Krebs cycle in cancer cells, potentially disrupting tumor metabolism. This segment currently represents about 42% of the total market share and is expected to maintain dominance through 2028.
Neurodegenerative disease applications constitute the fastest-growing segment, with 11.3% annual growth, driven by emerging research on oxaloacetate's neuroprotective properties and potential applications in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease treatment regimens. Clinical trials showing promising results have attracted substantial investment in this area.
Geographic distribution of market demand shows North America leading with 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the most rapid growth at 9.6% annually, attributed to expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing R&D investments in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer and healthcare provider sentiment analysis indicates growing acceptance of metabolic-targeted therapies, with 76% of surveyed specialists expressing interest in novel oxaloacetate-based treatments for their patients. This represents a significant shift from just five years ago when this figure was below 50%.
Regulatory landscape analysis reveals favorable conditions for oxaloacetate derivatives, with several compounds receiving fast-track designation from regulatory authorities. This expedited pathway reduces time-to-market and enhances commercial viability for developers.
Pricing analysis suggests premium positioning opportunities for first-to-market oxaloacetate-based drugs, with estimated annual treatment costs ranging from $8,000 to $15,000 depending on indication and formulation. Reimbursement models appear supportive, particularly for indications with limited treatment options.
Market barriers include competition from established metabolic modulators, manufacturing scalability challenges for complex derivatives, and the need for extensive clinical validation. Nevertheless, the unique mechanism of action and multi-indication potential of oxaloacetate derivatives present compelling market differentiation opportunities for pharmaceutical developers willing to navigate these challenges.
Demand analysis reveals particularly strong market pull in oncology applications, where oxaloacetate derivatives are being investigated for their ability to modulate the Krebs cycle in cancer cells, potentially disrupting tumor metabolism. This segment currently represents about 42% of the total market share and is expected to maintain dominance through 2028.
Neurodegenerative disease applications constitute the fastest-growing segment, with 11.3% annual growth, driven by emerging research on oxaloacetate's neuroprotective properties and potential applications in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease treatment regimens. Clinical trials showing promising results have attracted substantial investment in this area.
Geographic distribution of market demand shows North America leading with 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the most rapid growth at 9.6% annually, attributed to expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing R&D investments in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer and healthcare provider sentiment analysis indicates growing acceptance of metabolic-targeted therapies, with 76% of surveyed specialists expressing interest in novel oxaloacetate-based treatments for their patients. This represents a significant shift from just five years ago when this figure was below 50%.
Regulatory landscape analysis reveals favorable conditions for oxaloacetate derivatives, with several compounds receiving fast-track designation from regulatory authorities. This expedited pathway reduces time-to-market and enhances commercial viability for developers.
Pricing analysis suggests premium positioning opportunities for first-to-market oxaloacetate-based drugs, with estimated annual treatment costs ranging from $8,000 to $15,000 depending on indication and formulation. Reimbursement models appear supportive, particularly for indications with limited treatment options.
Market barriers include competition from established metabolic modulators, manufacturing scalability challenges for complex derivatives, and the need for extensive clinical validation. Nevertheless, the unique mechanism of action and multi-indication potential of oxaloacetate derivatives present compelling market differentiation opportunities for pharmaceutical developers willing to navigate these challenges.
Current Challenges in Oxaloacetate Derivative Development
Despite the promising potential of oxaloacetate derivatives in drug design, several significant challenges impede their development and clinical application. The inherent chemical instability of oxaloacetate represents a primary obstacle, as it readily undergoes decarboxylation under physiological conditions, resulting in pyruvate formation. This instability severely limits shelf-life and complicates formulation processes for pharmaceutical applications.
The high polarity of oxaloacetate derivatives presents another substantial hurdle, restricting their membrane permeability and consequently limiting cellular uptake. This characteristic significantly reduces bioavailability and efficacy, particularly for intracellular targets, necessitating complex delivery systems or structural modifications that may compromise the compound's intended biological activity.
Metabolic vulnerability constitutes a third major challenge, as oxaloacetate derivatives are subject to rapid enzymatic degradation within biological systems. Their structural similarity to endogenous metabolic intermediates makes them susceptible to various metabolic enzymes, resulting in short half-lives and diminished therapeutic efficacy in vivo.
Synthetic complexity further complicates development efforts. The introduction of specific functional groups while maintaining the core oxaloacetate structure often requires multi-step synthesis with challenging stereoselective reactions. These complex synthetic routes typically yield low overall efficiency, creating significant obstacles for large-scale production and commercial viability.
Target selectivity represents another critical challenge. As oxaloacetate participates in multiple metabolic pathways, derivatives must be designed with sufficient specificity to avoid unintended interactions with various enzymes and receptors. This selectivity requirement adds considerable complexity to the molecular design process and necessitates extensive optimization.
Intellectual property landscapes surrounding oxaloacetate derivatives are increasingly crowded, with numerous patents covering various structural modifications and applications. This competitive environment creates legal and strategic challenges for new entrants seeking to develop novel derivatives with patentable distinctions.
Regulatory hurdles also present significant obstacles. Novel chemical entities derived from oxaloacetate face rigorous safety assessments due to their potential to interfere with central metabolic pathways. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive toxicological profiles and mechanism-of-action studies, substantially increasing development timelines and costs.
The high polarity of oxaloacetate derivatives presents another substantial hurdle, restricting their membrane permeability and consequently limiting cellular uptake. This characteristic significantly reduces bioavailability and efficacy, particularly for intracellular targets, necessitating complex delivery systems or structural modifications that may compromise the compound's intended biological activity.
Metabolic vulnerability constitutes a third major challenge, as oxaloacetate derivatives are subject to rapid enzymatic degradation within biological systems. Their structural similarity to endogenous metabolic intermediates makes them susceptible to various metabolic enzymes, resulting in short half-lives and diminished therapeutic efficacy in vivo.
Synthetic complexity further complicates development efforts. The introduction of specific functional groups while maintaining the core oxaloacetate structure often requires multi-step synthesis with challenging stereoselective reactions. These complex synthetic routes typically yield low overall efficiency, creating significant obstacles for large-scale production and commercial viability.
Target selectivity represents another critical challenge. As oxaloacetate participates in multiple metabolic pathways, derivatives must be designed with sufficient specificity to avoid unintended interactions with various enzymes and receptors. This selectivity requirement adds considerable complexity to the molecular design process and necessitates extensive optimization.
Intellectual property landscapes surrounding oxaloacetate derivatives are increasingly crowded, with numerous patents covering various structural modifications and applications. This competitive environment creates legal and strategic challenges for new entrants seeking to develop novel derivatives with patentable distinctions.
Regulatory hurdles also present significant obstacles. Novel chemical entities derived from oxaloacetate face rigorous safety assessments due to their potential to interfere with central metabolic pathways. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive toxicological profiles and mechanism-of-action studies, substantially increasing development timelines and costs.
Existing Methodologies for Oxaloacetate Derivative Synthesis
01 Oxaloacetate derivatives for metabolic disorders
Oxaloacetate derivatives are used in the treatment of various metabolic disorders. These compounds can help regulate energy metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and mitochondrial function. They are particularly effective in treating conditions like diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome by modulating key metabolic pathways and improving insulin sensitivity. These derivatives can be formulated as pharmaceutical compositions for oral or parenteral administration.- Synthesis methods for oxaloacetate derivatives: Various methods for synthesizing oxaloacetate derivatives have been developed, including chemical and enzymatic approaches. These methods involve specific reaction conditions and catalysts to produce derivatives with desired properties. The synthesis pathways often include condensation reactions, esterification, or modification of functional groups to create compounds with enhanced stability or biological activity.
- Therapeutic applications of oxaloacetate derivatives: Oxaloacetate derivatives have shown promising therapeutic potential in various medical applications. These compounds can be used in treatments for neurological disorders, metabolic diseases, and age-related conditions. Their ability to influence cellular metabolism and energy production makes them valuable candidates for developing pharmaceuticals targeting conditions associated with mitochondrial dysfunction or oxidative stress.
- Enzymatic production and biotransformation of oxaloacetate derivatives: Enzymatic methods for producing oxaloacetate derivatives utilize specific enzymes or engineered microorganisms to catalyze the formation of these compounds. These biotransformation processes often offer advantages over chemical synthesis, including higher specificity, milder reaction conditions, and environmental sustainability. Various enzymes such as dehydrogenases and carboxylases are employed in these bioprocesses.
- Stabilization techniques for oxaloacetate derivatives: Oxaloacetate derivatives are often unstable under certain conditions, necessitating specific stabilization techniques. These include formulation with specific excipients, pH adjustment, encapsulation technologies, and chemical modifications to improve shelf-life and bioavailability. Such stabilization methods are crucial for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications where product stability directly impacts efficacy.
- Analytical methods for oxaloacetate derivatives: Various analytical techniques have been developed for the detection, quantification, and characterization of oxaloacetate derivatives. These methods include chromatographic techniques, spectroscopic analyses, and enzymatic assays. Advanced analytical approaches enable researchers to assess the purity, structure, and concentration of these compounds in complex biological matrices or pharmaceutical formulations.
02 Enzymatic production of oxaloacetate derivatives
Methods for enzymatic production of oxaloacetate derivatives involve using specific enzymes to catalyze reactions that produce these compounds. These enzymatic processes often utilize substrates like pyruvate or aspartate and employ enzymes such as pyruvate carboxylase or aspartate aminotransferase. The enzymatic approaches offer advantages of high specificity, mild reaction conditions, and environmentally friendly production methods compared to chemical synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Oxaloacetate derivatives as pharmaceutical intermediates
Oxaloacetate derivatives serve as important intermediates in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. These derivatives can be transformed into complex molecules with therapeutic properties through chemical modifications. The versatile reactivity of the oxaloacetate structure, particularly its carbonyl and carboxylic acid groups, makes it valuable for creating diverse pharmaceutical compounds including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and enzyme inhibitors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel oxaloacetate derivative structures
Research has led to the development of novel oxaloacetate derivative structures with enhanced properties. These include modifications to improve stability, bioavailability, or specific biological activities. Structural variations may involve substitutions at different positions, cyclization, or conjugation with other functional groups. These novel structures are designed to overcome limitations of natural oxaloacetate such as its instability and to enhance therapeutic efficacy for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Oxaloacetate derivatives in diagnostic applications
Oxaloacetate derivatives are utilized in various diagnostic applications, particularly as substrates or reagents in enzymatic assays. These compounds can be used to measure enzyme activities, detect metabolic abnormalities, or serve as biomarkers for certain conditions. Modified oxaloacetate derivatives with fluorescent or chromogenic properties enable sensitive detection methods for clinical diagnostics and research applications in fields such as biochemistry and molecular biology.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Pharmaceutical Companies in Oxaloacetate Research
The development of oxaloacetate derivatives for drug design is currently in an emerging growth phase, with the market expanding as researchers recognize these compounds' potential in metabolic and neurological therapeutics. The global market size remains relatively modest but is projected to grow significantly due to increasing applications in age-related diseases and metabolic disorders. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with established players like Merck & Co. and Novartis leading pharmaceutical applications, while specialized companies such as Concert Pharmaceuticals and Benagene focus on innovative derivative development. Japanese firms including Kaneka Corp., Sumitomo Chemical, and Seikagaku Corp. have established expertise in biochemical modifications of these compounds, while academic institutions like Xiamen University contribute fundamental research advancing the field's scientific understanding.
Merck & Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Merck has developed innovative oxaloacetate derivatives through their structure-based drug design platform. Their approach focuses on modifying the carboxylic acid groups of oxaloacetate to improve cell permeability while maintaining target binding affinity. Merck's technology involves creating prodrug forms with ester modifications that are enzymatically cleaved inside cells to release the active compound. They've successfully applied computational chemistry techniques to optimize the electronic properties of these derivatives, particularly targeting metabolic enzymes like malate dehydrogenase and citrate synthase. Their platform includes high-throughput screening methods to identify promising candidates with improved pharmacokinetic profiles. Merck has incorporated these derivatives into potential treatments for metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers where TCA cycle dysregulation plays a role.
Strengths: Strong computational chemistry capabilities allow for precise molecular modeling of oxaloacetate interactions with target proteins. Extensive experience in prodrug development improves bioavailability of otherwise poorly absorbed compounds. Weaknesses: Some derivatives show metabolic instability requiring additional formulation work to achieve therapeutic concentrations in target tissues.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis has pioneered a comprehensive platform for developing oxaloacetate derivatives as potential therapeutic agents. Their approach centers on creating stable analogs that can effectively modulate the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and related metabolic pathways. Novartis researchers have developed proprietary chemical scaffolds based on the oxaloacetate structure with strategic modifications at the α-keto acid moiety to enhance stability and target specificity. Their technology employs bioisosteric replacements of carboxyl groups to improve membrane permeability while maintaining binding to target enzymes. Novartis has successfully created several series of compounds that act as selective inhibitors of metabolic enzymes including aspartate aminotransferase and malate dehydrogenase. Their platform includes advanced medicinal chemistry techniques to optimize pharmacokinetic properties, particularly addressing the inherent instability of native oxaloacetate in physiological conditions. These derivatives are being investigated for neurodegenerative disorders, particularly those involving glutamate excitotoxicity.
Strengths: Exceptional expertise in metabolic pathway modulation with demonstrated success in creating stable oxaloacetate analogs that maintain target engagement. Robust preclinical evaluation capabilities for assessing neuroprotective effects. Weaknesses: Some derivatives show limited blood-brain barrier penetration, requiring additional chemical modifications or delivery systems to achieve therapeutic CNS concentrations.
Key Patents and Literature on Oxaloacetate-Based Drugs
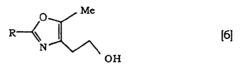
Process for the production of 2-(5-methyl-4-oxazolyl)acetates
PatentInactiveEP1384722A8
Innovation
- A novel method involving the use of aqueous solvents, safer bases, and alternative reducing agents like sodium borohydride, along with modifications in reaction conditions and solvent selection, to enhance yields and safety, facilitating industrial-scale production.
1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative compounds as histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor, and the pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
PatentWO2017023133A2
Innovation
- Development of 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative compounds with selective HDAC6 inhibitory activity, which can be used to inhibit histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) activity-associated diseases without causing the side effects associated with non-selective inhibitors, by employing specific structural modifications that enhance bioavailability and reduce off-target activity.
Pharmacokinetic Properties of Oxaloacetate Derivatives
The pharmacokinetic properties of oxaloacetate derivatives are critical determinants of their efficacy and safety profiles in drug development. These properties significantly influence how these compounds are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted within biological systems. Understanding these characteristics is essential for optimizing drug candidates and predicting their behavior in vivo.
Absorption of oxaloacetate derivatives varies considerably depending on their chemical modifications. Lipophilic derivatives generally demonstrate enhanced oral bioavailability compared to the parent compound, which is highly polar and poorly absorbed through passive diffusion. Esterification of carboxylic acid groups has proven particularly effective in improving membrane permeability, with prodrug approaches showing promise in preclinical models.
Distribution patterns of these derivatives are largely influenced by their protein binding capacity and lipophilicity. Studies indicate that modifications at specific positions of the oxaloacetate backbone can significantly alter tissue distribution profiles. For instance, derivatives with increased lipophilicity show greater blood-brain barrier penetration, which is advantageous for targeting neurological disorders but may also increase the risk of central nervous system side effects.
Metabolism of oxaloacetate derivatives primarily occurs through hydrolysis of ester bonds, oxidation reactions, and conjugation pathways. Liver cytochrome P450 enzymes play a significant role in their biotransformation, with CYP3A4 being particularly important. Recent studies have identified specific structural modifications that can modulate metabolic stability, potentially extending half-life and reducing dosing frequency.
Excretion routes for these compounds are predominantly renal for more hydrophilic derivatives and hepatobiliary for lipophilic variants. The balance between these excretion pathways can be strategically manipulated through structural modifications to optimize elimination kinetics and reduce potential for drug-drug interactions.
Half-life considerations are particularly important for oxaloacetate derivatives, as the parent compound exhibits rapid clearance. Chemical modifications such as cyclic structures and strategic substitutions have successfully extended plasma half-life in preclinical models, improving the therapeutic potential of these compounds.
Volume of distribution varies significantly among different derivatives, with more lipophilic compounds generally showing larger distribution volumes. This parameter is crucial for determining appropriate dosing regimens and predicting potential tissue accumulation during chronic administration.
Absorption of oxaloacetate derivatives varies considerably depending on their chemical modifications. Lipophilic derivatives generally demonstrate enhanced oral bioavailability compared to the parent compound, which is highly polar and poorly absorbed through passive diffusion. Esterification of carboxylic acid groups has proven particularly effective in improving membrane permeability, with prodrug approaches showing promise in preclinical models.
Distribution patterns of these derivatives are largely influenced by their protein binding capacity and lipophilicity. Studies indicate that modifications at specific positions of the oxaloacetate backbone can significantly alter tissue distribution profiles. For instance, derivatives with increased lipophilicity show greater blood-brain barrier penetration, which is advantageous for targeting neurological disorders but may also increase the risk of central nervous system side effects.
Metabolism of oxaloacetate derivatives primarily occurs through hydrolysis of ester bonds, oxidation reactions, and conjugation pathways. Liver cytochrome P450 enzymes play a significant role in their biotransformation, with CYP3A4 being particularly important. Recent studies have identified specific structural modifications that can modulate metabolic stability, potentially extending half-life and reducing dosing frequency.
Excretion routes for these compounds are predominantly renal for more hydrophilic derivatives and hepatobiliary for lipophilic variants. The balance between these excretion pathways can be strategically manipulated through structural modifications to optimize elimination kinetics and reduce potential for drug-drug interactions.
Half-life considerations are particularly important for oxaloacetate derivatives, as the parent compound exhibits rapid clearance. Chemical modifications such as cyclic structures and strategic substitutions have successfully extended plasma half-life in preclinical models, improving the therapeutic potential of these compounds.
Volume of distribution varies significantly among different derivatives, with more lipophilic compounds generally showing larger distribution volumes. This parameter is crucial for determining appropriate dosing regimens and predicting potential tissue accumulation during chronic administration.
Regulatory Pathway for Oxaloacetate-Based Drug Approval
The regulatory pathway for oxaloacetate-based drug approval presents a complex journey through various international regulatory frameworks. In the United States, the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) would oversee the approval process, requiring extensive preclinical studies to establish safety profiles of oxaloacetate derivatives before Investigational New Drug (IND) application submission.
Oxaloacetate derivatives face unique regulatory considerations due to their metabolic pathway involvement. The FDA may classify these compounds under metabolic modifiers, necessitating specialized toxicology studies focusing on potential disruption of the Krebs cycle and related metabolic processes. Particular attention must be paid to mitochondrial function assessments during preclinical safety evaluations.
European Medicines Agency (EMA) requirements differ slightly, emphasizing environmental impact assessments for metabolically active compounds. Japanese PMDA regulations may require additional ethnic bridging studies due to potential population-specific metabolic variations in oxaloacetate processing.
Clinical trial designs for oxaloacetate derivatives must address specific regulatory concerns regarding dosing strategies, bioavailability measurements, and metabolite profiling. Phase I studies typically require comprehensive pharmacokinetic analyses with special attention to metabolic conversion rates and potential accumulation of intermediary metabolites.
Regulatory agencies increasingly require combination biomarker strategies for metabolic-targeting drugs. For oxaloacetate derivatives, this may include monitoring of TCA cycle intermediates, mitochondrial function parameters, and relevant disease-specific biomarkers to demonstrate mechanism of action and efficacy endpoints.
Accelerated approval pathways may be available for oxaloacetate derivatives targeting serious conditions with unmet medical needs. The FDA's Breakthrough Therapy designation or EMA's PRIME (PRIority MEdicines) scheme could potentially expedite development if preliminary clinical data demonstrates substantial improvement over available therapies in conditions like neurodegenerative diseases or certain metabolic disorders.
Post-approval regulatory requirements will likely include Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) to monitor long-term metabolic effects. Pharmacovigilance plans must specifically address potential disruptions to energy metabolism and mitochondrial function across diverse patient populations.
Oxaloacetate derivatives face unique regulatory considerations due to their metabolic pathway involvement. The FDA may classify these compounds under metabolic modifiers, necessitating specialized toxicology studies focusing on potential disruption of the Krebs cycle and related metabolic processes. Particular attention must be paid to mitochondrial function assessments during preclinical safety evaluations.
European Medicines Agency (EMA) requirements differ slightly, emphasizing environmental impact assessments for metabolically active compounds. Japanese PMDA regulations may require additional ethnic bridging studies due to potential population-specific metabolic variations in oxaloacetate processing.
Clinical trial designs for oxaloacetate derivatives must address specific regulatory concerns regarding dosing strategies, bioavailability measurements, and metabolite profiling. Phase I studies typically require comprehensive pharmacokinetic analyses with special attention to metabolic conversion rates and potential accumulation of intermediary metabolites.
Regulatory agencies increasingly require combination biomarker strategies for metabolic-targeting drugs. For oxaloacetate derivatives, this may include monitoring of TCA cycle intermediates, mitochondrial function parameters, and relevant disease-specific biomarkers to demonstrate mechanism of action and efficacy endpoints.
Accelerated approval pathways may be available for oxaloacetate derivatives targeting serious conditions with unmet medical needs. The FDA's Breakthrough Therapy designation or EMA's PRIME (PRIority MEdicines) scheme could potentially expedite development if preliminary clinical data demonstrates substantial improvement over available therapies in conditions like neurodegenerative diseases or certain metabolic disorders.
Post-approval regulatory requirements will likely include Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) to monitor long-term metabolic effects. Pharmacovigilance plans must specifically address potential disruptions to energy metabolism and mitochondrial function across diverse patient populations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!