Isocyanate Developments: Shaping the Future of Manufacturing
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Evolution
Isocyanates have undergone a remarkable evolution since their discovery in the mid-20th century, shaping the landscape of manufacturing and industrial applications. The journey began with Otto Bayer's groundbreaking synthesis of polyurethanes in 1937, which laid the foundation for the widespread use of isocyanates in various industries.
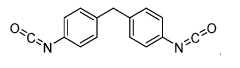
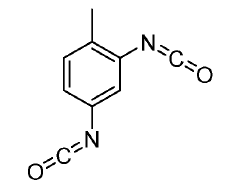
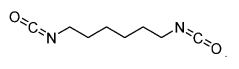
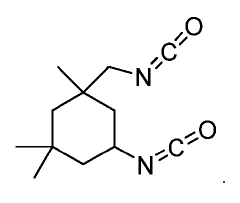
In the early stages, the focus was primarily on developing basic isocyanate compounds and understanding their chemical properties. The 1950s and 1960s saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, with researchers exploring different molecular structures and their potential applications. This period marked the emergence of key isocyanates such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), which would become cornerstones of the industry.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a shift towards improving the safety and handling of isocyanates. Concerns about the health effects of exposure led to the development of less volatile and more environmentally friendly formulations. This era also saw the introduction of blocked isocyanates, which enhanced the stability and ease of use in certain applications.
As environmental regulations tightened in the 1990s and 2000s, the isocyanate industry focused on developing low-emission and solvent-free systems. Water-based polyurethanes and high-solid formulations gained prominence, addressing both environmental concerns and performance requirements. Simultaneously, advancements in catalysis and process technologies enabled more efficient and controlled polymerization reactions.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new wave of innovation in isocyanate technology. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources emerged as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based products. This shift aligned with the growing demand for eco-friendly materials across various industries, from automotive to construction.
In recent years, the evolution of isocyanates has been driven by the need for enhanced functionality and performance. Smart materials incorporating isocyanate-based polymers with self-healing or shape-memory properties have opened up new possibilities in advanced manufacturing. Additionally, the development of nanostructured isocyanate materials has led to improvements in strength, durability, and thermal properties.
The ongoing evolution of isocyanates continues to focus on sustainability, safety, and performance optimization. Research efforts are directed towards developing isocyanate-free alternatives, improving recycling technologies for polyurethane products, and exploring novel applications in emerging fields such as 3D printing and flexible electronics. As manufacturing processes become increasingly automated and data-driven, the integration of isocyanate technologies with Industry 4.0 principles is shaping the future of production systems.
In the early stages, the focus was primarily on developing basic isocyanate compounds and understanding their chemical properties. The 1950s and 1960s saw rapid advancements in isocyanate chemistry, with researchers exploring different molecular structures and their potential applications. This period marked the emergence of key isocyanates such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), which would become cornerstones of the industry.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a shift towards improving the safety and handling of isocyanates. Concerns about the health effects of exposure led to the development of less volatile and more environmentally friendly formulations. This era also saw the introduction of blocked isocyanates, which enhanced the stability and ease of use in certain applications.
As environmental regulations tightened in the 1990s and 2000s, the isocyanate industry focused on developing low-emission and solvent-free systems. Water-based polyurethanes and high-solid formulations gained prominence, addressing both environmental concerns and performance requirements. Simultaneously, advancements in catalysis and process technologies enabled more efficient and controlled polymerization reactions.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new wave of innovation in isocyanate technology. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources emerged as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based products. This shift aligned with the growing demand for eco-friendly materials across various industries, from automotive to construction.
In recent years, the evolution of isocyanates has been driven by the need for enhanced functionality and performance. Smart materials incorporating isocyanate-based polymers with self-healing or shape-memory properties have opened up new possibilities in advanced manufacturing. Additionally, the development of nanostructured isocyanate materials has led to improvements in strength, durability, and thermal properties.
The ongoing evolution of isocyanates continues to focus on sustainability, safety, and performance optimization. Research efforts are directed towards developing isocyanate-free alternatives, improving recycling technologies for polyurethane products, and exploring novel applications in emerging fields such as 3D printing and flexible electronics. As manufacturing processes become increasingly automated and data-driven, the integration of isocyanate technologies with Industry 4.0 principles is shaping the future of production systems.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for isocyanates continues to grow steadily, driven by their versatile applications across various industries. The global isocyanate market is experiencing robust expansion, with a significant increase in demand from key sectors such as construction, automotive, and furniture manufacturing. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising use of polyurethanes, which are derived from isocyanates and widely utilized in insulation materials, coatings, adhesives, and elastomers.
In the construction industry, isocyanates play a crucial role in producing high-performance insulation materials, contributing to energy-efficient building practices. The increasing focus on sustainable construction and stringent energy regulations worldwide has led to a surge in demand for polyurethane-based insulation products. This trend is particularly evident in developing economies where rapid urbanization and infrastructure development are driving the need for advanced construction materials.
The automotive sector represents another significant market for isocyanates, with applications ranging from seat cushions and headliners to bumpers and exterior body parts. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency, the demand for lightweight polyurethane components continues to rise. Additionally, the growing electric vehicle market presents new opportunities for isocyanate-based materials in battery encapsulation and thermal management systems.
Furniture manufacturing is also contributing to the increased demand for isocyanates, particularly in the production of flexible and rigid foams used in mattresses, sofas, and other upholstered products. The rising consumer preference for comfortable and durable furniture, coupled with the growth of the e-commerce sector, is fueling market expansion in this segment.
The packaging industry is emerging as a promising market for isocyanates, with applications in adhesives and coatings for flexible packaging materials. The shift towards sustainable packaging solutions has led to increased interest in bio-based isocyanates, opening up new avenues for market growth and innovation.
Despite the positive market outlook, concerns regarding the environmental impact and potential health hazards associated with isocyanates are influencing market dynamics. This has led to a growing emphasis on developing safer and more sustainable alternatives, as well as improved handling and processing techniques. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these challenges and meet evolving regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, the market demand for isocyanates remains strong, driven by their essential role in various industrial applications. The construction, automotive, and furniture sectors continue to be the primary growth drivers, while emerging applications in packaging and sustainable products offer new opportunities for market expansion. As the industry addresses environmental and safety concerns, the isocyanate market is poised for continued growth and innovation in the coming years.
In the construction industry, isocyanates play a crucial role in producing high-performance insulation materials, contributing to energy-efficient building practices. The increasing focus on sustainable construction and stringent energy regulations worldwide has led to a surge in demand for polyurethane-based insulation products. This trend is particularly evident in developing economies where rapid urbanization and infrastructure development are driving the need for advanced construction materials.
The automotive sector represents another significant market for isocyanates, with applications ranging from seat cushions and headliners to bumpers and exterior body parts. As vehicle manufacturers strive to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency, the demand for lightweight polyurethane components continues to rise. Additionally, the growing electric vehicle market presents new opportunities for isocyanate-based materials in battery encapsulation and thermal management systems.
Furniture manufacturing is also contributing to the increased demand for isocyanates, particularly in the production of flexible and rigid foams used in mattresses, sofas, and other upholstered products. The rising consumer preference for comfortable and durable furniture, coupled with the growth of the e-commerce sector, is fueling market expansion in this segment.
The packaging industry is emerging as a promising market for isocyanates, with applications in adhesives and coatings for flexible packaging materials. The shift towards sustainable packaging solutions has led to increased interest in bio-based isocyanates, opening up new avenues for market growth and innovation.
Despite the positive market outlook, concerns regarding the environmental impact and potential health hazards associated with isocyanates are influencing market dynamics. This has led to a growing emphasis on developing safer and more sustainable alternatives, as well as improved handling and processing techniques. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these challenges and meet evolving regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, the market demand for isocyanates remains strong, driven by their essential role in various industrial applications. The construction, automotive, and furniture sectors continue to be the primary growth drivers, while emerging applications in packaging and sustainable products offer new opportunities for market expansion. As the industry addresses environmental and safety concerns, the isocyanate market is poised for continued growth and innovation in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The development of isocyanates faces several significant technical challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and optimal utilization in manufacturing processes. One of the primary concerns is the high reactivity of isocyanates, which makes them difficult to handle and control during production. This reactivity can lead to unwanted side reactions, compromising product quality and consistency.
Another major challenge lies in the toxicity of isocyanates, particularly their potential to cause respiratory sensitization and occupational asthma. This necessitates stringent safety measures and protective equipment, increasing production costs and complexity. The development of safer, less toxic alternatives or improved handling methods remains a critical area of research.
Environmental concerns also pose significant challenges. Many isocyanates are derived from fossil fuels, raising sustainability issues. The industry is under pressure to develop bio-based or renewable sources for isocyanate production, which presents both technical and economic hurdles.
The volatility of isocyanates is another technical obstacle, particularly in spray applications. Controlling vapor emissions and ensuring uniform application can be challenging, affecting both worker safety and product quality. Developing low-volatility formulations or improved application technologies is crucial for expanding isocyanate use in certain manufacturing sectors.
Isocyanate chemistry's sensitivity to moisture presents additional complications. Exposure to ambient humidity can lead to unwanted reactions and degradation of isocyanate-based products. This necessitates careful control of environmental conditions during production, storage, and application, adding to the complexity and cost of manufacturing processes.
The curing process of isocyanate-based products, particularly in polyurethane production, can be time-consuming and energy-intensive. Accelerating cure times while maintaining or improving product properties is a significant challenge that researchers are actively addressing.
Lastly, the development of isocyanate-free alternatives is gaining momentum due to regulatory pressures and market demands. This presents a technical challenge for the isocyanate industry to innovate and improve existing products to maintain their competitive edge against emerging technologies.
Overcoming these technical challenges requires interdisciplinary research efforts, combining chemistry, materials science, and engineering. Advances in catalyst technology, process engineering, and molecular design are key areas that could potentially address many of these issues, shaping the future of isocyanate use in manufacturing.
Another major challenge lies in the toxicity of isocyanates, particularly their potential to cause respiratory sensitization and occupational asthma. This necessitates stringent safety measures and protective equipment, increasing production costs and complexity. The development of safer, less toxic alternatives or improved handling methods remains a critical area of research.
Environmental concerns also pose significant challenges. Many isocyanates are derived from fossil fuels, raising sustainability issues. The industry is under pressure to develop bio-based or renewable sources for isocyanate production, which presents both technical and economic hurdles.
The volatility of isocyanates is another technical obstacle, particularly in spray applications. Controlling vapor emissions and ensuring uniform application can be challenging, affecting both worker safety and product quality. Developing low-volatility formulations or improved application technologies is crucial for expanding isocyanate use in certain manufacturing sectors.
Isocyanate chemistry's sensitivity to moisture presents additional complications. Exposure to ambient humidity can lead to unwanted reactions and degradation of isocyanate-based products. This necessitates careful control of environmental conditions during production, storage, and application, adding to the complexity and cost of manufacturing processes.
The curing process of isocyanate-based products, particularly in polyurethane production, can be time-consuming and energy-intensive. Accelerating cure times while maintaining or improving product properties is a significant challenge that researchers are actively addressing.
Lastly, the development of isocyanate-free alternatives is gaining momentum due to regulatory pressures and market demands. This presents a technical challenge for the isocyanate industry to innovate and improve existing products to maintain their competitive edge against emerging technologies.
Overcoming these technical challenges requires interdisciplinary research efforts, combining chemistry, materials science, and engineering. Advances in catalyst technology, process engineering, and molecular design are key areas that could potentially address many of these issues, shaping the future of isocyanate use in manufacturing.
Current Applications
01 Synthesis and production of isocyanates
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel catalysts, reaction conditions, and precursor materials to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.- Synthesis and production of isocyanates: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and process conditions to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.
- Isocyanate-based catalysts and reaction modifiers: Several patents focus on the use of isocyanates as catalysts or reaction modifiers in various chemical processes. These include applications in organic synthesis, polymerization reactions, and the production of specialty chemicals.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents in this category address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer formulations for industrial use.
- Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes: Some patents describe the development of isocyanate-free alternatives or substitutes for applications traditionally dominated by isocyanates. These innovations aim to address environmental and health concerns associated with isocyanate use.
02 Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry
Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various formulations, reaction conditions, and additives to optimize the properties of isocyanate-based polymers for different applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-based coatings and adhesives
Numerous patents focus on the development of coatings and adhesives using isocyanates. These formulations offer improved durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion properties for various substrates and applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isocyanate modifications and derivatives
Research into modifying isocyanates or creating novel derivatives is described. These modifications aim to enhance reactivity, reduce toxicity, or impart specific properties to the resulting compounds or materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, several patents address safety concerns and improved handling methods. These include storage solutions, exposure prevention techniques, and safer formulations to minimize risks associated with isocyanate use.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The isocyanate industry is in a mature growth phase, with a global market size expected to reach $38 billion by 2025. Technological advancements are driving innovation in this sector, particularly in eco-friendly and high-performance applications. Key players like BASF, Wanhua Chemical, and Covestro are leading the market with their extensive R&D capabilities and product portfolios. Emerging companies such as Novomer are introducing novel catalytic technologies, while established firms like Dow and Evonik are focusing on sustainable solutions. The industry is characterized by intense competition and a growing emphasis on bio-based alternatives, reflecting the increasing maturity and sophistication of isocyanate technologies.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative isocyanate technologies for sustainable manufacturing. Their approach includes the use of bio-based raw materials to produce isocyanates, reducing the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process[1]. They have also introduced novel catalysts that improve the efficiency of isocyanate production, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced waste[2]. BASF's research has led to the development of isocyanate-based materials with enhanced performance characteristics, such as improved durability and chemical resistance[3]. Additionally, they have implemented advanced process technologies that allow for the production of ultra-pure isocyanates, meeting the stringent requirements of high-tech industries[4].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, wide range of applications, and focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Dependence on petrochemical feedstocks and potential regulatory challenges related to isocyanate handling and use.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has made significant strides in isocyanate technology, particularly in the production of MDI (Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate). They have developed a proprietary gas-phase phosgenation process that improves production efficiency and reduces environmental impact[5]. This technology allows for higher purity MDI production with lower energy consumption. Wanhua has also invested in the development of novel polyurethane systems based on their isocyanate products, targeting applications in automotive, construction, and electronics industries[6]. Their research extends to the creation of bio-based isocyanates, aiming to reduce reliance on fossil-based raw materials[7].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, advanced process technologies, and a growing global presence. Weaknesses: Heavy focus on MDI may limit diversification, and potential challenges in adapting to stricter environmental regulations.
Key Innovations
Flow chemistry synthesis of isocyanates
PatentWO2021119606A1
Innovation
- A continuous flow process involving the mixing of acyl hydrazides with nitrous acid to form acyl azides, followed by heating in the presence of an organic solvent to produce isocyanates through Curtius rearrangement, offering a safer and more scalable method for isocyanate synthesis.
Continuous method for the production of isocyanates
PatentWO2009013303A1
Innovation
- A continuous process involving a cylindrical mixing chamber with rotating internals, where amines and phosgene solutions are introduced through separate inlets to create a film flow, optimizing mixing and contact time, with controlled temperature and molar ratios to minimize by-products and achieve high isocyanate yields.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of isocyanate developments in manufacturing is a critical consideration as the industry evolves. Isocyanates, while essential in producing polyurethanes and other materials, pose significant environmental challenges throughout their lifecycle. The production process of isocyanates often involves the use of fossil fuels and generates substantial greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Additionally, the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing and application processes can lead to air pollution and potential health risks for workers and nearby communities.
Water pollution is another concern associated with isocyanate production and use. Improper disposal or accidental spills can contaminate water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. The persistence of certain isocyanate compounds in the environment further exacerbates these issues, as they may not readily biodegrade and can accumulate in soil and water systems over time.
However, recent developments in isocyanate technology are addressing these environmental challenges. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting cleaner production methods, such as using renewable feedstocks and implementing more efficient catalytic processes. These innovations aim to reduce the carbon footprint of isocyanate production and minimize waste generation. Furthermore, the development of water-based and solvent-free polyurethane systems is helping to decrease VOC emissions and improve air quality in manufacturing settings.
Recycling and circular economy initiatives are also gaining traction in the isocyanate industry. Advanced chemical recycling techniques are being explored to break down polyurethane products into their constituent components, including recovering isocyanates for reuse. This approach not only reduces waste but also decreases the demand for virgin isocyanate production, thereby lowering overall environmental impact.
The shift towards bio-based isocyanates represents another promising avenue for environmental improvement. Researchers are developing isocyanates derived from renewable resources such as plant oils and biomass, which could significantly reduce reliance on petrochemical feedstocks. These bio-based alternatives often have a lower environmental footprint and can be more readily biodegradable, addressing concerns about persistence in the environment.
As regulations tighten and consumer demand for sustainable products grows, the isocyanate industry is increasingly focusing on life cycle assessments and green chemistry principles. This holistic approach considers the environmental impact from raw material extraction through to end-of-life disposal, driving innovations that minimize negative effects at each stage. By embracing these environmentally conscious developments, the isocyanate sector is working towards a more sustainable future in manufacturing, balancing industrial needs with ecological responsibility.
Water pollution is another concern associated with isocyanate production and use. Improper disposal or accidental spills can contaminate water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. The persistence of certain isocyanate compounds in the environment further exacerbates these issues, as they may not readily biodegrade and can accumulate in soil and water systems over time.
However, recent developments in isocyanate technology are addressing these environmental challenges. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting cleaner production methods, such as using renewable feedstocks and implementing more efficient catalytic processes. These innovations aim to reduce the carbon footprint of isocyanate production and minimize waste generation. Furthermore, the development of water-based and solvent-free polyurethane systems is helping to decrease VOC emissions and improve air quality in manufacturing settings.
Recycling and circular economy initiatives are also gaining traction in the isocyanate industry. Advanced chemical recycling techniques are being explored to break down polyurethane products into their constituent components, including recovering isocyanates for reuse. This approach not only reduces waste but also decreases the demand for virgin isocyanate production, thereby lowering overall environmental impact.
The shift towards bio-based isocyanates represents another promising avenue for environmental improvement. Researchers are developing isocyanates derived from renewable resources such as plant oils and biomass, which could significantly reduce reliance on petrochemical feedstocks. These bio-based alternatives often have a lower environmental footprint and can be more readily biodegradable, addressing concerns about persistence in the environment.
As regulations tighten and consumer demand for sustainable products grows, the isocyanate industry is increasingly focusing on life cycle assessments and green chemistry principles. This holistic approach considers the environmental impact from raw material extraction through to end-of-life disposal, driving innovations that minimize negative effects at each stage. By embracing these environmentally conscious developments, the isocyanate sector is working towards a more sustainable future in manufacturing, balancing industrial needs with ecological responsibility.
Safety Regulations
The development and use of isocyanates in manufacturing have been subject to increasingly stringent safety regulations over the years. These regulations aim to protect workers, consumers, and the environment from the potential hazards associated with isocyanate exposure. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for various isocyanates, including the widely used toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI).
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with isocyanates. This includes providing safety data sheets and implementing appropriate risk management measures. Additionally, the EU has introduced specific restrictions on the use of diisocyanates in industrial and professional applications, mandating training for workers handling these substances.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on reducing the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with isocyanate-based products. Many countries have introduced regulations limiting VOC content in paints, coatings, and adhesives, driving the development of low-VOC and water-based isocyanate formulations. These regulations have spurred innovation in the industry, leading to the creation of more environmentally friendly and safer isocyanate products.
The transportation and storage of isocyanates are also subject to strict regulations. In the United States, the Department of Transportation (DOT) classifies many isocyanates as hazardous materials, requiring specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures. Similarly, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code governs the international transport of isocyanates by sea, ensuring proper safety measures are in place during shipping.
As awareness of the potential health risks associated with isocyanate exposure has increased, many countries have implemented comprehensive worker protection programs. These programs often include mandatory medical surveillance, respiratory protection, and engineering controls to minimize exposure. In some jurisdictions, there are specific regulations governing the use of isocyanates in spray applications, such as in automotive refinishing, where the risk of inhalation exposure is particularly high.
The ongoing development of safer isocyanate alternatives and improved handling techniques continues to shape the regulatory landscape. Manufacturers are increasingly required to demonstrate the safety and environmental sustainability of their isocyanate products, driving further innovation in the field. As our understanding of the long-term effects of isocyanate exposure evolves, it is likely that safety regulations will continue to adapt, potentially leading to even more stringent controls and requirements in the future.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which requires manufacturers and importers to assess and manage the risks associated with isocyanates. This includes providing safety data sheets and implementing appropriate risk management measures. Additionally, the EU has introduced specific restrictions on the use of diisocyanates in industrial and professional applications, mandating training for workers handling these substances.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on reducing the volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions associated with isocyanate-based products. Many countries have introduced regulations limiting VOC content in paints, coatings, and adhesives, driving the development of low-VOC and water-based isocyanate formulations. These regulations have spurred innovation in the industry, leading to the creation of more environmentally friendly and safer isocyanate products.
The transportation and storage of isocyanates are also subject to strict regulations. In the United States, the Department of Transportation (DOT) classifies many isocyanates as hazardous materials, requiring specific packaging, labeling, and handling procedures. Similarly, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code governs the international transport of isocyanates by sea, ensuring proper safety measures are in place during shipping.
As awareness of the potential health risks associated with isocyanate exposure has increased, many countries have implemented comprehensive worker protection programs. These programs often include mandatory medical surveillance, respiratory protection, and engineering controls to minimize exposure. In some jurisdictions, there are specific regulations governing the use of isocyanates in spray applications, such as in automotive refinishing, where the risk of inhalation exposure is particularly high.
The ongoing development of safer isocyanate alternatives and improved handling techniques continues to shape the regulatory landscape. Manufacturers are increasingly required to demonstrate the safety and environmental sustainability of their isocyanate products, driving further innovation in the field. As our understanding of the long-term effects of isocyanate exposure evolves, it is likely that safety regulations will continue to adapt, potentially leading to even more stringent controls and requirements in the future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!