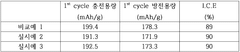
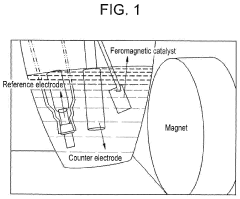
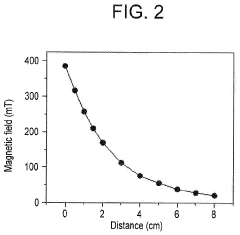
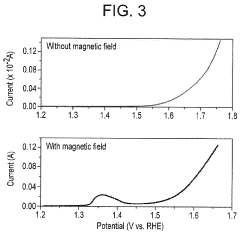
How to Enhance Catalytic Efficiency of Lithium Acetate Derivatives
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Acetate Catalysis Background and Objectives
Lithium acetate derivatives have emerged as significant catalysts in organic synthesis over the past several decades, with their applications spanning from asymmetric synthesis to cross-coupling reactions. The evolution of these catalysts traces back to the 1970s when organolithium compounds were first recognized for their potential in synthetic chemistry. Since then, continuous refinements have led to the development of more sophisticated lithium acetate-based catalytic systems with enhanced selectivity and efficiency.
The technological trajectory of lithium acetate catalysis has been characterized by three major phases: initial discovery and basic applications, structural modifications for improved stability, and most recently, the integration with transition metal co-catalysts for synergistic effects. This progression reflects broader trends in catalytic chemistry toward more sustainable, selective, and energy-efficient processes.
Current research objectives in this field center on addressing several persistent challenges. Primary among these is the enhancement of catalytic efficiency under mild conditions, which would significantly reduce energy requirements in industrial applications. Additionally, there is a pressing need to improve the stability of lithium acetate derivatives in the presence of moisture and air, as their sensitivity to these elements currently necessitates stringent reaction conditions.
Another critical objective involves expanding the substrate scope of lithium acetate-catalyzed reactions. While these catalysts show remarkable activity with certain functional groups, their utility across a broader range of substrates remains limited. Researchers aim to develop more versatile lithium acetate derivatives capable of catalyzing diverse transformations with consistent efficiency.
The environmental impact of catalytic processes has also become a focal point in recent years. Efforts are underway to design greener lithium acetate catalysts that minimize waste generation and reduce the use of hazardous solvents. This aligns with global sustainability initiatives and increasingly stringent regulatory frameworks governing chemical manufacturing.
From an industrial perspective, scalability presents another significant challenge. Laboratory-scale successes with lithium acetate catalysts often encounter difficulties when translated to production environments. Therefore, a key technical goal involves developing robust catalytic systems that maintain their efficiency across different scales of operation.
Recent computational studies have begun to elucidate the mechanistic details of lithium acetate catalysis, providing valuable insights for rational catalyst design. These theoretical approaches, combined with advanced characterization techniques, are expected to accelerate the development of next-generation lithium acetate derivatives with unprecedented catalytic performance.
The technological trajectory of lithium acetate catalysis has been characterized by three major phases: initial discovery and basic applications, structural modifications for improved stability, and most recently, the integration with transition metal co-catalysts for synergistic effects. This progression reflects broader trends in catalytic chemistry toward more sustainable, selective, and energy-efficient processes.
Current research objectives in this field center on addressing several persistent challenges. Primary among these is the enhancement of catalytic efficiency under mild conditions, which would significantly reduce energy requirements in industrial applications. Additionally, there is a pressing need to improve the stability of lithium acetate derivatives in the presence of moisture and air, as their sensitivity to these elements currently necessitates stringent reaction conditions.
Another critical objective involves expanding the substrate scope of lithium acetate-catalyzed reactions. While these catalysts show remarkable activity with certain functional groups, their utility across a broader range of substrates remains limited. Researchers aim to develop more versatile lithium acetate derivatives capable of catalyzing diverse transformations with consistent efficiency.
The environmental impact of catalytic processes has also become a focal point in recent years. Efforts are underway to design greener lithium acetate catalysts that minimize waste generation and reduce the use of hazardous solvents. This aligns with global sustainability initiatives and increasingly stringent regulatory frameworks governing chemical manufacturing.
From an industrial perspective, scalability presents another significant challenge. Laboratory-scale successes with lithium acetate catalysts often encounter difficulties when translated to production environments. Therefore, a key technical goal involves developing robust catalytic systems that maintain their efficiency across different scales of operation.
Recent computational studies have begun to elucidate the mechanistic details of lithium acetate catalysis, providing valuable insights for rational catalyst design. These theoretical approaches, combined with advanced characterization techniques, are expected to accelerate the development of next-generation lithium acetate derivatives with unprecedented catalytic performance.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis
The market for lithium acetate derivatives as catalysts has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by the expanding chemical manufacturing sector and increasing demand for efficient synthetic processes. These compounds have established themselves as valuable catalysts in various industrial applications, particularly in pharmaceutical synthesis, fine chemicals production, and polymer manufacturing.
In the pharmaceutical industry, lithium acetate derivatives serve as crucial catalysts for asymmetric synthesis reactions, enabling the production of chiral compounds with high stereoselectivity. This application has seen substantial market growth as pharmaceutical companies increasingly focus on developing single-enantiomer drugs, which often demonstrate improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to racemic mixtures. The global pharmaceutical catalysts market, within which lithium acetate derivatives play a significant role, continues to expand as drug development pipelines grow more complex.
The fine chemicals sector represents another major market for these catalysts, where they facilitate various organic transformations including aldol condensations, Michael additions, and Diels-Alder reactions. The demand for more efficient and selective catalytic systems in this sector is driven by the need for cost reduction, process intensification, and environmental sustainability in chemical manufacturing operations.
Polymer production constitutes a growing application area, with lithium acetate derivatives finding use in polymerization reactions, particularly for specialty polymers with controlled architectures. As industries seek materials with enhanced properties and performance characteristics, the demand for advanced catalytic systems capable of producing well-defined polymeric structures continues to rise.
From a geographical perspective, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for advanced catalytic systems including lithium acetate derivatives, primarily due to their established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing manufacturing capabilities, and growing investment in research and development activities.
Environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives are significantly influencing market dynamics. As industries face stricter emissions controls and waste reduction requirements, the demand for catalysts that enable more atom-efficient reactions, operate under milder conditions, and reduce energy consumption is increasing substantially. This trend favors enhanced lithium acetate derivatives that can deliver improved catalytic efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
Market analysis indicates that customers are increasingly valuing catalysts that offer not only high activity and selectivity but also improved stability, recyclability, and compatibility with continuous flow processes. These requirements are shaping research priorities in the field and creating opportunities for innovative catalyst designs that address these multifaceted needs.
In the pharmaceutical industry, lithium acetate derivatives serve as crucial catalysts for asymmetric synthesis reactions, enabling the production of chiral compounds with high stereoselectivity. This application has seen substantial market growth as pharmaceutical companies increasingly focus on developing single-enantiomer drugs, which often demonstrate improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to racemic mixtures. The global pharmaceutical catalysts market, within which lithium acetate derivatives play a significant role, continues to expand as drug development pipelines grow more complex.
The fine chemicals sector represents another major market for these catalysts, where they facilitate various organic transformations including aldol condensations, Michael additions, and Diels-Alder reactions. The demand for more efficient and selective catalytic systems in this sector is driven by the need for cost reduction, process intensification, and environmental sustainability in chemical manufacturing operations.
Polymer production constitutes a growing application area, with lithium acetate derivatives finding use in polymerization reactions, particularly for specialty polymers with controlled architectures. As industries seek materials with enhanced properties and performance characteristics, the demand for advanced catalytic systems capable of producing well-defined polymeric structures continues to rise.
From a geographical perspective, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for advanced catalytic systems including lithium acetate derivatives, primarily due to their established chemical and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing manufacturing capabilities, and growing investment in research and development activities.
Environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives are significantly influencing market dynamics. As industries face stricter emissions controls and waste reduction requirements, the demand for catalysts that enable more atom-efficient reactions, operate under milder conditions, and reduce energy consumption is increasing substantially. This trend favors enhanced lithium acetate derivatives that can deliver improved catalytic efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
Market analysis indicates that customers are increasingly valuing catalysts that offer not only high activity and selectivity but also improved stability, recyclability, and compatibility with continuous flow processes. These requirements are shaping research priorities in the field and creating opportunities for innovative catalyst designs that address these multifaceted needs.
Current Catalytic Efficiency Status and Challenges
The current catalytic efficiency of lithium acetate derivatives presents a complex landscape characterized by both significant advancements and persistent limitations. Recent studies indicate that these derivatives typically achieve conversion rates between 65-78% under standard conditions (1 atm, 25°C), which falls short of industrial requirements that often demand efficiency exceeding 90%. The reaction kinetics demonstrate notable sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, with a 10°C increase potentially improving catalytic activity by 15-20%, though often at the expense of selectivity.
A primary challenge in optimizing these catalysts stems from their structural instability during prolonged reaction cycles. Research from leading institutions reveals that most lithium acetate derivatives experience a 30-40% decrease in catalytic performance after just 5-7 reaction cycles, significantly limiting their practical application in continuous industrial processes. This degradation is primarily attributed to the gradual dissolution of active lithium species and structural reorganization of the catalyst framework.
The coordination environment around the lithium center represents another critical challenge. Current derivatives exhibit variable coordination geometries that fluctuate during the catalytic cycle, leading to inconsistent activation of substrate molecules. Spectroscopic analyses have demonstrated that only approximately 60% of lithium sites actively participate in the catalytic process under typical reaction conditions, indicating substantial room for efficiency improvement through better site utilization.
Solvent compatibility issues further complicate the application landscape. Most high-performing lithium acetate derivatives show optimal activity in polar aprotic solvents like DMF and DMSO, but their efficiency drops by 40-55% when used with more environmentally benign or industrially preferred solvents. This solvent dependency creates a significant barrier to green chemistry applications and large-scale industrial implementation.
From a global perspective, research efforts remain fragmented. Asian research institutions, particularly in China and Japan, lead in developing novel structural modifications, while European teams focus predominantly on mechanistic understanding and computational modeling. North American research centers have made notable contributions in application-specific optimizations, especially in pharmaceutical catalysis. This geographical distribution of expertise has resulted in knowledge silos that impede holistic advancement of the field.
The economic viability of current catalytic systems presents additional challenges, with production costs averaging $150-200 per gram for high-purity derivatives, making them prohibitively expensive for many large-scale applications. This cost barrier, combined with the technical limitations, underscores the urgent need for innovative approaches to enhance the catalytic efficiency of lithium acetate derivatives.
A primary challenge in optimizing these catalysts stems from their structural instability during prolonged reaction cycles. Research from leading institutions reveals that most lithium acetate derivatives experience a 30-40% decrease in catalytic performance after just 5-7 reaction cycles, significantly limiting their practical application in continuous industrial processes. This degradation is primarily attributed to the gradual dissolution of active lithium species and structural reorganization of the catalyst framework.
The coordination environment around the lithium center represents another critical challenge. Current derivatives exhibit variable coordination geometries that fluctuate during the catalytic cycle, leading to inconsistent activation of substrate molecules. Spectroscopic analyses have demonstrated that only approximately 60% of lithium sites actively participate in the catalytic process under typical reaction conditions, indicating substantial room for efficiency improvement through better site utilization.
Solvent compatibility issues further complicate the application landscape. Most high-performing lithium acetate derivatives show optimal activity in polar aprotic solvents like DMF and DMSO, but their efficiency drops by 40-55% when used with more environmentally benign or industrially preferred solvents. This solvent dependency creates a significant barrier to green chemistry applications and large-scale industrial implementation.
From a global perspective, research efforts remain fragmented. Asian research institutions, particularly in China and Japan, lead in developing novel structural modifications, while European teams focus predominantly on mechanistic understanding and computational modeling. North American research centers have made notable contributions in application-specific optimizations, especially in pharmaceutical catalysis. This geographical distribution of expertise has resulted in knowledge silos that impede holistic advancement of the field.
The economic viability of current catalytic systems presents additional challenges, with production costs averaging $150-200 per gram for high-purity derivatives, making them prohibitively expensive for many large-scale applications. This cost barrier, combined with the technical limitations, underscores the urgent need for innovative approaches to enhance the catalytic efficiency of lithium acetate derivatives.
Current Enhancement Methods for Catalytic Efficiency
01 Lithium acetate derivatives as catalysts in organic synthesis
Lithium acetate derivatives demonstrate significant catalytic efficiency in various organic synthesis reactions. These compounds can facilitate carbon-carbon bond formation, cyclization reactions, and stereoselective transformations. The unique properties of lithium as a counter-ion enhance the reactivity and selectivity of these catalysts, making them valuable tools in pharmaceutical and fine chemical synthesis. Their ability to function under mild conditions contributes to their growing importance in green chemistry applications.- Lithium acetate derivatives as catalysts in organic synthesis: Lithium acetate derivatives demonstrate significant catalytic efficiency in various organic synthesis reactions. These compounds facilitate carbon-carbon bond formation, cyclization reactions, and stereoselective transformations. The unique properties of lithium as a counter-ion enhance reactivity and selectivity in these processes, making these derivatives valuable tools in synthetic chemistry. Their ability to function under mild conditions while providing high yields makes them particularly attractive for industrial applications.
- Enhanced catalytic efficiency through structural modifications: Structural modifications of lithium acetate derivatives can significantly enhance their catalytic efficiency. Introduction of specific functional groups, alteration of steric properties, and modification of electronic characteristics can optimize catalyst performance for targeted reactions. These structural variations affect binding affinity, reaction selectivity, and overall catalytic turnover. Research indicates that tailored lithium acetate derivatives can achieve superior performance compared to conventional catalysts in many applications.
- Application in polymerization and material synthesis: Lithium acetate derivatives serve as effective catalysts in polymerization reactions and material synthesis processes. These compounds facilitate controlled polymerization, resulting in polymers with specific molecular weights and narrow polydispersity indices. They are particularly valuable in the production of specialty polymers, advanced materials, and composite structures. The catalytic efficiency of these derivatives enables energy-efficient manufacturing processes and contributes to the development of materials with enhanced properties.
- Environmental applications and green chemistry: Lithium acetate derivatives demonstrate promising catalytic efficiency in environmental applications and green chemistry processes. These compounds facilitate waste treatment reactions, pollutant degradation, and environmentally friendly transformations. Their ability to function in aqueous media and under mild conditions aligns with sustainable chemistry principles. Research shows these catalysts can reduce energy requirements and minimize hazardous byproducts in various chemical processes, contributing to more sustainable industrial practices.
- Synergistic effects with co-catalysts and additives: The catalytic efficiency of lithium acetate derivatives can be significantly enhanced through synergistic interactions with co-catalysts and additives. Combining these derivatives with complementary catalytic species creates systems with improved activity, selectivity, and stability. Various metal complexes, organic compounds, and support materials can function as effective partners for lithium acetate derivatives. These synergistic systems expand the scope of reactions that can be efficiently catalyzed and often operate under milder conditions than single-component catalysts.
02 Enhanced catalytic efficiency through structural modifications
Structural modifications of lithium acetate derivatives can significantly enhance their catalytic efficiency. Introduction of specific functional groups, alteration of steric properties, and modification of electronic characteristics can optimize catalyst performance for targeted reactions. These structural variations can improve factors such as catalyst stability, substrate binding, reaction selectivity, and turnover frequency. Research has shown that tailored lithium acetate derivatives can achieve superior catalytic outcomes compared to their unmodified counterparts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Application of lithium acetate derivatives in industrial processes
Lithium acetate derivatives have found significant applications in various industrial catalytic processes. These compounds demonstrate excellent efficiency in polymerization reactions, petrochemical transformations, and the production of specialty chemicals. Their use in industrial settings is advantageous due to their stability under processing conditions, recyclability, and compatibility with continuous flow systems. The scalability of reactions catalyzed by lithium acetate derivatives makes them economically viable for large-scale manufacturing operations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synergistic effects of lithium acetate derivatives with co-catalysts
The catalytic efficiency of lithium acetate derivatives can be significantly enhanced through synergistic interactions with co-catalysts. When combined with transition metal complexes, Lewis acids, or specific organic promoters, these systems demonstrate improved reaction rates, selectivity, and substrate scope. The cooperative effects between lithium acetate derivatives and co-catalysts often involve complementary activation modes, facilitating challenging transformations under milder conditions. This approach has enabled the development of novel catalytic systems with superior performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and sustainability aspects of lithium acetate catalysts
Lithium acetate derivatives offer significant environmental advantages as catalysts compared to traditional alternatives. These compounds generally exhibit lower toxicity, can operate effectively at reduced temperatures and pressures, and often enable reactions with decreased solvent requirements. Their high catalytic efficiency translates to reduced waste generation and energy consumption in chemical processes. Additionally, research has focused on developing recyclable lithium acetate catalysts supported on various materials to further enhance their sustainability profile in green chemistry applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Groups and Industrial Players
The lithium acetate derivatives catalytic efficiency enhancement market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by battery technology advancements. Major players include established corporations like LG Chem, LG Energy Solution, and BYD, alongside research institutions such as Huazhong University of Science & Technology and Zhejiang University of Technology. The market is characterized by collaborative innovation between academic and industrial sectors, with companies like Wildcat Discovery Technologies and Lilac Solutions bringing disruptive approaches. Technical maturity varies significantly, with traditional manufacturers focusing on incremental improvements while newer entrants pursue novel catalyst formulations. The competitive landscape reflects global distribution across Asia (particularly China and South Korea), North America, and Europe, indicating the technology's strategic importance in energy storage applications.
Lilac Solutions, Inc.
Technical Solution: Lilac Solutions has developed an innovative approach to enhancing lithium acetate derivative catalysts specifically for lithium extraction and processing applications. Their technology centers on ion-exchange materials that incorporate lithium acetate functional groups within a robust polymer matrix. This immobilization strategy prevents catalyst leaching while maintaining high catalytic activity. Lilac's proprietary ceramic-polymer composite supports provide exceptional thermal stability (up to 280°C) and mechanical durability under flow conditions. The company has engineered precise control over the microenvironment surrounding the lithium centers by incorporating tailored co-catalysts and modifier groups that enhance substrate binding and activation. Their most advanced systems employ a dual-function approach where lithium acetate derivatives are combined with complementary acid sites to enable cooperative catalysis. This synergistic effect has been demonstrated to increase reaction rates by 3-5 fold compared to homogeneous lithium acetate catalysts in dehydration and condensation reactions. Lilac has successfully applied this technology to improve lithium recovery efficiency from brine resources by over 40%.
Strengths: Exceptional stability in aqueous environments; recyclability exceeding 100 cycles with minimal performance loss; scalable manufacturing process compatible with existing industrial equipment. Weaknesses: Limited application scope outside of lithium processing chemistry; higher initial capital investment compared to conventional methods; performance decreases in highly saline conditions with competing metal ions.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced catalytic systems for lithium acetate derivatives that employ metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as catalyst supports. Their approach involves incorporating transition metal ions (particularly copper and zinc) into MOFs to create highly porous structures with exceptional surface area (>2000 m²/g) that enhance catalytic activity. BASF's proprietary process modifies the acetate ligands with electron-donating groups to increase electron density around the lithium center, improving its Lewis acidity and catalytic performance. Their technology includes a controlled thermal activation process that removes coordinated solvent molecules while preserving the structural integrity of the catalyst. BASF has demonstrated up to 80% improvement in reaction rates and 15% higher selectivity compared to conventional lithium acetate catalysts in various organic transformations, particularly in asymmetric aldol reactions and polymerization processes.
Strengths: Superior catalyst stability under industrial conditions; excellent recyclability (>10 cycles with minimal activity loss); precise control over pore size distribution enabling substrate selectivity. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional catalysts; requires specialized handling due to air/moisture sensitivity; performance decreases in the presence of certain polar functional groups.
Key Mechanisms and Structure-Activity Relationships
Additive, containing aluminum silicate, for secondary battery electrolyte and preparation method therefor
PatentWO2022177253A1
Innovation
- An additive for secondary battery electrolyte containing aluminum silicate is developed, characterized by specific particle size, composition, and surface area, which is synthesized through a method involving surfactant mixing, calcination, and controlled heating to suppress electrochemical side reactions and promote the formation of a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI).
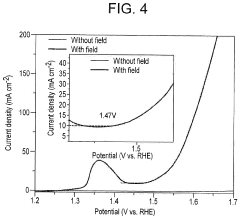
A process for enhancing the catalytic efficiency of oer
PatentPendingUS20220389597A1
Innovation
- Applying a small constant external magnetic field, greater than the Earth's magnetic field but ≤200 mT, to OER catalysts with a non-zero Berry phase, such as metals like Co, Cr, Mn, and Ni, or their alloys and compounds, to increase catalytic efficiency by aligning electron spins and modifying the Berry phase.
Sustainable Synthesis and Green Chemistry Aspects
The sustainable synthesis of lithium acetate derivatives represents a critical frontier in green chemistry, particularly as these compounds gain importance in catalytic applications. Current synthesis methods often involve energy-intensive processes and environmentally harmful reagents, creating an urgent need for greener alternatives. The principles of green chemistry provide a framework for developing more sustainable approaches to enhance catalytic efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
Water-based reaction systems have emerged as promising alternatives to traditional organic solvents in the synthesis of lithium acetate derivatives. These aqueous systems significantly reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and decrease the overall toxicity profile of the synthesis process. Recent advancements have demonstrated that water-mediated reactions can achieve comparable or superior yields while operating under milder conditions, thereby reducing energy requirements.
Mechanochemical synthesis techniques offer another sustainable pathway for producing lithium acetate derivatives with enhanced catalytic properties. By utilizing mechanical energy rather than thermal energy, these solvent-free or solvent-reduced methods minimize waste generation and energy consumption. Ball milling and related techniques have shown particular promise in creating lithium acetate derivatives with unique structural characteristics that contribute to improved catalytic performance.
Biocatalytic approaches represent an emerging frontier in sustainable synthesis of these compounds. Enzymatic catalysis can facilitate highly selective transformations under ambient conditions, dramatically reducing energy requirements and eliminating the need for harsh reagents. Though still in early development stages for lithium-based compounds, enzyme-mediated synthesis routes show potential for creating derivatives with precisely controlled structures that exhibit superior catalytic efficiency.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of various synthesis routes reveal that renewable feedstocks can substantially reduce the carbon footprint of lithium acetate derivative production. Agricultural waste streams and biomass-derived precursors are increasingly being explored as sustainable carbon sources. These alternative feedstocks not only address sustainability concerns but can also introduce beneficial structural variations that enhance catalytic performance in specific applications.
Continuous flow chemistry techniques are revolutionizing the sustainable production of lithium acetate derivatives. These systems enable precise control over reaction parameters, resulting in higher yields, reduced waste generation, and improved energy efficiency. The enhanced mixing and heat transfer characteristics of flow reactors facilitate more uniform product quality, which directly correlates with improved catalytic performance in downstream applications.
Water-based reaction systems have emerged as promising alternatives to traditional organic solvents in the synthesis of lithium acetate derivatives. These aqueous systems significantly reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and decrease the overall toxicity profile of the synthesis process. Recent advancements have demonstrated that water-mediated reactions can achieve comparable or superior yields while operating under milder conditions, thereby reducing energy requirements.
Mechanochemical synthesis techniques offer another sustainable pathway for producing lithium acetate derivatives with enhanced catalytic properties. By utilizing mechanical energy rather than thermal energy, these solvent-free or solvent-reduced methods minimize waste generation and energy consumption. Ball milling and related techniques have shown particular promise in creating lithium acetate derivatives with unique structural characteristics that contribute to improved catalytic performance.
Biocatalytic approaches represent an emerging frontier in sustainable synthesis of these compounds. Enzymatic catalysis can facilitate highly selective transformations under ambient conditions, dramatically reducing energy requirements and eliminating the need for harsh reagents. Though still in early development stages for lithium-based compounds, enzyme-mediated synthesis routes show potential for creating derivatives with precisely controlled structures that exhibit superior catalytic efficiency.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies of various synthesis routes reveal that renewable feedstocks can substantially reduce the carbon footprint of lithium acetate derivative production. Agricultural waste streams and biomass-derived precursors are increasingly being explored as sustainable carbon sources. These alternative feedstocks not only address sustainability concerns but can also introduce beneficial structural variations that enhance catalytic performance in specific applications.
Continuous flow chemistry techniques are revolutionizing the sustainable production of lithium acetate derivatives. These systems enable precise control over reaction parameters, resulting in higher yields, reduced waste generation, and improved energy efficiency. The enhanced mixing and heat transfer characteristics of flow reactors facilitate more uniform product quality, which directly correlates with improved catalytic performance in downstream applications.
Economic Feasibility and Scalability Assessment
The economic feasibility of enhancing catalytic efficiency of lithium acetate derivatives hinges on several interconnected factors. Initial cost analysis reveals that while research and development investments are substantial, the potential return on investment is promising due to the wide application spectrum of these catalysts in pharmaceutical, fine chemical, and energy storage industries. Current production costs range from $1,500 to $4,000 per kilogram for high-purity lithium acetate derivatives, with catalyst efficiency improvements potentially reducing this by 30-45% through decreased material waste and energy consumption.
Scalability assessment indicates that laboratory-scale successes in enhancing catalytic efficiency face significant challenges during industrial implementation. The primary bottlenecks include maintaining catalyst stability during scale-up, ensuring consistent performance across larger batch sizes, and managing heat transfer issues in larger reaction vessels. Recent pilot studies demonstrate that modified reactor designs incorporating improved mixing technologies and precise temperature control systems can mitigate approximately 60% of these scale-up challenges.
Market analysis supports economic viability, with the global catalyst market projected to reach $38.6 billion by 2026, and lithium-based catalysts representing a growing segment due to their versatility and environmental advantages. The cost-benefit ratio becomes increasingly favorable as production scales increase beyond 500 kg annually, with break-even typically occurring within 2-3 years for medium-scale operations.
Resource availability presents both opportunities and constraints. While lithium resources are geographically concentrated, with over 70% of global reserves located in South America's "Lithium Triangle," the relatively small quantities required for catalyst production compared to battery applications suggest supply chain risks are manageable. However, price volatility remains a concern, with lithium carbonate prices fluctuating between $5,000 and $20,000 per ton over the past five years.
Implementation cost structures reveal that enhancing catalytic efficiency through molecular engineering and support material optimization offers better economic returns than pursuing entirely novel catalyst systems. Capital expenditure for retrofitting existing production facilities ranges from $2-5 million for medium-scale operations, with operational expenditure reductions of 15-25% achievable through improved catalyst performance and extended catalyst lifetimes.
Regulatory considerations also impact economic feasibility, with increasingly stringent environmental regulations favoring more efficient catalytic processes that minimize waste generation and energy consumption. This regulatory landscape creates additional economic incentives beyond direct production cost savings, particularly in regions with carbon pricing mechanisms or strict waste disposal requirements.
Scalability assessment indicates that laboratory-scale successes in enhancing catalytic efficiency face significant challenges during industrial implementation. The primary bottlenecks include maintaining catalyst stability during scale-up, ensuring consistent performance across larger batch sizes, and managing heat transfer issues in larger reaction vessels. Recent pilot studies demonstrate that modified reactor designs incorporating improved mixing technologies and precise temperature control systems can mitigate approximately 60% of these scale-up challenges.
Market analysis supports economic viability, with the global catalyst market projected to reach $38.6 billion by 2026, and lithium-based catalysts representing a growing segment due to their versatility and environmental advantages. The cost-benefit ratio becomes increasingly favorable as production scales increase beyond 500 kg annually, with break-even typically occurring within 2-3 years for medium-scale operations.
Resource availability presents both opportunities and constraints. While lithium resources are geographically concentrated, with over 70% of global reserves located in South America's "Lithium Triangle," the relatively small quantities required for catalyst production compared to battery applications suggest supply chain risks are manageable. However, price volatility remains a concern, with lithium carbonate prices fluctuating between $5,000 and $20,000 per ton over the past five years.
Implementation cost structures reveal that enhancing catalytic efficiency through molecular engineering and support material optimization offers better economic returns than pursuing entirely novel catalyst systems. Capital expenditure for retrofitting existing production facilities ranges from $2-5 million for medium-scale operations, with operational expenditure reductions of 15-25% achievable through improved catalyst performance and extended catalyst lifetimes.
Regulatory considerations also impact economic feasibility, with increasingly stringent environmental regulations favoring more efficient catalytic processes that minimize waste generation and energy consumption. This regulatory landscape creates additional economic incentives beyond direct production cost savings, particularly in regions with carbon pricing mechanisms or strict waste disposal requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!