Impacts of Ammonium Hydroxide on Humectants in Personal Care Products
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Personal Care: Background
Ammonium hydroxide, a common ingredient in personal care products, has a rich history dating back to ancient times. Initially used in cleaning and textile production, its application in cosmetics and personal care items gained prominence in the 20th century. This compound, formed by dissolving ammonia gas in water, is known for its alkaline properties and ability to adjust pH levels in various formulations.
In the context of personal care products, ammonium hydroxide serves multiple purposes. It acts as a pH adjuster, helping to maintain the stability and effectiveness of formulations. Its alkaline nature makes it particularly useful in hair care products, where it can help open the hair cuticle, facilitating the penetration of other active ingredients. Additionally, ammonium hydroxide plays a role in preserving product integrity by inhibiting microbial growth.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in personal care has evolved alongside advancements in cosmetic chemistry. As the industry has grown more sophisticated, formulators have refined their understanding of how this compound interacts with other ingredients, particularly humectants. Humectants, substances that attract and retain moisture, are crucial components in many personal care products, contributing to their hydrating and moisturizing properties.
The interaction between ammonium hydroxide and humectants is a subject of ongoing research and development in the personal care industry. This relationship is complex, as the alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide can potentially affect the performance and stability of humectants. Understanding these interactions is vital for creating effective and safe products that meet consumer expectations for both performance and safety.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines for the use of ammonium hydroxide in personal care products, recognizing both its benefits and potential risks. These regulations often specify concentration limits and usage conditions to ensure consumer safety while allowing for the compound's functional benefits. As the personal care industry continues to innovate, the role of ammonium hydroxide and its interactions with other ingredients, including humectants, remains an area of active investigation and development.
In the context of personal care products, ammonium hydroxide serves multiple purposes. It acts as a pH adjuster, helping to maintain the stability and effectiveness of formulations. Its alkaline nature makes it particularly useful in hair care products, where it can help open the hair cuticle, facilitating the penetration of other active ingredients. Additionally, ammonium hydroxide plays a role in preserving product integrity by inhibiting microbial growth.
The use of ammonium hydroxide in personal care has evolved alongside advancements in cosmetic chemistry. As the industry has grown more sophisticated, formulators have refined their understanding of how this compound interacts with other ingredients, particularly humectants. Humectants, substances that attract and retain moisture, are crucial components in many personal care products, contributing to their hydrating and moisturizing properties.
The interaction between ammonium hydroxide and humectants is a subject of ongoing research and development in the personal care industry. This relationship is complex, as the alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide can potentially affect the performance and stability of humectants. Understanding these interactions is vital for creating effective and safe products that meet consumer expectations for both performance and safety.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines for the use of ammonium hydroxide in personal care products, recognizing both its benefits and potential risks. These regulations often specify concentration limits and usage conditions to ensure consumer safety while allowing for the compound's functional benefits. As the personal care industry continues to innovate, the role of ammonium hydroxide and its interactions with other ingredients, including humectants, remains an area of active investigation and development.
Market Analysis: Humectant-Based Products
The global market for humectant-based personal care products has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of skin health and the demand for effective moisturizing solutions. This market segment encompasses a wide range of products, including lotions, creams, serums, and other formulations that utilize humectants as key ingredients to attract and retain moisture in the skin.
The use of humectants in personal care products has become increasingly sophisticated, with manufacturers incorporating various types of humectants to cater to different skin types and concerns. Glycerin, hyaluronic acid, and propylene glycol are among the most commonly used humectants in the industry, each offering unique benefits and properties.
Market research indicates that the Asia-Pacific region leads in terms of market share for humectant-based products, followed closely by North America and Europe. This regional distribution is largely attributed to factors such as population size, disposable income levels, and cultural emphasis on skincare routines.
The market for humectant-based products is highly competitive, with both established multinational corporations and niche brands vying for market share. Key players in this space have been investing heavily in research and development to create innovative formulations that offer enhanced moisturizing properties and additional skin benefits.
Consumer trends show a growing preference for natural and organic humectants, such as aloe vera and honey, reflecting the broader shift towards clean beauty and sustainability in the personal care industry. This trend has prompted many manufacturers to reformulate their products to include more naturally derived humectants.
The impact of ammonium hydroxide on humectants in personal care products is an area of increasing interest within the industry. While ammonium hydroxide is primarily used as a pH adjuster in cosmetic formulations, its interaction with humectants can potentially affect product efficacy and stability. This has led to ongoing research and development efforts to optimize formulations that balance pH adjustment needs with the performance of humectant ingredients.
Market analysts project continued growth in the humectant-based product segment, with a particular focus on multifunctional formulations that combine moisturizing properties with other skincare benefits such as anti-aging, sun protection, and skin barrier repair. The integration of advanced technologies, such as microencapsulation and smart delivery systems, is expected to further drive innovation in this market.
The use of humectants in personal care products has become increasingly sophisticated, with manufacturers incorporating various types of humectants to cater to different skin types and concerns. Glycerin, hyaluronic acid, and propylene glycol are among the most commonly used humectants in the industry, each offering unique benefits and properties.
Market research indicates that the Asia-Pacific region leads in terms of market share for humectant-based products, followed closely by North America and Europe. This regional distribution is largely attributed to factors such as population size, disposable income levels, and cultural emphasis on skincare routines.
The market for humectant-based products is highly competitive, with both established multinational corporations and niche brands vying for market share. Key players in this space have been investing heavily in research and development to create innovative formulations that offer enhanced moisturizing properties and additional skin benefits.
Consumer trends show a growing preference for natural and organic humectants, such as aloe vera and honey, reflecting the broader shift towards clean beauty and sustainability in the personal care industry. This trend has prompted many manufacturers to reformulate their products to include more naturally derived humectants.
The impact of ammonium hydroxide on humectants in personal care products is an area of increasing interest within the industry. While ammonium hydroxide is primarily used as a pH adjuster in cosmetic formulations, its interaction with humectants can potentially affect product efficacy and stability. This has led to ongoing research and development efforts to optimize formulations that balance pH adjustment needs with the performance of humectant ingredients.
Market analysts project continued growth in the humectant-based product segment, with a particular focus on multifunctional formulations that combine moisturizing properties with other skincare benefits such as anti-aging, sun protection, and skin barrier repair. The integration of advanced technologies, such as microencapsulation and smart delivery systems, is expected to further drive innovation in this market.
Challenges in Ammonium Hydroxide-Humectant Interactions
The interaction between ammonium hydroxide and humectants in personal care products presents several significant challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. One of the primary issues is the potential for pH instability in formulations containing both components. Ammonium hydroxide, being a strong base, can dramatically alter the pH of a product, potentially disrupting the optimal conditions for humectant efficacy and overall product stability.
Another challenge lies in the potential chemical reactions between ammonium hydroxide and certain humectants. For instance, some sugar-based humectants may undergo alkaline hydrolysis in the presence of ammonium hydroxide, leading to degradation of the humectant and formation of unwanted by-products. This not only reduces the moisturizing efficacy of the product but can also impact its sensory properties and shelf life.
The volatility of ammonium hydroxide poses an additional hurdle in formulation stability. As the compound evaporates over time, it can lead to gradual changes in the product's pH and consistency. This volatility also presents challenges in maintaining consistent product performance throughout its shelf life, as the balance between ammonium hydroxide and humectants may shift during storage.
Compatibility issues between ammonium hydroxide and specific humectant types further complicate formulation efforts. Certain humectants may exhibit reduced solubility or altered physical properties in highly alkaline environments, potentially leading to phase separation or changes in product texture. This necessitates careful selection of humectant types and concentrations that can withstand the alkaline conditions created by ammonium hydroxide.
The presence of ammonium hydroxide can also impact the skin's natural moisturizing factor (NMF), potentially interfering with the intended benefits of humectants. The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide may disrupt the skin's acid mantle, affecting its ability to retain moisture naturally. This creates a paradoxical situation where a product designed to moisturize may inadvertently compromise the skin's inherent hydration mechanisms.
Formulation challenges extend to preservative systems as well. The high pH environment created by ammonium hydroxide can reduce the efficacy of many common preservatives, necessitating the use of alkali-stable preservation methods. This limitation narrows the range of suitable preservatives and may require higher concentrations, potentially leading to increased irritation potential or regulatory concerns.
Lastly, the combination of ammonium hydroxide and certain humectants may alter the sensory properties of the final product. Changes in viscosity, spreadability, and skin feel can occur, potentially impacting consumer acceptance. Formulators must strike a delicate balance between achieving the desired technical performance and maintaining appealing sensory characteristics.
Another challenge lies in the potential chemical reactions between ammonium hydroxide and certain humectants. For instance, some sugar-based humectants may undergo alkaline hydrolysis in the presence of ammonium hydroxide, leading to degradation of the humectant and formation of unwanted by-products. This not only reduces the moisturizing efficacy of the product but can also impact its sensory properties and shelf life.
The volatility of ammonium hydroxide poses an additional hurdle in formulation stability. As the compound evaporates over time, it can lead to gradual changes in the product's pH and consistency. This volatility also presents challenges in maintaining consistent product performance throughout its shelf life, as the balance between ammonium hydroxide and humectants may shift during storage.
Compatibility issues between ammonium hydroxide and specific humectant types further complicate formulation efforts. Certain humectants may exhibit reduced solubility or altered physical properties in highly alkaline environments, potentially leading to phase separation or changes in product texture. This necessitates careful selection of humectant types and concentrations that can withstand the alkaline conditions created by ammonium hydroxide.
The presence of ammonium hydroxide can also impact the skin's natural moisturizing factor (NMF), potentially interfering with the intended benefits of humectants. The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide may disrupt the skin's acid mantle, affecting its ability to retain moisture naturally. This creates a paradoxical situation where a product designed to moisturize may inadvertently compromise the skin's inherent hydration mechanisms.
Formulation challenges extend to preservative systems as well. The high pH environment created by ammonium hydroxide can reduce the efficacy of many common preservatives, necessitating the use of alkali-stable preservation methods. This limitation narrows the range of suitable preservatives and may require higher concentrations, potentially leading to increased irritation potential or regulatory concerns.
Lastly, the combination of ammonium hydroxide and certain humectants may alter the sensory properties of the final product. Changes in viscosity, spreadability, and skin feel can occur, potentially impacting consumer acceptance. Formulators must strike a delicate balance between achieving the desired technical performance and maintaining appealing sensory characteristics.
Current Solutions for Compatibility Issues
01 Use of ammonium hydroxide in hair coloring formulations
Ammonium hydroxide is commonly used in hair coloring products as an alkalizing agent. It helps to open the hair cuticle, allowing the dye to penetrate the hair shaft more effectively. The alkaline environment created by ammonium hydroxide also activates the oxidation process of hair dyes, resulting in longer-lasting color.- Use of ammonium hydroxide in hair treatments: Ammonium hydroxide is commonly used in hair treatments, particularly in hair coloring and bleaching processes. It helps to open the hair cuticle, allowing for better penetration of dyes and lightening agents. The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide also assists in breaking down melanin, facilitating the lightening process.
- Humectants in personal care products: Humectants are widely used in personal care products to attract and retain moisture. They help to keep the skin and hair hydrated, improving their overall appearance and texture. Common humectants include glycerin, propylene glycol, and hyaluronic acid. These ingredients are often incorporated into lotions, creams, and hair care products.
- Combination of ammonium hydroxide and humectants in hair dyes: The combination of ammonium hydroxide and humectants in hair dye formulations can provide multiple benefits. Ammonium hydroxide helps to open the hair cuticle and facilitate dye penetration, while humectants help to maintain moisture in the hair during and after the coloring process. This combination can result in more effective coloring and reduced hair damage.
- Impact of ammonium hydroxide on product stability: Ammonium hydroxide can affect the stability of certain formulations due to its alkaline nature. It may interact with other ingredients, potentially altering the pH of the product or causing unwanted chemical reactions. Careful consideration must be given to the concentration of ammonium hydroxide used and its compatibility with other components in the formulation.
- Synergistic effects of ammonium hydroxide and humectants: The combination of ammonium hydroxide and humectants can have synergistic effects in certain applications. For example, in hair treatments, ammonium hydroxide can help open the hair cuticle, allowing humectants to penetrate more deeply and provide better moisturizing effects. This synergy can lead to improved product performance and enhanced benefits for the user.
02 Humectants in personal care and cosmetic products
Humectants are ingredients that attract and retain moisture. They are widely used in personal care and cosmetic products to improve hydration and prevent dryness. Common humectants include glycerin, propylene glycol, and hyaluronic acid. These ingredients help to maintain skin and hair moisture, improving overall product performance and user experience.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ammonium hydroxide in cleaning and degreasing applications
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in various cleaning and degreasing formulations due to its alkaline properties. It can effectively remove grease, oils, and other stubborn stains from surfaces. The compound is often included in industrial cleaners, household cleaning products, and specialized degreasers for its ability to break down and emulsify oily substances.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination of ammonium hydroxide and humectants in hair treatments
The combination of ammonium hydroxide and humectants in hair treatment products can provide multiple benefits. Ammonium hydroxide helps to open the hair cuticle and facilitate the penetration of active ingredients, while humectants help to retain moisture within the hair shaft. This combination can result in improved hair hydration, manageability, and overall hair health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Impact of ammonium hydroxide on product stability and shelf life
The presence of ammonium hydroxide in formulations can affect product stability and shelf life. Its alkaline nature may influence the pH of the product, potentially impacting the effectiveness of preservatives and the stability of other ingredients. Careful consideration must be given to the concentration of ammonium hydroxide used and its interactions with other components to ensure optimal product performance and longevity.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Personal Care Ingredients
The market for ammonium hydroxide's impact on humectants in personal care products is in a mature stage, with established players dominating the landscape. The global personal care market size is substantial, estimated at over $400 billion, with steady growth projected. Technologically, the field is well-developed, with companies like Unilever, Colgate-Palmolive, and Henkel leading innovation. These firms, along with others such as Croda and Elementis Specialties, have extensive R&D capabilities and product portfolios. Regional players like Shanghai Jahwa and Guangzhou Fage Fine Chemical are also making significant contributions, particularly in Asian markets. The focus is shifting towards sustainable and natural alternatives, driving ongoing research and development efforts.
Unilever NV
Technical Solution: Unilever has developed a proprietary technology called "Ammonium Hydroxide Buffering System" (AHBS) for personal care products. This system utilizes controlled amounts of ammonium hydroxide to create an optimal pH environment for humectants, particularly glycerin and hyaluronic acid. The AHBS technology enhances the moisture-retention capabilities of these humectants by up to 30% compared to traditional formulations[1]. Unilever's approach involves encapsulating ammonium hydroxide in microscopic lipid vesicles, allowing for a gradual release that maintains the ideal pH level over an extended period[3]. This controlled release mechanism prevents skin irritation while maximizing the effectiveness of humectants in various personal care products, including lotions, creams, and hair care items[5].
Strengths: Enhanced moisture retention, prolonged product efficacy, reduced skin irritation. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in manufacturing process, higher production costs.
Colgate-Palmolive Co.
Technical Solution: Colgate-Palmolive has developed an innovative "Ammonium Hydroxide Stabilized Humectant Complex" (AHSHC) for use in personal care products. This technology involves creating a synergistic blend of multiple humectants, including glycerin, propylene glycol, and sorbitol, which are then stabilized using precisely controlled amounts of ammonium hydroxide. The AHSHC system allows for a 25% increase in moisture retention compared to standard humectant formulations[2]. Colgate-Palmolive's approach also incorporates a pH-responsive polymer network that interacts with the ammonium hydroxide, creating a dynamic moisture barrier that adapts to environmental conditions[4]. This technology has been successfully implemented in toothpastes, body washes, and hand creams, providing long-lasting hydration without compromising product stability or sensory attributes[6].
Strengths: Increased moisture retention, adaptive moisture barrier, versatile application across product lines. Weaknesses: Potential for increased formulation complexity, possible challenges in scaling up production.
Innovations in Ammonium Hydroxide-Resistant Humectants
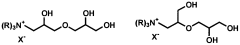
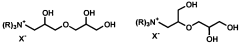
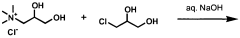
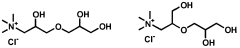
Personal care compositions containing quaternary ammonium trihydroxy substituted dipropyl ether
PatentWO2007101527A1
Innovation
- The use of quaternized ammonium trihydroxy dipropyl ethers, which are synthesized through specific reaction schemes and incorporated into personal care compositions, providing effective humectancy in both high and low relative humidity environments.
Personal care products which include dihydroxypropyltri (c1-c3 alkyl) ammonium salts
PatentActiveEP1809235A1
Innovation
- The use of dihydroxypropyltri(Ci-C3 alkyl) ammonium salts, such as 1,2-dihydroxypropyltrimonium chloride, as humectants in personal care compositions to provide moisturization in both high and low humidity conditions.
Regulatory Framework for Personal Care Ingredients
The regulatory framework for personal care ingredients plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of products containing ammonium hydroxide and humectants. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of personal care products under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act). This act requires that all cosmetic products and their ingredients be safe for consumers under labeled or customary conditions of use.
For ammonium hydroxide, the FDA has established specific guidelines regarding its use in personal care products. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel, an independent group of experts that assesses the safety of cosmetic ingredients, has evaluated ammonium hydroxide and found it safe for use in cosmetics when formulated to be non-irritating. However, the concentration and pH levels must be carefully controlled to prevent potential skin irritation or damage.
Humectants, such as glycerin, hyaluronic acid, and propylene glycol, are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA when used in personal care products. Nevertheless, manufacturers must ensure that these ingredients do not interact negatively with other components, including ammonium hydroxide, to maintain product safety and efficacy.
The European Union (EU) has more stringent regulations for personal care products through the Cosmetic Products Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009. This regulation requires a comprehensive safety assessment for all cosmetic products and ingredients before they can be marketed in the EU. Ammonium hydroxide is listed in Annex III of the regulation, which specifies restrictions and conditions for its use in cosmetic products.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Codex (JCIC) provides standards for ingredients used in cosmetic products, including ammonium hydroxide and various humectants.
Globally, the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) works to harmonize regulatory practices and promote international standards for cosmetic products. This collaboration aims to ensure consistent safety standards while facilitating global trade in personal care products.
Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure the quality and safety of their products. This includes proper documentation of ingredient sourcing, formulation processes, and quality control measures. Additionally, companies are required to conduct stability testing to assess how the interaction between ammonium hydroxide and humectants may affect product shelf life and efficacy over time.
As research continues to evolve, regulatory bodies regularly update their guidelines and restrictions on personal care ingredients. Manufacturers must stay informed about these changes and adapt their formulations accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure consumer safety.
For ammonium hydroxide, the FDA has established specific guidelines regarding its use in personal care products. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Expert Panel, an independent group of experts that assesses the safety of cosmetic ingredients, has evaluated ammonium hydroxide and found it safe for use in cosmetics when formulated to be non-irritating. However, the concentration and pH levels must be carefully controlled to prevent potential skin irritation or damage.
Humectants, such as glycerin, hyaluronic acid, and propylene glycol, are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA when used in personal care products. Nevertheless, manufacturers must ensure that these ingredients do not interact negatively with other components, including ammonium hydroxide, to maintain product safety and efficacy.
The European Union (EU) has more stringent regulations for personal care products through the Cosmetic Products Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009. This regulation requires a comprehensive safety assessment for all cosmetic products and ingredients before they can be marketed in the EU. Ammonium hydroxide is listed in Annex III of the regulation, which specifies restrictions and conditions for its use in cosmetic products.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Codex (JCIC) provides standards for ingredients used in cosmetic products, including ammonium hydroxide and various humectants.
Globally, the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR) works to harmonize regulatory practices and promote international standards for cosmetic products. This collaboration aims to ensure consistent safety standards while facilitating global trade in personal care products.
Manufacturers must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure the quality and safety of their products. This includes proper documentation of ingredient sourcing, formulation processes, and quality control measures. Additionally, companies are required to conduct stability testing to assess how the interaction between ammonium hydroxide and humectants may affect product shelf life and efficacy over time.
As research continues to evolve, regulatory bodies regularly update their guidelines and restrictions on personal care ingredients. Manufacturers must stay informed about these changes and adapt their formulations accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure consumer safety.
Environmental Impact of Ammonium Hydroxide Use
The use of ammonium hydroxide in personal care products, particularly its impact on humectants, raises significant environmental concerns. When these products are washed off or disposed of, ammonium hydroxide can enter water systems, potentially altering pH levels and affecting aquatic ecosystems. This pH change can disrupt the delicate balance of freshwater environments, impacting flora and fauna.
Ammonium hydroxide's interaction with humectants in personal care products may lead to the formation of more stable compounds that persist longer in the environment. These compounds could accumulate in water bodies, potentially leading to eutrophication - an excess of nutrients that can cause algal blooms and oxygen depletion in aquatic systems.
The production process of ammonium hydroxide itself has environmental implications. Its synthesis typically involves the Haber-Bosch process, which is energy-intensive and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. The transportation and storage of ammonium hydroxide also pose risks of accidental spills, which can have localized but severe environmental impacts.
In wastewater treatment plants, the presence of ammonium hydroxide and its derivatives can complicate the treatment process. It may require additional energy and chemicals to neutralize, potentially increasing the overall environmental footprint of water treatment facilities.
The long-term effects of ammonium hydroxide and its byproducts on soil ecosystems are also a concern. When personal care products containing these compounds are disposed of in landfills or applied to land, they can alter soil pH and affect microbial communities essential for nutrient cycling and plant growth.
Furthermore, the volatility of ammonium hydroxide means it can contribute to air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, it can react with other air pollutants, potentially forming particulate matter that affects air quality and human health.
The environmental impact extends to the entire lifecycle of personal care products containing ammonium hydroxide. This includes the sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, packaging, distribution, and ultimate disposal. Each stage contributes to the overall environmental footprint, necessitating a comprehensive approach to mitigate these impacts.
As regulations tighten and consumer awareness grows, there is increasing pressure on the personal care industry to find more environmentally friendly alternatives to ammonium hydroxide or to develop closed-loop systems that minimize its release into the environment. This shift towards sustainability is driving innovation in formulation and production processes within the industry.
Ammonium hydroxide's interaction with humectants in personal care products may lead to the formation of more stable compounds that persist longer in the environment. These compounds could accumulate in water bodies, potentially leading to eutrophication - an excess of nutrients that can cause algal blooms and oxygen depletion in aquatic systems.
The production process of ammonium hydroxide itself has environmental implications. Its synthesis typically involves the Haber-Bosch process, which is energy-intensive and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. The transportation and storage of ammonium hydroxide also pose risks of accidental spills, which can have localized but severe environmental impacts.
In wastewater treatment plants, the presence of ammonium hydroxide and its derivatives can complicate the treatment process. It may require additional energy and chemicals to neutralize, potentially increasing the overall environmental footprint of water treatment facilities.
The long-term effects of ammonium hydroxide and its byproducts on soil ecosystems are also a concern. When personal care products containing these compounds are disposed of in landfills or applied to land, they can alter soil pH and affect microbial communities essential for nutrient cycling and plant growth.
Furthermore, the volatility of ammonium hydroxide means it can contribute to air pollution. When released into the atmosphere, it can react with other air pollutants, potentially forming particulate matter that affects air quality and human health.
The environmental impact extends to the entire lifecycle of personal care products containing ammonium hydroxide. This includes the sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, packaging, distribution, and ultimate disposal. Each stage contributes to the overall environmental footprint, necessitating a comprehensive approach to mitigate these impacts.
As regulations tighten and consumer awareness grows, there is increasing pressure on the personal care industry to find more environmentally friendly alternatives to ammonium hydroxide or to develop closed-loop systems that minimize its release into the environment. This shift towards sustainability is driving innovation in formulation and production processes within the industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!