Mapping Isocyanate Regulatory Changes: Industry Impacts
Isocyanate Regulations: Background and Objectives
Isocyanates have been a cornerstone in various industries for decades, particularly in the production of polyurethanes, which find applications in diverse sectors such as automotive, construction, and furniture manufacturing. The regulatory landscape surrounding isocyanates has evolved significantly over the years, driven by growing awareness of their potential health and environmental impacts.
The primary objective of isocyanate regulations is to safeguard workers, consumers, and the environment from the potential hazards associated with these chemicals. Isocyanates are known respiratory sensitizers and can cause occupational asthma and other respiratory issues upon repeated exposure. As such, regulatory bodies worldwide have been increasingly focused on implementing stringent controls on their use, handling, and disposal.
The historical context of isocyanate regulations dates back to the 1970s when initial concerns about their health effects emerged. Since then, there has been a progressive tightening of regulations, with major milestones including the introduction of workplace exposure limits, mandatory personal protective equipment requirements, and enhanced safety protocols in manufacturing processes.
In recent years, the regulatory focus has shifted towards a more comprehensive approach, encompassing not only occupational safety but also environmental protection and consumer safety. This has led to the development of regulations governing the entire lifecycle of isocyanate-containing products, from production to end-of-life management.
The technological evolution in the isocyanate industry has been closely intertwined with regulatory changes. Innovations in production processes, safer handling techniques, and the development of alternative materials have all been driven, in part, by the need to comply with increasingly stringent regulations. This symbiotic relationship between regulation and innovation continues to shape the industry landscape.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of isocyanate regulations is expected to continue towards even greater stringency. Emerging areas of focus include the development of more sensitive detection methods, the implementation of real-time monitoring systems in workplaces, and the exploration of safer alternatives to traditional isocyanates. The industry is also witnessing a growing emphasis on sustainability, with regulations increasingly addressing the environmental footprint of isocyanate production and use.
As global harmonization of chemical regulations progresses, there is an increasing trend towards alignment of isocyanate regulations across different regions. This presents both challenges and opportunities for industry players, necessitating a global perspective in regulatory compliance strategies.
Market Impact Analysis of Isocyanate Regulatory Changes
The isocyanate industry is facing significant regulatory changes that are poised to reshape market dynamics and industry practices. These regulatory shifts primarily focus on enhancing worker safety, environmental protection, and consumer health. The impact of these changes is expected to be far-reaching, affecting various sectors that rely on isocyanates, including automotive, construction, furniture, and electronics industries.
One of the most notable market impacts is the anticipated increase in production costs for isocyanate manufacturers. Stricter regulations often require substantial investments in new equipment, safety measures, and process modifications to ensure compliance. This cost burden is likely to be passed down the supply chain, potentially leading to higher prices for end-products containing isocyanates. As a result, industries heavily reliant on isocyanate-based materials may face challenges in maintaining profit margins or may need to explore alternative materials.
The regulatory changes are also expected to drive innovation in the isocyanate industry. Manufacturers are likely to invest more in research and development to create safer, more environmentally friendly isocyanate formulations. This could lead to the emergence of new market segments for "green" or low-emission isocyanate products, catering to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to improve their sustainability profiles.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape may create barriers to entry for new players in the isocyanate market. Smaller companies might struggle to meet the stringent compliance requirements, potentially leading to market consolidation as larger, more established firms with greater resources gain a competitive advantage. This could result in a shift in market share distribution and alter the competitive dynamics within the industry.
The global nature of the isocyanate supply chain adds another layer of complexity to the market impact. Regulatory changes in one region may create disparities in production costs and product availability across different geographical markets. This could lead to shifts in trade patterns, with some regions becoming more attractive for production or consumption based on their regulatory environments.
Lastly, the regulatory changes may influence customer preferences and demand patterns. Increased awareness of health and environmental concerns associated with isocyanates could drive some customers to seek alternative materials, potentially impacting the overall market size for isocyanate-based products. Conversely, improved safety standards and more sustainable formulations may enhance consumer confidence in isocyanate products, potentially opening up new market opportunities in sectors previously hesitant to use these materials.
Current Regulatory Landscape and Industry Challenges
The current regulatory landscape for isocyanates is characterized by a complex web of international, national, and regional regulations aimed at protecting human health and the environment. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for various isocyanates, with the most common being methylene bisphenyl isocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), requiring manufacturers to report production volumes and potential risks.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of isocyanates. REACH mandates that companies register chemicals they produce or import in quantities over one ton per year, including detailed safety information. Additionally, the EU has implemented specific restrictions on diisocyanates, requiring professional and industrial users to undergo training on safe handling practices.
The industry faces significant challenges in adapting to these evolving regulations. One primary concern is the cost of compliance, which includes expenses related to implementing new safety measures, training employees, and potentially reformulating products to meet stricter standards. Many companies, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, struggle to keep up with the rapidly changing regulatory landscape and may face financial burdens in doing so.
Another challenge is the technical complexity of finding suitable alternatives to isocyanates in certain applications. While there is a growing push for safer substitutes, isocyanates remain critical in many industrial processes due to their unique properties. This creates a tension between regulatory pressures and practical limitations in product development and manufacturing.
The global nature of supply chains adds another layer of complexity to regulatory compliance. Companies operating in multiple jurisdictions must navigate varying standards and reporting requirements, which can lead to increased administrative burdens and potential market access issues. This is particularly challenging for multinational corporations that must ensure compliance across diverse regulatory frameworks.
Furthermore, the industry is grappling with the need for improved exposure monitoring and control measures. As regulations become more stringent, companies are required to implement more sophisticated systems for detecting and mitigating isocyanate exposure risks. This often necessitates significant investments in new equipment and technologies, as well as ongoing training and maintenance.
Lastly, there is a growing emphasis on transparency and communication of hazards throughout the supply chain. Regulations increasingly require detailed information sharing about the presence and risks of isocyanates in products, which can be challenging to implement effectively, especially for complex products with multiple suppliers.
Existing Compliance Strategies for Isocyanate Regulations
01 Environmental and safety regulations for isocyanates
Isocyanates are subject to strict environmental and safety regulations due to their potential health hazards. These regulations often include guidelines for handling, storage, and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials. Manufacturers and users must comply with exposure limits, implement proper ventilation systems, and provide personal protective equipment for workers handling isocyanates.- Environmental and safety regulations for isocyanates: Isocyanates are subject to strict environmental and safety regulations due to their potential health hazards. These regulations often include guidelines for handling, storage, and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials. Manufacturers and users must comply with exposure limits, implement proper ventilation systems, and provide appropriate personal protective equipment for workers.
- Monitoring and control systems for isocyanate exposure: Advanced monitoring and control systems are developed to ensure compliance with isocyanate regulations. These systems may include real-time air quality monitoring, automated alarms, and integrated data management solutions. Such technologies help businesses maintain safe working environments and demonstrate regulatory compliance.
- Regulatory compliance management for isocyanate-related industries: Industries dealing with isocyanates implement comprehensive regulatory compliance management systems. These systems often involve software solutions that track regulatory changes, manage documentation, and facilitate reporting to relevant authorities. They help companies stay up-to-date with evolving isocyanate regulations and maintain proper compliance records.
- Alternative materials and technologies to reduce isocyanate use: In response to stringent regulations, research is conducted to develop alternative materials and technologies that can reduce or eliminate the use of isocyanates. This includes exploring bio-based polymers, water-based systems, and other less hazardous substitutes. Such innovations aim to mitigate regulatory challenges while maintaining product performance.
- Training and certification programs for isocyanate handling: To ensure compliance with regulations, specialized training and certification programs are developed for workers handling isocyanates. These programs cover safe handling procedures, emergency response protocols, and proper use of protective equipment. Employers are often required to provide and document such training to meet regulatory requirements.
02 Monitoring and control systems for isocyanate exposure
Advanced monitoring and control systems are developed to ensure compliance with isocyanate regulations. These systems may include real-time air quality monitoring, automated alert mechanisms, and data logging for regulatory reporting. Such technologies help businesses maintain safe working environments and demonstrate adherence to isocyanate exposure limits.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes
In response to stringent regulations, there is a growing trend towards developing and adopting isocyanate-free alternatives. These substitutes aim to provide similar performance characteristics while reducing health and environmental risks associated with traditional isocyanates. Research focuses on new chemistries and formulations that comply with evolving regulatory standards.Expand Specific Solutions04 Regulatory compliance management for isocyanate-related industries
Companies dealing with isocyanates implement comprehensive regulatory compliance management systems. These systems often involve software solutions that track regulatory changes, manage documentation, conduct risk assessments, and ensure proper training of personnel. Such management systems help organizations navigate the complex landscape of isocyanate regulations across different jurisdictions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Waste management and disposal regulations for isocyanates
Specific regulations govern the management and disposal of isocyanate-containing waste. These regulations typically require specialized handling procedures, proper containment, and approved disposal methods to prevent environmental contamination. Companies must adhere to strict protocols for the transportation, treatment, and disposal of isocyanate waste materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Stakeholders in Isocyanate Industry and Regulation
The isocyanate regulatory landscape is evolving, reflecting a mature industry facing increased scrutiny. The market, valued at billions globally, is in a consolidation phase with established players like Wanhua Chemical, Covestro, and BASF dominating. Technological advancements focus on safer, more sustainable isocyanates, driven by stringent environmental regulations. Companies are investing in R&D to develop low-emission formulations and bio-based alternatives. The industry is characterized by high entry barriers due to complex manufacturing processes and regulatory compliance requirements, favoring large, integrated chemical companies with robust research capabilities and global distribution networks.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Critical Regulatory Updates and Their Implications
- A method using 1,8-diaminonaphthalene (DAN) as a bifunctional nucleophilic isocyanate derivatizing agent that reacts with isocyanates to form a cyclic reaction product, allowing for the detection and quantification of total isocyanate groups regardless of the specific species present, using a two-step process of derivatization and cyclization.
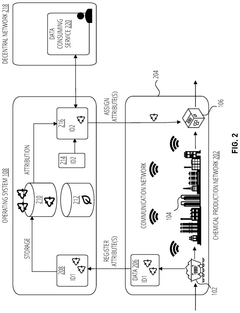
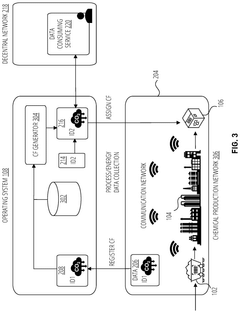
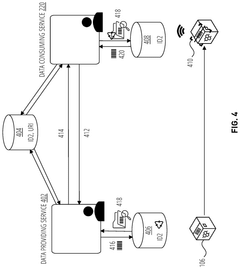
- A system is developed that produces isocyanate compositions associated with an isocyanate composition passport or digital asset. This system includes a chemical production network that produces isocyanate compositions from input materials through chemical processes, and a production operating apparatus that generates a decentral identifier linked to environmental attributes of the input materials and chemical processes, creating a digital asset that tracks environmental impact.
Economic Implications of Regulatory Changes
The regulatory changes surrounding isocyanates are poised to have significant economic implications across various industries. These changes are likely to impact production costs, market dynamics, and investment strategies for companies involved in the manufacture and use of isocyanate-based products.
One of the primary economic effects will be increased compliance costs for manufacturers. As regulations tighten, companies may need to invest in new equipment, modify production processes, or develop alternative formulations to meet stricter safety and environmental standards. This could lead to higher production costs in the short term, potentially affecting profit margins and competitiveness.
The automotive industry, a major consumer of isocyanate-based products, may face challenges in adapting to new regulations. Manufacturers may need to redesign components or seek alternative materials, potentially leading to increased vehicle costs. However, this could also drive innovation in lightweight materials and fuel-efficient designs, creating new market opportunities.
The construction sector, another significant user of isocyanate-containing products, may experience shifts in material choices and application methods. While initial costs may rise, there could be long-term benefits in terms of improved building performance and occupant health, potentially driving demand for compliant products.
Supply chain dynamics are likely to evolve as regulations change. Suppliers of raw materials and intermediates may need to adjust their offerings, potentially leading to price fluctuations and temporary supply disruptions. This could create opportunities for companies that can quickly adapt and provide compliant alternatives.
Investment patterns in the chemical industry may shift as companies reallocate resources towards research and development of safer alternatives or improved production technologies. This could lead to the emergence of new market leaders and potentially reshape the competitive landscape.
The regulatory changes may also impact international trade. Countries with stricter regulations may see changes in import/export patterns, potentially affecting their trade balance and domestic industry competitiveness. This could lead to the development of new trade agreements or adjustments to existing ones.
Labor markets in affected industries may experience shifts as companies adapt to new requirements. While some jobs may be at risk due to process changes or plant closures, new opportunities may arise in areas such as compliance management, environmental monitoring, and development of alternative technologies.
Overall, while the economic implications of isocyanate regulatory changes present challenges, they also offer opportunities for innovation, market differentiation, and long-term sustainability. Companies that proactively adapt to these changes may gain a competitive advantage in an evolving regulatory landscape.
Environmental and Health Considerations in Isocyanate Use
Isocyanates, widely used in various industrial applications, pose significant environmental and health risks that necessitate careful consideration and regulatory oversight. These compounds are known for their high reactivity and potential to cause severe respiratory issues, skin irritation, and other health problems upon exposure. The primary concern stems from their ability to form harmful vapors and aerosols during manufacturing processes and product use.
In the workplace, isocyanate exposure can lead to occupational asthma, a serious and potentially irreversible condition. Studies have shown that even low-level exposure over extended periods can sensitize workers, making them more susceptible to future reactions. This has prompted stringent occupational safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment, improved ventilation systems, and regular health monitoring for workers in industries utilizing isocyanates.
Environmental impacts of isocyanates are equally concerning. When released into the environment, these compounds can contaminate soil and water sources, potentially affecting ecosystems and wildlife. The degradation of isocyanates in the environment can lead to the formation of toxic byproducts, further complicating their environmental footprint. As a result, strict regulations govern the disposal and handling of isocyanate-containing materials to minimize environmental contamination.
The persistence of isocyanates in the environment varies depending on specific compounds and conditions. Some may break down relatively quickly, while others can persist for longer periods, potentially accumulating in environmental systems. This variability underscores the need for comprehensive environmental impact assessments and tailored regulatory approaches for different isocyanate compounds.
Recent research has focused on developing safer alternatives to traditional isocyanates, driven by both health and environmental concerns. These efforts include exploring bio-based isocyanates and alternative chemistries that can provide similar functional properties with reduced health and environmental risks. However, the widespread adoption of these alternatives faces challenges, including cost considerations and the need for extensive testing to ensure their long-term safety and efficacy.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have responded to these concerns by implementing increasingly stringent guidelines for isocyanate use, handling, and disposal. These regulations aim to protect workers, consumers, and the environment by setting exposure limits, mandating safety protocols, and requiring comprehensive risk assessments. The evolving regulatory landscape reflects a growing understanding of isocyanate risks and a commitment to balancing industrial needs with health and environmental protection.