Isocyanate Progress: From Concept to Commercialization
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Evolution
Isocyanates have undergone a remarkable evolution since their initial discovery in the mid-19th century. The journey from concept to commercialization has been marked by significant milestones and technological advancements. The first synthesis of isocyanates is attributed to Wurtz in 1848, who produced ethyl isocyanate through the reaction of ethyl iodide with silver cyanate. However, it wasn't until the early 20th century that the potential of isocyanates began to be fully realized.
The 1930s marked a turning point in isocyanate technology with Otto Bayer's groundbreaking work at I.G. Farben. Bayer's discovery of polyurethane chemistry, based on the reaction between diisocyanates and polyols, laid the foundation for the modern isocyanate industry. This innovation opened up a vast array of applications, from flexible foams to rigid insulation materials.
The post-World War II era saw rapid advancements in isocyanate production techniques. The development of more efficient synthesis methods, such as the phosgenation of amines, enabled large-scale industrial production. This period also witnessed the introduction of key isocyanates like toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), which remain cornerstones of the industry today.
The 1960s and 1970s brought about significant improvements in process safety and environmental considerations. Manufacturers developed closed-loop systems and implemented stringent handling protocols to mitigate the risks associated with isocyanate production and use. Concurrently, research into new applications expanded the market for isocyanates, particularly in the automotive, construction, and furniture industries.
The late 20th century saw a shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate technologies. This included the development of water-based systems, low-VOC formulations, and bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. These innovations were driven by increasing environmental regulations and growing consumer demand for greener products.
In recent years, the focus has been on enhancing the performance and versatility of isocyanate-based materials. Advanced catalysts and additives have enabled the fine-tuning of reaction kinetics and final product properties. Additionally, the advent of nanotechnology has opened up new possibilities for isocyanate applications, such as nanocomposite materials with enhanced strength and durability.
The evolution of isocyanates continues to this day, with ongoing research into novel chemistries, improved production methods, and expanded applications. As the industry moves forward, key areas of development include the pursuit of non-toxic alternatives, further improvements in energy efficiency, and the exploration of isocyanate-based materials for emerging technologies such as 3D printing and smart materials.
The 1930s marked a turning point in isocyanate technology with Otto Bayer's groundbreaking work at I.G. Farben. Bayer's discovery of polyurethane chemistry, based on the reaction between diisocyanates and polyols, laid the foundation for the modern isocyanate industry. This innovation opened up a vast array of applications, from flexible foams to rigid insulation materials.
The post-World War II era saw rapid advancements in isocyanate production techniques. The development of more efficient synthesis methods, such as the phosgenation of amines, enabled large-scale industrial production. This period also witnessed the introduction of key isocyanates like toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), which remain cornerstones of the industry today.
The 1960s and 1970s brought about significant improvements in process safety and environmental considerations. Manufacturers developed closed-loop systems and implemented stringent handling protocols to mitigate the risks associated with isocyanate production and use. Concurrently, research into new applications expanded the market for isocyanates, particularly in the automotive, construction, and furniture industries.
The late 20th century saw a shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly isocyanate technologies. This included the development of water-based systems, low-VOC formulations, and bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. These innovations were driven by increasing environmental regulations and growing consumer demand for greener products.
In recent years, the focus has been on enhancing the performance and versatility of isocyanate-based materials. Advanced catalysts and additives have enabled the fine-tuning of reaction kinetics and final product properties. Additionally, the advent of nanotechnology has opened up new possibilities for isocyanate applications, such as nanocomposite materials with enhanced strength and durability.
The evolution of isocyanates continues to this day, with ongoing research into novel chemistries, improved production methods, and expanded applications. As the industry moves forward, key areas of development include the pursuit of non-toxic alternatives, further improvements in energy efficiency, and the exploration of isocyanate-based materials for emerging technologies such as 3D printing and smart materials.
Market Demand Analysis
The isocyanate market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global isocyanate market size was valued at approximately $35 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $60 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 7% during the forecast period. This robust growth is primarily attributed to the expanding applications of isocyanates in the production of polyurethanes, which find extensive use in construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics industries.
In the construction sector, isocyanates are crucial components in the manufacture of insulation materials, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has led to increased demand for polyurethane-based insulation products, driving the isocyanate market forward. Similarly, the automotive industry's shift towards lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency has boosted the use of polyurethane foams in vehicle interiors and components, further propelling isocyanate consumption.
The furniture industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, with polyurethane foams being widely used in upholstery, mattresses, and cushions. As consumer preferences evolve towards more comfortable and durable furniture, the demand for high-quality polyurethane products continues to rise, consequently increasing the need for isocyanates.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest and fastest-growing market for isocyanates, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This growth is primarily driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India. The region's booming construction and automotive sectors are major contributors to the rising demand for isocyanates.
However, the isocyanate market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns. Stringent regulations regarding the use of certain isocyanates, particularly those containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs), have prompted manufacturers to invest in research and development of more environmentally friendly alternatives. This trend has led to the emergence of bio-based isocyanates and low-VOC formulations, which are expected to gain traction in the coming years.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for isocyanates remains positive. The ongoing technological advancements in production processes and the development of novel applications are expected to create new growth opportunities. For instance, the increasing adoption of spray polyurethane foam (SPF) insulation in the construction industry and the growing use of polyurethane coatings in industrial applications are likely to sustain the demand for isocyanates in the foreseeable future.
In the construction sector, isocyanates are crucial components in the manufacture of insulation materials, sealants, and adhesives. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient buildings and sustainable construction practices has led to increased demand for polyurethane-based insulation products, driving the isocyanate market forward. Similarly, the automotive industry's shift towards lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency has boosted the use of polyurethane foams in vehicle interiors and components, further propelling isocyanate consumption.
The furniture industry represents another significant market for isocyanates, with polyurethane foams being widely used in upholstery, mattresses, and cushions. As consumer preferences evolve towards more comfortable and durable furniture, the demand for high-quality polyurethane products continues to rise, consequently increasing the need for isocyanates.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest and fastest-growing market for isocyanates, accounting for over 40% of the global market share. This growth is primarily driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India. The region's booming construction and automotive sectors are major contributors to the rising demand for isocyanates.
However, the isocyanate market faces challenges related to environmental and health concerns. Stringent regulations regarding the use of certain isocyanates, particularly those containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs), have prompted manufacturers to invest in research and development of more environmentally friendly alternatives. This trend has led to the emergence of bio-based isocyanates and low-VOC formulations, which are expected to gain traction in the coming years.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for isocyanates remains positive. The ongoing technological advancements in production processes and the development of novel applications are expected to create new growth opportunities. For instance, the increasing adoption of spray polyurethane foam (SPF) insulation in the construction industry and the growing use of polyurethane coatings in industrial applications are likely to sustain the demand for isocyanates in the foreseeable future.
Technical Challenges
The development of isocyanates has faced numerous technical challenges since their inception. One of the primary obstacles has been the high reactivity of isocyanate groups, which makes them difficult to handle and control during synthesis and processing. This reactivity, while beneficial for their end-use applications, poses significant safety risks and requires specialized equipment and handling procedures.
Another major challenge lies in the raw material sourcing and production of isocyanates. The traditional route of phosgene-based synthesis has been a subject of concern due to the toxicity and environmental hazards associated with phosgene. This has led to a push for developing alternative, more sustainable production methods, which has proven to be technically complex and economically challenging.
The optimization of reaction conditions and catalysts for isocyanate production has been an ongoing area of research. Achieving high yields and selectivity while minimizing side reactions and impurities has required extensive experimentation and innovation in catalyst design and process engineering. The development of more efficient and environmentally friendly catalysts remains a key focus for improving isocyanate production.
Isocyanate manufacturers have also grappled with the challenge of reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during production and application processes. This has necessitated the development of new formulations and application techniques that minimize VOC release while maintaining product performance.
The toxicity of isocyanates, particularly their potential to cause respiratory sensitization, has been a significant concern. This has driven research into developing safer alternatives or modified isocyanates with reduced health risks. However, finding substitutes that match the performance characteristics of traditional isocyanates has proven difficult.
Scale-up and commercialization of new isocyanate technologies have presented their own set of challenges. Translating laboratory-scale processes to industrial production often requires overcoming unforeseen technical hurdles related to heat transfer, mixing, and process control. Additionally, ensuring consistent product quality and meeting stringent regulatory requirements at commercial scales has been a complex undertaking.
The development of water-based and solvent-free isocyanate systems has been another area of technical focus. These systems aim to address environmental and health concerns associated with traditional solvent-based formulations. However, achieving comparable performance and stability in water-based systems has required significant innovation in polymer chemistry and formulation technology.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is an increasing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates and improving the overall life cycle assessment of isocyanate products. This shift presents new technical challenges in terms of feedstock selection, process development, and product performance optimization to meet or exceed the standards set by petroleum-based isocyanates.
Another major challenge lies in the raw material sourcing and production of isocyanates. The traditional route of phosgene-based synthesis has been a subject of concern due to the toxicity and environmental hazards associated with phosgene. This has led to a push for developing alternative, more sustainable production methods, which has proven to be technically complex and economically challenging.
The optimization of reaction conditions and catalysts for isocyanate production has been an ongoing area of research. Achieving high yields and selectivity while minimizing side reactions and impurities has required extensive experimentation and innovation in catalyst design and process engineering. The development of more efficient and environmentally friendly catalysts remains a key focus for improving isocyanate production.
Isocyanate manufacturers have also grappled with the challenge of reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during production and application processes. This has necessitated the development of new formulations and application techniques that minimize VOC release while maintaining product performance.
The toxicity of isocyanates, particularly their potential to cause respiratory sensitization, has been a significant concern. This has driven research into developing safer alternatives or modified isocyanates with reduced health risks. However, finding substitutes that match the performance characteristics of traditional isocyanates has proven difficult.
Scale-up and commercialization of new isocyanate technologies have presented their own set of challenges. Translating laboratory-scale processes to industrial production often requires overcoming unforeseen technical hurdles related to heat transfer, mixing, and process control. Additionally, ensuring consistent product quality and meeting stringent regulatory requirements at commercial scales has been a complex undertaking.
The development of water-based and solvent-free isocyanate systems has been another area of technical focus. These systems aim to address environmental and health concerns associated with traditional solvent-based formulations. However, achieving comparable performance and stability in water-based systems has required significant innovation in polymer chemistry and formulation technology.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is an increasing emphasis on developing bio-based isocyanates and improving the overall life cycle assessment of isocyanate products. This shift presents new technical challenges in terms of feedstock selection, process development, and product performance optimization to meet or exceed the standards set by petroleum-based isocyanates.
Current Solutions
01 Synthesis and modification of isocyanates
This category focuses on methods for synthesizing and modifying isocyanates. It includes processes for producing various types of isocyanates, as well as techniques for altering their properties or creating derivatives. These methods can be used to develop new isocyanate compounds or improve existing ones for specific applications.- Synthesis and properties of isocyanates: Isocyanates are a class of highly reactive compounds characterized by the -NCO functional group. They are widely used in the production of polyurethanes and other polymeric materials. The synthesis of isocyanates often involves the reaction of amines with phosgene or other carbonyl compounds. Their properties, such as reactivity and stability, are crucial for various industrial applications.
- Applications of isocyanates in coatings and adhesives: Isocyanates play a significant role in the formulation of high-performance coatings and adhesives. They react with polyols to form polyurethanes, which offer excellent durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion properties. These materials find applications in automotive coatings, industrial finishes, and structural adhesives.
- Isocyanate-based foam production: Isocyanates are crucial components in the production of polyurethane foams. When combined with polyols and appropriate catalysts, they form flexible or rigid foams used in various applications such as insulation, cushioning, and packaging. The foam properties can be tailored by adjusting the isocyanate-polyol ratio and additives.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Due to their high reactivity, isocyanates require careful handling and safety precautions. Exposure to isocyanates can cause respiratory irritation and sensitization. Proper personal protective equipment, ventilation, and storage practices are essential when working with these compounds. Regulations and guidelines have been established to ensure safe use in industrial settings.
- Isocyanate-free alternatives and sustainable practices: There is growing interest in developing isocyanate-free alternatives for various applications due to health and environmental concerns. Research focuses on bio-based materials, non-isocyanate polyurethanes, and other sustainable chemistries that can provide similar performance characteristics while reducing potential hazards associated with traditional isocyanates.
02 Isocyanate-based polymers and coatings
This category covers the use of isocyanates in the production of polymers and coatings. It includes formulations and processes for creating polyurethanes, polyureas, and other isocyanate-based materials. These polymers and coatings find applications in various industries, including automotive, construction, and electronics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate curing and crosslinking agents
This category focuses on the use of isocyanates as curing and crosslinking agents in various materials. It includes formulations and methods for using isocyanates to improve the properties of adhesives, sealants, and other products. The curing and crosslinking properties of isocyanates can enhance durability, chemical resistance, and other performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isocyanate-free alternatives and replacements
This category addresses the development of alternatives to traditional isocyanates or methods to reduce or eliminate their use. It includes research into new chemistries, formulations, and processes that can provide similar performance characteristics without the potential health and environmental concerns associated with some isocyanates.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and handling of isocyanates
This category covers methods and equipment for the safe handling, storage, and use of isocyanates. It includes techniques for reducing exposure risks, improving workplace safety, and managing the potential health and environmental impacts of isocyanates. This may involve specialized equipment, protective measures, or process modifications to enhance safety in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The isocyanate industry is in a mature growth phase, with a global market size expected to reach $45 billion by 2025. Technological advancements are driving innovation in this sector, with major players like BASF, Wanhua Chemical, and Covestro leading the way. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop more sustainable and efficient isocyanate production processes. The technology is well-established, but there is ongoing research to improve environmental impact and performance. Emerging players like Novomer are exploring novel catalytic approaches, while established firms like Dow and Mitsui Chemicals are focusing on application-specific formulations. Overall, the competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large chemical conglomerates and specialized manufacturers working to meet growing demand across various end-use industries.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed innovative isocyanate technologies, focusing on sustainability and efficiency. Their approach includes the use of bio-based raw materials and advanced catalytic processes to produce isocyanates with reduced environmental impact. BASF has implemented a novel gas-phase phosgenation process that significantly reduces energy consumption and solvent use in isocyanate production[1]. They have also developed water-based polyurethane dispersions using specialized isocyanates, which offer improved performance and lower VOC emissions[2]. BASF's commitment to green chemistry is evident in their exploration of CO2-based polyols for isocyanate reactions, potentially reducing the carbon footprint of polyurethane products[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, focus on sustainable solutions, and broad product portfolio. Weaknesses: High dependence on petrochemical feedstocks, potential regulatory challenges due to environmental concerns associated with isocyanates.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has made significant strides in isocyanate technology, particularly in the production of MDI (methylene diphenyl diisocyanate). They have developed a proprietary continuous production process that enhances efficiency and product quality. Wanhua's innovation includes the use of advanced catalysts that improve selectivity and reduce byproduct formation[4]. The company has also invested in large-scale production facilities, implementing state-of-the-art automation and process control systems to ensure consistent product quality and optimize resource utilization[5]. Wanhua has focused on developing specialized grades of isocyanates for niche applications, such as high-performance adhesives and coatings, expanding their market reach[6].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, strong presence in the Asian market, and vertical integration. Weaknesses: Relatively new entrant to global markets, potential challenges in meeting stringent environmental regulations in some regions.
Innovative Technologies
Isocyanates, derivatives, and processes for producing the same
PatentWO2019070981A1
Innovation
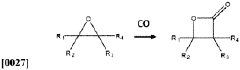
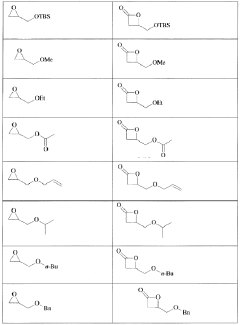
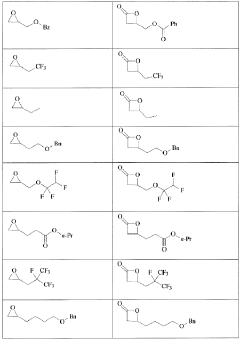
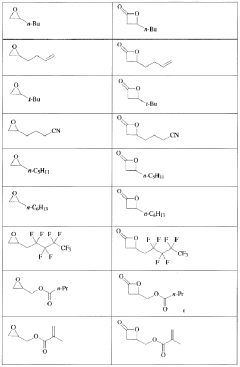
- The development of processes using epoxide and carbon monoxide reagents to produce isocyanates and isocyanate derivatives through chemical pathways such as Schmidt, Hofmann, Curtius, and Lossen rearrangements, allowing for the production of bio-based polyurethanes with customizable properties.
Isocyanates, derivatives, and processes for producing the same
PatentActiveUS11814360B2
Innovation
- The development of processes using epoxide and carbon monoxide reagents to produce isocyanates and isocyanate derivatives through reactions such as Schmidt, Hofmann, Curtius, and Lossen rearrangements, allowing for the production of diisocyanates and polyisocyanates that can be copolymerized with polyols to create versatile polyurethane products.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of isocyanates has been a significant concern throughout their development and commercialization. These compounds, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have raised issues related to both human health and ecological systems. The manufacturing process of isocyanates involves the use of phosgene, a highly toxic gas, which poses potential risks to workers and surrounding communities if not properly managed.
During the early stages of isocyanate production, environmental regulations were less stringent, leading to instances of pollution and contamination. As awareness grew, stricter controls were implemented to mitigate these risks. Modern production facilities now employ advanced containment and treatment systems to minimize emissions and protect workers. Despite these improvements, the potential for accidental releases remains a concern, necessitating robust emergency response protocols.
The use of isocyanates in various products has also raised environmental concerns. When polyurethane products degrade or burn, they can release toxic substances, including hydrogen cyanide and other harmful compounds. This has led to increased focus on proper disposal and recycling methods for isocyanate-containing materials. Additionally, the persistence of certain isocyanates in the environment has prompted research into their long-term ecological effects.
Water contamination is another environmental issue associated with isocyanates. Spills or improper disposal can lead to the presence of these chemicals in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Studies have shown that some isocyanates can be toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms, even at low concentrations. This has led to the development of more stringent wastewater treatment protocols in manufacturing facilities.
The industry has responded to these environmental challenges by investing in greener production methods and safer alternatives. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are being explored as a more sustainable option. Additionally, research into non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) represents a potential paradigm shift in reducing the environmental footprint of these materials.
As regulations continue to evolve, particularly in response to climate change concerns, the isocyanate industry faces ongoing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. This has spurred innovations in energy-efficient production processes and the exploration of carbon capture technologies. The industry's ability to adapt to these environmental challenges will be crucial for its long-term sustainability and acceptance in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
During the early stages of isocyanate production, environmental regulations were less stringent, leading to instances of pollution and contamination. As awareness grew, stricter controls were implemented to mitigate these risks. Modern production facilities now employ advanced containment and treatment systems to minimize emissions and protect workers. Despite these improvements, the potential for accidental releases remains a concern, necessitating robust emergency response protocols.
The use of isocyanates in various products has also raised environmental concerns. When polyurethane products degrade or burn, they can release toxic substances, including hydrogen cyanide and other harmful compounds. This has led to increased focus on proper disposal and recycling methods for isocyanate-containing materials. Additionally, the persistence of certain isocyanates in the environment has prompted research into their long-term ecological effects.
Water contamination is another environmental issue associated with isocyanates. Spills or improper disposal can lead to the presence of these chemicals in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. Studies have shown that some isocyanates can be toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms, even at low concentrations. This has led to the development of more stringent wastewater treatment protocols in manufacturing facilities.
The industry has responded to these environmental challenges by investing in greener production methods and safer alternatives. Bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are being explored as a more sustainable option. Additionally, research into non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) represents a potential paradigm shift in reducing the environmental footprint of these materials.
As regulations continue to evolve, particularly in response to climate change concerns, the isocyanate industry faces ongoing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint. This has spurred innovations in energy-efficient production processes and the exploration of carbon capture technologies. The industry's ability to adapt to these environmental challenges will be crucial for its long-term sustainability and acceptance in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Safety Regulations
The development and commercialization of isocyanates have been accompanied by stringent safety regulations due to their potential health and environmental hazards. These regulations have evolved significantly over time, reflecting growing awareness of the risks associated with isocyanate exposure and handling.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for various isocyanates. For instance, the PEL for methylene bisphenyl isocyanate (MDI) is set at 0.02 parts per million (ppm) as a ceiling limit. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has recommended even lower exposure limits, emphasizing the need for strict control measures in industrial settings.
The European Union has implemented comprehensive regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Under REACH, isocyanates are subject to rigorous registration and evaluation processes. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified several isocyanates as substances of very high concern (SVHC), necessitating additional control measures and potential restrictions on their use.
In response to these regulations, manufacturers have developed advanced containment systems and personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers handling isocyanates. Closed-system reactors, automated dispensing systems, and specialized ventilation equipment have become standard in isocyanate production facilities. Additionally, stringent protocols for storage, transportation, and disposal of isocyanates have been established to minimize environmental risks.
The automotive industry, a major consumer of isocyanate-based products, has implemented specific safety measures in manufacturing processes. These include the use of robotic spray systems in painting booths and the development of low-emission polyurethane foams for vehicle interiors. Such innovations have not only improved worker safety but also reduced environmental impact.
Global harmonization efforts have led to the adoption of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) by many countries. This system has standardized hazard communication for isocyanates and other chemicals, facilitating international trade while ensuring consistent safety practices across borders.
As research continues to uncover potential long-term effects of isocyanate exposure, regulatory bodies are likely to further tighten safety standards. This ongoing evolution of safety regulations will continue to shape the isocyanate industry, driving innovation in safer production methods and applications while ensuring the protection of workers and the environment.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for various isocyanates. For instance, the PEL for methylene bisphenyl isocyanate (MDI) is set at 0.02 parts per million (ppm) as a ceiling limit. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has recommended even lower exposure limits, emphasizing the need for strict control measures in industrial settings.
The European Union has implemented comprehensive regulations through the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework. Under REACH, isocyanates are subject to rigorous registration and evaluation processes. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified several isocyanates as substances of very high concern (SVHC), necessitating additional control measures and potential restrictions on their use.
In response to these regulations, manufacturers have developed advanced containment systems and personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers handling isocyanates. Closed-system reactors, automated dispensing systems, and specialized ventilation equipment have become standard in isocyanate production facilities. Additionally, stringent protocols for storage, transportation, and disposal of isocyanates have been established to minimize environmental risks.
The automotive industry, a major consumer of isocyanate-based products, has implemented specific safety measures in manufacturing processes. These include the use of robotic spray systems in painting booths and the development of low-emission polyurethane foams for vehicle interiors. Such innovations have not only improved worker safety but also reduced environmental impact.
Global harmonization efforts have led to the adoption of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) by many countries. This system has standardized hazard communication for isocyanates and other chemicals, facilitating international trade while ensuring consistent safety practices across borders.
As research continues to uncover potential long-term effects of isocyanate exposure, regulatory bodies are likely to further tighten safety standards. This ongoing evolution of safety regulations will continue to shape the isocyanate industry, driving innovation in safer production methods and applications while ensuring the protection of workers and the environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!