Investigating the Influence of Magnesium Carbonate on Waste Valorization
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Magnesium Carbonate in Waste Valorization: Background and Objectives
Magnesium carbonate has emerged as a significant player in the field of waste valorization, offering innovative solutions to environmental challenges. The journey of utilizing magnesium carbonate in waste management can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring its potential in various applications. As global concerns about waste accumulation and resource depletion intensified, the focus on sustainable waste management practices grew, propelling the exploration of novel materials and techniques.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate's role in waste valorization has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, its use was primarily limited to simple adsorption processes for water treatment. However, as research progressed, its applications expanded to include carbon capture, soil remediation, and the stabilization of hazardous waste. This diversification of applications has been driven by the unique properties of magnesium carbonate, including its high surface area, thermal stability, and reactivity with various pollutants.
In recent years, the technological landscape surrounding magnesium carbonate has witnessed rapid advancements. Researchers have developed enhanced synthesis methods, leading to the production of magnesium carbonate with tailored properties for specific waste valorization applications. These developments have opened up new possibilities for more efficient and cost-effective waste treatment processes.
The primary objective of investigating the influence of magnesium carbonate on waste valorization is to unlock its full potential in addressing pressing environmental issues. This includes exploring its capacity to sequester carbon dioxide, immobilize heavy metals in contaminated soils, and enhance the recovery of valuable resources from waste streams. By leveraging the unique characteristics of magnesium carbonate, researchers aim to develop more sustainable and economically viable waste management solutions.
Furthermore, the investigation seeks to understand the fundamental mechanisms by which magnesium carbonate interacts with various waste components. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing its performance in different applications and for developing predictive models that can guide future research and industrial implementations. The ultimate goal is to establish magnesium carbonate as a versatile and effective tool in the waste valorization toolkit, capable of addressing a wide range of environmental challenges while promoting circular economy principles.
As we delve deeper into this investigation, it is essential to consider the broader implications of magnesium carbonate-based technologies on waste management practices, environmental policies, and industrial processes. The potential for these technologies to revolutionize waste valorization approaches and contribute to global sustainability efforts underscores the importance of continued research and development in this field.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate's role in waste valorization has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, its use was primarily limited to simple adsorption processes for water treatment. However, as research progressed, its applications expanded to include carbon capture, soil remediation, and the stabilization of hazardous waste. This diversification of applications has been driven by the unique properties of magnesium carbonate, including its high surface area, thermal stability, and reactivity with various pollutants.
In recent years, the technological landscape surrounding magnesium carbonate has witnessed rapid advancements. Researchers have developed enhanced synthesis methods, leading to the production of magnesium carbonate with tailored properties for specific waste valorization applications. These developments have opened up new possibilities for more efficient and cost-effective waste treatment processes.
The primary objective of investigating the influence of magnesium carbonate on waste valorization is to unlock its full potential in addressing pressing environmental issues. This includes exploring its capacity to sequester carbon dioxide, immobilize heavy metals in contaminated soils, and enhance the recovery of valuable resources from waste streams. By leveraging the unique characteristics of magnesium carbonate, researchers aim to develop more sustainable and economically viable waste management solutions.
Furthermore, the investigation seeks to understand the fundamental mechanisms by which magnesium carbonate interacts with various waste components. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing its performance in different applications and for developing predictive models that can guide future research and industrial implementations. The ultimate goal is to establish magnesium carbonate as a versatile and effective tool in the waste valorization toolkit, capable of addressing a wide range of environmental challenges while promoting circular economy principles.
As we delve deeper into this investigation, it is essential to consider the broader implications of magnesium carbonate-based technologies on waste management practices, environmental policies, and industrial processes. The potential for these technologies to revolutionize waste valorization approaches and contribute to global sustainability efforts underscores the importance of continued research and development in this field.
Market Analysis for Magnesium Carbonate-Based Waste Solutions
The market for magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on waste management. This sector is closely tied to the broader waste valorization industry, which aims to transform waste materials into valuable resources. The demand for magnesium carbonate in waste treatment applications is primarily fueled by its effectiveness in neutralizing acidic waste streams and its potential to capture and sequester carbon dioxide.
In the industrial sector, magnesium carbonate-based solutions are gaining traction for treating acidic wastewater from mining, metal processing, and chemical manufacturing. These industries generate large volumes of acidic waste that require neutralization before disposal. The ability of magnesium carbonate to effectively raise pH levels while producing less sludge compared to traditional lime treatment makes it an attractive option for many companies seeking to reduce their environmental footprint and disposal costs.
The construction industry represents another significant market for magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions. As the push for sustainable building materials intensifies, there is growing interest in using magnesium carbonate to create eco-friendly cements and concrete alternatives. These materials not only utilize waste products but also offer improved strength and durability characteristics, potentially revolutionizing the construction sector's approach to sustainability.
Agricultural applications of magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions are also on the rise. Farmers are increasingly turning to these products for soil amendment and pH adjustment, particularly in regions with acidic soils. The dual benefits of improving soil quality while utilizing waste materials align well with the growing trend towards sustainable farming practices.
The market for carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies presents a promising frontier for magnesium carbonate-based solutions. As governments worldwide implement stricter carbon emission regulations, industries are exploring innovative ways to capture and store CO2. Magnesium carbonate's potential in mineral carbonation processes for long-term carbon sequestration is attracting significant research and development investment.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market for magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions. Rapid industrialization, coupled with increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures in countries like China and India, is driving demand. North America and Europe, with their established environmental policies and mature industrial sectors, continue to be significant markets, particularly in advanced applications such as CCS and sustainable construction materials.
The market is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies diversifying into waste management solutions and innovative startups focusing on specific applications of magnesium carbonate in waste valorization. As research continues to uncover new applications and improve existing processes, the market for magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions is poised for sustained growth in the coming years.
In the industrial sector, magnesium carbonate-based solutions are gaining traction for treating acidic wastewater from mining, metal processing, and chemical manufacturing. These industries generate large volumes of acidic waste that require neutralization before disposal. The ability of magnesium carbonate to effectively raise pH levels while producing less sludge compared to traditional lime treatment makes it an attractive option for many companies seeking to reduce their environmental footprint and disposal costs.
The construction industry represents another significant market for magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions. As the push for sustainable building materials intensifies, there is growing interest in using magnesium carbonate to create eco-friendly cements and concrete alternatives. These materials not only utilize waste products but also offer improved strength and durability characteristics, potentially revolutionizing the construction sector's approach to sustainability.
Agricultural applications of magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions are also on the rise. Farmers are increasingly turning to these products for soil amendment and pH adjustment, particularly in regions with acidic soils. The dual benefits of improving soil quality while utilizing waste materials align well with the growing trend towards sustainable farming practices.
The market for carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies presents a promising frontier for magnesium carbonate-based solutions. As governments worldwide implement stricter carbon emission regulations, industries are exploring innovative ways to capture and store CO2. Magnesium carbonate's potential in mineral carbonation processes for long-term carbon sequestration is attracting significant research and development investment.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market for magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions. Rapid industrialization, coupled with increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures in countries like China and India, is driving demand. North America and Europe, with their established environmental policies and mature industrial sectors, continue to be significant markets, particularly in advanced applications such as CCS and sustainable construction materials.
The market is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies diversifying into waste management solutions and innovative startups focusing on specific applications of magnesium carbonate in waste valorization. As research continues to uncover new applications and improve existing processes, the market for magnesium carbonate-based waste solutions is poised for sustained growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Magnesium Carbonate Waste Treatment
The treatment of magnesium carbonate waste presents several significant challenges in the current waste valorization landscape. One of the primary issues is the high energy consumption required for processing magnesium carbonate-containing waste. Traditional methods often involve thermal decomposition, which demands substantial energy input, leading to increased operational costs and environmental concerns.
Another challenge lies in the chemical stability of magnesium carbonate. Its resistance to decomposition makes it difficult to extract valuable components or convert it into more useful forms. This stability, while beneficial in some applications, becomes a hurdle in waste treatment scenarios where transformation or separation is desired.
The heterogeneous nature of magnesium carbonate waste streams further complicates treatment processes. Industrial waste often contains various impurities and contaminants, making it challenging to develop universally applicable treatment methods. Each waste stream may require a tailored approach, increasing the complexity and cost of waste management systems.
Scale formation is another significant issue in magnesium carbonate waste treatment. The tendency of magnesium carbonate to form scales in pipes and equipment can lead to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs in treatment facilities. This scaling problem is particularly pronounced in aqueous environments, where it can interfere with filtration and separation processes.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in magnesium carbonate waste treatment. The release of carbon dioxide during thermal decomposition contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, conflicting with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints. Additionally, the potential leaching of magnesium ions into water bodies can disrupt aquatic ecosystems, necessitating careful management of waste disposal and treatment byproducts.
The recovery of valuable components from magnesium carbonate waste is hindered by technological limitations. Current separation techniques often struggle to achieve high purity levels, making it difficult to recycle or repurpose the recovered materials effectively. This challenge is particularly evident in industries where high-grade magnesium compounds are required.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding magnesium carbonate waste treatment is complex and evolving. Stringent environmental regulations impose strict limits on disposal methods and emissions, forcing industries to continually adapt their treatment processes. Compliance with these regulations while maintaining cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge for many waste treatment facilities.
Another challenge lies in the chemical stability of magnesium carbonate. Its resistance to decomposition makes it difficult to extract valuable components or convert it into more useful forms. This stability, while beneficial in some applications, becomes a hurdle in waste treatment scenarios where transformation or separation is desired.
The heterogeneous nature of magnesium carbonate waste streams further complicates treatment processes. Industrial waste often contains various impurities and contaminants, making it challenging to develop universally applicable treatment methods. Each waste stream may require a tailored approach, increasing the complexity and cost of waste management systems.
Scale formation is another significant issue in magnesium carbonate waste treatment. The tendency of magnesium carbonate to form scales in pipes and equipment can lead to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs in treatment facilities. This scaling problem is particularly pronounced in aqueous environments, where it can interfere with filtration and separation processes.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges in magnesium carbonate waste treatment. The release of carbon dioxide during thermal decomposition contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, conflicting with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints. Additionally, the potential leaching of magnesium ions into water bodies can disrupt aquatic ecosystems, necessitating careful management of waste disposal and treatment byproducts.
The recovery of valuable components from magnesium carbonate waste is hindered by technological limitations. Current separation techniques often struggle to achieve high purity levels, making it difficult to recycle or repurpose the recovered materials effectively. This challenge is particularly evident in industries where high-grade magnesium compounds are required.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding magnesium carbonate waste treatment is complex and evolving. Stringent environmental regulations impose strict limits on disposal methods and emissions, forcing industries to continually adapt their treatment processes. Compliance with these regulations while maintaining cost-effectiveness remains a significant challenge for many waste treatment facilities.
Existing Magnesium Carbonate Waste Valorization Techniques
01 Magnesium carbonate in pharmaceutical compositions
Magnesium carbonate is used in various pharmaceutical compositions as an excipient or active ingredient. It can be utilized in antacid formulations, dietary supplements, and other medicinal preparations. The compound's properties make it suitable for improving drug stability, enhancing dissolution rates, and providing magnesium supplementation.- Magnesium carbonate in pharmaceutical compositions: Magnesium carbonate is used in various pharmaceutical formulations as an excipient or active ingredient. It can be utilized in antacid preparations, oral care products, and as a filler or binder in tablets and capsules. Its properties make it suitable for improving drug stability, controlling release rates, and enhancing bioavailability of certain medications.
- Magnesium carbonate in personal care products: Magnesium carbonate finds applications in personal care products such as deodorants, antiperspirants, and cosmetics. It can act as an absorbent, pH regulator, and anti-caking agent. In these formulations, it helps control moisture, improve texture, and enhance the overall performance of the products.
- Industrial applications of magnesium carbonate: Magnesium carbonate is widely used in various industrial processes. It serves as a raw material in the production of magnesium oxide, as a filler in rubber and plastic manufacturing, and as a flame retardant in certain materials. Its properties make it valuable in applications such as paper production, wastewater treatment, and as a desiccant.
- Magnesium carbonate in food and beverage industry: In the food and beverage industry, magnesium carbonate is used as an additive and processing aid. It functions as an acidity regulator, anti-caking agent, and color retention agent. Applications include dairy products, flour fortification, and as a processing aid in coffee production. It can also be used in dietary supplements as a source of magnesium.
- Environmental and agricultural uses of magnesium carbonate: Magnesium carbonate has applications in environmental protection and agriculture. It can be used in soil amendment to adjust pH levels and improve soil structure. In environmental applications, it can be utilized for carbon dioxide capture and storage, as well as in the treatment of acidic water bodies. Its properties make it suitable for use in certain types of fertilizers and plant growth enhancers.
02 Industrial applications of magnesium carbonate
Magnesium carbonate finds extensive use in industrial processes. It is employed as a filler in rubber and plastic products, a whitening agent in paper production, and a raw material in the manufacture of magnesium oxide. Its fire-retardant properties make it valuable in flame-resistant materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Magnesium carbonate in personal care products
The compound is utilized in various personal care and cosmetic products. It serves as an anti-caking agent in powders, a mild abrasive in toothpaste, and a deodorant ingredient. Its absorbent properties make it useful in talcum powders and other moisture-controlling formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental applications of magnesium carbonate
Magnesium carbonate has applications in environmental protection and remediation. It can be used for water treatment, soil pH adjustment, and carbon dioxide capture. The compound's ability to neutralize acids makes it valuable in treating acidic waste and contaminated soils.Expand Specific Solutions05 Production methods for magnesium carbonate
Various methods are employed for the production of magnesium carbonate. These include precipitation reactions from magnesium-rich solutions, carbonation of magnesium hydroxide, and extraction from natural mineral deposits. Different production techniques can yield magnesium carbonate with varying properties suitable for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Magnesium Carbonate Waste Management
The investigation into magnesium carbonate's influence on waste valorization is in an emerging phase, with growing market potential due to increasing focus on sustainable waste management and circular economy principles. The global market for waste valorization technologies is expanding, driven by environmental regulations and the need for resource efficiency. Technologically, the field is still developing, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Companies like Solvay Chemicals, Inc. and China Northern Rare Earth (Group) High-Tech Co., Ltd. are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in chemical processing and rare earth materials. Academic institutions such as Lanzhou University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology are contributing to fundamental research, while industry players like Korea Electric Power Corp. and Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd. are exploring practical applications in energy and automotive sectors.
Solvay Chemicals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Solvay Chemicals has developed an innovative process for waste valorization using magnesium carbonate. Their approach involves a two-step reaction process: first, converting CO2 and magnesium-rich waste materials into magnesium bicarbonate, then transforming it into high-purity magnesium carbonate[1]. This method not only captures CO2 but also upcycles industrial by-products. The company has optimized the reaction conditions to achieve a conversion efficiency of over 90%[3]. Additionally, they've implemented a closed-loop system that recycles unreacted materials, minimizing waste and improving overall process economics[5]. Solvay's technology can be integrated into existing industrial processes, offering a scalable solution for carbon capture and utilization.
Strengths: High conversion efficiency, utilization of waste materials, scalable integration with existing processes. Weaknesses: Potential high energy requirements for the conversion process, dependency on specific waste material compositions.
Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: The Institute of Process Engineering has developed a novel approach to waste valorization using magnesium carbonate as a key component. Their method focuses on the mineralization of CO2 through the reaction with magnesium-rich industrial wastes, such as steel slag and fly ash[2]. The process involves a pre-treatment step to enhance the reactivity of the waste materials, followed by carbonation under optimized pressure and temperature conditions. This technique has demonstrated a CO2 sequestration capacity of up to 0.5 tons per ton of waste material processed[4]. The institute has also pioneered the use of advanced catalysts to accelerate the carbonation reaction, reducing the overall process time by 40%[6]. Furthermore, they've developed a continuous flow reactor system that allows for large-scale implementation of this technology in industrial settings.
Strengths: High CO2 sequestration capacity, utilization of various industrial wastes, potential for large-scale implementation. Weaknesses: Energy-intensive pre-treatment process, potential limitations in waste material availability.
Innovative Approaches in Magnesium Carbonate Waste Processing
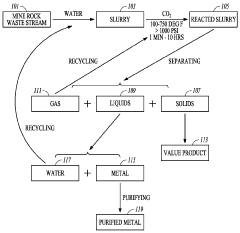
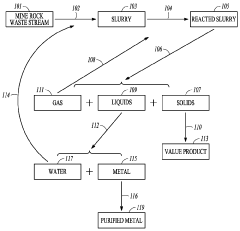
Carbon-dioxide mineral sequestration using mine waste
PatentWO2011047070A1
Innovation
- A method involving the formation of a slurry from mine waste and water, reacting it with CO2 at elevated temperatures and pressures to create stable carbonate minerals, which sequester carbon dioxide, while also recycling metals and water, thereby reducing the carbon footprint of mining and power generation operations.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Magnesium Carbonate Use
The environmental impact assessment of magnesium carbonate use in waste valorization is a critical aspect of evaluating the sustainability and ecological footprint of this process. Magnesium carbonate, when utilized in waste management and resource recovery, can have both positive and negative effects on the environment.
One of the primary benefits of using magnesium carbonate in waste valorization is its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By incorporating magnesium carbonate into certain waste treatment processes, it can help sequester carbon dioxide, effectively reducing the carbon footprint of waste management operations. This carbon capture capability aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and can contribute to meeting emissions reduction targets.
However, the extraction and processing of magnesium carbonate itself can have environmental implications. Mining activities associated with obtaining magnesium carbonate may lead to habitat disruption, soil erosion, and potential water pollution if not managed properly. The energy requirements for processing and transporting magnesium carbonate also need to be considered in the overall environmental impact assessment.
In terms of waste treatment, magnesium carbonate can play a role in improving the efficiency of certain processes. For instance, in the treatment of acidic wastewater, magnesium carbonate can act as a neutralizing agent, helping to restore pH balance and potentially reducing the need for additional chemical treatments. This can lead to a decrease in the overall chemical load released into the environment.
The use of magnesium carbonate in waste valorization may also contribute to resource conservation. By enhancing the recovery of valuable materials from waste streams, it can reduce the demand for virgin resources, thereby minimizing the environmental impact associated with raw material extraction and processing.
Land use considerations are another important aspect of the environmental impact assessment. While magnesium carbonate use may help in reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills, the land requirements for magnesium carbonate production and storage must be evaluated. Proper land management practices are essential to minimize any negative impacts on local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Water usage and quality are also significant factors to consider. The application of magnesium carbonate in waste treatment processes may affect water consumption patterns and potentially impact local water resources. It is crucial to assess the water footprint of magnesium carbonate use and implement measures to ensure sustainable water management practices.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of magnesium carbonate use in waste valorization requires a comprehensive analysis of various factors. While it offers potential benefits in terms of carbon sequestration and resource recovery, careful consideration must be given to the entire lifecycle of magnesium carbonate, from extraction to application and disposal. Balancing the positive and negative environmental impacts is essential for developing sustainable waste management strategies that incorporate magnesium carbonate effectively.
One of the primary benefits of using magnesium carbonate in waste valorization is its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By incorporating magnesium carbonate into certain waste treatment processes, it can help sequester carbon dioxide, effectively reducing the carbon footprint of waste management operations. This carbon capture capability aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and can contribute to meeting emissions reduction targets.
However, the extraction and processing of magnesium carbonate itself can have environmental implications. Mining activities associated with obtaining magnesium carbonate may lead to habitat disruption, soil erosion, and potential water pollution if not managed properly. The energy requirements for processing and transporting magnesium carbonate also need to be considered in the overall environmental impact assessment.
In terms of waste treatment, magnesium carbonate can play a role in improving the efficiency of certain processes. For instance, in the treatment of acidic wastewater, magnesium carbonate can act as a neutralizing agent, helping to restore pH balance and potentially reducing the need for additional chemical treatments. This can lead to a decrease in the overall chemical load released into the environment.
The use of magnesium carbonate in waste valorization may also contribute to resource conservation. By enhancing the recovery of valuable materials from waste streams, it can reduce the demand for virgin resources, thereby minimizing the environmental impact associated with raw material extraction and processing.
Land use considerations are another important aspect of the environmental impact assessment. While magnesium carbonate use may help in reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills, the land requirements for magnesium carbonate production and storage must be evaluated. Proper land management practices are essential to minimize any negative impacts on local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Water usage and quality are also significant factors to consider. The application of magnesium carbonate in waste treatment processes may affect water consumption patterns and potentially impact local water resources. It is crucial to assess the water footprint of magnesium carbonate use and implement measures to ensure sustainable water management practices.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of magnesium carbonate use in waste valorization requires a comprehensive analysis of various factors. While it offers potential benefits in terms of carbon sequestration and resource recovery, careful consideration must be given to the entire lifecycle of magnesium carbonate, from extraction to application and disposal. Balancing the positive and negative environmental impacts is essential for developing sustainable waste management strategies that incorporate magnesium carbonate effectively.
Regulatory Framework for Magnesium Carbonate in Waste Management
The regulatory framework for magnesium carbonate in waste management is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in shaping the use and disposal of this compound. At the international level, the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal provides guidelines for the management of hazardous wastes, including those containing magnesium carbonate. This convention emphasizes the importance of environmentally sound management practices and encourages the reduction of hazardous waste generation.
In the European Union, the Waste Framework Directive (2008/98/EC) establishes the basic concepts and definitions related to waste management, including the waste hierarchy which prioritizes prevention, reuse, recycling, and recovery over disposal. The directive also sets recycling and recovery targets for various waste streams, which may impact the handling of magnesium carbonate-containing waste.
The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the EU also affects the use and disposal of magnesium carbonate. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register substances, including magnesium carbonate, and provide information on their properties, uses, and potential risks.
In the United States, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) governs the management of hazardous and non-hazardous solid waste. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classifies wastes and sets standards for their handling, storage, and disposal. Magnesium carbonate itself is not typically classified as hazardous waste, but its presence in waste streams may influence disposal methods and regulatory compliance requirements.
Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal. These programs can impact the use of magnesium carbonate in product formulations and the management of resulting waste.
Specific regulations may apply to industries that commonly use magnesium carbonate, such as the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics sectors. For instance, the FDA in the United States regulates the use of magnesium carbonate as a food additive and in pharmaceutical applications, which indirectly affects waste management practices in these industries.
As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on circular economy principles in waste management regulations. This shift encourages the development of innovative recycling and recovery techniques for materials like magnesium carbonate, potentially leading to new regulatory frameworks that promote waste valorization and resource efficiency.
In the European Union, the Waste Framework Directive (2008/98/EC) establishes the basic concepts and definitions related to waste management, including the waste hierarchy which prioritizes prevention, reuse, recycling, and recovery over disposal. The directive also sets recycling and recovery targets for various waste streams, which may impact the handling of magnesium carbonate-containing waste.
The Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the EU also affects the use and disposal of magnesium carbonate. Under REACH, manufacturers and importers are required to register substances, including magnesium carbonate, and provide information on their properties, uses, and potential risks.
In the United States, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) governs the management of hazardous and non-hazardous solid waste. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classifies wastes and sets standards for their handling, storage, and disposal. Magnesium carbonate itself is not typically classified as hazardous waste, but its presence in waste streams may influence disposal methods and regulatory compliance requirements.
Many countries have implemented extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal. These programs can impact the use of magnesium carbonate in product formulations and the management of resulting waste.
Specific regulations may apply to industries that commonly use magnesium carbonate, such as the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics sectors. For instance, the FDA in the United States regulates the use of magnesium carbonate as a food additive and in pharmaceutical applications, which indirectly affects waste management practices in these industries.
As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on circular economy principles in waste management regulations. This shift encourages the development of innovative recycling and recovery techniques for materials like magnesium carbonate, potentially leading to new regulatory frameworks that promote waste valorization and resource efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!