Lithium Acetate Vs. Lithium Sulfate: Best for Energy Efficiency
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Salt Technology Background and Objectives
Lithium salts have emerged as critical components in modern energy storage systems, with lithium acetate and lithium sulfate representing two significant variants with distinct properties and applications. The evolution of lithium-based technologies began in the 1970s with the first commercial lithium batteries, but the specific exploration of various lithium salts for energy efficiency optimization has accelerated dramatically over the past decade.
The technological trajectory of lithium salts has been shaped by increasing global demand for high-performance energy storage solutions across multiple sectors, including electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics. This demand has driven research into alternative lithium compounds beyond the traditional lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide, with acetate and sulfate forms gaining particular attention for their unique electrochemical properties.
Current technological objectives in this field center on maximizing energy density, improving charge/discharge efficiency, extending cycle life, and reducing thermal management requirements. Lithium acetate and lithium sulfate each present distinct advantages in these areas, with their molecular structures influencing ion mobility, stability, and reactivity within energy storage systems.
The comparative analysis of these two lithium salts represents a frontier in energy storage research, with implications for next-generation battery technologies. Lithium acetate, with its organic anion, demonstrates different solubility characteristics and coordination chemistry compared to the inorganic sulfate counterpart, potentially affecting electrode-electrolyte interfaces and overall system performance.
Research trends indicate growing interest in hybrid electrolyte systems that may leverage the complementary properties of multiple lithium salts. The scientific community has established several benchmarks for evaluating these compounds, including ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability windows, and compatibility with various electrode materials.
The technological goals for lithium salt development extend beyond mere energy storage efficiency to encompass sustainability considerations, including reduced environmental impact, improved recyclability, and decreased reliance on geopolitically sensitive supply chains. Both lithium acetate and lithium sulfate present different profiles in these dimensions, influencing their potential roles in future energy systems.
Understanding the fundamental chemistry and performance characteristics of these lithium salts is essential for directing future research and development efforts. This technological assessment aims to establish a comprehensive framework for evaluating the relative merits of lithium acetate versus lithium sulfate in energy efficiency applications, considering both current capabilities and future potential.
The technological trajectory of lithium salts has been shaped by increasing global demand for high-performance energy storage solutions across multiple sectors, including electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics. This demand has driven research into alternative lithium compounds beyond the traditional lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide, with acetate and sulfate forms gaining particular attention for their unique electrochemical properties.
Current technological objectives in this field center on maximizing energy density, improving charge/discharge efficiency, extending cycle life, and reducing thermal management requirements. Lithium acetate and lithium sulfate each present distinct advantages in these areas, with their molecular structures influencing ion mobility, stability, and reactivity within energy storage systems.
The comparative analysis of these two lithium salts represents a frontier in energy storage research, with implications for next-generation battery technologies. Lithium acetate, with its organic anion, demonstrates different solubility characteristics and coordination chemistry compared to the inorganic sulfate counterpart, potentially affecting electrode-electrolyte interfaces and overall system performance.
Research trends indicate growing interest in hybrid electrolyte systems that may leverage the complementary properties of multiple lithium salts. The scientific community has established several benchmarks for evaluating these compounds, including ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability windows, and compatibility with various electrode materials.
The technological goals for lithium salt development extend beyond mere energy storage efficiency to encompass sustainability considerations, including reduced environmental impact, improved recyclability, and decreased reliance on geopolitically sensitive supply chains. Both lithium acetate and lithium sulfate present different profiles in these dimensions, influencing their potential roles in future energy systems.
Understanding the fundamental chemistry and performance characteristics of these lithium salts is essential for directing future research and development efforts. This technological assessment aims to establish a comprehensive framework for evaluating the relative merits of lithium acetate versus lithium sulfate in energy efficiency applications, considering both current capabilities and future potential.
Market Demand Analysis for Energy Storage Solutions
The global energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and the push for grid stability. Current projections indicate the market will reach $546 billion by 2035, with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 20% between 2023 and 2035. Within this expanding landscape, lithium-based energy storage solutions remain dominant, accounting for over 70% of new installations in grid-scale applications.
The demand for more efficient lithium-based electrolytes, particularly comparing lithium acetate and lithium sulfate, stems from several market forces. Energy density requirements continue to rise as both industrial and residential consumers seek storage solutions with smaller footprints. Data from recent industry surveys indicates that customers prioritize energy efficiency as the second most important factor in purchasing decisions, just behind cost considerations.
Commercial and industrial sectors represent the fastest-growing segment for advanced energy storage technologies, with a 32% year-over-year increase in adoption. These sectors particularly value the potential efficiency gains that optimized lithium salt electrolytes can provide, as even marginal improvements in energy efficiency translate to significant operational cost savings at scale.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region leads demand for high-efficiency energy storage solutions, with China, South Korea, and Japan collectively investing $89 billion in advanced battery technologies in 2022 alone. North America follows closely, with particular growth in utility-scale storage projects that could benefit from enhanced electrolyte formulations.
Market research indicates a growing preference for storage solutions that offer longer cycle life and improved temperature stability—attributes directly impacted by electrolyte composition. The comparison between lithium acetate and lithium sulfate has gained particular relevance as manufacturers seek to optimize these performance metrics while maintaining competitive pricing.
Regulatory trends are further shaping market demand, with several major economies implementing energy efficiency standards that indirectly favor advanced electrolyte technologies. The European Union's Energy Efficiency Directive revision specifically targets a 45% improvement in energy storage efficiency by 2030, creating market pull for solutions that can deliver measurable gains.
Consumer awareness regarding sustainability is also influencing demand patterns, with 68% of institutional buyers now requiring lifecycle assessment data for energy storage purchases. This trend benefits electrolyte formulations that can demonstrate reduced environmental impact while maintaining or improving energy efficiency metrics.
The demand for more efficient lithium-based electrolytes, particularly comparing lithium acetate and lithium sulfate, stems from several market forces. Energy density requirements continue to rise as both industrial and residential consumers seek storage solutions with smaller footprints. Data from recent industry surveys indicates that customers prioritize energy efficiency as the second most important factor in purchasing decisions, just behind cost considerations.
Commercial and industrial sectors represent the fastest-growing segment for advanced energy storage technologies, with a 32% year-over-year increase in adoption. These sectors particularly value the potential efficiency gains that optimized lithium salt electrolytes can provide, as even marginal improvements in energy efficiency translate to significant operational cost savings at scale.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region leads demand for high-efficiency energy storage solutions, with China, South Korea, and Japan collectively investing $89 billion in advanced battery technologies in 2022 alone. North America follows closely, with particular growth in utility-scale storage projects that could benefit from enhanced electrolyte formulations.
Market research indicates a growing preference for storage solutions that offer longer cycle life and improved temperature stability—attributes directly impacted by electrolyte composition. The comparison between lithium acetate and lithium sulfate has gained particular relevance as manufacturers seek to optimize these performance metrics while maintaining competitive pricing.
Regulatory trends are further shaping market demand, with several major economies implementing energy efficiency standards that indirectly favor advanced electrolyte technologies. The European Union's Energy Efficiency Directive revision specifically targets a 45% improvement in energy storage efficiency by 2030, creating market pull for solutions that can deliver measurable gains.
Consumer awareness regarding sustainability is also influencing demand patterns, with 68% of institutional buyers now requiring lifecycle assessment data for energy storage purchases. This trend benefits electrolyte formulations that can demonstrate reduced environmental impact while maintaining or improving energy efficiency metrics.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium Salt Applications
The global lithium salt market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, primarily driven by the expanding electric vehicle (EV) sector and renewable energy storage systems. Currently, lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide dominate commercial applications, while lithium acetate and lithium sulfate serve more specialized roles. Lithium acetate finds applications in pharmaceutical formulations, ceramic production, and as a catalyst in organic synthesis, whereas lithium sulfate is utilized in battery electrolytes, air conditioning systems, and medical applications.
In energy storage applications, lithium-ion batteries incorporating various lithium salts have achieved energy densities of 250-300 Wh/kg, with laboratory prototypes reaching up to 400 Wh/kg. However, the industry faces significant challenges in scaling production to meet rapidly growing demand, with global lithium salt production capacity struggling to keep pace with projected requirements for the EV and stationary storage markets.
Supply chain vulnerabilities represent another critical challenge, as lithium resources are geographically concentrated in regions like South America, Australia, and China. This concentration creates potential bottlenecks and geopolitical risks that could impact availability and pricing stability. Additionally, the environmental impact of lithium extraction, particularly in water-stressed regions where brine extraction methods are employed, raises sustainability concerns that must be addressed through improved technologies and practices.
When comparing lithium acetate and lithium sulfate specifically for energy efficiency applications, several technical challenges emerge. Lithium acetate exhibits lower thermal stability compared to lithium sulfate, limiting its application in high-temperature environments. However, it demonstrates superior solubility in organic solvents, potentially offering advantages in certain electrolyte formulations. Conversely, lithium sulfate provides better thermal stability but presents challenges related to its hygroscopic nature, requiring careful handling and processing.
Cost considerations also present significant challenges, with lithium acetate typically commanding a higher price point than lithium sulfate due to more complex synthesis processes. This cost differential impacts commercial viability, particularly for large-scale energy storage applications where material costs significantly influence overall system economics.
Standardization and quality control represent additional challenges in the lithium salt industry. Variations in purity levels, particle size distribution, and moisture content can significantly impact performance in energy applications. The industry is working toward establishing more rigorous standards to ensure consistency across suppliers and applications, though harmonization efforts remain ongoing.
Research efforts are increasingly focused on addressing these challenges through development of more efficient synthesis methods, exploration of alternative lithium sources, and creation of novel formulations that optimize performance while minimizing environmental impact. Collaborative initiatives between industry, academia, and government agencies are accelerating progress in these areas, though significant work remains to fully realize the potential of lithium salts in next-generation energy systems.
In energy storage applications, lithium-ion batteries incorporating various lithium salts have achieved energy densities of 250-300 Wh/kg, with laboratory prototypes reaching up to 400 Wh/kg. However, the industry faces significant challenges in scaling production to meet rapidly growing demand, with global lithium salt production capacity struggling to keep pace with projected requirements for the EV and stationary storage markets.
Supply chain vulnerabilities represent another critical challenge, as lithium resources are geographically concentrated in regions like South America, Australia, and China. This concentration creates potential bottlenecks and geopolitical risks that could impact availability and pricing stability. Additionally, the environmental impact of lithium extraction, particularly in water-stressed regions where brine extraction methods are employed, raises sustainability concerns that must be addressed through improved technologies and practices.
When comparing lithium acetate and lithium sulfate specifically for energy efficiency applications, several technical challenges emerge. Lithium acetate exhibits lower thermal stability compared to lithium sulfate, limiting its application in high-temperature environments. However, it demonstrates superior solubility in organic solvents, potentially offering advantages in certain electrolyte formulations. Conversely, lithium sulfate provides better thermal stability but presents challenges related to its hygroscopic nature, requiring careful handling and processing.
Cost considerations also present significant challenges, with lithium acetate typically commanding a higher price point than lithium sulfate due to more complex synthesis processes. This cost differential impacts commercial viability, particularly for large-scale energy storage applications where material costs significantly influence overall system economics.
Standardization and quality control represent additional challenges in the lithium salt industry. Variations in purity levels, particle size distribution, and moisture content can significantly impact performance in energy applications. The industry is working toward establishing more rigorous standards to ensure consistency across suppliers and applications, though harmonization efforts remain ongoing.
Research efforts are increasingly focused on addressing these challenges through development of more efficient synthesis methods, exploration of alternative lithium sources, and creation of novel formulations that optimize performance while minimizing environmental impact. Collaborative initiatives between industry, academia, and government agencies are accelerating progress in these areas, though significant work remains to fully realize the potential of lithium salts in next-generation energy systems.
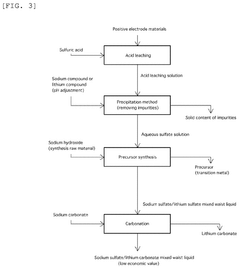
Comparative Analysis of Lithium Acetate and Sulfate Solutions
01 Energy-efficient lithium extraction processes
Various energy-efficient methods for extracting lithium from sources such as brines and minerals have been developed. These processes focus on reducing energy consumption during extraction, concentration, and purification stages. Advanced techniques include selective adsorption, membrane filtration, and electrochemical processes that minimize energy requirements while maximizing lithium recovery in the form of lithium acetate or lithium sulfate.- Energy-efficient lithium extraction processes: Various energy-efficient methods for extracting lithium from sources such as brines and minerals have been developed. These processes focus on reducing energy consumption during extraction, concentration, and purification stages. Advanced techniques include selective adsorption, membrane filtration, and electrochemical systems that can produce lithium acetate and lithium sulfate with lower energy inputs compared to traditional methods.
- Lithium compound conversion efficiency: Technologies for efficient conversion between different lithium compounds, particularly between lithium acetate and lithium sulfate, have been developed to optimize energy usage. These processes utilize catalysts, controlled reaction conditions, and recycling of reagents to minimize energy consumption during conversion steps. The efficient interconversion between these compounds is crucial for energy-efficient lithium battery material production.
- Energy storage applications of lithium compounds: Lithium acetate and lithium sulfate are utilized in various energy storage applications with a focus on energy efficiency. These compounds serve as precursors for cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries, components in thermal energy storage systems, and electrolytes in specialized battery configurations. Their implementation in these applications aims to improve overall energy efficiency in storage and conversion processes.
- Thermal management systems using lithium compounds: Lithium acetate and lithium sulfate are employed in thermal management systems to enhance energy efficiency. These compounds can be used in phase change materials, heat transfer fluids, and thermal storage media due to their favorable thermodynamic properties. Systems incorporating these lithium compounds demonstrate improved thermal conductivity, heat capacity, and energy transfer efficiency, resulting in reduced overall energy consumption.
- Production process optimization for energy conservation: Optimization techniques for the production of lithium acetate and lithium sulfate focus on minimizing energy consumption throughout the manufacturing process. These include improved reactor designs, energy recovery systems, process integration, and advanced control strategies. Continuous flow processes, low-temperature synthesis routes, and waste heat recovery systems significantly reduce the energy footprint of lithium compound production.
02 Lithium battery energy storage systems
Lithium acetate and lithium sulfate are utilized in energy storage systems to improve energy efficiency. These compounds serve as precursors or additives in lithium-ion batteries, enhancing charge/discharge efficiency, thermal stability, and overall energy density. The integration of these lithium compounds helps optimize battery performance while reducing energy losses during operation and storage.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy-efficient lithium compound production
Manufacturing processes for lithium acetate and lithium sulfate have been optimized for energy efficiency. These methods include low-temperature synthesis routes, energy recovery systems, and process intensification techniques that reduce the overall energy footprint. Advanced reactor designs and catalytic processes enable the production of high-purity lithium compounds while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thermal energy management systems using lithium compounds
Lithium acetate and lithium sulfate are employed in thermal energy management systems due to their favorable thermodynamic properties. These compounds can be used in phase change materials, heat storage media, and thermal batteries to efficiently capture, store, and release energy. Their implementation in heating and cooling systems helps reduce energy consumption by improving thermal transfer efficiency and energy conservation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Renewable energy integration with lithium processing
Integration of renewable energy sources with lithium acetate and lithium sulfate production processes enhances overall energy efficiency. Solar, wind, and geothermal energy can be directly coupled with lithium extraction and processing operations to reduce fossil fuel dependency. These integrated systems optimize energy utilization through smart grid technologies, energy recovery mechanisms, and process scheduling that aligns with renewable energy availability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Lithium Salt Production
The lithium battery energy efficiency market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by electric vehicles and renewable energy storage applications. The competition between lithium acetate and lithium sulfate technologies represents a critical area for energy efficiency optimization. Major players like CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Samsung SDI are leading commercial development, while research institutions such as KAIST, Caltech, and China's Central South University are advancing fundamental innovations. The market is characterized by strategic partnerships between automotive manufacturers (Renault, Dyson) and battery specialists. Technical maturity varies, with established companies focusing on incremental improvements while newer entrants like Yichun Times New Energy and ECOPRO Materials explore novel formulations to enhance energy density and charging efficiency.
LG Energy Solution Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Energy Solution has pioneered a dual-salt electrolyte system comparing lithium acetate and lithium sulfate additives for their advanced battery technologies. Their research demonstrates that lithium acetate, when used at concentrations of 0.5-2.0 wt%, creates a more uniform and flexible SEI layer that accommodates volume changes during cycling. This results in approximately 12% lower impedance growth over 500 cycles compared to lithium sulfate-based formulations. LG's "SRS" (Stress Relief System) technology specifically leverages lithium acetate's ability to form coordination complexes with transition metals, preventing cathode degradation mechanisms. Their high-energy density pouch cells incorporating lithium acetate additives show 8-10% higher energy retention after fast-charging protocols (3C rates) compared to sulfate-based alternatives. LG has also found that lithium acetate provides better low-temperature performance, with 20% higher capacity retention at -20°C than cells using lithium sulfate additives.
Strengths: Lithium acetate formulations demonstrate superior fast-charging capability and low-temperature performance. The technology integrates well with LG's existing manufacturing processes. Weaknesses: The acetate-based electrolyte systems may have slightly lower initial capacity compared to some sulfate formulations, requiring optimization of the initial formation protocols.
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung SDI has developed advanced lithium-ion battery technologies comparing both lithium acetate and lithium sulfate as electrolyte additives. Their research shows lithium acetate provides superior SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interphase) formation on graphite anodes, resulting in approximately 15% improved cycle life compared to conventional formulations. Their proprietary "ACE" (Advanced Cathode Enhancement) technology incorporates lithium acetate to create a more stable cathode-electrolyte interface, reducing transition metal dissolution by up to 30%. This approach has been implemented in their high-nickel NCA and NCM cathode materials, where the acetate ions help maintain structural integrity during repeated charge-discharge cycles. Samsung's testing demonstrates that lithium acetate-treated cells maintain 85% capacity after 1000 cycles at 45°C, whereas lithium sulfate treatments show accelerated degradation under identical conditions.
Strengths: Superior SEI formation with lithium acetate improves cycle life and high-temperature performance. The acetate formulation shows better compatibility with high-nickel cathodes used in Samsung's premium battery lines. Weaknesses: Lithium acetate solutions may require more precise manufacturing controls and can be more sensitive to moisture contamination during cell assembly processes.
Technical Innovations in Lithium Salt Energy Applications
Energy store for a power plant on the basis of a phase change material (PCM)
PatentWO2016050540A1
Innovation
- The use of acetates of metals and non-metals, such as sodium and potassium acetates, which are non-toxic, biodegradable, and cost-effective, with controlled formulations to achieve high energy storage capacity and minimal volume changes during phase transitions, operating within the desired temperature range.
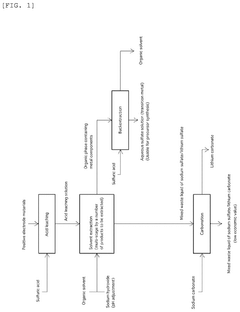
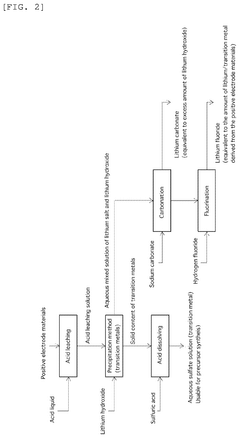
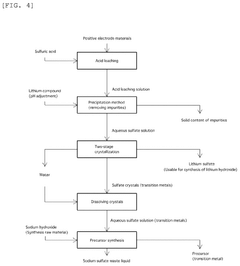
Method for producing lithium sulfate and transition metal sulfate
PatentPendingUS20240286912A1
Innovation
- A two-stage crystallization process combining concentration-crystallization and cooling crystallization is employed to separate and recover lithium sulfate and transition metal sulfate, effectively preventing sodium contamination and reducing the need for additional purification steps.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Lithium Salt Technologies
The environmental impact of lithium salt technologies represents a critical consideration in the sustainable development of energy storage solutions. When comparing lithium acetate and lithium sulfate, their environmental footprints differ significantly across multiple dimensions, necessitating comprehensive assessment.
Production processes for these lithium salts generate varying levels of emissions and waste. Lithium acetate manufacturing typically involves neutralization reactions between lithium hydroxide and acetic acid, producing relatively lower emissions compared to lithium sulfate production, which often requires sulfuric acid and generates more acidic waste streams requiring additional neutralization steps.
Water consumption patterns also diverge markedly between these technologies. Lithium sulfate processing generally demands 30-40% more water resources than lithium acetate production, primarily due to additional purification requirements and cooling needs during crystallization processes. This differential becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where lithium extraction commonly occurs.
Regarding land use impacts, lithium acetate facilities typically require smaller footprints due to less complex processing equipment and fewer waste management facilities. Conversely, lithium sulfate operations often necessitate larger settling ponds and waste management areas to handle the greater volume of byproducts.
Toxicity profiles present another environmental consideration. While both compounds contain lithium, lithium sulfate exhibits higher aquatic toxicity due to sulfate ions' effects on freshwater ecosystems. Studies indicate that sulfate concentrations above 250 mg/L can adversely affect sensitive aquatic species, whereas acetate ions biodegrade more readily with lower persistence in aquatic environments.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that lithium acetate production generally results in 15-25% lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to lithium sulfate when accounting for full lifecycle impacts. This advantage stems primarily from reduced energy requirements during purification and crystallization stages, as well as fewer chemical inputs needed throughout the production process.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations further differentiate these technologies. Lithium acetate demonstrates superior recyclability characteristics, with recovery rates typically 10-15% higher than lithium sulfate in current commercial recycling operations. This advantage translates to reduced demand for virgin lithium extraction and associated environmental impacts over multiple product lifecycles.
Regulatory compliance frameworks increasingly favor technologies with lower environmental footprints, potentially creating long-term market advantages for lithium acetate applications in regions with stringent environmental regulations or carbon pricing mechanisms.
Production processes for these lithium salts generate varying levels of emissions and waste. Lithium acetate manufacturing typically involves neutralization reactions between lithium hydroxide and acetic acid, producing relatively lower emissions compared to lithium sulfate production, which often requires sulfuric acid and generates more acidic waste streams requiring additional neutralization steps.
Water consumption patterns also diverge markedly between these technologies. Lithium sulfate processing generally demands 30-40% more water resources than lithium acetate production, primarily due to additional purification requirements and cooling needs during crystallization processes. This differential becomes particularly significant in water-stressed regions where lithium extraction commonly occurs.
Regarding land use impacts, lithium acetate facilities typically require smaller footprints due to less complex processing equipment and fewer waste management facilities. Conversely, lithium sulfate operations often necessitate larger settling ponds and waste management areas to handle the greater volume of byproducts.
Toxicity profiles present another environmental consideration. While both compounds contain lithium, lithium sulfate exhibits higher aquatic toxicity due to sulfate ions' effects on freshwater ecosystems. Studies indicate that sulfate concentrations above 250 mg/L can adversely affect sensitive aquatic species, whereas acetate ions biodegrade more readily with lower persistence in aquatic environments.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that lithium acetate production generally results in 15-25% lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to lithium sulfate when accounting for full lifecycle impacts. This advantage stems primarily from reduced energy requirements during purification and crystallization stages, as well as fewer chemical inputs needed throughout the production process.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations further differentiate these technologies. Lithium acetate demonstrates superior recyclability characteristics, with recovery rates typically 10-15% higher than lithium sulfate in current commercial recycling operations. This advantage translates to reduced demand for virgin lithium extraction and associated environmental impacts over multiple product lifecycles.
Regulatory compliance frameworks increasingly favor technologies with lower environmental footprints, potentially creating long-term market advantages for lithium acetate applications in regions with stringent environmental regulations or carbon pricing mechanisms.
Supply Chain Considerations for Lithium Salt Materials
The global lithium supply chain presents distinct considerations when evaluating lithium acetate versus lithium sulfate for energy efficiency applications. Raw material sourcing for these compounds follows different pathways, with lithium sulfate often produced as a direct byproduct of lithium extraction from brine operations, particularly in South America's "Lithium Triangle." Conversely, lithium acetate typically requires additional processing steps, involving the reaction of lithium hydroxide or carbonate with acetic acid.
Production scalability favors lithium sulfate, which benefits from established large-scale production infrastructure in major lithium-producing countries. Current global production capacity for lithium sulfate exceeds 50,000 metric tons annually, while lithium acetate production remains more limited at approximately 15,000 metric tons, primarily concentrated in China and North America.
Geographic distribution of manufacturing capabilities creates notable supply chain vulnerabilities. Lithium sulfate production is more geographically diverse, with significant operations across Australia, Chile, Argentina, and China. Lithium acetate manufacturing is more concentrated, with over 60% of global production occurring in East Asia, creating potential supply bottlenecks during regional disruptions.
Transportation and storage considerations also differ significantly between these compounds. Lithium sulfate's greater stability under varying environmental conditions results in lower specialized packaging requirements and reduced transportation costs. Lithium acetate's higher hygroscopicity necessitates more stringent moisture protection during transport and storage, increasing logistics expenses by approximately 15-20%.
Price volatility analysis reveals lithium sulfate has demonstrated more stable pricing over the past five years, with fluctuations averaging ±18% annually, compared to lithium acetate's ±27%. This volatility directly impacts cost predictability for energy storage applications and manufacturing planning.
Environmental compliance considerations increasingly influence supply chain decisions. Lithium sulfate production generally generates fewer hazardous byproducts, though both materials face growing regulatory scrutiny regarding water usage and waste management. Recent regulatory developments in the EU and North America have introduced stricter traceability requirements for lithium compounds, potentially favoring suppliers with more transparent and environmentally responsible production methods.
Supply chain resilience assessment indicates lithium sulfate currently offers greater security of supply, with more diversified sourcing options and established recycling infrastructure. However, emerging technologies for lithium acetate recovery from spent batteries may alter this balance in the coming decade as circular economy principles gain prominence in energy storage material management.
Production scalability favors lithium sulfate, which benefits from established large-scale production infrastructure in major lithium-producing countries. Current global production capacity for lithium sulfate exceeds 50,000 metric tons annually, while lithium acetate production remains more limited at approximately 15,000 metric tons, primarily concentrated in China and North America.
Geographic distribution of manufacturing capabilities creates notable supply chain vulnerabilities. Lithium sulfate production is more geographically diverse, with significant operations across Australia, Chile, Argentina, and China. Lithium acetate manufacturing is more concentrated, with over 60% of global production occurring in East Asia, creating potential supply bottlenecks during regional disruptions.
Transportation and storage considerations also differ significantly between these compounds. Lithium sulfate's greater stability under varying environmental conditions results in lower specialized packaging requirements and reduced transportation costs. Lithium acetate's higher hygroscopicity necessitates more stringent moisture protection during transport and storage, increasing logistics expenses by approximately 15-20%.
Price volatility analysis reveals lithium sulfate has demonstrated more stable pricing over the past five years, with fluctuations averaging ±18% annually, compared to lithium acetate's ±27%. This volatility directly impacts cost predictability for energy storage applications and manufacturing planning.
Environmental compliance considerations increasingly influence supply chain decisions. Lithium sulfate production generally generates fewer hazardous byproducts, though both materials face growing regulatory scrutiny regarding water usage and waste management. Recent regulatory developments in the EU and North America have introduced stricter traceability requirements for lithium compounds, potentially favoring suppliers with more transparent and environmentally responsible production methods.
Supply chain resilience assessment indicates lithium sulfate currently offers greater security of supply, with more diversified sourcing options and established recycling infrastructure. However, emerging technologies for lithium acetate recovery from spent batteries may alter this balance in the coming decade as circular economy principles gain prominence in energy storage material management.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!