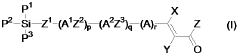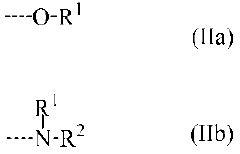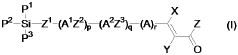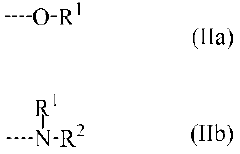How to Guide Structural Alignment of Polysilane Polymers?
JUL 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Alignment Background and Objectives
Polysilanes, a class of silicon-based polymers with a backbone consisting of silicon atoms, have garnered significant attention in the field of materials science and engineering. The structural alignment of these polymers plays a crucial role in determining their unique optical, electronic, and mechanical properties. Understanding and controlling this alignment is essential for harnessing the full potential of polysilanes in various applications.
The development of polysilanes can be traced back to the 1920s when early synthesis methods were first explored. However, it wasn't until the 1980s that researchers began to focus on the structural aspects of these polymers, particularly their alignment. This shift in focus was driven by the realization that the orientation of polysilane chains could dramatically influence their performance in optoelectronic devices and other advanced applications.
The primary objective of guiding structural alignment in polysilane polymers is to enhance their functionality and expand their potential uses. By achieving precise control over the orientation of polymer chains, researchers aim to optimize properties such as charge transport, light emission, and mechanical strength. This control is particularly crucial for applications in organic electronics, photonics, and sensing technologies.
One of the key challenges in this field is developing reliable and scalable methods for inducing and maintaining the desired alignment of polysilane chains. Traditional approaches have included mechanical stretching, shear-induced alignment, and the use of external fields. However, these methods often suffer from limitations in terms of uniformity, stability, and applicability to different polysilane structures.
Recent technological advancements have opened up new avenues for addressing these challenges. The emergence of nanofabrication techniques, such as lithography and self-assembly, has provided researchers with tools to manipulate polysilane structures at the molecular level. Additionally, the development of advanced characterization methods, including synchrotron-based X-ray scattering and high-resolution electron microscopy, has enabled more precise analysis of polymer alignment and morphology.
The ongoing research in this area is driven by the potential applications of aligned polysilane polymers. These range from next-generation display technologies and solar cells to chemical sensors and biomedical devices. As such, the field continues to evolve, with researchers exploring novel synthesis routes, alignment techniques, and characterization methods to push the boundaries of what is possible with these fascinating materials.
The development of polysilanes can be traced back to the 1920s when early synthesis methods were first explored. However, it wasn't until the 1980s that researchers began to focus on the structural aspects of these polymers, particularly their alignment. This shift in focus was driven by the realization that the orientation of polysilane chains could dramatically influence their performance in optoelectronic devices and other advanced applications.
The primary objective of guiding structural alignment in polysilane polymers is to enhance their functionality and expand their potential uses. By achieving precise control over the orientation of polymer chains, researchers aim to optimize properties such as charge transport, light emission, and mechanical strength. This control is particularly crucial for applications in organic electronics, photonics, and sensing technologies.
One of the key challenges in this field is developing reliable and scalable methods for inducing and maintaining the desired alignment of polysilane chains. Traditional approaches have included mechanical stretching, shear-induced alignment, and the use of external fields. However, these methods often suffer from limitations in terms of uniformity, stability, and applicability to different polysilane structures.
Recent technological advancements have opened up new avenues for addressing these challenges. The emergence of nanofabrication techniques, such as lithography and self-assembly, has provided researchers with tools to manipulate polysilane structures at the molecular level. Additionally, the development of advanced characterization methods, including synchrotron-based X-ray scattering and high-resolution electron microscopy, has enabled more precise analysis of polymer alignment and morphology.
The ongoing research in this area is driven by the potential applications of aligned polysilane polymers. These range from next-generation display technologies and solar cells to chemical sensors and biomedical devices. As such, the field continues to evolve, with researchers exploring novel synthesis routes, alignment techniques, and characterization methods to push the boundaries of what is possible with these fascinating materials.
Market Analysis for Aligned Polysilane Applications
The market for aligned polysilane applications is experiencing significant growth, driven by the unique properties and potential applications of these materials. Polysilanes, with their silicon-based backbone, offer a combination of electrical conductivity, optical properties, and thermal stability that make them attractive for various industries. The ability to guide structural alignment of polysilane polymers further enhances their potential, opening up new market opportunities.
In the electronics sector, aligned polysilanes show promise for use in organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). The improved charge carrier mobility resulting from structural alignment could lead to more efficient and higher-performing devices. This aligns with the growing demand for flexible and lightweight electronic components in consumer electronics, wearable technology, and IoT devices.
The photonics industry is another key market for aligned polysilanes. Their unique optical properties, including high refractive indices and non-linear optical responses, make them suitable for applications in optical waveguides, photonic crystals, and optical switches. As the demand for high-speed data transmission and processing continues to rise, the market for advanced photonic materials is expected to expand, creating opportunities for aligned polysilanes.
In the field of energy storage and conversion, aligned polysilanes have potential applications in solar cells and batteries. Their ability to conduct electricity and their tunable electronic properties make them candidates for improving the efficiency of photovoltaic devices and enhancing the performance of battery electrodes. With the global push towards renewable energy and sustainable technologies, this market segment is poised for substantial growth.
The aerospace and automotive industries are also showing interest in aligned polysilanes for their potential in lightweight, high-strength composite materials. The ability to control the structural alignment of these polymers could lead to materials with enhanced mechanical properties, thermal stability, and resistance to harsh environments. This aligns with the ongoing trend towards lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles and aircraft.
While the market for aligned polysilane applications is still in its early stages, it is expected to grow as research progresses and manufacturing techniques improve. The development of scalable methods for guiding structural alignment will be crucial for market expansion. As these challenges are addressed, the market is likely to see increased adoption across various industries, driven by the unique properties and versatility of aligned polysilanes.
In the electronics sector, aligned polysilanes show promise for use in organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). The improved charge carrier mobility resulting from structural alignment could lead to more efficient and higher-performing devices. This aligns with the growing demand for flexible and lightweight electronic components in consumer electronics, wearable technology, and IoT devices.
The photonics industry is another key market for aligned polysilanes. Their unique optical properties, including high refractive indices and non-linear optical responses, make them suitable for applications in optical waveguides, photonic crystals, and optical switches. As the demand for high-speed data transmission and processing continues to rise, the market for advanced photonic materials is expected to expand, creating opportunities for aligned polysilanes.
In the field of energy storage and conversion, aligned polysilanes have potential applications in solar cells and batteries. Their ability to conduct electricity and their tunable electronic properties make them candidates for improving the efficiency of photovoltaic devices and enhancing the performance of battery electrodes. With the global push towards renewable energy and sustainable technologies, this market segment is poised for substantial growth.
The aerospace and automotive industries are also showing interest in aligned polysilanes for their potential in lightweight, high-strength composite materials. The ability to control the structural alignment of these polymers could lead to materials with enhanced mechanical properties, thermal stability, and resistance to harsh environments. This aligns with the ongoing trend towards lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles and aircraft.
While the market for aligned polysilane applications is still in its early stages, it is expected to grow as research progresses and manufacturing techniques improve. The development of scalable methods for guiding structural alignment will be crucial for market expansion. As these challenges are addressed, the market is likely to see increased adoption across various industries, driven by the unique properties and versatility of aligned polysilanes.
Current Challenges in Polysilane Structural Alignment
The structural alignment of polysilane polymers presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent flexibility of the silicon backbone in polysilanes, which makes it difficult to achieve and maintain a specific alignment. This flexibility allows for various conformations, leading to a lack of consistent orientation in the polymer chains.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the molecular weight and polydispersity of polysilanes during synthesis. The degree of polymerization significantly affects the alignment properties, and achieving a narrow molecular weight distribution is crucial for uniform structural alignment. However, current synthetic methods often result in broad molecular weight distributions, complicating alignment efforts.
The sensitivity of polysilanes to environmental factors poses an additional hurdle. Factors such as temperature, solvent interactions, and external fields can dramatically influence the structural arrangement of these polymers. This sensitivity makes it challenging to maintain a stable alignment under varying conditions, limiting the practical applications of aligned polysilane structures.
Furthermore, the characterization of polysilane alignment presents its own set of difficulties. Traditional techniques for polymer characterization may not always be suitable or sufficient for accurately assessing the degree and quality of alignment in polysilane systems. This limitation hampers the development of precise control strategies and the evaluation of alignment techniques.
The scalability of alignment processes is another significant challenge. While some methods may achieve good alignment on a small scale or in laboratory settings, translating these techniques to large-scale production or device fabrication remains problematic. This scaling issue is a major barrier to the commercial application of aligned polysilane polymers.
Interfacial interactions between polysilanes and substrates or other materials in composite systems also present challenges. These interactions can significantly affect the alignment process and the stability of the aligned structures. Developing methods to control and optimize these interfacial effects is crucial for many potential applications of aligned polysilanes.
Lastly, the long-term stability of aligned polysilane structures remains a concern. Even when initial alignment is achieved, maintaining this alignment over extended periods, especially under various environmental conditions or in the presence of mechanical stress, is challenging. This stability issue is particularly critical for applications in electronic or optical devices where consistent performance over time is essential.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the molecular weight and polydispersity of polysilanes during synthesis. The degree of polymerization significantly affects the alignment properties, and achieving a narrow molecular weight distribution is crucial for uniform structural alignment. However, current synthetic methods often result in broad molecular weight distributions, complicating alignment efforts.
The sensitivity of polysilanes to environmental factors poses an additional hurdle. Factors such as temperature, solvent interactions, and external fields can dramatically influence the structural arrangement of these polymers. This sensitivity makes it challenging to maintain a stable alignment under varying conditions, limiting the practical applications of aligned polysilane structures.
Furthermore, the characterization of polysilane alignment presents its own set of difficulties. Traditional techniques for polymer characterization may not always be suitable or sufficient for accurately assessing the degree and quality of alignment in polysilane systems. This limitation hampers the development of precise control strategies and the evaluation of alignment techniques.
The scalability of alignment processes is another significant challenge. While some methods may achieve good alignment on a small scale or in laboratory settings, translating these techniques to large-scale production or device fabrication remains problematic. This scaling issue is a major barrier to the commercial application of aligned polysilane polymers.
Interfacial interactions between polysilanes and substrates or other materials in composite systems also present challenges. These interactions can significantly affect the alignment process and the stability of the aligned structures. Developing methods to control and optimize these interfacial effects is crucial for many potential applications of aligned polysilanes.
Lastly, the long-term stability of aligned polysilane structures remains a concern. Even when initial alignment is achieved, maintaining this alignment over extended periods, especially under various environmental conditions or in the presence of mechanical stress, is challenging. This stability issue is particularly critical for applications in electronic or optical devices where consistent performance over time is essential.
Existing Methods for Polysilane Structural Alignment
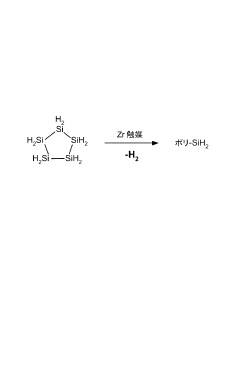
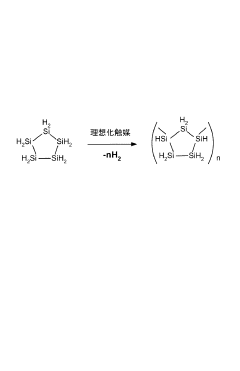
01 Synthesis and structure of polysilane polymers
Polysilane polymers are synthesized and their structural properties are studied. These polymers have unique electronic and optical properties due to their silicon-silicon backbone. The structural alignment of polysilanes can be controlled during synthesis to achieve desired characteristics.- Synthesis and structure of polysilane polymers: Polysilane polymers are synthesized and their structural properties are studied. The alignment and organization of these polymers are crucial for their applications in various fields. Research focuses on controlling the molecular structure and improving the synthesis methods to achieve desired properties.
- Optical and electronic properties of aligned polysilanes: The structural alignment of polysilane polymers significantly influences their optical and electronic properties. Studies explore the relationship between polymer alignment and characteristics such as conductivity, photoconductivity, and light emission. These properties are essential for applications in optoelectronic devices.
- Thin film formation and alignment techniques: Various techniques are developed to form thin films of polysilane polymers with controlled alignment. These methods include spin-coating, vapor deposition, and self-assembly processes. The alignment of polymers in thin films is crucial for enhancing their performance in electronic and optical applications.
- Polysilane-based composite materials: Polysilane polymers are used to create composite materials with enhanced properties. These composites combine the unique characteristics of polysilanes with other materials to achieve improved mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties. The structural alignment of polysilanes within these composites plays a crucial role in determining their overall performance.
- Applications in semiconductor and display technologies: Aligned polysilane polymers find applications in semiconductor devices and display technologies. Their unique electronic properties and ability to form ordered structures make them suitable for use in transistors, photoresists, and liquid crystal displays. Research focuses on optimizing the alignment of these polymers to enhance device performance.
02 Alignment techniques for polysilane polymers
Various techniques are employed to achieve structural alignment of polysilane polymers. These may include mechanical stretching, electric field alignment, or the use of alignment layers. The alignment process can enhance the polymers' properties for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of aligned polysilane polymers
Structurally aligned polysilane polymers find applications in various fields. They can be used in electronic devices, optical materials, and as precursors for silicon-based materials. The aligned structure enhances their performance in these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Characterization of polysilane polymer alignment
Methods for characterizing the structural alignment of polysilane polymers are developed. These may include spectroscopic techniques, X-ray diffraction, or electron microscopy. Understanding the degree and nature of alignment is crucial for optimizing polymer properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modification of polysilane polymers for improved alignment
Strategies for modifying polysilane polymers to enhance their structural alignment capabilities are explored. This may involve the incorporation of functional groups, copolymerization, or the use of additives that promote alignment during processing.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Polysilane Research and Development
The structural alignment of polysilane polymers is an emerging field with growing interest due to potential applications in optoelectronics and nanotechnology. The market is still in its early stages, with limited commercial products available. Key players like Wacker Chemie AG, Dow Silicones Corp., and Evonik Operations GmbH are investing in research and development to advance the technology. Academic institutions such as Katholieke Universiteit Leuven and the Chinese Academy of Science Institute of Chemistry are also contributing to fundamental research. While the technology shows promise, challenges remain in achieving consistent alignment and scalability for industrial applications. As the field progresses, collaborations between industry and academia will likely drive further innovations and market growth.
Wacker Chemie AG
Technical Solution: Wacker Chemie AG has developed a novel approach to guide structural alignment of polysilane polymers using controlled silylation techniques. Their method involves the use of specially designed silane coupling agents that can selectively attach to specific sites on the polysilane backbone, inducing a preferred orientation[1]. This process is combined with a proprietary annealing treatment that further enhances the alignment of the polymer chains. The company has also implemented a unique solvent-assisted stretching technique that applies mechanical stress during the polymer film formation, resulting in highly oriented polysilane structures[3]. Additionally, Wacker has explored the use of nanoscale templates and surface modification techniques to promote epitaxial growth of aligned polysilane layers[5].
Strengths: Precise control over polymer orientation, scalable manufacturing process, and compatibility with existing semiconductor fabrication techniques. Weaknesses: Potential for increased production costs due to specialized materials and processing steps, and possible limitations in achieving uniform alignment over large areas.
Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft eV
Technical Solution: Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft eV has developed an innovative approach to guide structural alignment of polysilane polymers using a combination of advanced processing techniques and nanoscale engineering. Their method involves the use of specially designed block copolymers that self-assemble into ordered nanostructures, serving as templates for polysilane alignment[2]. This is coupled with a controlled vapor deposition process that allows for precise control over the polymer growth and orientation. Fraunhofer has also pioneered the use of electric field-assisted alignment techniques, where an applied electric field during polymer synthesis or post-processing helps to orient the polysilane chains along a preferred direction[4]. Furthermore, they have developed a novel surface functionalization method that creates nanoscale grooves or patterns on substrates, promoting epitaxial growth of aligned polysilane layers[6].
Strengths: High degree of control over nanoscale structures, potential for large-area alignment, and compatibility with various substrate materials. Weaknesses: Complexity of the multi-step process may lead to higher production costs and potential scalability challenges for industrial applications.
Innovative Approaches in Polysilane Alignment
Silicon polymers, methods of polymerizing silicon compounds, and methods of forming thin films from such silicon polymers
PatentInactiveJP2017061702A
Innovation
- A method involving the use of hydrogen and silicon or germanium-based oligosilanes or polysilanes, catalyzed by transition metal complexes, to form amorphous hydrogenated semiconductor films with controlled molecular weight and low carbon content, allowing for solubility and stable coating or printing.
Silane compound and polymer thereof, and liquid crystal alignment layer comprising the polymer
PatentInactiveJP2015203019A
Innovation
- A liquid crystal alignment layer using a silane compound and polyorganosiloxane, formulated to control alignment and pretilt angle, with high VHR and low RDC, is developed through a photo-alignment method involving specific silane compounds and their hydrolysis/condensation to form a polyorganosiloxane layer, which is then coated and irradiated to achieve precise alignment structures.
Environmental Impact of Polysilane Production
The production of polysilane polymers, while offering unique properties for various applications, raises significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. The synthesis of these materials typically involves energy-intensive processes and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals, which can have far-reaching ecological implications.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with polysilane production is the high energy consumption required for the synthesis process. The reduction of silicon-containing precursors, often carried out at elevated temperatures, demands substantial energy input. This energy-intensive nature contributes to increased carbon emissions and places a burden on energy resources, particularly if non-renewable sources are utilized.
Chemical waste generation is another critical environmental aspect of polysilane manufacturing. The synthesis often involves the use of chlorosilanes, which can produce hydrochloric acid as a by-product. If not properly managed, this acidic waste can lead to soil and water contamination, potentially harming local ecosystems and biodiversity. Additionally, unreacted precursors and solvents used in the production process may contribute to air pollution if not adequately contained and treated.
The disposal of polysilane-containing products at the end of their lifecycle presents further environmental challenges. These polymers are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. Improper disposal may lead to the accumulation of microplastics in aquatic systems, posing risks to marine life and potentially entering the food chain.
However, it is important to note that ongoing research is focused on developing more environmentally friendly production methods for polysilanes. Green chemistry approaches, such as the use of less toxic precursors and catalysts, are being explored to minimize the environmental footprint of these materials. Furthermore, efforts are being made to improve the recyclability and biodegradability of polysilane-based products, which could significantly reduce their long-term environmental impact.
The environmental impact of polysilane production also extends to resource depletion, particularly concerning silicon, the primary raw material. While silicon is abundant in the Earth's crust, the extraction and purification processes required for high-purity silicon used in polysilane synthesis can have significant environmental consequences, including habitat disruption and energy-intensive refining processes.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer promising technological applications, their production poses several environmental challenges that must be addressed. Balancing the potential benefits of these materials with their ecological impact requires ongoing research into greener synthesis methods, improved waste management strategies, and the development of more sustainable end-of-life solutions for polysilane-based products.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with polysilane production is the high energy consumption required for the synthesis process. The reduction of silicon-containing precursors, often carried out at elevated temperatures, demands substantial energy input. This energy-intensive nature contributes to increased carbon emissions and places a burden on energy resources, particularly if non-renewable sources are utilized.
Chemical waste generation is another critical environmental aspect of polysilane manufacturing. The synthesis often involves the use of chlorosilanes, which can produce hydrochloric acid as a by-product. If not properly managed, this acidic waste can lead to soil and water contamination, potentially harming local ecosystems and biodiversity. Additionally, unreacted precursors and solvents used in the production process may contribute to air pollution if not adequately contained and treated.
The disposal of polysilane-containing products at the end of their lifecycle presents further environmental challenges. These polymers are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. Improper disposal may lead to the accumulation of microplastics in aquatic systems, posing risks to marine life and potentially entering the food chain.
However, it is important to note that ongoing research is focused on developing more environmentally friendly production methods for polysilanes. Green chemistry approaches, such as the use of less toxic precursors and catalysts, are being explored to minimize the environmental footprint of these materials. Furthermore, efforts are being made to improve the recyclability and biodegradability of polysilane-based products, which could significantly reduce their long-term environmental impact.
The environmental impact of polysilane production also extends to resource depletion, particularly concerning silicon, the primary raw material. While silicon is abundant in the Earth's crust, the extraction and purification processes required for high-purity silicon used in polysilane synthesis can have significant environmental consequences, including habitat disruption and energy-intensive refining processes.
In conclusion, while polysilanes offer promising technological applications, their production poses several environmental challenges that must be addressed. Balancing the potential benefits of these materials with their ecological impact requires ongoing research into greener synthesis methods, improved waste management strategies, and the development of more sustainable end-of-life solutions for polysilane-based products.
Scalability of Polysilane Alignment Processes
The scalability of polysilane alignment processes is a critical factor in the industrial application of these materials. Current alignment techniques, such as mechanical stretching and electric field alignment, face significant challenges when scaled up to large-scale production. Mechanical stretching, while effective for small samples, becomes increasingly difficult to maintain uniform stress distribution across larger areas. This non-uniformity can lead to inconsistent alignment and potential material failure.
Electric field alignment, on the other hand, offers better scalability potential but requires careful control of field strength and uniformity across the entire sample. As the sample size increases, maintaining a consistent electric field becomes more challenging, often necessitating complex electrode designs and power distribution systems. Additionally, the alignment process duration may need to be extended for larger samples, potentially impacting production efficiency.
Another promising approach for scalable alignment is the use of liquid crystal templates. This method allows for the alignment of polysilanes within a liquid crystal matrix, which can then be polymerized to fix the orientation. While this technique shows promise for larger-scale applications, it still faces challenges in terms of achieving uniform liquid crystal alignment over large areas and ensuring complete removal of the template material post-alignment.
Photoinduced alignment techniques, utilizing polarized light to orient polysilane chains, offer an attractive option for scalability. These methods can potentially be applied to large surface areas simultaneously, making them suitable for roll-to-roll processing. However, the depth of alignment penetration and the ability to maintain alignment during subsequent processing steps remain areas of concern.
As the demand for aligned polysilane materials in various applications grows, addressing these scalability challenges becomes increasingly important. Future research directions may focus on developing hybrid approaches that combine multiple alignment techniques to overcome individual limitations. For instance, combining mechanical pre-stretching with electric field alignment could potentially enhance overall alignment efficiency and uniformity in large-scale production.
Moreover, the development of novel processing equipment specifically designed for polysilane alignment at industrial scales will be crucial. This may include the design of large-area electrodes for electric field alignment, advanced stretching mechanisms for mechanical alignment, or specialized optical systems for photoinduced alignment processes.
Electric field alignment, on the other hand, offers better scalability potential but requires careful control of field strength and uniformity across the entire sample. As the sample size increases, maintaining a consistent electric field becomes more challenging, often necessitating complex electrode designs and power distribution systems. Additionally, the alignment process duration may need to be extended for larger samples, potentially impacting production efficiency.
Another promising approach for scalable alignment is the use of liquid crystal templates. This method allows for the alignment of polysilanes within a liquid crystal matrix, which can then be polymerized to fix the orientation. While this technique shows promise for larger-scale applications, it still faces challenges in terms of achieving uniform liquid crystal alignment over large areas and ensuring complete removal of the template material post-alignment.
Photoinduced alignment techniques, utilizing polarized light to orient polysilane chains, offer an attractive option for scalability. These methods can potentially be applied to large surface areas simultaneously, making them suitable for roll-to-roll processing. However, the depth of alignment penetration and the ability to maintain alignment during subsequent processing steps remain areas of concern.
As the demand for aligned polysilane materials in various applications grows, addressing these scalability challenges becomes increasingly important. Future research directions may focus on developing hybrid approaches that combine multiple alignment techniques to overcome individual limitations. For instance, combining mechanical pre-stretching with electric field alignment could potentially enhance overall alignment efficiency and uniformity in large-scale production.
Moreover, the development of novel processing equipment specifically designed for polysilane alignment at industrial scales will be crucial. This may include the design of large-area electrodes for electric field alignment, advanced stretching mechanisms for mechanical alignment, or specialized optical systems for photoinduced alignment processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!