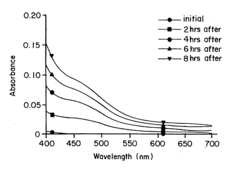
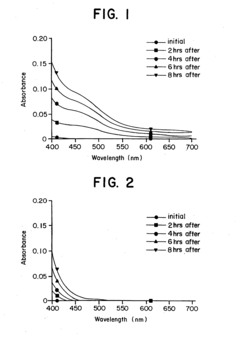
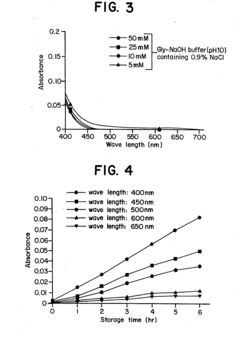
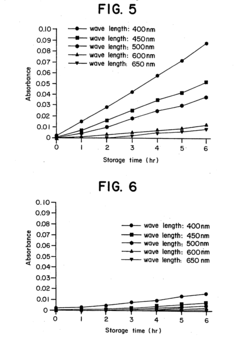
Isotonic solutions and their role in pharmaceutical formulations
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isotonic Solutions Overview
Isotonic solutions play a crucial role in pharmaceutical formulations, serving as a cornerstone in the development of safe and effective drug delivery systems. These solutions are designed to have the same osmotic pressure as bodily fluids, typically matching that of blood plasma. This isotonicity is essential for maintaining cellular integrity and preventing adverse reactions when administered to patients.
The concept of isotonicity in pharmaceutical preparations dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements in understanding and application occurring over the past few decades. Isotonic solutions are widely used in various pharmaceutical products, including intravenous fluids, eye drops, nasal sprays, and injectable medications. Their primary function is to ensure that the drug formulation does not cause osmotic stress to cells or tissues upon administration.
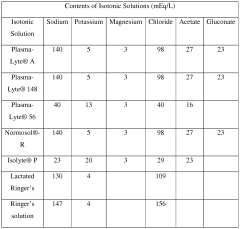
In the context of pharmaceutical formulations, isotonic solutions are typically composed of water and solutes such as sodium chloride, dextrose, or other compatible compounds. The concentration of these solutes is carefully adjusted to achieve an osmotic pressure equivalent to that of blood plasma, which is approximately 290 mOsm/L. This precise balance is critical for preventing cell lysis or shrinkage, which could occur if the solution were hypotonic or hypertonic, respectively.
The importance of isotonic solutions extends beyond mere compatibility with bodily fluids. They also play a significant role in drug stability, solubility, and bioavailability. By maintaining a stable osmotic environment, isotonic solutions can help preserve the integrity of active pharmaceutical ingredients, especially in the case of protein-based drugs or other sensitive compounds. Furthermore, they can influence the rate of drug absorption and distribution within the body, thereby affecting the overall therapeutic efficacy of the formulation.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated isotonic formulations. These include the use of novel excipients, buffer systems, and stabilizing agents that not only maintain isotonicity but also enhance drug performance and patient comfort. For instance, in ophthalmic preparations, isotonic solutions are now being formulated with additional components that mimic the natural tear film, providing both isotonicity and lubrication.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the role of isotonic solutions in drug formulations is expected to expand further. Emerging areas of research include the development of isotonic solutions for targeted drug delivery systems, long-acting depot formulations, and personalized medicine applications. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing isotonicity with other critical formulation parameters to create pharmaceutical products that are not only safe and effective but also stable and patient-friendly.
The concept of isotonicity in pharmaceutical preparations dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements in understanding and application occurring over the past few decades. Isotonic solutions are widely used in various pharmaceutical products, including intravenous fluids, eye drops, nasal sprays, and injectable medications. Their primary function is to ensure that the drug formulation does not cause osmotic stress to cells or tissues upon administration.
In the context of pharmaceutical formulations, isotonic solutions are typically composed of water and solutes such as sodium chloride, dextrose, or other compatible compounds. The concentration of these solutes is carefully adjusted to achieve an osmotic pressure equivalent to that of blood plasma, which is approximately 290 mOsm/L. This precise balance is critical for preventing cell lysis or shrinkage, which could occur if the solution were hypotonic or hypertonic, respectively.
The importance of isotonic solutions extends beyond mere compatibility with bodily fluids. They also play a significant role in drug stability, solubility, and bioavailability. By maintaining a stable osmotic environment, isotonic solutions can help preserve the integrity of active pharmaceutical ingredients, especially in the case of protein-based drugs or other sensitive compounds. Furthermore, they can influence the rate of drug absorption and distribution within the body, thereby affecting the overall therapeutic efficacy of the formulation.
Recent technological advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated isotonic formulations. These include the use of novel excipients, buffer systems, and stabilizing agents that not only maintain isotonicity but also enhance drug performance and patient comfort. For instance, in ophthalmic preparations, isotonic solutions are now being formulated with additional components that mimic the natural tear film, providing both isotonicity and lubrication.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the role of isotonic solutions in drug formulations is expected to expand further. Emerging areas of research include the development of isotonic solutions for targeted drug delivery systems, long-acting depot formulations, and personalized medicine applications. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing isotonicity with other critical formulation parameters to create pharmaceutical products that are not only safe and effective but also stable and patient-friendly.
Pharmaceutical Market Demand
The pharmaceutical market for isotonic solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for parenteral formulations and ophthalmic products. Isotonic solutions play a crucial role in maintaining osmotic balance and preventing cellular damage, making them essential in various pharmaceutical applications. The global market for isotonic solutions is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate projected to exceed 6% over the next five years.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the subsequent need for intravenous therapies. Hospitals, clinics, and ambulatory care centers are key consumers of isotonic solutions, particularly for fluid replacement and electrolyte balance in patients. The aging population in many developed countries has also contributed to increased demand, as older individuals often require more frequent medical interventions involving isotonic solutions.
In the ophthalmic sector, isotonic solutions are widely used in eye drops and contact lens care products. The growing awareness of eye health and the increasing incidence of dry eye syndrome have fueled market growth in this segment. Additionally, the expanding contact lens market, particularly in emerging economies, has created new opportunities for isotonic solution manufacturers.
The pharmaceutical industry's focus on biologics and personalized medicine has further boosted the demand for isotonic solutions. These solutions are critical in the formulation and delivery of complex biopharmaceuticals, ensuring stability and efficacy of the active ingredients. As the biotechnology sector continues to expand, the need for specialized isotonic formulations is expected to grow correspondingly.
Geographically, North America and Europe remain the largest markets for isotonic solutions, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth market, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing adoption of Western medical practices.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also impacted the market dynamics for isotonic solutions. The surge in hospitalizations and critical care requirements during the pandemic led to a spike in demand for intravenous fluids and electrolyte solutions. This event has highlighted the importance of maintaining robust supply chains for essential pharmaceutical products, including isotonic solutions.
Looking ahead, the market for isotonic solutions is expected to benefit from ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving formulation techniques and expanding applications. Innovations in packaging and delivery systems, such as pre-filled syringes and multi-dose containers, are likely to enhance the convenience and safety of isotonic solution usage, further driving market growth.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the subsequent need for intravenous therapies. Hospitals, clinics, and ambulatory care centers are key consumers of isotonic solutions, particularly for fluid replacement and electrolyte balance in patients. The aging population in many developed countries has also contributed to increased demand, as older individuals often require more frequent medical interventions involving isotonic solutions.
In the ophthalmic sector, isotonic solutions are widely used in eye drops and contact lens care products. The growing awareness of eye health and the increasing incidence of dry eye syndrome have fueled market growth in this segment. Additionally, the expanding contact lens market, particularly in emerging economies, has created new opportunities for isotonic solution manufacturers.
The pharmaceutical industry's focus on biologics and personalized medicine has further boosted the demand for isotonic solutions. These solutions are critical in the formulation and delivery of complex biopharmaceuticals, ensuring stability and efficacy of the active ingredients. As the biotechnology sector continues to expand, the need for specialized isotonic formulations is expected to grow correspondingly.
Geographically, North America and Europe remain the largest markets for isotonic solutions, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth market, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing adoption of Western medical practices.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also impacted the market dynamics for isotonic solutions. The surge in hospitalizations and critical care requirements during the pandemic led to a spike in demand for intravenous fluids and electrolyte solutions. This event has highlighted the importance of maintaining robust supply chains for essential pharmaceutical products, including isotonic solutions.
Looking ahead, the market for isotonic solutions is expected to benefit from ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving formulation techniques and expanding applications. Innovations in packaging and delivery systems, such as pre-filled syringes and multi-dose containers, are likely to enhance the convenience and safety of isotonic solution usage, further driving market growth.
Technical Challenges
The development of isotonic solutions for pharmaceutical formulations faces several technical challenges that researchers and manufacturers must address to ensure product efficacy and safety. One of the primary challenges is maintaining the correct osmotic pressure in the formulation. Achieving and maintaining isotonicity is crucial for preventing cell damage or lysis when the solution comes into contact with biological tissues or fluids. This requires precise calculations and careful selection of solutes to match the osmolarity of body fluids.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of isotonic solutions over time. Many pharmaceutical formulations need to maintain their isotonic properties throughout their shelf life, which can be affected by factors such as temperature fluctuations, light exposure, and container interactions. Ensuring long-term stability without compromising the isotonic nature of the solution demands advanced formulation techniques and appropriate packaging solutions.
The choice of tonicity agents presents another technical hurdle. While sodium chloride is commonly used, it may not be suitable for all formulations due to potential interactions with active pharmaceutical ingredients or specific patient needs. Developing alternative tonicity agents that are compatible with a wide range of drugs and do not interfere with their therapeutic effects is an ongoing challenge in the field.
pH control in isotonic solutions is also a critical technical issue. Many drugs have optimal stability and efficacy within specific pH ranges, which may not always align with the pH required for isotonicity. Balancing the need for isotonicity with the optimal pH for drug stability and effectiveness often requires complex buffer systems and careful formulation design.
The manufacturing process itself presents technical challenges, particularly in ensuring batch-to-batch consistency of isotonic properties. Precise control of production parameters, such as temperature, mixing conditions, and ingredient quality, is essential to maintain the desired osmolarity across different production runs. This becomes even more challenging when scaling up from laboratory to industrial production.
Sterilization of isotonic solutions is another area of technical difficulty. Many sterilization methods, such as heat treatment, can potentially alter the osmolarity of the solution or degrade sensitive components. Developing sterilization techniques that preserve the isotonic properties while ensuring microbial safety is a continuous area of research and development in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Lastly, the development of multi-component isotonic solutions, especially those containing complex biologics or nanoparticles, presents unique challenges. Ensuring that all components remain stable and functional in an isotonic environment, without compromising the overall tonicity of the solution, requires advanced formulation strategies and extensive compatibility studies.
Another significant challenge lies in the stability of isotonic solutions over time. Many pharmaceutical formulations need to maintain their isotonic properties throughout their shelf life, which can be affected by factors such as temperature fluctuations, light exposure, and container interactions. Ensuring long-term stability without compromising the isotonic nature of the solution demands advanced formulation techniques and appropriate packaging solutions.
The choice of tonicity agents presents another technical hurdle. While sodium chloride is commonly used, it may not be suitable for all formulations due to potential interactions with active pharmaceutical ingredients or specific patient needs. Developing alternative tonicity agents that are compatible with a wide range of drugs and do not interfere with their therapeutic effects is an ongoing challenge in the field.
pH control in isotonic solutions is also a critical technical issue. Many drugs have optimal stability and efficacy within specific pH ranges, which may not always align with the pH required for isotonicity. Balancing the need for isotonicity with the optimal pH for drug stability and effectiveness often requires complex buffer systems and careful formulation design.
The manufacturing process itself presents technical challenges, particularly in ensuring batch-to-batch consistency of isotonic properties. Precise control of production parameters, such as temperature, mixing conditions, and ingredient quality, is essential to maintain the desired osmolarity across different production runs. This becomes even more challenging when scaling up from laboratory to industrial production.
Sterilization of isotonic solutions is another area of technical difficulty. Many sterilization methods, such as heat treatment, can potentially alter the osmolarity of the solution or degrade sensitive components. Developing sterilization techniques that preserve the isotonic properties while ensuring microbial safety is a continuous area of research and development in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Lastly, the development of multi-component isotonic solutions, especially those containing complex biologics or nanoparticles, presents unique challenges. Ensuring that all components remain stable and functional in an isotonic environment, without compromising the overall tonicity of the solution, requires advanced formulation strategies and extensive compatibility studies.
Current Formulation Methods
01 Composition of isotonic solutions
Isotonic solutions are formulated to have the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, typically containing a balance of electrolytes and other solutes. These solutions are crucial in medical applications, including intravenous therapy and cell culture media, as they maintain cellular integrity and prevent osmotic shock.- Composition of isotonic solutions: Isotonic solutions are formulated to have the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, typically containing a balance of electrolytes and other solutes. These solutions are crucial in medical applications, including intravenous therapy and cell culture media, as they maintain cellular integrity and prevent osmotic shock.
- Medical applications of isotonic solutions: Isotonic solutions are widely used in various medical procedures, such as wound irrigation, eye care, and intravenous fluid replacement. They help maintain proper hydration, electrolyte balance, and cellular function in patients, particularly during surgery or in cases of dehydration.
- Isotonic solutions in dialysis and blood processing: Specialized isotonic solutions are used in dialysis and blood processing procedures to ensure the safe and effective treatment of patients with kidney disorders. These solutions help maintain electrolyte balance and remove waste products from the blood while preventing cellular damage.
- Isotonic solutions for cell culture and preservation: In biotechnology and research applications, isotonic solutions play a crucial role in cell culture media and preservation solutions. These formulations help maintain cell viability, support growth, and prevent osmotic stress during various experimental procedures and long-term storage of biological samples.
- Devices and methods for preparing isotonic solutions: Various devices and methods have been developed for the preparation, delivery, and monitoring of isotonic solutions. These innovations include automated mixing systems, precise dispensing mechanisms, and quality control measures to ensure the accuracy and safety of isotonic solutions in medical and research settings.
02 Medical applications of isotonic solutions
Isotonic solutions are widely used in various medical procedures, such as wound irrigation, eye care, and nasal sprays. They are also employed in dialysis treatments and as a base for drug delivery systems, ensuring optimal absorption and minimizing adverse effects on body tissues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isotonic solutions in sports and exercise
Specially formulated isotonic drinks are used in sports nutrition to replenish fluids and electrolytes lost during intense physical activity. These solutions help maintain proper hydration, electrolyte balance, and performance levels in athletes and active individuals.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing and quality control of isotonic solutions
The production of isotonic solutions involves precise formulation, sterilization, and packaging processes to ensure product safety and efficacy. Advanced quality control measures, including osmolality testing and microbiological analysis, are employed to maintain consistency and purity in manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative applications of isotonic solutions
Recent advancements have expanded the use of isotonic solutions in novel areas such as 3D bioprinting, organ preservation, and advanced wound care technologies. These innovations leverage the biocompatible nature of isotonic solutions to improve tissue engineering and regenerative medicine outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for isotonic solutions in pharmaceutical formulations is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing innovation. The global market for isotonic solutions is substantial, driven by their widespread use in various medical applications. Key players like Baxter International, Pfizer, and Novo Nordisk have significant market presence, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and global distribution networks. The technology is well-established, with companies focusing on developing improved formulations and delivery systems. Emerging players such as Zealand Pharma and Suven Life Sciences are also contributing to the field, potentially introducing novel approaches. The market is expected to grow steadily due to increasing healthcare needs and the expanding pharmaceutical industry, with a focus on enhancing product efficacy and patient compliance.
Novo Nordisk A/S
Technical Solution: Novo Nordisk has developed advanced isotonic formulations for their insulin products, utilizing a balanced mixture of glycerol and mannitol as isotonicity agents. Their approach involves creating a stable isotonic environment that closely mimics physiological conditions, enhancing the stability and efficacy of their insulin preparations. The company has implemented a proprietary buffer system that maintains optimal pH levels, crucial for preserving insulin potency[1]. Additionally, Novo Nordisk has pioneered the use of m-cresol as a preservative in their isotonic solutions, which has shown superior antimicrobial properties while maintaining solution stability[2]. Their formulations also incorporate zinc ions to further stabilize insulin hexamers, contributing to prolonged shelf life and improved in vivo performance[3].
Strengths: Highly stable formulations with extended shelf life; improved in vivo performance due to physiological mimicry. Weaknesses: Potential for increased production costs due to complex formulation; may require specialized handling and storage conditions.
Pfizer Inc.
Technical Solution: Pfizer has developed a range of isotonic solutions for various pharmaceutical applications, with a focus on parenteral formulations. Their approach includes the use of sodium chloride as a primary tonicity agent, complemented by dextrose in certain formulations to achieve isotonicity without excessive electrolyte load[4]. Pfizer has also incorporated novel surfactants in their isotonic solutions to enhance the solubility and stability of poorly water-soluble drugs[5]. The company has implemented a unique freeze-thaw stability protocol in the development of their isotonic solutions, ensuring product integrity under various storage and transport conditions[6]. Additionally, Pfizer has explored the use of cyclodextrins in isotonic formulations to improve the solubility and bioavailability of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients[7].
Strengths: Versatile formulations suitable for a wide range of drugs; improved stability and solubility of challenging compounds. Weaknesses: Potential for increased complexity in manufacturing processes; may face regulatory challenges with novel excipients.
Innovative Isotonic Agents
Pharmaceutical formulation comprising glycine as a stabilizer
PatentInactiveUS20070276008A1
Innovation
- Reconstituting lyophilized compounds in isotonic solutions with a glycine-sodium hydroxide buffer at a pH between 9 and 12, which maintains chemical and physical stability and prevents color change for several hours at room temperature and up to 48 hours at refrigerated temperatures.
Pharmaceutical composition comprising CD34+ cells
PatentWO2013126590A2
Innovation
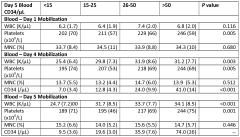
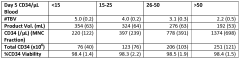
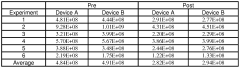
- A pharmaceutical composition comprising CD34+ cells, plasma protein, and an isotonic solution with a preservative or stabilizing agent, allowing for stable storage and direct administration, which maximizes the number of viable cells and eliminates the need for separate storage and administration solutions.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the development and use of isotonic solutions in pharmaceutical formulations. The primary objective of regulatory bodies is to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products, including those containing isotonic solutions.
One of the key regulatory aspects is the requirement for isotonicity in parenteral formulations. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, mandate that injectable products must be isotonic or nearly isotonic with blood to prevent tissue damage and pain upon administration. This necessitates careful formulation and testing of isotonic solutions to meet these standards.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provide guidelines and specifications for isotonic solutions. These include methods for determining tonicity, acceptable ranges for osmolality, and requirements for labeling. Manufacturers must adhere to these pharmacopoeial standards to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are another critical regulatory consideration. Isotonic solutions must be produced under strict GMP conditions to ensure consistency, purity, and sterility. This includes validated manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and appropriate documentation.
Stability testing is a regulatory requirement for isotonic solutions in pharmaceutical formulations. Manufacturers must demonstrate the stability of the product throughout its intended shelf life under specified storage conditions. This includes assessing changes in tonicity, pH, and other critical quality attributes over time.
Regulatory bodies also require comprehensive documentation and data submission for approval of pharmaceutical products containing isotonic solutions. This includes detailed information on formulation development, analytical methods, manufacturing processes, and clinical data demonstrating safety and efficacy.
For ophthalmic preparations, which often utilize isotonic solutions, additional regulatory considerations apply. These include specific requirements for sterility, preservative efficacy, and compatibility with ocular tissues.
In the context of combination products, such as drug-device combinations involving isotonic solutions, regulatory oversight becomes more complex. Manufacturers must navigate regulations from multiple agencies or departments, addressing both the drug and device components of the product.
As the pharmaceutical landscape evolves, regulatory bodies continually update their guidelines. Recent trends include increased focus on patient-centric formulations and the use of novel excipients in isotonic solutions. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these regulatory developments to ensure ongoing compliance and market success.
One of the key regulatory aspects is the requirement for isotonicity in parenteral formulations. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, mandate that injectable products must be isotonic or nearly isotonic with blood to prevent tissue damage and pain upon administration. This necessitates careful formulation and testing of isotonic solutions to meet these standards.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provide guidelines and specifications for isotonic solutions. These include methods for determining tonicity, acceptable ranges for osmolality, and requirements for labeling. Manufacturers must adhere to these pharmacopoeial standards to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are another critical regulatory consideration. Isotonic solutions must be produced under strict GMP conditions to ensure consistency, purity, and sterility. This includes validated manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and appropriate documentation.
Stability testing is a regulatory requirement for isotonic solutions in pharmaceutical formulations. Manufacturers must demonstrate the stability of the product throughout its intended shelf life under specified storage conditions. This includes assessing changes in tonicity, pH, and other critical quality attributes over time.
Regulatory bodies also require comprehensive documentation and data submission for approval of pharmaceutical products containing isotonic solutions. This includes detailed information on formulation development, analytical methods, manufacturing processes, and clinical data demonstrating safety and efficacy.
For ophthalmic preparations, which often utilize isotonic solutions, additional regulatory considerations apply. These include specific requirements for sterility, preservative efficacy, and compatibility with ocular tissues.
In the context of combination products, such as drug-device combinations involving isotonic solutions, regulatory oversight becomes more complex. Manufacturers must navigate regulations from multiple agencies or departments, addressing both the drug and device components of the product.
As the pharmaceutical landscape evolves, regulatory bodies continually update their guidelines. Recent trends include increased focus on patient-centric formulations and the use of novel excipients in isotonic solutions. Manufacturers must stay abreast of these regulatory developments to ensure ongoing compliance and market success.
Stability and Shelf Life
The stability and shelf life of isotonic solutions are critical factors in pharmaceutical formulations, directly impacting the safety, efficacy, and commercial viability of drug products. Isotonic solutions are designed to maintain osmotic balance with biological fluids, making them essential in various pharmaceutical applications, including intravenous fluids, eye drops, and nasal sprays.
The stability of isotonic solutions is influenced by several factors, including temperature, pH, light exposure, and container materials. Temperature fluctuations can accelerate chemical degradation processes, affecting the potency and safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredients. Proper storage conditions, typically between 2°C and 8°C, are crucial for maintaining the integrity of these formulations.
pH plays a significant role in the stability of isotonic solutions. Many drugs have optimal pH ranges for stability, and deviations can lead to degradation or precipitation of active ingredients. Buffer systems are often incorporated to maintain the desired pH throughout the product's shelf life, ensuring consistent performance and safety.
Light sensitivity is another critical consideration, particularly for photolabile compounds. Appropriate packaging, such as amber glass bottles or opaque containers, can protect light-sensitive formulations from degradation, extending their shelf life and maintaining efficacy.
The choice of container materials can significantly impact the stability of isotonic solutions. Glass containers are often preferred due to their inertness, but plastic containers may be used for certain formulations. The interaction between the solution and container materials must be carefully evaluated to prevent leaching or adsorption of components, which could compromise the product's stability and safety.
Preservatives are frequently added to multi-dose isotonic formulations to prevent microbial growth and maintain sterility throughout the product's use. However, the compatibility of preservatives with other formulation components and their long-term stability must be thoroughly assessed.
Accelerated stability testing is a common practice in pharmaceutical development to predict the long-term stability of isotonic solutions. These studies expose the formulations to elevated temperatures and humidity levels, simulating extended storage periods in a shorter timeframe. The results help determine appropriate storage conditions and expiration dates.
The shelf life of isotonic solutions is typically determined through real-time stability studies, where the product is stored under recommended conditions and periodically tested for quality attributes. These studies may span several years to establish a reliable expiration date, ensuring that the product remains safe and effective throughout its intended use period.
In conclusion, the stability and shelf life of isotonic solutions in pharmaceutical formulations require careful consideration of multiple factors. Proper formulation design, packaging selection, and storage conditions are essential for maintaining product quality and efficacy throughout the intended shelf life, ultimately ensuring patient safety and treatment effectiveness.
The stability of isotonic solutions is influenced by several factors, including temperature, pH, light exposure, and container materials. Temperature fluctuations can accelerate chemical degradation processes, affecting the potency and safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredients. Proper storage conditions, typically between 2°C and 8°C, are crucial for maintaining the integrity of these formulations.
pH plays a significant role in the stability of isotonic solutions. Many drugs have optimal pH ranges for stability, and deviations can lead to degradation or precipitation of active ingredients. Buffer systems are often incorporated to maintain the desired pH throughout the product's shelf life, ensuring consistent performance and safety.
Light sensitivity is another critical consideration, particularly for photolabile compounds. Appropriate packaging, such as amber glass bottles or opaque containers, can protect light-sensitive formulations from degradation, extending their shelf life and maintaining efficacy.
The choice of container materials can significantly impact the stability of isotonic solutions. Glass containers are often preferred due to their inertness, but plastic containers may be used for certain formulations. The interaction between the solution and container materials must be carefully evaluated to prevent leaching or adsorption of components, which could compromise the product's stability and safety.
Preservatives are frequently added to multi-dose isotonic formulations to prevent microbial growth and maintain sterility throughout the product's use. However, the compatibility of preservatives with other formulation components and their long-term stability must be thoroughly assessed.
Accelerated stability testing is a common practice in pharmaceutical development to predict the long-term stability of isotonic solutions. These studies expose the formulations to elevated temperatures and humidity levels, simulating extended storage periods in a shorter timeframe. The results help determine appropriate storage conditions and expiration dates.
The shelf life of isotonic solutions is typically determined through real-time stability studies, where the product is stored under recommended conditions and periodically tested for quality attributes. These studies may span several years to establish a reliable expiration date, ensuring that the product remains safe and effective throughout its intended use period.
In conclusion, the stability and shelf life of isotonic solutions in pharmaceutical formulations require careful consideration of multiple factors. Proper formulation design, packaging selection, and storage conditions are essential for maintaining product quality and efficacy throughout the intended shelf life, ultimately ensuring patient safety and treatment effectiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!