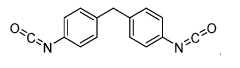
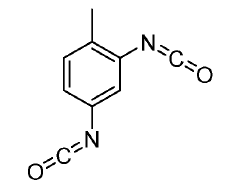
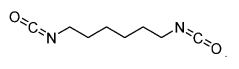
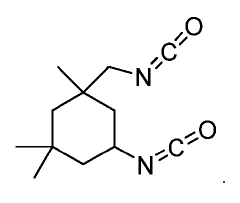
Isocyanate Innovations: A Look at Global Market Trends
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Evolution and Objectives
Isocyanates have played a pivotal role in the chemical industry since their discovery in the late 19th century. The evolution of isocyanate technology has been marked by significant milestones, driven by the increasing demand for polyurethane products across various sectors. Initially developed for military applications during World War II, isocyanates quickly found their way into civilian markets, revolutionizing industries such as automotive, construction, and furniture manufacturing.
The technological progression of isocyanates has been characterized by continuous improvements in production processes, product quality, and environmental sustainability. Early developments focused on enhancing the efficiency of isocyanate synthesis, with breakthroughs in catalysis and reaction engineering leading to more economical production methods. As environmental concerns gained prominence, the industry shifted towards developing low-emission and zero-emission isocyanate formulations, addressing health and safety issues associated with their use.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in research aimed at bio-based isocyanates, reflecting the global push towards sustainable chemistry. This trend aligns with the broader objectives of reducing dependence on fossil fuels and minimizing the carbon footprint of isocyanate production. Concurrently, advancements in nanotechnology have opened new avenues for isocyanate applications, particularly in high-performance coatings and materials with enhanced properties.
The current technological landscape of isocyanates is characterized by a dual focus on innovation and sustainability. Key objectives include the development of novel isocyanate chemistries that offer improved performance characteristics while meeting stringent environmental regulations. There is a growing emphasis on creating isocyanate-based products with enhanced durability, weather resistance, and energy efficiency, particularly in the construction and automotive sectors.
Looking ahead, the isocyanate industry is poised for transformative changes driven by emerging technologies and evolving market demands. Objectives for future development include the commercialization of fully bio-based isocyanates, the integration of smart materials technology for responsive polyurethane products, and the exploration of isocyanate applications in cutting-edge fields such as 3D printing and advanced electronics. These goals reflect the industry's commitment to innovation, sustainability, and meeting the complex needs of a rapidly changing global market.
The technological progression of isocyanates has been characterized by continuous improvements in production processes, product quality, and environmental sustainability. Early developments focused on enhancing the efficiency of isocyanate synthesis, with breakthroughs in catalysis and reaction engineering leading to more economical production methods. As environmental concerns gained prominence, the industry shifted towards developing low-emission and zero-emission isocyanate formulations, addressing health and safety issues associated with their use.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in research aimed at bio-based isocyanates, reflecting the global push towards sustainable chemistry. This trend aligns with the broader objectives of reducing dependence on fossil fuels and minimizing the carbon footprint of isocyanate production. Concurrently, advancements in nanotechnology have opened new avenues for isocyanate applications, particularly in high-performance coatings and materials with enhanced properties.
The current technological landscape of isocyanates is characterized by a dual focus on innovation and sustainability. Key objectives include the development of novel isocyanate chemistries that offer improved performance characteristics while meeting stringent environmental regulations. There is a growing emphasis on creating isocyanate-based products with enhanced durability, weather resistance, and energy efficiency, particularly in the construction and automotive sectors.
Looking ahead, the isocyanate industry is poised for transformative changes driven by emerging technologies and evolving market demands. Objectives for future development include the commercialization of fully bio-based isocyanates, the integration of smart materials technology for responsive polyurethane products, and the exploration of isocyanate applications in cutting-edge fields such as 3D printing and advanced electronics. These goals reflect the industry's commitment to innovation, sustainability, and meeting the complex needs of a rapidly changing global market.
Global Isocyanate Market Analysis
The global isocyanate market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various end-use industries. Isocyanates, primarily used in the production of polyurethanes, have become essential components in numerous applications, including construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics.
Market size and growth projections indicate a robust expansion of the isocyanate industry. The market has been steadily growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-6% over the past few years. This growth trajectory is expected to continue in the foreseeable future, with some analysts predicting the market to reach a value of over $40 billion by 2025.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the dominant market for isocyanates, accounting for a substantial share of global consumption. This is primarily due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, driven by established manufacturing sectors and ongoing technological advancements.
The market is characterized by the presence of several key players, including BASF SE, Covestro AG, Wanhua Chemical Group, and Huntsman Corporation. These companies have been focusing on research and development to introduce innovative products and expand their market presence. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships have also been prevalent strategies in the industry.
In terms of product types, methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI) dominate the market. MDI, in particular, has seen increased demand due to its superior properties and versatility in applications. The automotive and construction sectors are major consumers of these isocyanates, using them in insulation materials, adhesives, and coatings.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have been significant factors shaping the isocyanate market. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly alternatives and improving production processes to reduce environmental impact. This has led to increased investment in bio-based isocyanates and more sustainable manufacturing techniques.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially disrupted the isocyanate market, causing supply chain issues and reduced demand in certain sectors. However, the market has shown resilience, with a quick recovery observed in many regions. The pandemic has also accelerated certain trends, such as the increased focus on hygiene and safety, which has boosted demand for isocyanate-based products in medical and personal protective equipment.
Market size and growth projections indicate a robust expansion of the isocyanate industry. The market has been steadily growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5-6% over the past few years. This growth trajectory is expected to continue in the foreseeable future, with some analysts predicting the market to reach a value of over $40 billion by 2025.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the dominant market for isocyanates, accounting for a substantial share of global consumption. This is primarily due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow as significant markets, driven by established manufacturing sectors and ongoing technological advancements.
The market is characterized by the presence of several key players, including BASF SE, Covestro AG, Wanhua Chemical Group, and Huntsman Corporation. These companies have been focusing on research and development to introduce innovative products and expand their market presence. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships have also been prevalent strategies in the industry.
In terms of product types, methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI) dominate the market. MDI, in particular, has seen increased demand due to its superior properties and versatility in applications. The automotive and construction sectors are major consumers of these isocyanates, using them in insulation materials, adhesives, and coatings.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures have been significant factors shaping the isocyanate market. There is a growing emphasis on developing eco-friendly alternatives and improving production processes to reduce environmental impact. This has led to increased investment in bio-based isocyanates and more sustainable manufacturing techniques.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially disrupted the isocyanate market, causing supply chain issues and reduced demand in certain sectors. However, the market has shown resilience, with a quick recovery observed in many regions. The pandemic has also accelerated certain trends, such as the increased focus on hygiene and safety, which has boosted demand for isocyanate-based products in medical and personal protective equipment.
Technical Challenges in Isocyanate Production
The production of isocyanates faces several significant technical challenges that impact both the efficiency and safety of the manufacturing process. One of the primary hurdles is the highly exothermic nature of the reactions involved, particularly in the phosgenation step. This exothermic reaction requires precise temperature control to prevent runaway reactions and ensure product quality. Implementing effective heat management systems and developing advanced reactor designs are ongoing challenges for manufacturers.
Another major technical issue is the handling and storage of phosgene, a key raw material in isocyanate production. Phosgene is highly toxic and corrosive, necessitating stringent safety measures and specialized equipment. The development of phosgene-free production methods remains an active area of research, but current alternatives often struggle to match the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of traditional processes.
The purification of isocyanates presents additional challenges. Residual chlorine compounds and other impurities can affect product quality and downstream applications. Advanced separation and purification techniques, such as improved distillation methods and membrane technologies, are being explored to enhance product purity while minimizing energy consumption.
Environmental concerns also pose significant technical challenges. The reduction of volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and the treatment of waste streams are critical issues. Developing closed-loop systems, improving catalysts for more selective reactions, and implementing more efficient scrubbing technologies are areas of ongoing research and development.
The scale-up of laboratory processes to industrial production levels presents its own set of challenges. Maintaining reaction selectivity, managing heat transfer, and ensuring consistent product quality at larger scales require sophisticated engineering solutions. The design of modular and flexible production units that can adapt to changing market demands is an emerging trend in addressing these scale-up issues.
Raw material efficiency is another area of focus. Improving atom economy and reducing byproduct formation are crucial for enhancing the sustainability and economic viability of isocyanate production. This includes developing more selective catalysts and optimizing reaction conditions to maximize yield and minimize waste.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in developing bio-based or renewable feedstocks for isocyanate production. While progress has been made in creating bio-based polyols, finding sustainable alternatives for the isocyanate component remains a significant technical hurdle. Research into bio-based isocyanates or isocyanate-free chemistries that can provide similar performance characteristics is ongoing but has yet to yield commercially viable solutions at scale.
Another major technical issue is the handling and storage of phosgene, a key raw material in isocyanate production. Phosgene is highly toxic and corrosive, necessitating stringent safety measures and specialized equipment. The development of phosgene-free production methods remains an active area of research, but current alternatives often struggle to match the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of traditional processes.
The purification of isocyanates presents additional challenges. Residual chlorine compounds and other impurities can affect product quality and downstream applications. Advanced separation and purification techniques, such as improved distillation methods and membrane technologies, are being explored to enhance product purity while minimizing energy consumption.
Environmental concerns also pose significant technical challenges. The reduction of volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and the treatment of waste streams are critical issues. Developing closed-loop systems, improving catalysts for more selective reactions, and implementing more efficient scrubbing technologies are areas of ongoing research and development.
The scale-up of laboratory processes to industrial production levels presents its own set of challenges. Maintaining reaction selectivity, managing heat transfer, and ensuring consistent product quality at larger scales require sophisticated engineering solutions. The design of modular and flexible production units that can adapt to changing market demands is an emerging trend in addressing these scale-up issues.
Raw material efficiency is another area of focus. Improving atom economy and reducing byproduct formation are crucial for enhancing the sustainability and economic viability of isocyanate production. This includes developing more selective catalysts and optimizing reaction conditions to maximize yield and minimize waste.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges in developing bio-based or renewable feedstocks for isocyanate production. While progress has been made in creating bio-based polyols, finding sustainable alternatives for the isocyanate component remains a significant technical hurdle. Research into bio-based isocyanates or isocyanate-free chemistries that can provide similar performance characteristics is ongoing but has yet to yield commercially viable solutions at scale.
Current Isocyanate Production Methods
01 Synthesis and production of isocyanates
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel catalysts, reaction conditions, and precursor materials to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.- Synthesis and production of isocyanates: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and production techniques to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.
- Isocyanate-based catalysts and reaction modifiers: Several patents focus on the use of isocyanates as catalysts or reaction modifiers in various chemical processes. These include their role in polymerization reactions, cross-linking agents, and as components in complex catalyst systems.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer formulations for industrial use.
- Isocyanate derivatives and modified compounds: Patents describe various isocyanate derivatives and modified compounds with enhanced properties or specific functionalities. These include blocked isocyanates, isocyanate-terminated prepolymers, and novel isocyanate-containing molecules for specialized applications.
02 Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry
Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-based catalysts and reagents
Several patents focus on the development of isocyanate-based catalysts and reagents for various chemical reactions. These include novel organometallic complexes, cross-linking agents, and functionalized isocyanates for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents in this category address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer alternatives to traditional isocyanates.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isocyanate-free alternatives and modifications
Some patents focus on developing isocyanate-free alternatives or modified isocyanates with improved properties. These include novel chemical structures, bio-based alternatives, and modified isocyanates with reduced reactivity or improved compatibility.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Isocyanate Industry Players
The global isocyanate market is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and established applications across various industries. The market size is substantial, driven by the widespread use of isocyanates in polyurethane production for automotive, construction, and consumer goods sectors. Technologically, the field is well-developed but continues to evolve, with major players like Wanhua Chemical Group, Covestro, BASF, and Dow focusing on innovations in sustainable and bio-based isocyanates. These companies, along with others such as Asahi Kasei and Mitsui Chemicals, are investing in R&D to improve product performance and reduce environmental impact, indicating a competitive landscape that balances market consolidation with ongoing technological advancements.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. has been at the forefront of isocyanate innovations, particularly in the development of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI). The company has invested heavily in research and development to improve production processes and product quality. They have developed a proprietary technology for producing ultra-pure MDI, which has significantly reduced impurities and improved the performance of polyurethane products[1]. Wanhua has also focused on sustainable production methods, implementing a closed-loop system that reduces waste and energy consumption in isocyanate manufacturing[2]. Their innovative approach extends to the development of bio-based isocyanates, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of polyurethane products[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, proprietary technologies for high-purity isocyanates, focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Heavy reliance on petrochemical feedstocks, potential regulatory challenges due to environmental concerns associated with isocyanates.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro Deutschland AG has been a key player in isocyanate innovations, particularly in the development of aliphatic isocyanates for high-performance coatings. The company has pioneered the use of hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) in various applications. Covestro's recent innovations include the development of bio-based pentamethylene diisocyanate (PDI), which offers a more sustainable alternative to traditional isocyanates[4]. They have also focused on improving the safety and handling of isocyanates, developing low-monomer technology that reduces worker exposure during application[5]. Covestro's research extends to novel curing technologies, such as UV-curable isocyanate-based coatings, which offer faster processing times and reduced energy consumption[6].
Strengths: Leadership in aliphatic isocyanates, focus on bio-based alternatives, advancements in safety technologies. Weaknesses: Higher production costs for specialty isocyanates, potential market limitations for high-performance products.
Breakthrough Isocyanate Patents
Process for producing isocyanate using diaryl carbonate
PatentInactiveEP2275405A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of diaryl carbonates with amine compounds to form aryl carbamates, followed by transferring the reaction mixture to a thermal decomposition vessel where the aryl carbamates undergo thermal decomposition to produce isocyanates, with specific conditions and solvents used to enhance yield and purity, including the use of aromatic hydroxy compounds as solvents and acid cleaning to remove high-boiling point by-products.
Flow chemistry synthesis of isocyanates
PatentWO2021119606A1
Innovation
- A continuous flow process involving the mixing of acyl hydrazides with nitrous acid to form acyl azides, followed by heating in the presence of an organic solvent to produce isocyanates through Curtius rearrangement, offering a safer and more scalable method for isocyanate synthesis.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanates
The environmental impact of isocyanates is a critical concern in the global market trends of these versatile chemicals. Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have significant implications for both human health and ecological systems throughout their lifecycle.
In the manufacturing process, isocyanates pose potential risks of air and water pollution. Emissions from production facilities can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous air pollutants. These emissions contribute to smog formation and can have adverse effects on local air quality. Additionally, improper handling or accidental spills during production or transportation can lead to soil and water contamination, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and groundwater resources.
The use phase of isocyanate-based products also presents environmental challenges. Many polyurethane products, such as foams and coatings, may off-gas residual isocyanates over time, contributing to indoor air pollution. This is particularly concerning in applications like furniture, bedding, and building insulation, where prolonged human exposure is likely.
End-of-life disposal of isocyanate-containing products is another significant environmental issue. Many polyurethane materials are not easily recyclable, leading to increased landfill waste. When incinerated, these products can release toxic fumes, including hydrogen cyanide and other harmful compounds, necessitating advanced emission control systems in waste treatment facilities.
However, the industry is actively working to mitigate these environmental impacts. Innovations in green chemistry are leading to the development of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, reducing reliance on petrochemicals. These alternatives often have a lower carbon footprint and can be more biodegradable than their traditional counterparts.
Improved production technologies are also being implemented to reduce emissions and enhance energy efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing. Closed-loop systems and advanced scrubbing technologies are increasingly adopted to minimize environmental releases. Furthermore, there is a growing focus on developing isocyanate-free alternatives for certain applications, particularly in consumer products, to address health and environmental concerns.
The regulatory landscape is evolving to address the environmental impacts of isocyanates. Stricter emissions standards and waste management regulations are being implemented in many countries, driving industry innovation and cleaner production practices. Additionally, extended producer responsibility programs are encouraging manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, including end-of-life management.
As the global market for isocyanates continues to grow, balancing economic benefits with environmental stewardship remains a key challenge. The industry's response to these environmental concerns will play a crucial role in shaping future market trends and technological innovations in the isocyanate sector.
In the manufacturing process, isocyanates pose potential risks of air and water pollution. Emissions from production facilities can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous air pollutants. These emissions contribute to smog formation and can have adverse effects on local air quality. Additionally, improper handling or accidental spills during production or transportation can lead to soil and water contamination, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and groundwater resources.
The use phase of isocyanate-based products also presents environmental challenges. Many polyurethane products, such as foams and coatings, may off-gas residual isocyanates over time, contributing to indoor air pollution. This is particularly concerning in applications like furniture, bedding, and building insulation, where prolonged human exposure is likely.
End-of-life disposal of isocyanate-containing products is another significant environmental issue. Many polyurethane materials are not easily recyclable, leading to increased landfill waste. When incinerated, these products can release toxic fumes, including hydrogen cyanide and other harmful compounds, necessitating advanced emission control systems in waste treatment facilities.
However, the industry is actively working to mitigate these environmental impacts. Innovations in green chemistry are leading to the development of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources, reducing reliance on petrochemicals. These alternatives often have a lower carbon footprint and can be more biodegradable than their traditional counterparts.
Improved production technologies are also being implemented to reduce emissions and enhance energy efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing. Closed-loop systems and advanced scrubbing technologies are increasingly adopted to minimize environmental releases. Furthermore, there is a growing focus on developing isocyanate-free alternatives for certain applications, particularly in consumer products, to address health and environmental concerns.
The regulatory landscape is evolving to address the environmental impacts of isocyanates. Stricter emissions standards and waste management regulations are being implemented in many countries, driving industry innovation and cleaner production practices. Additionally, extended producer responsibility programs are encouraging manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of their products, including end-of-life management.
As the global market for isocyanates continues to grow, balancing economic benefits with environmental stewardship remains a key challenge. The industry's response to these environmental concerns will play a crucial role in shaping future market trends and technological innovations in the isocyanate sector.
Isocyanate Safety Regulations
The global isocyanate market has witnessed significant regulatory developments in recent years, driven by growing concerns over the health and environmental impacts of these chemicals. Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stringent safety measures to protect workers and consumers from potential hazards associated with isocyanate exposure.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established comprehensive standards for isocyanate handling in industrial settings. These regulations mandate strict exposure limits, proper personal protective equipment (PPE), and regular medical surveillance for workers in contact with isocyanates. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also introduced guidelines for the safe disposal and environmental management of isocyanate-containing materials.
The European Union has taken a proactive stance on isocyanate safety through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register isocyanates and provide detailed safety information. Additionally, the EU has implemented specific restrictions on the use of certain isocyanates in consumer products, particularly in spray applications.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have strengthened their regulatory frameworks for isocyanate safety. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has introduced stricter environmental protection standards for isocyanate production facilities. Japan's Industrial Safety and Health Law mandates regular health check-ups for workers exposed to isocyanates and sets clear guidelines for workplace safety measures.
Global harmonization efforts, such as the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), have played a crucial role in standardizing safety communication for isocyanates across different countries. This system has improved hazard identification and risk communication throughout the supply chain.
The automotive and construction industries, major consumers of isocyanate-based products, have been particularly impacted by these regulations. Manufacturers in these sectors have had to adapt their processes and formulations to comply with evolving safety standards, often leading to innovations in low-emission and safer isocyanate technologies.
Recent trends indicate a move towards more sustainable and less hazardous alternatives to traditional isocyanates. This shift is partly driven by regulatory pressures and increasing consumer demand for safer products. As a result, the industry is witnessing growing investment in research and development of bio-based isocyanates and isocyanate-free technologies.
The implementation of these safety regulations has had a significant impact on the global isocyanate market dynamics. While compliance costs have increased for manufacturers, these regulations have also spurred innovation and improved overall industry standards. As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, the isocyanate industry is expected to further adapt, potentially leading to new market opportunities and technological advancements in safer isocyanate applications.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established comprehensive standards for isocyanate handling in industrial settings. These regulations mandate strict exposure limits, proper personal protective equipment (PPE), and regular medical surveillance for workers in contact with isocyanates. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also introduced guidelines for the safe disposal and environmental management of isocyanate-containing materials.
The European Union has taken a proactive stance on isocyanate safety through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register isocyanates and provide detailed safety information. Additionally, the EU has implemented specific restrictions on the use of certain isocyanates in consumer products, particularly in spray applications.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have strengthened their regulatory frameworks for isocyanate safety. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment has introduced stricter environmental protection standards for isocyanate production facilities. Japan's Industrial Safety and Health Law mandates regular health check-ups for workers exposed to isocyanates and sets clear guidelines for workplace safety measures.
Global harmonization efforts, such as the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), have played a crucial role in standardizing safety communication for isocyanates across different countries. This system has improved hazard identification and risk communication throughout the supply chain.
The automotive and construction industries, major consumers of isocyanate-based products, have been particularly impacted by these regulations. Manufacturers in these sectors have had to adapt their processes and formulations to comply with evolving safety standards, often leading to innovations in low-emission and safer isocyanate technologies.
Recent trends indicate a move towards more sustainable and less hazardous alternatives to traditional isocyanates. This shift is partly driven by regulatory pressures and increasing consumer demand for safer products. As a result, the industry is witnessing growing investment in research and development of bio-based isocyanates and isocyanate-free technologies.
The implementation of these safety regulations has had a significant impact on the global isocyanate market dynamics. While compliance costs have increased for manufacturers, these regulations have also spurred innovation and improved overall industry standards. As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, the isocyanate industry is expected to further adapt, potentially leading to new market opportunities and technological advancements in safer isocyanate applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!