Investigating isotonic solutions in plant secondary metabolite yield
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isotonic Solutions in Plant Metabolite Production
Isotonic solutions have emerged as a promising approach in enhancing the yield of plant secondary metabolites. These solutions, which have the same osmotic pressure as the plant cells, create an optimal environment for metabolite production without causing cellular stress. The concept of isotonicity in plant cultivation has its roots in plant physiology research dating back to the early 20th century. However, its application in secondary metabolite production has gained significant traction only in recent decades.
The evolution of this technology has been driven by the increasing demand for plant-derived compounds in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food additives. As traditional cultivation methods often result in low yields of desired metabolites, researchers have been exploring innovative techniques to enhance production. Isotonic solutions represent a cutting-edge approach in this pursuit, offering a way to optimize the cellular environment for metabolite synthesis.
The primary goal of implementing isotonic solutions in plant metabolite production is to maximize the yield of target compounds while maintaining plant cell viability. This technique aims to create a balanced osmotic environment that allows cells to direct more energy towards secondary metabolite production rather than osmotic regulation. By minimizing cellular stress, isotonic solutions can potentially unlock the full biosynthetic potential of plant cells.
Recent advancements in this field have focused on fine-tuning the composition of isotonic solutions to match the specific requirements of different plant species and target metabolites. Researchers are investigating various combinations of salts, sugars, and other osmolytes to create tailored solutions that optimize metabolite production for each unique plant-compound system. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining isotonic solutions with other biotechnological approaches, such as elicitation and metabolic engineering, to further enhance secondary metabolite yields.
The development of this technology is expected to continue along several key trajectories. These include the integration of real-time monitoring systems to maintain isotonicity throughout the cultivation process, the exploration of dynamic isotonic environments that change in response to different growth stages, and the application of artificial intelligence to predict optimal solution compositions for novel plant-metabolite combinations. As research progresses, isotonic solutions are poised to play an increasingly important role in sustainable and efficient production of valuable plant-derived compounds.
The evolution of this technology has been driven by the increasing demand for plant-derived compounds in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food additives. As traditional cultivation methods often result in low yields of desired metabolites, researchers have been exploring innovative techniques to enhance production. Isotonic solutions represent a cutting-edge approach in this pursuit, offering a way to optimize the cellular environment for metabolite synthesis.
The primary goal of implementing isotonic solutions in plant metabolite production is to maximize the yield of target compounds while maintaining plant cell viability. This technique aims to create a balanced osmotic environment that allows cells to direct more energy towards secondary metabolite production rather than osmotic regulation. By minimizing cellular stress, isotonic solutions can potentially unlock the full biosynthetic potential of plant cells.
Recent advancements in this field have focused on fine-tuning the composition of isotonic solutions to match the specific requirements of different plant species and target metabolites. Researchers are investigating various combinations of salts, sugars, and other osmolytes to create tailored solutions that optimize metabolite production for each unique plant-compound system. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining isotonic solutions with other biotechnological approaches, such as elicitation and metabolic engineering, to further enhance secondary metabolite yields.
The development of this technology is expected to continue along several key trajectories. These include the integration of real-time monitoring systems to maintain isotonicity throughout the cultivation process, the exploration of dynamic isotonic environments that change in response to different growth stages, and the application of artificial intelligence to predict optimal solution compositions for novel plant-metabolite combinations. As research progresses, isotonic solutions are poised to play an increasingly important role in sustainable and efficient production of valuable plant-derived compounds.
Market Demand for Plant Secondary Metabolites
The market demand for plant secondary metabolites has been steadily increasing over the past decade, driven by growing consumer interest in natural products and the expanding applications of these compounds across various industries. The global market for plant-derived secondary metabolites is projected to reach significant value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate outpacing many other sectors in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries.
One of the primary drivers of this market growth is the pharmaceutical industry's renewed focus on natural products as a source of novel drug candidates. Plant secondary metabolites have shown promise in treating a wide range of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. This has led to increased investment in research and development activities aimed at identifying and isolating these valuable compounds.
The nutraceutical and functional food industries have also contributed substantially to the rising demand for plant secondary metabolites. Consumers are increasingly seeking natural alternatives to synthetic additives and are willing to pay premium prices for products containing plant-derived bioactive compounds. This trend has spurred the development of new functional foods, dietary supplements, and fortified products incorporating plant secondary metabolites.
In the cosmetics and personal care sector, plant-derived compounds are gaining popularity as consumers shift towards natural and organic products. Antioxidants, flavonoids, and other secondary metabolites are being incorporated into skincare formulations, anti-aging products, and hair care solutions, driving further market expansion.
The agricultural industry has also recognized the potential of plant secondary metabolites in crop protection and enhancement. Biopesticides and plant growth regulators derived from these compounds are increasingly being adopted as environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic chemicals, contributing to the overall market growth.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain in meeting the growing demand for plant secondary metabolites. The low yield of these compounds in natural plant sources has been a significant bottleneck, leading to high production costs and limited supply. This has created a strong market pull for innovative technologies that can enhance the production of secondary metabolites, such as the investigation of isotonic solutions to improve yield.
As sustainability becomes a key concern for consumers and industries alike, there is a growing demand for eco-friendly and efficient production methods for plant secondary metabolites. This has led to increased interest in biotechnological approaches, including plant cell and tissue culture techniques, which offer the potential for controlled and optimized production of these valuable compounds.
The market demand for plant secondary metabolites is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by advancements in extraction and purification technologies, expanding applications across industries, and increasing consumer awareness of the benefits of natural products. This presents significant opportunities for companies and researchers working on innovative solutions to enhance the yield and production efficiency of these compounds.
One of the primary drivers of this market growth is the pharmaceutical industry's renewed focus on natural products as a source of novel drug candidates. Plant secondary metabolites have shown promise in treating a wide range of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. This has led to increased investment in research and development activities aimed at identifying and isolating these valuable compounds.
The nutraceutical and functional food industries have also contributed substantially to the rising demand for plant secondary metabolites. Consumers are increasingly seeking natural alternatives to synthetic additives and are willing to pay premium prices for products containing plant-derived bioactive compounds. This trend has spurred the development of new functional foods, dietary supplements, and fortified products incorporating plant secondary metabolites.
In the cosmetics and personal care sector, plant-derived compounds are gaining popularity as consumers shift towards natural and organic products. Antioxidants, flavonoids, and other secondary metabolites are being incorporated into skincare formulations, anti-aging products, and hair care solutions, driving further market expansion.
The agricultural industry has also recognized the potential of plant secondary metabolites in crop protection and enhancement. Biopesticides and plant growth regulators derived from these compounds are increasingly being adopted as environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic chemicals, contributing to the overall market growth.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges remain in meeting the growing demand for plant secondary metabolites. The low yield of these compounds in natural plant sources has been a significant bottleneck, leading to high production costs and limited supply. This has created a strong market pull for innovative technologies that can enhance the production of secondary metabolites, such as the investigation of isotonic solutions to improve yield.
As sustainability becomes a key concern for consumers and industries alike, there is a growing demand for eco-friendly and efficient production methods for plant secondary metabolites. This has led to increased interest in biotechnological approaches, including plant cell and tissue culture techniques, which offer the potential for controlled and optimized production of these valuable compounds.
The market demand for plant secondary metabolites is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by advancements in extraction and purification technologies, expanding applications across industries, and increasing consumer awareness of the benefits of natural products. This presents significant opportunities for companies and researchers working on innovative solutions to enhance the yield and production efficiency of these compounds.
Current Challenges in Metabolite Extraction
The extraction of plant secondary metabolites presents several significant challenges that researchers and industry professionals must overcome to optimize yield and quality. One of the primary issues is the complex nature of plant matrices, which often contain a diverse array of compounds that can interfere with the extraction process. This complexity necessitates the development of highly selective extraction methods to isolate the desired metabolites effectively.
Another major challenge is the stability of secondary metabolites during the extraction process. Many of these compounds are sensitive to heat, light, and pH changes, which can lead to degradation or alteration of their chemical structure. This sensitivity requires careful control of extraction conditions to preserve the integrity of the target molecules.
The low concentration of many secondary metabolites in plant tissues poses an additional hurdle. Some valuable compounds may be present in trace amounts, making their extraction and subsequent purification particularly difficult. This often necessitates the processing of large volumes of plant material to obtain sufficient quantities for analysis or commercial use.
Variability in metabolite content across different plant specimens is another significant challenge. Factors such as growth conditions, harvest time, and genetic variations can lead to substantial differences in the concentration and composition of secondary metabolites. This variability complicates the standardization of extraction protocols and can result in inconsistent yields.
The choice of extraction solvent presents its own set of challenges. While organic solvents are often effective for extracting non-polar compounds, they may not be suitable for more polar metabolites. Additionally, the use of certain solvents can raise environmental and safety concerns, prompting the need for greener alternatives.
Scale-up of extraction processes from laboratory to industrial scale introduces further complications. Methods that work well at small scales may not be economically viable or technically feasible when applied to large-scale production. This scaling issue often requires significant process optimization and sometimes the development of entirely new extraction technologies.
Lastly, the recovery and purification of extracted metabolites from the extraction medium can be challenging. Many extraction processes result in complex mixtures that require additional separation steps, which can be time-consuming, costly, and may lead to loss of valuable compounds. The development of efficient purification techniques that maintain the integrity of the extracted metabolites while achieving high purity is an ongoing area of research in the field of plant secondary metabolite extraction.
Another major challenge is the stability of secondary metabolites during the extraction process. Many of these compounds are sensitive to heat, light, and pH changes, which can lead to degradation or alteration of their chemical structure. This sensitivity requires careful control of extraction conditions to preserve the integrity of the target molecules.
The low concentration of many secondary metabolites in plant tissues poses an additional hurdle. Some valuable compounds may be present in trace amounts, making their extraction and subsequent purification particularly difficult. This often necessitates the processing of large volumes of plant material to obtain sufficient quantities for analysis or commercial use.
Variability in metabolite content across different plant specimens is another significant challenge. Factors such as growth conditions, harvest time, and genetic variations can lead to substantial differences in the concentration and composition of secondary metabolites. This variability complicates the standardization of extraction protocols and can result in inconsistent yields.
The choice of extraction solvent presents its own set of challenges. While organic solvents are often effective for extracting non-polar compounds, they may not be suitable for more polar metabolites. Additionally, the use of certain solvents can raise environmental and safety concerns, prompting the need for greener alternatives.
Scale-up of extraction processes from laboratory to industrial scale introduces further complications. Methods that work well at small scales may not be economically viable or technically feasible when applied to large-scale production. This scaling issue often requires significant process optimization and sometimes the development of entirely new extraction technologies.
Lastly, the recovery and purification of extracted metabolites from the extraction medium can be challenging. Many extraction processes result in complex mixtures that require additional separation steps, which can be time-consuming, costly, and may lead to loss of valuable compounds. The development of efficient purification techniques that maintain the integrity of the extracted metabolites while achieving high purity is an ongoing area of research in the field of plant secondary metabolite extraction.
Existing Isotonic Solution Techniques
01 Formulation of isotonic solutions
Isotonic solutions are formulated to have the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, ensuring they do not cause cell damage when administered. These solutions typically contain a balance of electrolytes and other solutes to match physiological conditions. The yield of isotonic solutions can be optimized by carefully controlling the concentration of solutes and adjusting the manufacturing process.- Formulation of isotonic solutions: Isotonic solutions are formulated to have the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, ensuring they do not cause cell damage when administered. These solutions typically contain a balance of electrolytes and other solutes to match physiological conditions. The formulation process involves careful selection and combination of ingredients to achieve the desired osmolarity.
- Production methods for isotonic solutions: Various production methods are employed to manufacture isotonic solutions with consistent quality and yield. These may include precise mixing techniques, filtration processes, and sterilization methods. Advanced production technologies are used to ensure the stability and efficacy of the final product while maximizing yield.
- Yield optimization in isotonic solution production: Optimizing yield in the production of isotonic solutions involves refining manufacturing processes, reducing waste, and improving efficiency. This may include implementing continuous flow production systems, utilizing advanced process control technologies, and optimizing ingredient utilization. Yield improvement strategies focus on maximizing output while maintaining product quality and consistency.
- Quality control and testing of isotonic solutions: Rigorous quality control measures and testing protocols are essential in the production of isotonic solutions to ensure consistent yield and product efficacy. This includes monitoring osmolarity, pH, and electrolyte concentrations throughout the manufacturing process. Advanced analytical techniques and automated testing systems are employed to maintain high standards and optimize yield.
- Packaging and storage considerations for isotonic solutions: Proper packaging and storage are crucial for maintaining the integrity and yield of isotonic solutions. This involves selecting appropriate container materials, implementing aseptic filling processes, and ensuring optimal storage conditions. Considerations such as light protection, temperature control, and shelf-life extension techniques are important factors in preserving product quality and maximizing yield throughout the supply chain.
02 Production methods for isotonic solutions
Various production methods are employed to manufacture isotonic solutions with high yield. These may include precise mixing techniques, filtration processes, and quality control measures to ensure consistency and purity. Advanced manufacturing technologies can be utilized to improve efficiency and increase the overall yield of isotonic solutions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Composition optimization for yield improvement
The composition of isotonic solutions can be optimized to enhance yield. This may involve selecting specific electrolytes, buffers, or other additives that contribute to stability and efficacy while maximizing production efficiency. Careful consideration of ingredient interactions and their impact on solution properties is crucial for improving yield.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quality control and yield enhancement
Implementing robust quality control measures is essential for maintaining high yields in isotonic solution production. This includes monitoring key parameters such as pH, osmolality, and sterility throughout the manufacturing process. Advanced analytical techniques and in-process controls can help identify and address issues that may affect yield.Expand Specific Solutions05 Packaging and storage considerations for yield optimization
Proper packaging and storage of isotonic solutions play a crucial role in maintaining yield and product quality. Selecting appropriate container materials, closure systems, and storage conditions can minimize product loss and extend shelf life. Innovations in packaging technology and storage methods can contribute to overall yield improvement in isotonic solution production.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Plant Biotechnology Industry
The investigation of isotonic solutions in plant secondary metabolite yield is currently in an early development stage, with a growing market potential as the demand for natural plant-derived compounds increases. The global market for plant extracts is projected to reach $59.4 billion by 2025, driven by applications in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with companies like BASF Plant Science, Pioneer Hi-Bred International, and Impello Biosciences leading research efforts. Universities such as The University of Queensland and Anhui Agricultural University are also contributing to advancements. While some basic principles are established, optimizing isotonic solutions for specific plant metabolites remains a challenge, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity with significant room for innovation and improvement.
BASF Plant Science LLC
Technical Solution: BASF Plant Science LLC has developed a comprehensive approach to investigating isotonic solutions in plant secondary metabolite yield. Their method involves utilizing advanced metabolomics techniques to identify and quantify secondary metabolites in plant tissues under various isotonic conditions. They employ high-throughput screening platforms to assess the impact of different osmotic agents on metabolite production[1]. BASF's researchers have also developed proprietary algorithms for data analysis, enabling rapid identification of optimal isotonic conditions for specific metabolites of interest[3]. Additionally, they have implemented CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing techniques to enhance plant cells' ability to produce target metabolites under isotonic stress[5].
Strengths: Extensive research infrastructure, cutting-edge technologies, and a strong track record in plant biotechnology. Weaknesses: High research and development costs, potential regulatory hurdles for genetically modified organisms.
Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc.
Technical Solution: Pioneer Hi-Bred International has developed a novel approach to investigating isotonic solutions in plant secondary metabolite yield. Their method combines traditional plant breeding techniques with advanced biotechnology tools. They utilize a proprietary high-throughput phenotyping system to screen thousands of plant varieties for their response to various isotonic conditions[2]. This system employs machine learning algorithms to analyze plant growth patterns and metabolite production under different osmotic stresses. Pioneer has also developed a unique "osmotic priming" technique, where seeds are pre-treated with specific isotonic solutions to enhance secondary metabolite production throughout the plant's life cycle[4]. Furthermore, they have implemented CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to fine-tune plant responses to isotonic stress, targeting specific metabolic pathways[6].
Strengths: Extensive germplasm collection, advanced phenotyping capabilities, and expertise in both traditional breeding and modern biotechnology. Weaknesses: Long development cycles for new varieties, potential public resistance to genetically modified crops.
Innovations in Osmotic Stress Manipulation
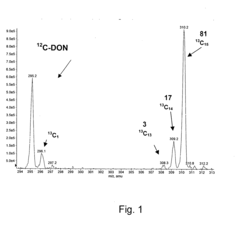
Production of Highly Isotopically Labelled, Secondary, Microbial Metabolic Products, and Corresponding Metabolic Products
PatentInactiveUS20090068706A1
Innovation
- The method involves immobilizing fungi or bacteria on an inert carrier in a liquid synthetic culture medium where substantially all carbon, nitrogen, and sulphur atoms are replaced by stable isotopes, ensuring high labelling efficiency and producing a single, selectively detectable isotopically labelled metabolic product.
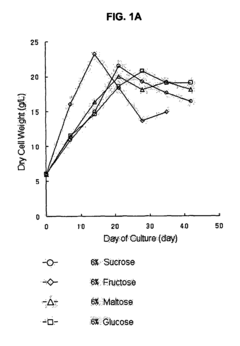
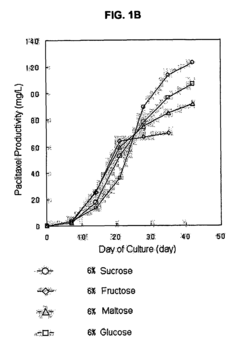
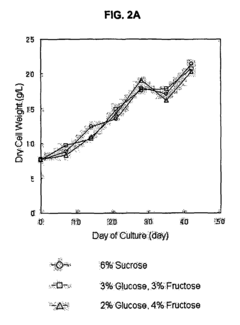
Mass production of secondary metabolite in plant cell culture by treatment of saccharide mixture in medium
PatentActiveUS8936940B2
Innovation
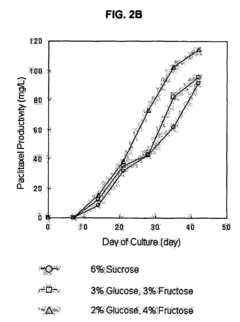
- A method involving a culture medium with a saccharide mixture of at least two saccharides, such as glucose and fructose, or sucrose and fructose, is used as a carbon source to stimulate plant cell growth and increase secondary metabolite productivity, with controlled mixture ratios to optimize growth and production.
Regulatory Framework for Plant-Based Products
The regulatory framework for plant-based products is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the research, development, and commercialization of isotonic solutions for enhancing plant secondary metabolite yield. This framework encompasses various regulatory bodies and guidelines that govern the use of plant-derived compounds in different industries, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and agriculture.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating plant-based products, particularly those intended for human consumption or medical use. The FDA's Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition (CFSAN) oversees the safety and labeling of dietary supplements and food additives derived from plants. For plant-based pharmaceuticals, the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for ensuring their safety and efficacy.
The European Union has established a comprehensive regulatory system for plant-based products through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EMA's Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) focuses on the assessment and registration of herbal medicinal products, while the EFSA evaluates the safety of plant-derived food additives and novel foods.
In the context of agricultural applications, regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the US and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the EU oversee the use of plant-based products in crop protection and soil enhancement. These agencies assess the environmental impact and safety of such products before granting approval for their use.
International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) provide guidelines and standards for the quality, safety, and efficacy of plant-based products on a global scale. These guidelines often serve as a reference for national regulatory bodies in developing countries that may lack comprehensive regulatory frameworks of their own.
The regulatory landscape also addresses intellectual property rights related to plant-based products. Patent offices worldwide, such as the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and the European Patent Office (EPO), play a crucial role in protecting innovations in this field. This includes patents on novel isotonic solutions, extraction methods, and applications for enhancing secondary metabolite production in plants.
As research into isotonic solutions for plant secondary metabolite yield continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to address new challenges and opportunities. This may include the development of specific guidelines for the use of isotonic solutions in agriculture, as well as updated regulations for the commercialization of plant-derived compounds with enhanced bioactive properties.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating plant-based products, particularly those intended for human consumption or medical use. The FDA's Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition (CFSAN) oversees the safety and labeling of dietary supplements and food additives derived from plants. For plant-based pharmaceuticals, the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) is responsible for ensuring their safety and efficacy.
The European Union has established a comprehensive regulatory system for plant-based products through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EMA's Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) focuses on the assessment and registration of herbal medicinal products, while the EFSA evaluates the safety of plant-derived food additives and novel foods.
In the context of agricultural applications, regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the US and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the EU oversee the use of plant-based products in crop protection and soil enhancement. These agencies assess the environmental impact and safety of such products before granting approval for their use.
International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) provide guidelines and standards for the quality, safety, and efficacy of plant-based products on a global scale. These guidelines often serve as a reference for national regulatory bodies in developing countries that may lack comprehensive regulatory frameworks of their own.
The regulatory landscape also addresses intellectual property rights related to plant-based products. Patent offices worldwide, such as the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and the European Patent Office (EPO), play a crucial role in protecting innovations in this field. This includes patents on novel isotonic solutions, extraction methods, and applications for enhancing secondary metabolite production in plants.
As research into isotonic solutions for plant secondary metabolite yield continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to address new challenges and opportunities. This may include the development of specific guidelines for the use of isotonic solutions in agriculture, as well as updated regulations for the commercialization of plant-derived compounds with enhanced bioactive properties.
Sustainability in Metabolite Production
Sustainability in metabolite production is becoming increasingly crucial as the demand for plant-derived secondary metabolites continues to grow. The use of isotonic solutions in plant cultivation offers a promising approach to enhance metabolite yield while promoting sustainable practices.
Isotonic solutions, which have the same osmotic pressure as the plant cells, can significantly reduce water and nutrient stress on plants. This reduction in stress allows plants to allocate more resources towards the production of secondary metabolites, potentially increasing yield without the need for additional inputs. By optimizing the osmotic environment, plants can maintain their cellular integrity and metabolic functions more efficiently.
The implementation of isotonic solutions in metabolite production aligns with several key sustainability principles. Firstly, it promotes water conservation by reducing the overall water requirements for plant cultivation. This is particularly important in regions facing water scarcity or in controlled environment agriculture where water use efficiency is paramount.
Furthermore, the use of isotonic solutions can lead to a decrease in the application of fertilizers and other chemical inputs. By creating an optimal osmotic environment, plants can more effectively uptake and utilize nutrients, reducing the need for excessive fertilization. This not only lowers production costs but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with fertilizer runoff and soil degradation.
The adoption of isotonic solutions in metabolite production also supports the concept of circular economy in agriculture. The precise control of nutrient solutions allows for the potential recycling and reuse of water and nutrients, further enhancing the sustainability of the production process. This closed-loop system can significantly reduce waste and improve resource efficiency.
Additionally, the use of isotonic solutions can contribute to the development of more resilient and adaptable production systems. By fine-tuning the osmotic environment, plants can be better prepared to withstand environmental stresses, potentially reducing crop losses and improving overall production stability. This resilience is crucial in the face of climate change and increasing environmental uncertainties.
As research in this area progresses, there is potential for the development of tailored isotonic solutions for specific metabolite production. This targeted approach could further optimize yield and quality while maintaining a strong focus on sustainability. The integration of isotonic solutions with other sustainable practices, such as vertical farming or aquaponics, could lead to highly efficient and environmentally friendly production systems for valuable plant secondary metabolites.
Isotonic solutions, which have the same osmotic pressure as the plant cells, can significantly reduce water and nutrient stress on plants. This reduction in stress allows plants to allocate more resources towards the production of secondary metabolites, potentially increasing yield without the need for additional inputs. By optimizing the osmotic environment, plants can maintain their cellular integrity and metabolic functions more efficiently.
The implementation of isotonic solutions in metabolite production aligns with several key sustainability principles. Firstly, it promotes water conservation by reducing the overall water requirements for plant cultivation. This is particularly important in regions facing water scarcity or in controlled environment agriculture where water use efficiency is paramount.
Furthermore, the use of isotonic solutions can lead to a decrease in the application of fertilizers and other chemical inputs. By creating an optimal osmotic environment, plants can more effectively uptake and utilize nutrients, reducing the need for excessive fertilization. This not only lowers production costs but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with fertilizer runoff and soil degradation.
The adoption of isotonic solutions in metabolite production also supports the concept of circular economy in agriculture. The precise control of nutrient solutions allows for the potential recycling and reuse of water and nutrients, further enhancing the sustainability of the production process. This closed-loop system can significantly reduce waste and improve resource efficiency.
Additionally, the use of isotonic solutions can contribute to the development of more resilient and adaptable production systems. By fine-tuning the osmotic environment, plants can be better prepared to withstand environmental stresses, potentially reducing crop losses and improving overall production stability. This resilience is crucial in the face of climate change and increasing environmental uncertainties.
As research in this area progresses, there is potential for the development of tailored isotonic solutions for specific metabolite production. This targeted approach could further optimize yield and quality while maintaining a strong focus on sustainability. The integration of isotonic solutions with other sustainable practices, such as vertical farming or aquaponics, could lead to highly efficient and environmentally friendly production systems for valuable plant secondary metabolites.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!