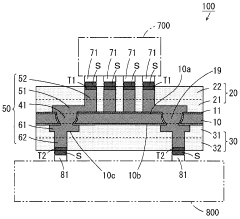
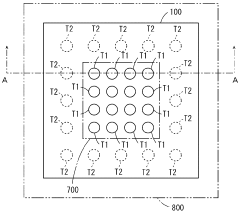
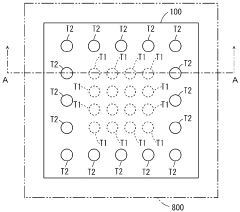
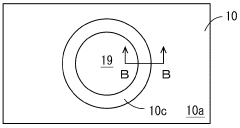
How to Implement Conformal Coating for Improved Heat Dissipation
SEP 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Conformal Coating Heat Dissipation Background & Objectives
Conformal coating technology has evolved significantly over the past four decades, transitioning from simple protective layers to multifunctional materials with enhanced thermal management capabilities. Originally developed for military and aerospace applications in the 1970s, these coatings were primarily designed to protect electronic components from moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants. The evolution of electronic devices toward higher power densities and miniaturization has created unprecedented thermal management challenges, pushing conformal coating technology to address both protection and heat dissipation simultaneously.
Recent advancements in material science have enabled the development of thermally conductive conformal coatings that can significantly improve heat transfer while maintaining traditional protective functions. The global market for these specialized coatings has grown at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 7% since 2018, reflecting the increasing demand for effective thermal management solutions in electronics manufacturing.
Current research focuses on nano-enhanced polymeric materials that can achieve thermal conductivity values of 1-5 W/m·K, substantially higher than conventional coatings (0.1-0.3 W/m·K). These advanced formulations incorporate materials such as aluminum oxide, boron nitride, and graphene to enhance thermal properties while maintaining electrical insulation characteristics.
The primary objective of implementing thermally conductive conformal coatings is to establish an efficient thermal pathway that facilitates heat dissipation from electronic components to the ambient environment. This approach aims to reduce operating temperatures by 10-15°C in typical applications, potentially extending device lifespan by 30-50% according to industry reliability models.
Secondary objectives include maintaining or enhancing traditional protective functions against environmental factors, ensuring compatibility with existing manufacturing processes, and developing cost-effective solutions that can be widely adopted across various electronic manufacturing sectors. The coating must also meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants.
Technical goals for next-generation thermally conductive conformal coatings include achieving thermal conductivity values exceeding 10 W/m·K while maintaining application viscosity suitable for standard coating processes, developing water-based formulations with minimal environmental impact, and creating coatings with self-healing properties to extend protection lifespan.
The convergence of thermal management and environmental protection in a single coating solution represents a significant technological opportunity, with potential applications extending beyond traditional electronics into emerging fields such as flexible electronics, wearable devices, and high-power LED systems.
Recent advancements in material science have enabled the development of thermally conductive conformal coatings that can significantly improve heat transfer while maintaining traditional protective functions. The global market for these specialized coatings has grown at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 7% since 2018, reflecting the increasing demand for effective thermal management solutions in electronics manufacturing.
Current research focuses on nano-enhanced polymeric materials that can achieve thermal conductivity values of 1-5 W/m·K, substantially higher than conventional coatings (0.1-0.3 W/m·K). These advanced formulations incorporate materials such as aluminum oxide, boron nitride, and graphene to enhance thermal properties while maintaining electrical insulation characteristics.
The primary objective of implementing thermally conductive conformal coatings is to establish an efficient thermal pathway that facilitates heat dissipation from electronic components to the ambient environment. This approach aims to reduce operating temperatures by 10-15°C in typical applications, potentially extending device lifespan by 30-50% according to industry reliability models.
Secondary objectives include maintaining or enhancing traditional protective functions against environmental factors, ensuring compatibility with existing manufacturing processes, and developing cost-effective solutions that can be widely adopted across various electronic manufacturing sectors. The coating must also meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations regarding volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants.
Technical goals for next-generation thermally conductive conformal coatings include achieving thermal conductivity values exceeding 10 W/m·K while maintaining application viscosity suitable for standard coating processes, developing water-based formulations with minimal environmental impact, and creating coatings with self-healing properties to extend protection lifespan.
The convergence of thermal management and environmental protection in a single coating solution represents a significant technological opportunity, with potential applications extending beyond traditional electronics into emerging fields such as flexible electronics, wearable devices, and high-power LED systems.
Market Demand Analysis for Thermal Management Solutions
The thermal management solutions market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing power densities in electronic devices across multiple industries. The global market for thermal management technologies was valued at approximately 11.4 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 18.7 billion USD by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 10.3%. This growth is primarily fueled by the miniaturization trend in electronics, which creates significant heat dissipation challenges that traditional cooling methods struggle to address effectively.
Conformal coating solutions for heat dissipation represent a rapidly expanding segment within this market, with particular demand coming from high-performance computing, automotive electronics, aerospace applications, and consumer electronics. The automotive sector shows especially strong growth potential as electric vehicles require sophisticated thermal management for battery systems and power electronics, with the market for EV thermal solutions growing at 14.2% annually.
Industry surveys indicate that 78% of electronics manufacturers consider thermal management a critical design challenge, with 63% actively seeking innovative coating solutions that can provide both protection and enhanced heat dissipation properties. This dual functionality is particularly valuable as it addresses multiple engineering challenges simultaneously while potentially reducing overall system complexity and cost.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 42% share, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (23%). China and South Korea are experiencing the fastest growth rates due to their expanding electronics manufacturing sectors and increasing adoption of advanced thermal management technologies in consumer products.
From an application perspective, the demand for conformal coatings with thermal properties is segmented across several key industries: telecommunications infrastructure (21%), consumer electronics (19%), automotive (17%), industrial equipment (15%), medical devices (14%), and aerospace/defense (14%). Each sector has specific requirements regarding thermal conductivity, dielectric properties, and environmental resistance.
Customer pain points driving market demand include the need for solutions that can withstand higher operating temperatures, provide uniform heat distribution, maintain long-term reliability, and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, 67% of potential customers cite ease of application and reworkability as important factors in their purchasing decisions, indicating that process integration considerations are nearly as important as the thermal performance characteristics themselves.
Conformal coating solutions for heat dissipation represent a rapidly expanding segment within this market, with particular demand coming from high-performance computing, automotive electronics, aerospace applications, and consumer electronics. The automotive sector shows especially strong growth potential as electric vehicles require sophisticated thermal management for battery systems and power electronics, with the market for EV thermal solutions growing at 14.2% annually.
Industry surveys indicate that 78% of electronics manufacturers consider thermal management a critical design challenge, with 63% actively seeking innovative coating solutions that can provide both protection and enhanced heat dissipation properties. This dual functionality is particularly valuable as it addresses multiple engineering challenges simultaneously while potentially reducing overall system complexity and cost.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with 42% share, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (23%). China and South Korea are experiencing the fastest growth rates due to their expanding electronics manufacturing sectors and increasing adoption of advanced thermal management technologies in consumer products.
From an application perspective, the demand for conformal coatings with thermal properties is segmented across several key industries: telecommunications infrastructure (21%), consumer electronics (19%), automotive (17%), industrial equipment (15%), medical devices (14%), and aerospace/defense (14%). Each sector has specific requirements regarding thermal conductivity, dielectric properties, and environmental resistance.
Customer pain points driving market demand include the need for solutions that can withstand higher operating temperatures, provide uniform heat distribution, maintain long-term reliability, and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, 67% of potential customers cite ease of application and reworkability as important factors in their purchasing decisions, indicating that process integration considerations are nearly as important as the thermal performance characteristics themselves.
Current Conformal Coating Technologies and Thermal Challenges
Conformal coating technologies have evolved significantly over the past decades, with several distinct types now dominating the market. Acrylic coatings offer excellent moisture resistance and easy rework capabilities but provide only moderate thermal conductivity. Silicone coatings demonstrate superior temperature range tolerance (-65°C to 200°C) and flexibility, making them suitable for components subject to mechanical stress, though their thermal conductivity remains limited. Polyurethane coatings excel in chemical and abrasion resistance but typically offer poor thermal performance. Epoxy coatings provide excellent protection against harsh environments and chemicals but create rigid structures that can stress components during thermal cycling.
Parylene coatings, applied through vapor deposition polymerization, create extremely thin, uniform layers with excellent dielectric properties but traditionally poor thermal characteristics. Newer nano-enhanced coatings incorporate materials like aluminum oxide, boron nitride, or graphene to significantly improve thermal conductivity while maintaining protective properties.
The primary thermal challenge in conformal coating implementation stems from the inherent conflict between electrical insulation and thermal conductivity. Most traditional coating materials that excel at protecting electronic components from moisture and contaminants simultaneously act as thermal insulators, trapping heat within the coated components. This thermal barrier effect becomes increasingly problematic as electronic devices continue to miniaturize while processing power increases.
Another significant challenge involves coating thickness control. Excessive coating creates greater thermal resistance, while insufficient coverage compromises protection. Modern electronics with high component density present application difficulties, as coating material can accumulate in tight spaces between components, creating localized thick spots that impede heat dissipation.
Surface preparation represents another critical challenge, as contaminants or improper adhesion can create air gaps that severely impact thermal transfer efficiency. The industry also struggles with balancing thermal performance against other essential properties like flexibility, reworkability, and long-term reliability under thermal cycling conditions.
Recent advancements focus on thermally conductive conformal coatings that incorporate ceramic fillers, metallic particles, or carbon-based nanomaterials. However, these solutions often face trade-offs between thermal conductivity and traditional protective properties. The addition of conductive fillers can compromise electrical insulation properties if not precisely formulated and applied.
Manufacturing challenges include ensuring uniform dispersion of thermal enhancers throughout the coating matrix and developing application methods that maintain consistent thickness across complex circuit geometries. The industry continues to seek optimal solutions that balance thermal performance with the protective functions that make conformal coatings essential in modern electronics.
Parylene coatings, applied through vapor deposition polymerization, create extremely thin, uniform layers with excellent dielectric properties but traditionally poor thermal characteristics. Newer nano-enhanced coatings incorporate materials like aluminum oxide, boron nitride, or graphene to significantly improve thermal conductivity while maintaining protective properties.
The primary thermal challenge in conformal coating implementation stems from the inherent conflict between electrical insulation and thermal conductivity. Most traditional coating materials that excel at protecting electronic components from moisture and contaminants simultaneously act as thermal insulators, trapping heat within the coated components. This thermal barrier effect becomes increasingly problematic as electronic devices continue to miniaturize while processing power increases.
Another significant challenge involves coating thickness control. Excessive coating creates greater thermal resistance, while insufficient coverage compromises protection. Modern electronics with high component density present application difficulties, as coating material can accumulate in tight spaces between components, creating localized thick spots that impede heat dissipation.
Surface preparation represents another critical challenge, as contaminants or improper adhesion can create air gaps that severely impact thermal transfer efficiency. The industry also struggles with balancing thermal performance against other essential properties like flexibility, reworkability, and long-term reliability under thermal cycling conditions.
Recent advancements focus on thermally conductive conformal coatings that incorporate ceramic fillers, metallic particles, or carbon-based nanomaterials. However, these solutions often face trade-offs between thermal conductivity and traditional protective properties. The addition of conductive fillers can compromise electrical insulation properties if not precisely formulated and applied.
Manufacturing challenges include ensuring uniform dispersion of thermal enhancers throughout the coating matrix and developing application methods that maintain consistent thickness across complex circuit geometries. The industry continues to seek optimal solutions that balance thermal performance with the protective functions that make conformal coatings essential in modern electronics.
Current Technical Solutions for Heat-Dissipating Coatings
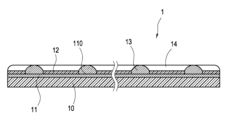
01 Thermally conductive conformal coatings
Specialized conformal coatings that incorporate thermally conductive materials to enhance heat dissipation while maintaining electrical insulation properties. These coatings typically contain fillers such as ceramic particles, metal oxides, or other thermally conductive additives that create pathways for heat transfer away from electronic components. The coatings provide both protection against environmental factors and improved thermal management for heat-generating devices.- Thermally conductive conformal coatings: Specialized conformal coatings that incorporate thermally conductive materials to enhance heat dissipation while maintaining protection for electronic components. These coatings typically contain fillers such as metal oxides, ceramic particles, or other thermally conductive additives that create pathways for heat transfer while providing the standard protective benefits of conformal coatings against moisture, dust, and chemicals.
- Heat dissipation structures with conformal coating protection: Designs that integrate heat dissipation structures such as heat sinks, thermal vias, or cooling fins with conformal coating protection. These approaches maintain effective thermal management while ensuring electronic components remain protected from environmental factors. The conformal coating is strategically applied to allow maximum heat transfer through designated thermal pathways while protecting sensitive areas from contamination.
- Selective coating techniques for thermal optimization: Methods for selectively applying conformal coatings to optimize heat dissipation in electronic assemblies. These techniques involve precisely controlling coating thickness or creating coating-free zones in areas requiring maximum thermal transfer, while ensuring complete protection in moisture-sensitive regions. Advanced application methods such as automated selective spraying, masking techniques, or precision dispensing are employed to achieve this balance.
- Thermally enhanced conformal coating materials: Novel conformal coating materials formulated specifically to address thermal management challenges. These include phase-change materials that absorb heat during temperature spikes, coatings with directional thermal conductivity properties, or materials with temperature-dependent characteristics that adapt to changing thermal conditions. These advanced materials maintain protective properties while significantly improving heat dissipation compared to traditional conformal coatings.
- Integrated cooling systems with conformal coating compatibility: Comprehensive cooling solutions that work in conjunction with conformal coatings to maximize heat dissipation in electronic devices. These systems may include liquid cooling channels, embedded heat pipes, or active cooling elements designed to function effectively with conformal coated electronics. Special consideration is given to the interface between cooling systems and coated surfaces to ensure optimal thermal transfer without compromising protection.
02 Heat dissipation structures with conformal coating
Innovative structural designs that combine heat sinks, heat spreaders, or thermal interface materials with conformal coatings. These solutions feature specially designed physical structures that maximize surface area for heat dissipation while being protected by conformal coatings. The designs may include fins, channels, or other geometries that facilitate airflow and heat transfer while maintaining the protective benefits of the coating.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phase change materials in conformal coatings
Integration of phase change materials (PCMs) into conformal coatings to absorb and dissipate heat through latent heat storage. These advanced coatings utilize materials that change phase (typically from solid to liquid) at specific temperatures, absorbing large amounts of heat during the transition. This approach helps maintain more consistent temperatures for electronic components during operational cycles, preventing thermal spikes while still providing the protective benefits of conformal coatings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Layered conformal coating systems for thermal management
Multi-layer coating systems that combine different materials to optimize both protection and heat dissipation. These systems typically feature a base layer for adhesion, a middle layer with thermal conductivity properties, and a top layer for environmental protection. The layered approach allows for customization of thermal and protective properties based on specific application requirements, creating an optimized solution for electronic components that generate significant heat.Expand Specific Solutions05 Nano-enhanced conformal coatings for heat transfer
Advanced conformal coatings incorporating nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, or metallic nanoparticles to dramatically improve thermal conductivity. These nano-enhanced coatings create efficient heat transfer pathways at the molecular level while maintaining the thin profile and conformability required for modern electronics. The nanomaterials provide exceptional thermal conductivity without compromising the electrical insulation properties of the coating, making them ideal for high-density electronic assemblies.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Thermal Conformal Coating Market
The conformal coating market for heat dissipation is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by miniaturization trends in electronics and thermal management challenges. The global market size is expanding rapidly, expected to reach significant valuation as industries adopt advanced thermal solutions. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovations. Leading players include Nordson Corp., specializing in coating systems and application equipment; 3M Innovative Properties, offering advanced thermal materials; and Texas Instruments, integrating thermal solutions into semiconductor designs. Other significant contributors include IBM and Applied Materials, focusing on high-performance computing thermal management, while Asian manufacturers like Gree Electric and AMOGREENTECH are advancing practical applications in consumer electronics. Research institutions such as Hebei University of Technology and IFP Energies Nouvelles are driving fundamental innovations in coating formulations.
Nordson Corp.
Technical Solution: Nordson has developed advanced conformal coating systems that utilize precision dispensing technology for improved heat dissipation. Their automated selective coating systems apply thin, uniform layers of thermally conductive materials to electronic components. The company's patented process combines precise material application with controlled thickness management, ensuring optimal thermal transfer while maintaining electrical insulation properties. Nordson's systems incorporate real-time viscosity monitoring and temperature control to maintain coating consistency across production runs. Their technology allows for targeted application to heat-generating components, creating customized thermal pathways that efficiently direct heat away from sensitive electronics. The company has also developed specialized formulations that combine traditional conformal coating protection with enhanced thermal conductivity properties, addressing both environmental protection and thermal management needs simultaneously.
Strengths: Precision dispensing technology allows for targeted application to specific heat-generating components, reducing material waste and optimizing thermal performance. Automated systems ensure consistency across high-volume production. Weaknesses: Higher initial investment compared to manual coating methods, and specialized formulations may have compatibility limitations with certain substrate materials.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has pioneered thermally conductive conformal coatings that incorporate ceramic-filled polymer matrices to enhance heat dissipation while maintaining excellent dielectric properties. Their proprietary technology utilizes nano-scale ceramic particles suspended in specialized polymer systems that create microscopic thermal pathways throughout the coating. These pathways facilitate efficient heat transfer away from electronic components while maintaining the protective barrier against environmental contaminants. 3M's coatings feature phase-change materials that absorb heat during operation and release it during cooling cycles, effectively dampening thermal spikes. Their multi-layer approach combines a base layer optimized for adhesion, a middle layer with high thermal conductivity (typically 1-3 W/m·K), and a top layer that provides environmental protection. The company has also developed spray-applied versions that can achieve thinner coatings (25-75 microns) while maintaining thermal performance, allowing for application in space-constrained designs.
Strengths: Industry-leading thermal conductivity values while maintaining excellent dielectric properties and environmental protection. Established global supply chain ensures product availability and consistency. Weaknesses: Premium pricing compared to standard conformal coatings, and some formulations require specialized application equipment and curing processes that may increase manufacturing complexity.
Core Patents and Innovations in Thermal Conformal Coatings
Wiring circuit board and method for manufacturing same
PatentWO2023157502A1
Innovation
- A printed circuit board design with a metal substrate featuring a conductor layer and insulating coating on both surfaces and within via holes, where the contour of the via hole's inner surface is inclined, increasing the surface area for heat transfer while maintaining reliable insulation through an optimized thickness and thermal conductivity of the metal support.
Printed Circuit Board and Heat Dissipating Metal Surface Layout thereof
PatentActiveUS20070261882A1
Innovation
- A printed circuit board design featuring a heat dissipating layer with alternately arranged bare copper portions in perpendicular directions, allowing for even solder attachment and formation of a consistent, larger protruding surface area during soldering, enhancing heat dissipation and current transmission.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The implementation of conformal coating for heat dissipation applications carries significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered throughout the product lifecycle. Traditional conformal coating materials often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to workers during application processes. The manufacturing of these coatings typically involves energy-intensive processes and petroleum-based raw materials, resulting in considerable carbon footprints. As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent worldwide, manufacturers must prioritize the development and adoption of eco-friendly alternatives.
Water-based and UV-curable conformal coatings represent promising sustainable options, offering reduced VOC emissions and lower energy requirements during curing processes. These environmentally preferable formulations maintain comparable thermal conductivity properties while minimizing ecological impact. Additionally, bio-based conformal coatings derived from renewable resources are emerging as viable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based products, though their thermal performance characteristics continue to undergo optimization.
The disposal and end-of-life management of electronic components with conformal coatings present another environmental challenge. Many traditional coatings impede recycling efforts by creating barriers to the separation and recovery of valuable materials from electronic waste. Developing easily removable or biodegradable coatings that maintain thermal enhancement properties would significantly improve the sustainability profile of these materials. Some manufacturers have begun implementing take-back programs and designing coatings specifically formulated for easier removal during recycling processes.
Energy efficiency considerations extend beyond the coating itself to its application in thermal management systems. By improving heat dissipation, properly implemented conformal coatings can extend electronic device lifespans and reduce energy consumption during operation. This indirect environmental benefit must be factored into comprehensive sustainability assessments, as longer-lasting electronics reduce resource consumption and waste generation over time.
Regulatory compliance represents another critical dimension of environmental considerations. Different regions enforce varying standards regarding chemical composition, VOC content, and disposal requirements for industrial coatings. Companies implementing conformal coating solutions must navigate this complex regulatory landscape while maintaining thermal performance objectives. Forward-thinking organizations are adopting life cycle assessment methodologies to quantify the environmental impacts of different coating options and make data-driven sustainability decisions that balance thermal performance with ecological responsibility.
Water-based and UV-curable conformal coatings represent promising sustainable options, offering reduced VOC emissions and lower energy requirements during curing processes. These environmentally preferable formulations maintain comparable thermal conductivity properties while minimizing ecological impact. Additionally, bio-based conformal coatings derived from renewable resources are emerging as viable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based products, though their thermal performance characteristics continue to undergo optimization.
The disposal and end-of-life management of electronic components with conformal coatings present another environmental challenge. Many traditional coatings impede recycling efforts by creating barriers to the separation and recovery of valuable materials from electronic waste. Developing easily removable or biodegradable coatings that maintain thermal enhancement properties would significantly improve the sustainability profile of these materials. Some manufacturers have begun implementing take-back programs and designing coatings specifically formulated for easier removal during recycling processes.
Energy efficiency considerations extend beyond the coating itself to its application in thermal management systems. By improving heat dissipation, properly implemented conformal coatings can extend electronic device lifespans and reduce energy consumption during operation. This indirect environmental benefit must be factored into comprehensive sustainability assessments, as longer-lasting electronics reduce resource consumption and waste generation over time.
Regulatory compliance represents another critical dimension of environmental considerations. Different regions enforce varying standards regarding chemical composition, VOC content, and disposal requirements for industrial coatings. Companies implementing conformal coating solutions must navigate this complex regulatory landscape while maintaining thermal performance objectives. Forward-thinking organizations are adopting life cycle assessment methodologies to quantify the environmental impacts of different coating options and make data-driven sustainability decisions that balance thermal performance with ecological responsibility.
Reliability Testing and Performance Validation Methods
Reliability testing and performance validation are critical components in the implementation of conformal coating for improved heat dissipation. These processes ensure that the coating performs as expected under various environmental conditions and maintains its thermal management properties throughout the product lifecycle.
Standard thermal cycling tests represent a fundamental validation method, typically involving exposure of coated components to temperature extremes ranging from -65°C to +150°C. These tests evaluate the coating's ability to maintain adhesion and thermal conductivity properties despite repeated expansion and contraction cycles. Most industry standards require 500-1000 cycles without degradation in performance to meet qualification requirements.
Humidity resistance testing is equally important, as moisture ingress can significantly compromise the thermal conductivity of conformal coatings. Components are subjected to 85% relative humidity at 85°C for periods ranging from 500 to 1000 hours, with thermal performance measurements taken at regular intervals to detect any degradation in heat dissipation capabilities.
Thermal shock testing provides more aggressive validation by subjecting coated components to rapid temperature changes, typically from -55°C to +125°C with transition times under 10 seconds. This method specifically evaluates the coating's ability to maintain adhesion and thermal transfer properties under extreme thermal stress conditions.
For applications requiring precise thermal management, thermal resistance measurement using techniques such as laser flash analysis or steady-state heat flow methods provides quantitative data on the coating's thermal conductivity before and after environmental exposure. Industry benchmarks typically require less than 5% degradation in thermal conductivity after reliability testing.
Accelerated aging tests simulate long-term performance by exposing coated components to elevated temperatures (typically 125°C) for extended periods (1000+ hours). These tests help predict the coating's thermal management capabilities over the product's expected lifetime, with performance degradation mathematically modeled to estimate end-of-life thermal characteristics.
Salt spray testing evaluates corrosion resistance, which indirectly affects thermal performance, as corrosion can create air gaps that impede heat transfer. Standard tests expose coated components to salt fog environments for 96-500 hours, followed by thermal performance evaluation to ensure heat dissipation remains within specification.
Mechanical stress testing, including vibration and mechanical shock, ensures that the coating maintains its thermal interface properties under physical stress. This is particularly important for applications in automotive, aerospace, or industrial environments where mechanical forces could compromise the coating's contact with heat-generating components.
Standard thermal cycling tests represent a fundamental validation method, typically involving exposure of coated components to temperature extremes ranging from -65°C to +150°C. These tests evaluate the coating's ability to maintain adhesion and thermal conductivity properties despite repeated expansion and contraction cycles. Most industry standards require 500-1000 cycles without degradation in performance to meet qualification requirements.
Humidity resistance testing is equally important, as moisture ingress can significantly compromise the thermal conductivity of conformal coatings. Components are subjected to 85% relative humidity at 85°C for periods ranging from 500 to 1000 hours, with thermal performance measurements taken at regular intervals to detect any degradation in heat dissipation capabilities.
Thermal shock testing provides more aggressive validation by subjecting coated components to rapid temperature changes, typically from -55°C to +125°C with transition times under 10 seconds. This method specifically evaluates the coating's ability to maintain adhesion and thermal transfer properties under extreme thermal stress conditions.
For applications requiring precise thermal management, thermal resistance measurement using techniques such as laser flash analysis or steady-state heat flow methods provides quantitative data on the coating's thermal conductivity before and after environmental exposure. Industry benchmarks typically require less than 5% degradation in thermal conductivity after reliability testing.
Accelerated aging tests simulate long-term performance by exposing coated components to elevated temperatures (typically 125°C) for extended periods (1000+ hours). These tests help predict the coating's thermal management capabilities over the product's expected lifetime, with performance degradation mathematically modeled to estimate end-of-life thermal characteristics.
Salt spray testing evaluates corrosion resistance, which indirectly affects thermal performance, as corrosion can create air gaps that impede heat transfer. Standard tests expose coated components to salt fog environments for 96-500 hours, followed by thermal performance evaluation to ensure heat dissipation remains within specification.
Mechanical stress testing, including vibration and mechanical shock, ensures that the coating maintains its thermal interface properties under physical stress. This is particularly important for applications in automotive, aerospace, or industrial environments where mechanical forces could compromise the coating's contact with heat-generating components.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!