Lithium Acetate in Pharmaceutical Synthesis: Process Comparisons
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Acetate Pharmaceutical Applications and Objectives
Lithium acetate has emerged as a significant compound in pharmaceutical synthesis over the past decades, evolving from a niche reagent to a versatile tool in modern drug development. The historical trajectory of lithium acetate usage in pharmaceuticals began in the 1970s with limited applications, primarily as a buffering agent. By the 1990s, researchers discovered its catalytic properties in stereoselective reactions, marking a pivotal shift in its utilization within the industry.
The technological evolution of lithium acetate applications has been characterized by continuous refinement of synthesis methodologies. Early applications focused on simple salt formation, while contemporary uses leverage its unique properties in complex multi-step syntheses. Recent advancements have positioned lithium acetate as a critical reagent in green chemistry approaches, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
Current technical objectives for lithium acetate in pharmaceutical synthesis center on process optimization, yield improvement, and cost reduction. Specifically, researchers aim to enhance reaction selectivity when lithium acetate serves as a catalyst, minimize side reactions that compromise product purity, and develop scalable processes suitable for industrial implementation. The development of continuous flow processes utilizing lithium acetate represents a particularly promising frontier.
Another significant objective involves the standardization of lithium acetate quality specifications across the pharmaceutical industry. Variations in lithium acetate purity and physical characteristics can significantly impact reaction outcomes, necessitating robust quality control protocols. Establishing industry-wide standards would facilitate more predictable and reproducible synthesis processes.
Environmental considerations have also shaped technical objectives, with increasing focus on reducing waste generation in lithium acetate-mediated reactions. This includes developing recycling methodologies for lithium compounds and minimizing the environmental footprint of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes that incorporate this reagent.
The integration of lithium acetate into novel drug delivery systems represents an emerging technical goal. Research indicates potential applications in controlled-release formulations, where lithium acetate's solubility characteristics can be leveraged to modulate drug release profiles. This application extends beyond traditional synthesis roles, potentially opening new therapeutic possibilities.
Comparative analysis of lithium acetate against alternative reagents remains an ongoing objective, with particular emphasis on reaction efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact. Understanding these comparative advantages informs strategic decisions regarding synthesis route selection in pharmaceutical development pipelines.
The technological evolution of lithium acetate applications has been characterized by continuous refinement of synthesis methodologies. Early applications focused on simple salt formation, while contemporary uses leverage its unique properties in complex multi-step syntheses. Recent advancements have positioned lithium acetate as a critical reagent in green chemistry approaches, aligning with the industry's sustainability goals.
Current technical objectives for lithium acetate in pharmaceutical synthesis center on process optimization, yield improvement, and cost reduction. Specifically, researchers aim to enhance reaction selectivity when lithium acetate serves as a catalyst, minimize side reactions that compromise product purity, and develop scalable processes suitable for industrial implementation. The development of continuous flow processes utilizing lithium acetate represents a particularly promising frontier.
Another significant objective involves the standardization of lithium acetate quality specifications across the pharmaceutical industry. Variations in lithium acetate purity and physical characteristics can significantly impact reaction outcomes, necessitating robust quality control protocols. Establishing industry-wide standards would facilitate more predictable and reproducible synthesis processes.
Environmental considerations have also shaped technical objectives, with increasing focus on reducing waste generation in lithium acetate-mediated reactions. This includes developing recycling methodologies for lithium compounds and minimizing the environmental footprint of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes that incorporate this reagent.
The integration of lithium acetate into novel drug delivery systems represents an emerging technical goal. Research indicates potential applications in controlled-release formulations, where lithium acetate's solubility characteristics can be leveraged to modulate drug release profiles. This application extends beyond traditional synthesis roles, potentially opening new therapeutic possibilities.
Comparative analysis of lithium acetate against alternative reagents remains an ongoing objective, with particular emphasis on reaction efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact. Understanding these comparative advantages informs strategic decisions regarding synthesis route selection in pharmaceutical development pipelines.
Market Analysis of Lithium Acetate in Pharmaceutical Industry
The global market for lithium acetate in pharmaceutical applications has been experiencing steady growth, driven primarily by its versatile applications in drug synthesis processes. Currently valued at approximately 320 million USD, this specialized chemical market segment is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% through 2028, according to industry analyses from chemical market research firms.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers represent the largest consumer segment for lithium acetate, accounting for roughly 42% of total consumption. Within this sector, lithium acetate serves as a critical reagent in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds, particularly in reactions requiring mild basic conditions and specific lithium-mediated transformations. The demand is especially strong in the production of complex active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) where selective chemical transformations are required.
Regional analysis reveals that North America and Europe collectively dominate the pharmaceutical-grade lithium acetate market with approximately 65% market share, attributed to their robust pharmaceutical manufacturing infrastructure and stringent quality requirements. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at 7.8% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and increasing domestic drug development activities.
Price trends for pharmaceutical-grade lithium acetate have shown moderate volatility over the past five years, with prices ranging from 12-18 USD per kilogram depending on purity levels and supply conditions. Recent supply chain disruptions have created temporary price increases of up to 22%, though analysts expect stabilization as alternative production methods gain traction.
Market segmentation by application shows that lithium acetate is predominantly used in small molecule drug synthesis (58%), followed by peptide synthesis (23%), and specialized pharmaceutical intermediates (19%). The growing trend toward complex molecule therapeutics is expected to further drive demand for high-purity lithium acetate in coming years.
Competition in this market is characterized by moderate concentration, with the top five suppliers controlling approximately 63% of global production capacity. These suppliers include established chemical manufacturers who have developed specialized pharmaceutical-grade production capabilities to meet the stringent requirements of pharmaceutical customers.
Future market growth is expected to be influenced by several factors, including the development of more efficient synthetic routes using lithium acetate, increasing pharmaceutical R&D activities in emerging markets, and potential expansion into biopharmaceutical applications where lithium-based reagents are finding new utilities in protein modification chemistry.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers represent the largest consumer segment for lithium acetate, accounting for roughly 42% of total consumption. Within this sector, lithium acetate serves as a critical reagent in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds, particularly in reactions requiring mild basic conditions and specific lithium-mediated transformations. The demand is especially strong in the production of complex active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) where selective chemical transformations are required.
Regional analysis reveals that North America and Europe collectively dominate the pharmaceutical-grade lithium acetate market with approximately 65% market share, attributed to their robust pharmaceutical manufacturing infrastructure and stringent quality requirements. However, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing the fastest growth rate at 7.8% annually, driven by expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and increasing domestic drug development activities.
Price trends for pharmaceutical-grade lithium acetate have shown moderate volatility over the past five years, with prices ranging from 12-18 USD per kilogram depending on purity levels and supply conditions. Recent supply chain disruptions have created temporary price increases of up to 22%, though analysts expect stabilization as alternative production methods gain traction.
Market segmentation by application shows that lithium acetate is predominantly used in small molecule drug synthesis (58%), followed by peptide synthesis (23%), and specialized pharmaceutical intermediates (19%). The growing trend toward complex molecule therapeutics is expected to further drive demand for high-purity lithium acetate in coming years.
Competition in this market is characterized by moderate concentration, with the top five suppliers controlling approximately 63% of global production capacity. These suppliers include established chemical manufacturers who have developed specialized pharmaceutical-grade production capabilities to meet the stringent requirements of pharmaceutical customers.
Future market growth is expected to be influenced by several factors, including the development of more efficient synthetic routes using lithium acetate, increasing pharmaceutical R&D activities in emerging markets, and potential expansion into biopharmaceutical applications where lithium-based reagents are finding new utilities in protein modification chemistry.
Current Challenges in Lithium Acetate Synthesis Methods
The synthesis of lithium acetate presents several significant challenges that impact pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. Traditional methods often involve direct reaction of lithium hydroxide or carbonate with acetic acid, which appears straightforward but encounters numerous practical difficulties in industrial settings. These conventional approaches frequently result in inconsistent product quality, with batch-to-batch variations in purity levels that can range from 95% to 99.5%, creating substantial downstream processing complications.
Temperature control represents a critical challenge in lithium acetate synthesis. The reaction between lithium precursors and acetic acid is highly exothermic, requiring sophisticated cooling systems to prevent localized overheating. Industrial-scale reactors frequently struggle with heat distribution issues, leading to product degradation and formation of colored impurities that necessitate additional purification steps, increasing production costs by approximately 15-20%.
Water content management poses another significant hurdle. Lithium acetate readily forms various hydrates (monohydrate, dihydrate, and trihydrate forms), making it difficult to produce anhydrous material with consistent specifications. Current dehydration processes typically employ high temperatures (>100°C) that risk partial decomposition of the acetate, introducing carbonaceous impurities that are particularly problematic for pharmaceutical applications.
Trace metal contamination remains a persistent issue across synthesis methods. Commercial lithium sources often contain sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium impurities at levels between 50-500 ppm. These contaminants can interfere with pharmaceutical formulations and catalytic processes. Current purification techniques, including recrystallization and ion exchange methods, add significant cost and time to production cycles.
Scale-up challenges further complicate industrial implementation. Laboratory-scale processes that achieve >99% purity often experience yield reductions of 10-15% when transferred to production scale. Filtration difficulties arise from the tendency of lithium acetate to form fine crystals that clog filter media, while crystallization kinetics vary unpredictably at larger scales, affecting crystal morphology and particle size distribution.
Environmental considerations have also become increasingly important. Traditional synthesis methods generate substantial waste streams, with typical E-factors (environmental factors, measuring kg waste per kg product) ranging from 15-25. Solvent recovery rates rarely exceed 85%, creating disposal challenges and regulatory compliance issues in many jurisdictions. Alternative green chemistry approaches remain limited by lower yields and higher production costs, creating a significant barrier to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Temperature control represents a critical challenge in lithium acetate synthesis. The reaction between lithium precursors and acetic acid is highly exothermic, requiring sophisticated cooling systems to prevent localized overheating. Industrial-scale reactors frequently struggle with heat distribution issues, leading to product degradation and formation of colored impurities that necessitate additional purification steps, increasing production costs by approximately 15-20%.
Water content management poses another significant hurdle. Lithium acetate readily forms various hydrates (monohydrate, dihydrate, and trihydrate forms), making it difficult to produce anhydrous material with consistent specifications. Current dehydration processes typically employ high temperatures (>100°C) that risk partial decomposition of the acetate, introducing carbonaceous impurities that are particularly problematic for pharmaceutical applications.
Trace metal contamination remains a persistent issue across synthesis methods. Commercial lithium sources often contain sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium impurities at levels between 50-500 ppm. These contaminants can interfere with pharmaceutical formulations and catalytic processes. Current purification techniques, including recrystallization and ion exchange methods, add significant cost and time to production cycles.
Scale-up challenges further complicate industrial implementation. Laboratory-scale processes that achieve >99% purity often experience yield reductions of 10-15% when transferred to production scale. Filtration difficulties arise from the tendency of lithium acetate to form fine crystals that clog filter media, while crystallization kinetics vary unpredictably at larger scales, affecting crystal morphology and particle size distribution.
Environmental considerations have also become increasingly important. Traditional synthesis methods generate substantial waste streams, with typical E-factors (environmental factors, measuring kg waste per kg product) ranging from 15-25. Solvent recovery rates rarely exceed 85%, creating disposal challenges and regulatory compliance issues in many jurisdictions. Alternative green chemistry approaches remain limited by lower yields and higher production costs, creating a significant barrier to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Comparative Analysis of Current Lithium Acetate Synthesis Processes
01 Optimization of lithium acetate production processes
Various methods have been developed to optimize the production of lithium acetate, focusing on improving reaction conditions, catalyst selection, and process parameters. These optimizations aim to increase yield, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste generation. Techniques include temperature control, pressure regulation, and reaction time optimization to enhance the efficiency of converting lithium precursors to lithium acetate.- Optimization of lithium acetate production methods: Various methods have been developed to optimize the production of lithium acetate, focusing on improving reaction conditions, catalyst selection, and process parameters. These optimizations aim to increase yield, reduce reaction time, and minimize energy consumption. Techniques include controlled temperature reactions, pressure management, and selection of appropriate reaction vessels to enhance efficiency in the conversion of lithium compounds to lithium acetate.
- Recovery and purification techniques for lithium acetate: Advanced recovery and purification methods have been developed to increase the efficiency of lithium acetate processing. These techniques include crystallization, filtration, and solvent extraction processes that remove impurities and increase the purity of the final product. Improved separation technologies help minimize product loss during purification stages, thereby increasing overall process yield and reducing waste generation.
- Sustainable and eco-friendly lithium acetate production: Environmentally conscious approaches to lithium acetate production focus on reducing environmental impact while maintaining process efficiency. These methods include using renewable energy sources, implementing closed-loop systems for reagent recycling, and developing water conservation strategies. Green chemistry principles are applied to minimize waste generation and reduce the use of harmful chemicals, resulting in more sustainable production processes.
- Continuous flow processes for lithium acetate synthesis: Continuous flow processing technologies have been implemented to replace traditional batch production methods for lithium acetate. These systems allow for constant production with better control over reaction parameters, resulting in more consistent product quality and higher throughput. Continuous processes reduce labor requirements, minimize downtime between batches, and often require less physical space than equivalent batch operations.
- Integration of lithium acetate production with battery manufacturing: Innovative approaches have been developed to integrate lithium acetate production directly into battery manufacturing processes. These integrated systems reduce transportation costs and handling losses while ensuring consistent quality of lithium compounds used in battery production. Process integration allows for just-in-time production of lithium acetate precursors, optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing storage requirements for reactive intermediates.
02 Recovery and recycling methods in lithium acetate processing
Efficient recovery and recycling systems have been implemented in lithium acetate production to improve overall process efficiency. These methods focus on reclaiming unreacted materials, recovering solvents, and recycling process water. By implementing closed-loop systems and advanced separation techniques, manufacturers can significantly reduce raw material consumption and waste generation, leading to more sustainable and cost-effective production processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Purification techniques for lithium acetate
Advanced purification methods have been developed to obtain high-purity lithium acetate with minimal energy consumption. These techniques include crystallization, filtration, ion exchange, and membrane separation processes. Improved purification efficiency not only enhances the quality of the final product but also reduces processing time and resource utilization, contributing to overall process efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy-efficient lithium acetate synthesis
Energy-efficient approaches to lithium acetate synthesis focus on reducing the thermal energy requirements and optimizing reaction pathways. These methods include the use of alternative energy sources, microwave-assisted synthesis, continuous flow processes, and low-temperature reaction routes. By minimizing energy consumption while maintaining or improving yield, these techniques significantly enhance the sustainability and economic viability of lithium acetate production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative catalysts and reaction media for lithium acetate processing
The development of novel catalysts and reaction media has revolutionized lithium acetate processing efficiency. These innovations include heterogeneous catalysts, ionic liquids, and green solvents that facilitate faster reaction rates and higher selectivity. By enabling reactions under milder conditions and improving conversion rates, these advanced materials significantly enhance process efficiency while reducing environmental impact and operational costs.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Lithium Acetate Production
The lithium acetate pharmaceutical synthesis market is in a growth phase, characterized by increasing demand for efficient and sustainable synthesis processes. The market is expanding due to rising pharmaceutical applications, with an estimated global value exceeding $300 million. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across different synthesis methods. Leading pharmaceutical companies like Merck Patent GmbH, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Pfizer are driving innovation through advanced process development, while specialized chemical manufacturers such as Chemetall GmbH and Eastman Chemical provide essential raw materials. Battery material companies including LG Chem and Tianqi Lithium are exploring crossover applications, leveraging their lithium expertise. Academic-industry collaborations with institutions like Monash University are accelerating process optimization research, focusing on greener synthesis pathways.
Merck Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Merck Patent GmbH has developed a sophisticated lithium acetate-based catalytic system for asymmetric synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates. Their approach centers on a chiral lithium acetate complex that functions as both a Lewis acid and Brønsted base in tandem catalytic cycles. This dual-function catalyst system achieves enantioselectivity exceeding 98% ee for a broad range of substrates while operating at catalyst loadings as low as 0.2 mol%. The company's process employs a proprietary immobilization technique that anchors the lithium acetate catalyst to a functionalized polymer support, enabling efficient catalyst recovery (>95% recovery rate) and minimizing product contamination with lithium residues to below 10 ppm. Merck has successfully implemented this technology in continuous manufacturing settings, achieving productivity improvements of approximately 300% compared to batch processes for select API intermediates. Their method also incorporates in-line monitoring of lithium species to ensure consistent catalyst performance and product quality.
Strengths: Exceptional enantioselectivity, extremely low catalyst loading requirements, excellent catalyst recyclability, minimal metal contamination in final products. Weaknesses: Complex catalyst preparation procedure, sensitivity to certain functional groups that can coordinate with lithium, higher implementation costs for continuous manufacturing setup.
UCB Biopharma SRL
Technical Solution: UCB Biopharma has developed a comprehensive lithium acetate-based synthetic platform specifically tailored for their neurological and immunological drug candidates. Their "LiAc-Cascade" methodology employs lithium acetate as a multifunctional reagent that mediates sequential transformations in one-pot processes, reducing isolation steps by up to 40% compared to traditional synthetic routes. The company has optimized reaction conditions to achieve selective functionalization of heterocyclic scaffolds with positional selectivity exceeding 95% for challenging substrates. UCB's approach incorporates a novel co-solvent system that enhances lithium acetate solubility and reactivity while maintaining compatibility with a wide range of functional groups. Their process features an innovative in-situ lithium species monitoring technique using spectroscopic methods, allowing real-time reaction tracking and automated parameter adjustment. The company has successfully scaled this technology to kilogram quantities for several development candidates, demonstrating consistent quality and reproducibility across multiple batches.
Strengths: Excellent process efficiency through one-pot cascade reactions, high positional selectivity, robust scalability with consistent results, real-time reaction monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: Complex co-solvent system requires careful optimization, higher analytical overhead for process monitoring, limited application to certain molecular scaffolds central to UCB's therapeutic areas.
Key Patents and Innovations in Lithium Acetate Synthesis
Method for producing lithium hydroxide
PatentActiveJP2019131448A
Innovation
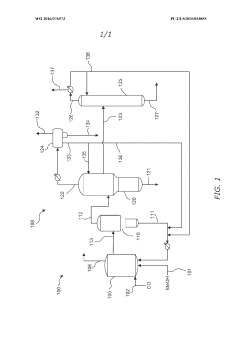
- A method involving the reaction of lithium carbonate with acetic acid to produce lithium acetate, followed by reaction with metal hydroxides like potassium or sodium hydroxide to generate lithium hydroxide, accompanied by crystallization and recycling of residual lithium compounds, allowing for efficient production at room temperature and reduced energy consumption.
Process for flashing a reaction medium comprising lithium acetate
PatentWO2016076973A1
Innovation
- A process involving carbonylation of a reactant feed stream with water, rhodium catalyst, iodide salt, and methyl iodide, where a lithium compound is introduced to maintain a lithium acetate concentration in the reaction medium from 0.3 to 0.7 wt%, allowing for controlled separation in a flash vessel to produce a vapor product stream with optimized methyl iodide, acetic acid, and water concentrations, thereby reducing hydrogen iodide levels and enhancing production efficiency.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Lithium Acetate Production Methods
The environmental impact of lithium acetate production methods represents a critical consideration in pharmaceutical synthesis processes. Traditional manufacturing routes often involve energy-intensive operations and generate significant waste streams, contributing to higher carbon footprints. The conventional method utilizing lithium hydroxide and acetic acid typically requires substantial heating and cooling cycles, resulting in considerable energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Water usage presents another significant environmental concern, with traditional batch processes consuming between 15-20 liters of water per kilogram of lithium acetate produced. This water footprint becomes particularly problematic in regions facing water scarcity issues, where pharmaceutical manufacturing may compete with other essential water needs.
Waste generation varies significantly across production methods. The direct reaction approach produces approximately 0.3-0.5 kg of waste per kilogram of product, while the ion-exchange method generates nearly double this amount. Recent life cycle assessments indicate that the electrochemical route offers the most favorable environmental profile, reducing waste generation by up to 40% compared to conventional methods.
Air quality impacts also differ substantially between production techniques. Solvent-based processes release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to photochemical smog formation and respiratory health concerns. Measurements from production facilities indicate VOC emissions ranging from 2.5-4.8 g/kg of product for conventional methods, compared to just 0.8-1.2 g/kg for newer catalytic approaches.
Land use and ecological disruption extend beyond the manufacturing facility to the entire supply chain. Lithium mining operations associated with raw material procurement can lead to habitat destruction, soil contamination, and biodiversity loss. The environmental footprint of lithium extraction has been estimated at 9-14 m² of disturbed land per kilogram of lithium carbonate equivalent.
Recent innovations have demonstrated promising improvements in environmental performance. Continuous flow manufacturing techniques have reduced energy requirements by 30-45% while simultaneously decreasing solvent usage by up to 60%. Additionally, green chemistry approaches incorporating biocatalysts and renewable feedstocks have shown potential to further minimize environmental impacts across multiple categories.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence production method selection, with stringent environmental standards in Europe and North America driving adoption of cleaner technologies. Carbon pricing mechanisms and extended producer responsibility policies are creating economic incentives that favor environmentally optimized production routes, despite potentially higher initial capital investments.
Water usage presents another significant environmental concern, with traditional batch processes consuming between 15-20 liters of water per kilogram of lithium acetate produced. This water footprint becomes particularly problematic in regions facing water scarcity issues, where pharmaceutical manufacturing may compete with other essential water needs.
Waste generation varies significantly across production methods. The direct reaction approach produces approximately 0.3-0.5 kg of waste per kilogram of product, while the ion-exchange method generates nearly double this amount. Recent life cycle assessments indicate that the electrochemical route offers the most favorable environmental profile, reducing waste generation by up to 40% compared to conventional methods.
Air quality impacts also differ substantially between production techniques. Solvent-based processes release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to photochemical smog formation and respiratory health concerns. Measurements from production facilities indicate VOC emissions ranging from 2.5-4.8 g/kg of product for conventional methods, compared to just 0.8-1.2 g/kg for newer catalytic approaches.
Land use and ecological disruption extend beyond the manufacturing facility to the entire supply chain. Lithium mining operations associated with raw material procurement can lead to habitat destruction, soil contamination, and biodiversity loss. The environmental footprint of lithium extraction has been estimated at 9-14 m² of disturbed land per kilogram of lithium carbonate equivalent.
Recent innovations have demonstrated promising improvements in environmental performance. Continuous flow manufacturing techniques have reduced energy requirements by 30-45% while simultaneously decreasing solvent usage by up to 60%. Additionally, green chemistry approaches incorporating biocatalysts and renewable feedstocks have shown potential to further minimize environmental impacts across multiple categories.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly influence production method selection, with stringent environmental standards in Europe and North America driving adoption of cleaner technologies. Carbon pricing mechanisms and extended producer responsibility policies are creating economic incentives that favor environmentally optimized production routes, despite potentially higher initial capital investments.
Quality Control Standards and Regulatory Compliance for Pharmaceutical-Grade Lithium Acetate
The pharmaceutical industry maintains stringent quality control standards for all raw materials, including lithium acetate, to ensure patient safety and product efficacy. For pharmaceutical-grade lithium acetate, manufacturers must adhere to pharmacopeial standards such as those outlined in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), and Japanese Pharmacopoeia (JP). These standards specify acceptable limits for impurities, heavy metals, residual solvents, and microbial contamination.
Quality control testing for lithium acetate typically includes assay determination (minimum 99.0% purity), identification tests (IR spectroscopy, flame test), pH measurement (typically 7.5-9.0 for a 5% solution), and specific tests for related substances. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) is commonly employed to detect trace metal impurities, with limits for lead, arsenic, mercury, and cadmium strictly defined.
Regulatory compliance for pharmaceutical-grade lithium acetate extends beyond quality specifications to encompass Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Manufacturers must maintain validated production processes, conduct regular stability studies, and implement robust change control procedures. Documentation requirements include batch records, analytical methods validation, and certificates of analysis for each production lot.
The FDA's Q7 guidance on Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) manufacturing applies to lithium acetate production when used in drug formulations. While lithium acetate itself is typically classified as an excipient rather than an API, similar quality standards apply. Manufacturers must register with regulatory authorities and submit to periodic inspections to verify compliance.
Supply chain integrity represents another critical aspect of regulatory compliance. Pharmaceutical companies must qualify suppliers through audits and maintain traceability documentation. The Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the US and similar regulations in other regions require electronic tracking of pharmaceutical materials throughout the distribution network.
Environmental considerations also factor into regulatory compliance for lithium acetate production. Waste management practices must comply with local regulations, and manufacturers increasingly adopt green chemistry principles to minimize environmental impact. Water usage, energy consumption, and carbon footprint metrics are becoming standard reporting requirements in many jurisdictions.
Harmonization efforts through the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) have standardized many quality requirements globally, though regional variations persist. Manufacturers must navigate these differences when producing lithium acetate for international pharmaceutical markets.
Quality control testing for lithium acetate typically includes assay determination (minimum 99.0% purity), identification tests (IR spectroscopy, flame test), pH measurement (typically 7.5-9.0 for a 5% solution), and specific tests for related substances. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) is commonly employed to detect trace metal impurities, with limits for lead, arsenic, mercury, and cadmium strictly defined.
Regulatory compliance for pharmaceutical-grade lithium acetate extends beyond quality specifications to encompass Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Manufacturers must maintain validated production processes, conduct regular stability studies, and implement robust change control procedures. Documentation requirements include batch records, analytical methods validation, and certificates of analysis for each production lot.
The FDA's Q7 guidance on Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) manufacturing applies to lithium acetate production when used in drug formulations. While lithium acetate itself is typically classified as an excipient rather than an API, similar quality standards apply. Manufacturers must register with regulatory authorities and submit to periodic inspections to verify compliance.
Supply chain integrity represents another critical aspect of regulatory compliance. Pharmaceutical companies must qualify suppliers through audits and maintain traceability documentation. The Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the US and similar regulations in other regions require electronic tracking of pharmaceutical materials throughout the distribution network.
Environmental considerations also factor into regulatory compliance for lithium acetate production. Waste management practices must comply with local regulations, and manufacturers increasingly adopt green chemistry principles to minimize environmental impact. Water usage, energy consumption, and carbon footprint metrics are becoming standard reporting requirements in many jurisdictions.
Harmonization efforts through the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) have standardized many quality requirements globally, though regional variations persist. Manufacturers must navigate these differences when producing lithium acetate for international pharmaceutical markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!