Investigating the Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Carbonate-Based Composites
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MgCO3 Composite Background and Objectives
Magnesium carbonate-based composites have emerged as a promising class of materials in recent years, attracting significant attention from researchers and industries alike. These composites combine the unique properties of magnesium carbonate with various reinforcing materials to create advanced materials with enhanced mechanical, thermal, and chemical characteristics. The development of these composites stems from the growing demand for lightweight, high-strength materials in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate-based composites can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of incorporating magnesium carbonate into polymer matrices. This initial work laid the foundation for subsequent advancements in composite technology, leading to the development of more sophisticated and tailored materials. Over the past two decades, significant progress has been made in understanding the fundamental properties of these composites and optimizing their performance for specific applications.
The primary objective of investigating the mechanical properties of magnesium carbonate-based composites is to develop materials that offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, improved durability, and enhanced resistance to environmental factors. Researchers aim to achieve a delicate balance between the inherent properties of magnesium carbonate and the reinforcing components to create composites that outperform traditional materials in key areas such as tensile strength, compressive strength, and impact resistance.
Current technological trends in this field focus on exploring novel reinforcement materials, optimizing processing techniques, and developing innovative surface treatments to enhance the interfacial bonding between the magnesium carbonate matrix and the reinforcing phase. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on understanding the microstructural characteristics of these composites and their influence on macroscopic mechanical properties.
The expected outcomes of this research include the development of magnesium carbonate-based composites with tailored mechanical properties suitable for specific industrial applications. These materials are anticipated to offer significant advantages over conventional composites, including reduced weight, improved corrosion resistance, and enhanced thermal stability. Furthermore, the investigation aims to establish comprehensive structure-property relationships that will guide future material design and optimization efforts.
As the field of magnesium carbonate-based composites continues to evolve, researchers are also exploring the potential for multifunctional composites that combine mechanical strength with other desirable properties such as electrical conductivity, thermal insulation, or self-healing capabilities. This holistic approach to material design is expected to open up new avenues for innovation and expand the range of applications for these advanced composites across various industries.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate-based composites can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring the potential of incorporating magnesium carbonate into polymer matrices. This initial work laid the foundation for subsequent advancements in composite technology, leading to the development of more sophisticated and tailored materials. Over the past two decades, significant progress has been made in understanding the fundamental properties of these composites and optimizing their performance for specific applications.
The primary objective of investigating the mechanical properties of magnesium carbonate-based composites is to develop materials that offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, improved durability, and enhanced resistance to environmental factors. Researchers aim to achieve a delicate balance between the inherent properties of magnesium carbonate and the reinforcing components to create composites that outperform traditional materials in key areas such as tensile strength, compressive strength, and impact resistance.
Current technological trends in this field focus on exploring novel reinforcement materials, optimizing processing techniques, and developing innovative surface treatments to enhance the interfacial bonding between the magnesium carbonate matrix and the reinforcing phase. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on understanding the microstructural characteristics of these composites and their influence on macroscopic mechanical properties.
The expected outcomes of this research include the development of magnesium carbonate-based composites with tailored mechanical properties suitable for specific industrial applications. These materials are anticipated to offer significant advantages over conventional composites, including reduced weight, improved corrosion resistance, and enhanced thermal stability. Furthermore, the investigation aims to establish comprehensive structure-property relationships that will guide future material design and optimization efforts.
As the field of magnesium carbonate-based composites continues to evolve, researchers are also exploring the potential for multifunctional composites that combine mechanical strength with other desirable properties such as electrical conductivity, thermal insulation, or self-healing capabilities. This holistic approach to material design is expected to open up new avenues for innovation and expand the range of applications for these advanced composites across various industries.
Market Analysis for MgCO3-Based Materials
The market for magnesium carbonate-based composites is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials across various industries. These composites offer a unique combination of properties, including low density, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent thermal stability, making them attractive for applications in aerospace, automotive, construction, and healthcare sectors.
In the aerospace industry, magnesium carbonate-based composites are gaining traction as manufacturers seek to reduce aircraft weight and improve fuel efficiency. The automotive sector is also showing increased interest in these materials for lightweighting vehicles, particularly in the growing electric vehicle market where range extension is crucial. The construction industry is exploring the use of these composites for sustainable building materials, leveraging their fire-resistant and insulating properties.
The healthcare sector presents another promising market for magnesium carbonate-based composites. Their biocompatibility and potential for use in orthopedic implants and tissue engineering scaffolds are driving research and development efforts. Additionally, the growing focus on environmental sustainability is boosting the demand for these materials in packaging and consumer goods industries.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for magnesium carbonate-based composites to exceed the average growth rate of the overall composites market over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of these materials in emerging applications and the ongoing research into improving their mechanical properties and manufacturing processes.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of magnesium carbonate-based composites. The relatively higher production costs compared to traditional materials and the need for specialized manufacturing techniques are limiting factors. Additionally, the market faces competition from other advanced composites and alternative lightweight materials.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for magnesium carbonate-based composites, driven by strong aerospace and automotive industries. Asia-Pacific is expected to emerge as the fastest-growing market, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing automotive production, and government initiatives promoting lightweight materials in China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies diversifying into advanced materials and specialized composite manufacturers. Key players are investing in research and development to enhance the mechanical properties of these composites and develop cost-effective production methods. Collaborations between material suppliers, manufacturers, and end-users are becoming increasingly common to accelerate innovation and market adoption.
In the aerospace industry, magnesium carbonate-based composites are gaining traction as manufacturers seek to reduce aircraft weight and improve fuel efficiency. The automotive sector is also showing increased interest in these materials for lightweighting vehicles, particularly in the growing electric vehicle market where range extension is crucial. The construction industry is exploring the use of these composites for sustainable building materials, leveraging their fire-resistant and insulating properties.
The healthcare sector presents another promising market for magnesium carbonate-based composites. Their biocompatibility and potential for use in orthopedic implants and tissue engineering scaffolds are driving research and development efforts. Additionally, the growing focus on environmental sustainability is boosting the demand for these materials in packaging and consumer goods industries.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for magnesium carbonate-based composites to exceed the average growth rate of the overall composites market over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of these materials in emerging applications and the ongoing research into improving their mechanical properties and manufacturing processes.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of magnesium carbonate-based composites. The relatively higher production costs compared to traditional materials and the need for specialized manufacturing techniques are limiting factors. Additionally, the market faces competition from other advanced composites and alternative lightweight materials.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for magnesium carbonate-based composites, driven by strong aerospace and automotive industries. Asia-Pacific is expected to emerge as the fastest-growing market, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing automotive production, and government initiatives promoting lightweight materials in China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established chemical companies diversifying into advanced materials and specialized composite manufacturers. Key players are investing in research and development to enhance the mechanical properties of these composites and develop cost-effective production methods. Collaborations between material suppliers, manufacturers, and end-users are becoming increasingly common to accelerate innovation and market adoption.
Current State and Challenges in MgCO3 Composites
Magnesium carbonate-based composites have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential applications in various industries. The current state of research in this field is characterized by a growing body of knowledge, yet several challenges remain to be addressed.
One of the primary areas of focus has been on improving the mechanical properties of MgCO3 composites. Researchers have made considerable progress in enhancing the strength and durability of these materials through various techniques, such as the incorporation of reinforcing agents and the optimization of processing methods. However, achieving a balance between strength and ductility remains a significant challenge.
The development of lightweight MgCO3 composites with high specific strength has been another key area of investigation. While some success has been achieved in reducing the density of these materials without compromising their mechanical properties, further improvements are needed to make them competitive with traditional engineering materials in certain applications.
Corrosion resistance is a critical factor limiting the widespread adoption of MgCO3 composites. Current research efforts have focused on developing protective coatings and surface treatments to enhance the material's resistance to environmental degradation. However, long-term stability and performance under diverse conditions remain areas of concern.
The manufacturing processes for MgCO3 composites present their own set of challenges. Achieving uniform dispersion of reinforcing agents and controlling the microstructure during processing are crucial for obtaining consistent mechanical properties. Scalability of production methods is another hurdle that needs to be overcome for widespread industrial adoption.
Environmental considerations have also come to the forefront of research in this field. While MgCO3 composites offer potential advantages in terms of sustainability, there is a need for comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand their environmental impact. Additionally, developing eco-friendly processing methods and exploring the use of renewable reinforcing agents are areas that require further investigation.
The integration of MgCO3 composites with other materials and technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. Researchers are exploring hybrid composites and multi-functional materials that combine the properties of MgCO3 with those of other materials. However, ensuring compatibility and optimizing interfaces between different components remain significant technical hurdles.
In conclusion, while substantial progress has been made in understanding and improving the mechanical properties of MgCO3 composites, several challenges persist. Addressing these issues will require interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative approaches to material design, processing, and characterization.
One of the primary areas of focus has been on improving the mechanical properties of MgCO3 composites. Researchers have made considerable progress in enhancing the strength and durability of these materials through various techniques, such as the incorporation of reinforcing agents and the optimization of processing methods. However, achieving a balance between strength and ductility remains a significant challenge.
The development of lightweight MgCO3 composites with high specific strength has been another key area of investigation. While some success has been achieved in reducing the density of these materials without compromising their mechanical properties, further improvements are needed to make them competitive with traditional engineering materials in certain applications.
Corrosion resistance is a critical factor limiting the widespread adoption of MgCO3 composites. Current research efforts have focused on developing protective coatings and surface treatments to enhance the material's resistance to environmental degradation. However, long-term stability and performance under diverse conditions remain areas of concern.
The manufacturing processes for MgCO3 composites present their own set of challenges. Achieving uniform dispersion of reinforcing agents and controlling the microstructure during processing are crucial for obtaining consistent mechanical properties. Scalability of production methods is another hurdle that needs to be overcome for widespread industrial adoption.
Environmental considerations have also come to the forefront of research in this field. While MgCO3 composites offer potential advantages in terms of sustainability, there is a need for comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand their environmental impact. Additionally, developing eco-friendly processing methods and exploring the use of renewable reinforcing agents are areas that require further investigation.
The integration of MgCO3 composites with other materials and technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. Researchers are exploring hybrid composites and multi-functional materials that combine the properties of MgCO3 with those of other materials. However, ensuring compatibility and optimizing interfaces between different components remain significant technical hurdles.
In conclusion, while substantial progress has been made in understanding and improving the mechanical properties of MgCO3 composites, several challenges persist. Addressing these issues will require interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative approaches to material design, processing, and characterization.
Existing MgCO3 Composite Solutions
01 Composition and structure of magnesium carbonate-based composites
Magnesium carbonate-based composites can be formulated with various additives and structures to enhance their mechanical properties. These composites may include reinforcing materials, binders, and other components to improve strength, durability, and overall performance. The specific composition and structure can be tailored to meet desired mechanical characteristics for different applications.- Composition and structure of magnesium carbonate-based composites: Magnesium carbonate-based composites can be formulated with various additives and structures to enhance their mechanical properties. These composites may include reinforcing materials, binders, and other components to improve strength, durability, and flexibility. The specific composition and structure can be tailored to meet desired mechanical characteristics for different applications.
- Surface treatment and modification of magnesium carbonate particles: Surface treatment and modification of magnesium carbonate particles can significantly impact the mechanical properties of the resulting composites. Techniques such as coating, functionalization, or chemical modification of the particles can improve their compatibility with the matrix material, enhance interfacial bonding, and ultimately lead to better mechanical performance of the composite.
- Incorporation of magnesium carbonate in polymer matrices: Magnesium carbonate can be incorporated into various polymer matrices to create composites with enhanced mechanical properties. The dispersion and interaction of magnesium carbonate particles within the polymer matrix play crucial roles in determining the overall mechanical performance of the composite. Factors such as particle size, distribution, and polymer-filler interactions are important considerations in optimizing these composites.
- Effect of processing conditions on mechanical properties: The processing conditions used in the manufacture of magnesium carbonate-based composites can significantly influence their mechanical properties. Factors such as temperature, pressure, mixing methods, and curing processes can affect the final structure and performance of the composite. Optimizing these parameters is crucial for achieving desired mechanical characteristics in the finished product.
- Testing and characterization of mechanical properties: Various testing and characterization methods are employed to evaluate the mechanical properties of magnesium carbonate-based composites. These may include tensile strength tests, compression tests, flexural tests, impact resistance tests, and microscopic analysis of the composite structure. Understanding and accurately measuring these properties are essential for assessing the performance and suitability of the composites for specific applications.
02 Surface treatment and modification of magnesium carbonate particles
Surface treatment and modification of magnesium carbonate particles can significantly impact the mechanical properties of the resulting composites. Techniques such as coating, functionalization, or chemical modification of the particles can improve their compatibility with the matrix material, enhance interfacial bonding, and ultimately lead to improved mechanical performance of the composite.Expand Specific Solutions03 Incorporation of magnesium carbonate in polymer matrices
Magnesium carbonate can be incorporated into various polymer matrices to create composites with enhanced mechanical properties. The addition of magnesium carbonate particles can improve stiffness, strength, and dimensional stability of the polymer. The dispersion and interaction between the magnesium carbonate and the polymer matrix play crucial roles in determining the final mechanical characteristics of the composite.Expand Specific Solutions04 Magnesium carbonate-based composites for specific applications
Magnesium carbonate-based composites can be tailored for specific applications that require particular mechanical properties. These may include construction materials, automotive components, aerospace parts, or industrial products. The composites can be designed to meet specific requirements such as high strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, or thermal stability, depending on the intended use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and characterization of mechanical properties
Various testing and characterization methods are employed to evaluate the mechanical properties of magnesium carbonate-based composites. These may include tensile strength tests, compression tests, flexural tests, impact resistance tests, and microscopic analysis of the composite structure. Advanced techniques such as X-ray diffraction or electron microscopy can provide insights into the microstructure and its relationship to mechanical properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in MgCO3 Composite Industry
The investigation into the mechanical properties of magnesium carbonate-based composites is currently in an emerging phase, with growing interest due to potential applications in lightweight and sustainable materials. The market size is relatively small but expanding, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly construction materials and advanced composites. Technologically, the field is still developing, with research institutions like Beijing University of Technology, Tsinghua University, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University leading academic efforts. Companies such as Calix Ltd. and Liquid Minerals Group Ltd. are exploring commercial applications, while established players like Heidelberg Materials AG are investing in related research. The technology's maturity is progressing, but significant advancements are still needed for widespread industrial adoption.
Tsinghua University
Technical Solution: Tsinghua University has been at the forefront of research on magnesium carbonate-based composites. Their approach involves the development of a novel magnesium oxychloride cement (MOC) composite reinforced with micro-fibers. This composite exhibits superior mechanical properties, including enhanced compressive strength (up to 100 MPa) and flexural strength (up to 25 MPa)[1]. The university's research team has also explored the incorporation of various additives, such as fly ash and silica fume, to further improve the composite's durability and resistance to water[2]. Their innovative manufacturing process includes a carefully controlled curing regime, which significantly contributes to the formation of a dense microstructure, resulting in improved mechanical performance[3].
Strengths: High compressive and flexural strength, improved durability, and water resistance. Weaknesses: Potential complexity in manufacturing process and higher production costs compared to traditional cement composites.
Topy Industries, Ltd.
Technical Solution: Topy Industries has developed a proprietary process for manufacturing magnesium carbonate-based composites with enhanced mechanical properties. Their approach involves a unique combination of magnesium carbonate with organic polymers, resulting in a hybrid composite material. This composite demonstrates improved flexibility and impact resistance compared to traditional ceramic-based materials. Topy's research has shown that their composite can achieve a tensile strength of up to 70 MPa and an elongation at break of 15%[7]. The company has also focused on optimizing the interface between the inorganic and organic components, leading to better stress transfer and overall mechanical performance. Their manufacturing process includes a specialized extrusion technique that ensures uniform dispersion of the magnesium carbonate within the polymer matrix[8].
Strengths: Improved flexibility and impact resistance, good tensile strength, and potential for large-scale manufacturing. Weaknesses: May have limitations in high-temperature applications compared to purely inorganic composites.
Core Innovations in MgCO3 Composite Research
Method for making magnesium-based composite material
PatentInactiveUS20110154952A1
Innovation
- A method involving the use of semi-solid-state magnesium-based materials, stirring with nanoscale reinforcements, high-intensity ultrasonic processing, and controlled cooling to ensure uniform dispersion of nanoscale reinforcements throughout the composite material.
Filling material for compound materials containing magnesium carbonate, method for its production and application
PatentInactiveEP2418241A1
Innovation
- A magnesium carbonate-containing filler material is produced by hydrolysis and reaction with CO2 from partially calcined magnesium compounds, forming a fibrous structure that interacts with other components to enhance mechanical properties of composite materials, particularly strength and fracture resistance, using natural minerals like dolomite as a cost-effective and resource-efficient raw material.
Environmental Impact of MgCO3 Composites
The environmental impact of magnesium carbonate-based composites is a crucial aspect to consider in their development and application. These composites offer potential benefits in terms of sustainability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional materials. However, their production, use, and disposal also present environmental challenges that require careful assessment.
One of the primary environmental advantages of MgCO3 composites is their potential for carbon sequestration. The production of magnesium carbonate can involve the capture and storage of atmospheric CO2, contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change. This process, known as mineral carbonation, can effectively lock away carbon dioxide in a stable, solid form for long periods.
However, the extraction and processing of raw materials for MgCO3 composites can have significant environmental impacts. Mining activities for magnesium-rich minerals may lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution if not managed properly. The energy-intensive nature of some production methods also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, potentially offsetting some of the carbon sequestration benefits.
The durability and longevity of MgCO3 composites play a crucial role in their overall environmental impact. If these materials can effectively replace less durable alternatives, they may reduce the need for frequent replacements and repairs, thereby lowering the long-term environmental burden associated with material production and waste generation.
End-of-life considerations for MgCO3 composites are also important. The recyclability and biodegradability of these materials can significantly influence their environmental footprint. Research into efficient recycling methods and the development of biodegradable variants could enhance the sustainability profile of these composites.
The use of MgCO3 composites in construction and other industries may also contribute to improved energy efficiency in buildings and structures. Their potential for thermal insulation and fire resistance could lead to reduced energy consumption and enhanced safety, indirectly benefiting the environment through lower operational emissions.
Water usage and pollution are additional factors to consider. The production processes for MgCO3 composites may require substantial water resources, and proper management of wastewater is essential to prevent contamination of local ecosystems.
As research into MgCO3 composites progresses, life cycle assessments (LCAs) will be crucial in comprehensively evaluating their environmental impact. These assessments should consider all stages from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing a holistic view of the ecological footprint associated with these materials.
One of the primary environmental advantages of MgCO3 composites is their potential for carbon sequestration. The production of magnesium carbonate can involve the capture and storage of atmospheric CO2, contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change. This process, known as mineral carbonation, can effectively lock away carbon dioxide in a stable, solid form for long periods.
However, the extraction and processing of raw materials for MgCO3 composites can have significant environmental impacts. Mining activities for magnesium-rich minerals may lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution if not managed properly. The energy-intensive nature of some production methods also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, potentially offsetting some of the carbon sequestration benefits.
The durability and longevity of MgCO3 composites play a crucial role in their overall environmental impact. If these materials can effectively replace less durable alternatives, they may reduce the need for frequent replacements and repairs, thereby lowering the long-term environmental burden associated with material production and waste generation.
End-of-life considerations for MgCO3 composites are also important. The recyclability and biodegradability of these materials can significantly influence their environmental footprint. Research into efficient recycling methods and the development of biodegradable variants could enhance the sustainability profile of these composites.
The use of MgCO3 composites in construction and other industries may also contribute to improved energy efficiency in buildings and structures. Their potential for thermal insulation and fire resistance could lead to reduced energy consumption and enhanced safety, indirectly benefiting the environment through lower operational emissions.
Water usage and pollution are additional factors to consider. The production processes for MgCO3 composites may require substantial water resources, and proper management of wastewater is essential to prevent contamination of local ecosystems.
As research into MgCO3 composites progresses, life cycle assessments (LCAs) will be crucial in comprehensively evaluating their environmental impact. These assessments should consider all stages from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing a holistic view of the ecological footprint associated with these materials.
Standardization and Quality Control
Standardization and quality control are crucial aspects in the development and production of magnesium carbonate-based composites. These processes ensure consistency, reliability, and reproducibility of the mechanical properties across different batches and applications. To establish effective standardization and quality control measures, it is essential to develop comprehensive testing protocols and guidelines specific to magnesium carbonate-based composites.
One of the primary challenges in standardizing these composites is the variability in raw materials and manufacturing processes. Magnesium carbonate can exist in different forms, such as hydromagnesite or nesquehonite, each with distinct properties. Standardization efforts should focus on defining acceptable ranges for key parameters, including particle size distribution, purity, and moisture content of the magnesium carbonate used in the composites.
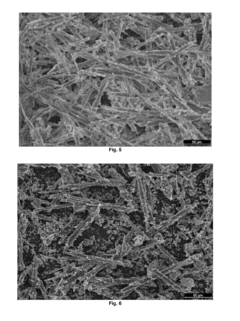
Quality control measures should encompass both the raw materials and the finished products. For raw materials, regular testing of chemical composition, particle size, and morphology is necessary. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can be employed to verify the crystalline structure and surface characteristics of the magnesium carbonate particles. For the finished composites, a battery of mechanical tests should be conducted, including tensile strength, compressive strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance.
To ensure reproducibility, it is crucial to establish standardized sample preparation methods. This includes specifying the mixing ratios, curing conditions, and molding techniques. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity during production and testing should be carefully controlled and documented. The development of reference materials and calibration standards specific to magnesium carbonate-based composites would greatly enhance the accuracy and comparability of test results across different laboratories and production facilities.
Implementing statistical process control (SPC) techniques can help monitor the production process and identify any deviations from the established standards. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be defined and regularly monitored, such as the coefficient of variation in mechanical properties across batches. The use of non-destructive testing methods, like ultrasonic testing or thermography, can provide additional quality assurance without compromising the integrity of the produced components.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and standardization bodies is essential to develop widely accepted standards for magnesium carbonate-based composites. This may involve the creation of technical committees dedicated to drafting and revising standards specific to these materials. As the field evolves, these standards should be periodically reviewed and updated to incorporate new findings and technological advancements.
One of the primary challenges in standardizing these composites is the variability in raw materials and manufacturing processes. Magnesium carbonate can exist in different forms, such as hydromagnesite or nesquehonite, each with distinct properties. Standardization efforts should focus on defining acceptable ranges for key parameters, including particle size distribution, purity, and moisture content of the magnesium carbonate used in the composites.
Quality control measures should encompass both the raw materials and the finished products. For raw materials, regular testing of chemical composition, particle size, and morphology is necessary. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can be employed to verify the crystalline structure and surface characteristics of the magnesium carbonate particles. For the finished composites, a battery of mechanical tests should be conducted, including tensile strength, compressive strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance.
To ensure reproducibility, it is crucial to establish standardized sample preparation methods. This includes specifying the mixing ratios, curing conditions, and molding techniques. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity during production and testing should be carefully controlled and documented. The development of reference materials and calibration standards specific to magnesium carbonate-based composites would greatly enhance the accuracy and comparability of test results across different laboratories and production facilities.
Implementing statistical process control (SPC) techniques can help monitor the production process and identify any deviations from the established standards. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be defined and regularly monitored, such as the coefficient of variation in mechanical properties across batches. The use of non-destructive testing methods, like ultrasonic testing or thermography, can provide additional quality assurance without compromising the integrity of the produced components.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and standardization bodies is essential to develop widely accepted standards for magnesium carbonate-based composites. This may involve the creation of technical committees dedicated to drafting and revising standards specific to these materials. As the field evolves, these standards should be periodically reviewed and updated to incorporate new findings and technological advancements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!