Measure Solubility of Lithium Acetate in Different Solvents
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Acetate Solubility Research Background and Objectives
The solubility of lithium acetate in various solvents represents a critical area of research with significant implications across multiple industries. Historically, lithium compounds have gained prominence since the early 20th century, with accelerated interest following the development of lithium-ion batteries in the 1990s. The evolution of lithium acetate applications has expanded from traditional uses in ceramics and pharmaceuticals to advanced energy storage systems, catalysis, and organic synthesis processes.
Recent technological trends indicate a growing demand for precise solubility data of lithium salts, particularly lithium acetate, as industries seek to optimize formulations and processes. The fundamental understanding of lithium acetate's solvation behavior remains incomplete despite its widespread use, creating a knowledge gap that impedes innovation in several high-value applications.
This research aims to systematically investigate and quantify the solubility parameters of lithium acetate across a diverse range of solvents under varying temperature and pressure conditions. By establishing comprehensive solubility profiles, we intend to develop predictive models that can accelerate formulation development and process optimization in relevant industries.
The primary technical objectives include determining precise solubility values in polar protic solvents (water, alcohols, organic acids), polar aprotic solvents (acetone, DMF, DMSO), and non-polar solvents, while analyzing the influence of temperature gradients (0-100°C) on dissolution behavior. Additionally, we aim to characterize the thermodynamic properties governing the dissolution process through enthalpy and entropy measurements.
Secondary objectives encompass the investigation of co-solvent effects on lithium acetate solubility, identification of potential solvation mechanisms through spectroscopic analysis, and development of mathematical models to predict solubility in mixed solvent systems. These insights will enable more efficient extraction processes, battery electrolyte formulations, and pharmaceutical applications.
The technological trajectory suggests increasing importance of lithium compounds in energy transition technologies, with lithium acetate serving as both a direct component and a precursor in various applications. Understanding its fundamental solubility behavior represents a cornerstone for advancing multiple technological domains, including next-generation battery systems, green chemistry processes, and pharmaceutical formulations with enhanced bioavailability.
This research addresses the growing need for precise, reproducible solubility data that can support computational modeling approaches and accelerate materials development cycles across industries reliant on lithium chemistry.
Recent technological trends indicate a growing demand for precise solubility data of lithium salts, particularly lithium acetate, as industries seek to optimize formulations and processes. The fundamental understanding of lithium acetate's solvation behavior remains incomplete despite its widespread use, creating a knowledge gap that impedes innovation in several high-value applications.
This research aims to systematically investigate and quantify the solubility parameters of lithium acetate across a diverse range of solvents under varying temperature and pressure conditions. By establishing comprehensive solubility profiles, we intend to develop predictive models that can accelerate formulation development and process optimization in relevant industries.
The primary technical objectives include determining precise solubility values in polar protic solvents (water, alcohols, organic acids), polar aprotic solvents (acetone, DMF, DMSO), and non-polar solvents, while analyzing the influence of temperature gradients (0-100°C) on dissolution behavior. Additionally, we aim to characterize the thermodynamic properties governing the dissolution process through enthalpy and entropy measurements.
Secondary objectives encompass the investigation of co-solvent effects on lithium acetate solubility, identification of potential solvation mechanisms through spectroscopic analysis, and development of mathematical models to predict solubility in mixed solvent systems. These insights will enable more efficient extraction processes, battery electrolyte formulations, and pharmaceutical applications.
The technological trajectory suggests increasing importance of lithium compounds in energy transition technologies, with lithium acetate serving as both a direct component and a precursor in various applications. Understanding its fundamental solubility behavior represents a cornerstone for advancing multiple technological domains, including next-generation battery systems, green chemistry processes, and pharmaceutical formulations with enhanced bioavailability.
This research addresses the growing need for precise, reproducible solubility data that can support computational modeling approaches and accelerate materials development cycles across industries reliant on lithium chemistry.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Lithium Acetate Solutions
The global market for lithium acetate solutions has been experiencing significant growth, driven primarily by the expanding applications in pharmaceutical, industrial, and energy storage sectors. The pharmaceutical industry represents the largest market segment, where lithium acetate is utilized in the production of psychiatric medications, particularly for bipolar disorder treatment. This application alone accounts for a substantial portion of the market demand, with the global mental health pharmaceuticals market projected to grow at a steady rate of 6.4% annually through 2028.
In the industrial sector, lithium acetate solutions find extensive applications in ceramic and glass manufacturing processes, where they serve as fluxing agents that lower melting temperatures and improve product quality. The ceramic industry's growth, particularly in emerging economies of Asia-Pacific, has substantially increased demand for high-purity lithium acetate solutions. Market research indicates that this segment has grown by approximately 8% annually over the past five years.
The energy storage sector represents the fastest-growing application area for lithium acetate solutions. As an electrolyte component in certain types of batteries and energy storage systems, lithium acetate's solubility characteristics in various solvents directly impact battery performance and efficiency. With the global push toward renewable energy and electric vehicles, this application segment is expected to grow at double-digit rates in the coming decade.
Regional analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently dominate the pharmaceutical applications market for lithium acetate, while Asia-Pacific leads in industrial applications. China, Japan, and South Korea have emerged as key markets due to their robust electronics manufacturing sectors and growing battery production facilities.
Market demand is increasingly focused on high-purity lithium acetate solutions with precisely controlled solubility profiles in specific solvents. This trend is driven by the need for enhanced performance in advanced applications such as next-generation batteries and specialized pharmaceutical formulations. Manufacturers who can provide detailed solubility data across various solvent systems command premium pricing in the market.
Supply chain considerations have become critical following recent disruptions. The lithium supply chain remains concentrated, with over 70% of global lithium processing occurring in China. This concentration has prompted manufacturers in Europe and North America to seek diversification of supply sources and invest in research to optimize lithium acetate usage through improved solubility understanding and application efficiency.
In the industrial sector, lithium acetate solutions find extensive applications in ceramic and glass manufacturing processes, where they serve as fluxing agents that lower melting temperatures and improve product quality. The ceramic industry's growth, particularly in emerging economies of Asia-Pacific, has substantially increased demand for high-purity lithium acetate solutions. Market research indicates that this segment has grown by approximately 8% annually over the past five years.
The energy storage sector represents the fastest-growing application area for lithium acetate solutions. As an electrolyte component in certain types of batteries and energy storage systems, lithium acetate's solubility characteristics in various solvents directly impact battery performance and efficiency. With the global push toward renewable energy and electric vehicles, this application segment is expected to grow at double-digit rates in the coming decade.
Regional analysis reveals that North America and Europe currently dominate the pharmaceutical applications market for lithium acetate, while Asia-Pacific leads in industrial applications. China, Japan, and South Korea have emerged as key markets due to their robust electronics manufacturing sectors and growing battery production facilities.
Market demand is increasingly focused on high-purity lithium acetate solutions with precisely controlled solubility profiles in specific solvents. This trend is driven by the need for enhanced performance in advanced applications such as next-generation batteries and specialized pharmaceutical formulations. Manufacturers who can provide detailed solubility data across various solvent systems command premium pricing in the market.
Supply chain considerations have become critical following recent disruptions. The lithium supply chain remains concentrated, with over 70% of global lithium processing occurring in China. This concentration has prompted manufacturers in Europe and North America to seek diversification of supply sources and invest in research to optimize lithium acetate usage through improved solubility understanding and application efficiency.
Current Solubility Measurement Techniques and Challenges
The measurement of lithium acetate solubility in various solvents requires precise analytical techniques to ensure accurate and reproducible results. Currently, several established methods are employed across research and industrial settings, each with specific advantages and limitations that must be considered when selecting an appropriate approach.
Gravimetric analysis remains one of the most traditional and widely used techniques for solubility determination. This method involves dissolving excess solute in the solvent, allowing equilibration, filtering the solution, and then evaporating the solvent to determine the mass of dissolved solute. While conceptually simple, this technique faces challenges with volatile solvents and requires significant time for equilibration and evaporation processes.
Spectrophotometric methods offer higher sensitivity and are particularly valuable for systems where lithium acetate exhibits characteristic absorption patterns. UV-Vis spectroscopy can be employed when the salt or its complexes absorb in the ultraviolet or visible regions. However, this approach requires careful calibration and may be limited by interference from other solutes or the solvent itself.
Conductometric titration represents another valuable technique, leveraging the ionic nature of lithium acetate to measure changes in solution conductivity as the salt dissolves. This method provides real-time data but may be complicated by the presence of other electrolytes or temperature fluctuations that affect conductivity readings.
Advanced instrumental methods including atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) offer exceptional sensitivity for lithium detection, allowing precise quantification even at very low concentrations. These techniques, however, require sophisticated equipment and specialized training, making them less accessible for routine analyses.
A significant challenge across all methodologies is maintaining consistent temperature control during measurements, as solubility is highly temperature-dependent. Even minor temperature fluctuations can lead to substantial variations in solubility data, particularly for solvents with high thermal coefficients of solubility.
The physical properties of different solvents present additional complications. Viscous solvents may impede dissolution kinetics and filtration processes, while highly volatile solvents can introduce errors during sample preparation and analysis. Furthermore, the potential for lithium acetate to form solvates or undergo chemical reactions with certain solvents necessitates careful consideration of solvent-solute interactions.
Reproducibility remains a persistent challenge, with interlaboratory studies often revealing significant variations in reported solubility values. These discrepancies stem from differences in experimental protocols, equipment calibration, and data analysis methodologies, highlighting the need for standardized procedures in solubility measurements.
Gravimetric analysis remains one of the most traditional and widely used techniques for solubility determination. This method involves dissolving excess solute in the solvent, allowing equilibration, filtering the solution, and then evaporating the solvent to determine the mass of dissolved solute. While conceptually simple, this technique faces challenges with volatile solvents and requires significant time for equilibration and evaporation processes.
Spectrophotometric methods offer higher sensitivity and are particularly valuable for systems where lithium acetate exhibits characteristic absorption patterns. UV-Vis spectroscopy can be employed when the salt or its complexes absorb in the ultraviolet or visible regions. However, this approach requires careful calibration and may be limited by interference from other solutes or the solvent itself.
Conductometric titration represents another valuable technique, leveraging the ionic nature of lithium acetate to measure changes in solution conductivity as the salt dissolves. This method provides real-time data but may be complicated by the presence of other electrolytes or temperature fluctuations that affect conductivity readings.
Advanced instrumental methods including atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) offer exceptional sensitivity for lithium detection, allowing precise quantification even at very low concentrations. These techniques, however, require sophisticated equipment and specialized training, making them less accessible for routine analyses.
A significant challenge across all methodologies is maintaining consistent temperature control during measurements, as solubility is highly temperature-dependent. Even minor temperature fluctuations can lead to substantial variations in solubility data, particularly for solvents with high thermal coefficients of solubility.
The physical properties of different solvents present additional complications. Viscous solvents may impede dissolution kinetics and filtration processes, while highly volatile solvents can introduce errors during sample preparation and analysis. Furthermore, the potential for lithium acetate to form solvates or undergo chemical reactions with certain solvents necessitates careful consideration of solvent-solute interactions.
Reproducibility remains a persistent challenge, with interlaboratory studies often revealing significant variations in reported solubility values. These discrepancies stem from differences in experimental protocols, equipment calibration, and data analysis methodologies, highlighting the need for standardized procedures in solubility measurements.
Established Protocols for Solvent-Solute Interaction Studies
01 Solubility characteristics of lithium acetate in various solvents
Lithium acetate exhibits different solubility characteristics in various solvents. It is highly soluble in water, with solubility increasing significantly with temperature. It also shows moderate solubility in polar organic solvents such as methanol and ethanol, but limited solubility in non-polar organic solvents. The solubility properties of lithium acetate make it suitable for various applications including electrolyte solutions and chemical synthesis processes.- Solubility characteristics of lithium acetate in various solvents: Lithium acetate exhibits different solubility characteristics in various solvents. It is highly soluble in water and certain polar organic solvents, while showing limited solubility in non-polar solvents. The solubility is temperature-dependent, generally increasing with temperature. These properties make lithium acetate suitable for specific applications in chemical processes where controlled dissolution is required.
- Lithium acetate in battery electrolyte formulations: Lithium acetate is used in battery electrolyte formulations due to its solubility characteristics. When dissolved in appropriate solvents, it contributes to the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte solution. The solubility of lithium acetate affects the performance of lithium-ion batteries, including their capacity, cycle life, and safety. Controlling the solubility parameters is crucial for optimizing battery performance.
- Methods to enhance lithium acetate solubility: Various methods can be employed to enhance the solubility of lithium acetate, including the use of co-solvents, temperature adjustment, pH modification, and the addition of complexing agents. These techniques are particularly important in applications where higher concentrations of lithium acetate are required. Enhanced solubility can lead to improved process efficiency and product performance in various industrial applications.
- Lithium acetate solubility in industrial processes: The solubility properties of lithium acetate are leveraged in various industrial processes, including extraction, purification, and synthesis reactions. Understanding the solubility behavior is essential for process design and optimization. In industrial settings, lithium acetate's solubility characteristics influence process parameters such as reaction rates, yield, and product purity. Controlled solubility is particularly important in crystallization and separation processes.
- Impact of additives on lithium acetate solubility: Various additives can significantly impact the solubility of lithium acetate in solution. These additives include other salts, polymers, surfactants, and organic compounds. The presence of these additives can either enhance or reduce the solubility of lithium acetate depending on their chemical nature and concentration. Understanding these interactions is crucial for formulating stable solutions for specific applications in areas such as energy storage, materials processing, and pharmaceutical development.
02 Lithium acetate in battery electrolyte formulations
Lithium acetate is utilized in battery electrolyte formulations due to its solubility characteristics and ionic conductivity. When dissolved in appropriate solvents, it can enhance the performance of lithium-ion batteries by improving ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability. The solubility of lithium acetate in various organic carbonates and other electrolyte components allows for tailored formulations that optimize battery performance, safety, and cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions03 Methods to enhance lithium acetate solubility
Various methods can be employed to enhance the solubility of lithium acetate in different media. These include temperature modulation, pH adjustment, use of co-solvents, and addition of complexing agents. Ultrasonic treatment and mechanical agitation can also improve dissolution rates. These enhancement methods are particularly important in applications requiring high concentrations of lithium acetate or when working with solvent systems where lithium acetate has limited natural solubility.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium acetate solubility in polymer and composite systems
The solubility behavior of lithium acetate in polymer matrices and composite systems is critical for applications in solid electrolytes and functional materials. Lithium acetate can be incorporated into polymer systems through solution casting, melt processing, or in-situ polymerization methods. The degree of dissolution and dispersion affects ionic conductivity, mechanical properties, and overall performance of the resulting materials. Controlling the solubility parameters is essential for developing advanced materials for energy storage and other applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial applications leveraging lithium acetate solubility
The solubility properties of lithium acetate are leveraged in various industrial applications. These include use as a catalyst in organic synthesis, as a component in heat transfer fluids, in textile processing, and in pharmaceutical formulations. The controlled solubility of lithium acetate in different media enables precise dosing and application in manufacturing processes. Additionally, its solubility characteristics make it useful in extraction and separation technologies for lithium recovery from various sources.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Industrial Players
The lithium acetate solubility measurement market is in a growth phase, driven by expanding applications in pharmaceutical and battery industries. The global market for solubility testing solutions is projected to reach significant scale as lithium-based compounds gain importance in energy storage technologies. Leading pharmaceutical companies like Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Novartis are advancing solubility measurement techniques for drug development applications, while battery manufacturers including Samsung SDI, BYD, and LG Energy Solution are focusing on lithium compound solubility for improved battery performance. Chemical specialists such as Kanto Chemical and Merck Patent GmbH provide specialized solvents and analytical tools, creating a competitive ecosystem where academic institutions like Central South University and Nanjing University collaborate with industry to develop standardized measurement protocols.
Pfizer Inc.
Technical Solution: Pfizer has pioneered advanced methodologies for measuring lithium acetate solubility across diverse solvent systems, critical for pharmaceutical formulation development. Their approach integrates high-precision gravimetric analysis with dynamic light scattering (DLS) and UV-visible spectrophotometry to determine solubility parameters under varying temperature and pH conditions. Pfizer's proprietary "SolubilityPro" platform employs automated liquid handling systems that can simultaneously evaluate lithium acetate solubility in up to 96 different solvent compositions, including water-alcohol mixtures, polyethylene glycols, and specialized pharmaceutical excipients. The company utilizes isothermal equilibration periods (typically 24-72 hours) followed by filtration through 0.22μm membranes and quantification via inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for lithium content determination. This methodology achieves detection limits below 0.1 μg/mL, enabling precise characterization of solubility profiles even in complex multi-component solvent systems relevant to drug formulation.
Strengths: Exceptional precision and reproducibility with relative standard deviations typically below 2% across multiple measurements. Comprehensive solvent compatibility database spanning over 200 pharmaceutical-relevant solvents and excipient combinations. Weaknesses: Methods are primarily optimized for pharmaceutical applications rather than industrial or battery applications. High equipment costs and specialized training requirements limit accessibility of their complete methodology outside major pharmaceutical laboratories.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis has developed a sophisticated multi-tiered approach to measuring lithium acetate solubility across diverse solvent systems relevant to pharmaceutical applications. Their methodology combines traditional saturation shake-flask techniques with innovative microfluidic platforms that enable real-time solubility monitoring. The company's "SolTrack" system employs temperature-controlled crystallization cells coupled with in-situ Raman spectroscopy to detect the precise point of solute precipitation or dissolution, allowing determination of thermodynamic solubility parameters with minimal sample quantities (typically 1-5 mg). For complex solvent mixtures, Novartis utilizes a proprietary computational model that incorporates Hansen solubility parameters and molecular dynamics simulations to predict lithium acetate solvation behavior. Their analytical protocol includes rigorous pH control (using automated titration systems) and ionic strength adjustments to mimic physiological conditions relevant to drug delivery applications. The company has extensively characterized lithium acetate solubility in water-cosolvent systems including ethanol, propylene glycol, and PEG-400 mixtures across temperature ranges from 5°C to 60°C, generating comprehensive phase diagrams that inform formulation development.
Strengths: Exceptional precision with minimal sample requirements, making the approach suitable for high-value compounds. Integration of experimental and computational approaches enables rapid screening of novel solvent systems. Weaknesses: The sophisticated instrumentation required limits accessibility to well-equipped laboratories. The methodology is primarily optimized for pharmaceutical solvents rather than industrial applications requiring larger scales.
Key Scientific Principles Governing Lithium Salt Solubility
Electrolytes for lithium ion and lithium metal batteries
PatentPendingUS20240387874A1
Innovation
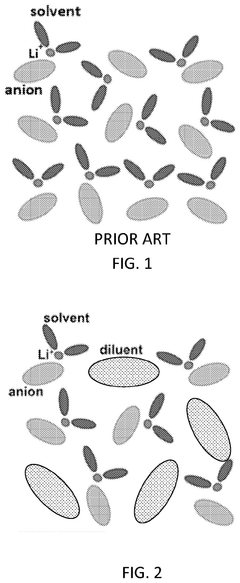
- Development of electrolytes comprising a lithium salt, a nonaqueous solvent with a flame retardant, and a diluent with a flash point greater than 90°C, where the lithium salt has reduced solubility in the diluent compared to the solvent, creating a localized high concentration electrolyte structure that enhances safety and stability.
Environmental Impact of Various Solvent Systems
The environmental impact of solvent systems used in lithium acetate solubility measurements represents a critical consideration for sustainable chemical processes. Different solvents exhibit varying degrees of environmental hazards, including toxicity, persistence in ecosystems, and greenhouse gas emissions during production and disposal. Water-based systems generally present the lowest environmental footprint, with minimal toxicity and biodegradability advantages, though energy requirements for subsequent separation processes must be factored into lifecycle assessments.
Organic solvents commonly used for lithium acetate dissolution, such as alcohols (methanol, ethanol), ketones (acetone), and ethers (tetrahydrofuran), present more significant environmental challenges. Methanol exhibits aquatic toxicity and potential groundwater contamination risks, while acetone's high volatility contributes to atmospheric VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions. These emissions can participate in photochemical reactions leading to ground-level ozone formation and associated respiratory health impacts.
Mixed solvent systems, while potentially offering enhanced solubility performance, often complicate waste treatment processes and increase environmental burden. The separation and recovery of multiple solvents typically requires additional energy inputs and may generate secondary waste streams. Recent regulatory frameworks, including REACH in Europe and similar initiatives globally, have increasingly restricted certain solvents based on environmental persistence and bioaccumulation potential.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing various solvent systems reveal that factors beyond direct toxicity—including energy requirements for production, purification, and recovery—significantly influence overall environmental impact. For instance, while acetonitrile provides excellent lithium acetate solubility characteristics, its production process involves substantial carbon emissions and hazardous intermediates. Green chemistry metrics such as E-factor (waste-to-product ratio) and process mass intensity (PMI) increasingly guide solvent selection decisions.
Emerging green alternatives for lithium acetate dissolution include bio-derived solvents such as 2-methyltetrahydrofuran and cyrene, which offer reduced environmental footprints through renewable feedstocks and improved biodegradability profiles. Supercritical CO₂ and ionic liquids represent additional sustainable options, though scale-up challenges and cost considerations have limited their widespread adoption in commercial applications.
Waste management protocols for different solvent systems vary considerably, with implications for environmental impact. Incineration of organic solvent waste generates carbon emissions and potential toxic byproducts, while distillation recovery processes consume significant energy. Water-based systems generally permit biological treatment options, though dissolved lithium compounds may require specialized removal techniques to prevent aquatic ecosystem disruption.
Organic solvents commonly used for lithium acetate dissolution, such as alcohols (methanol, ethanol), ketones (acetone), and ethers (tetrahydrofuran), present more significant environmental challenges. Methanol exhibits aquatic toxicity and potential groundwater contamination risks, while acetone's high volatility contributes to atmospheric VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions. These emissions can participate in photochemical reactions leading to ground-level ozone formation and associated respiratory health impacts.
Mixed solvent systems, while potentially offering enhanced solubility performance, often complicate waste treatment processes and increase environmental burden. The separation and recovery of multiple solvents typically requires additional energy inputs and may generate secondary waste streams. Recent regulatory frameworks, including REACH in Europe and similar initiatives globally, have increasingly restricted certain solvents based on environmental persistence and bioaccumulation potential.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing various solvent systems reveal that factors beyond direct toxicity—including energy requirements for production, purification, and recovery—significantly influence overall environmental impact. For instance, while acetonitrile provides excellent lithium acetate solubility characteristics, its production process involves substantial carbon emissions and hazardous intermediates. Green chemistry metrics such as E-factor (waste-to-product ratio) and process mass intensity (PMI) increasingly guide solvent selection decisions.
Emerging green alternatives for lithium acetate dissolution include bio-derived solvents such as 2-methyltetrahydrofuran and cyrene, which offer reduced environmental footprints through renewable feedstocks and improved biodegradability profiles. Supercritical CO₂ and ionic liquids represent additional sustainable options, though scale-up challenges and cost considerations have limited their widespread adoption in commercial applications.
Waste management protocols for different solvent systems vary considerably, with implications for environmental impact. Incineration of organic solvent waste generates carbon emissions and potential toxic byproducts, while distillation recovery processes consume significant energy. Water-based systems generally permit biological treatment options, though dissolved lithium compounds may require specialized removal techniques to prevent aquatic ecosystem disruption.
Computational Modeling for Solubility Prediction
Computational modeling has emerged as a powerful approach for predicting the solubility of compounds like lithium acetate in various solvents, offering significant advantages over traditional experimental methods. These computational techniques combine thermodynamic principles, quantum chemistry, and machine learning algorithms to provide accurate solubility predictions while reducing the time and resources required for extensive laboratory testing.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations represent one of the most established computational methods for solubility prediction. For lithium acetate, these simulations can model the interactions between Li+ and CH3COO- ions with different solvent molecules, accounting for factors such as hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions, and solvation shell formation. Recent advancements in force field parameters have significantly improved the accuracy of these simulations for ionic compounds in polar solvents.
Quantum mechanical calculations, particularly those based on density functional theory (DFT), provide another valuable approach for predicting lithium acetate solubility. These methods can accurately calculate solvation free energies by modeling electronic structures and interactions at the molecular level. The COSMO-RS (Conductor-like Screening Model for Real Solvents) method has shown particular promise for ionic compounds like lithium acetate, as it effectively accounts for the strong electrostatic interactions between ions and solvent molecules.
Machine learning algorithms have recently revolutionized solubility prediction by leveraging existing experimental data to develop predictive models. For lithium acetate, these models correlate solvent properties (dielectric constant, hydrogen bonding capacity, polarity) with observed solubility values to generate accurate predictions for untested solvents. Neural networks and gradient boosting algorithms have demonstrated exceptional predictive power in this domain, achieving correlation coefficients above 0.9 in recent studies.
Group contribution methods offer a more accessible computational approach, where solubility is estimated based on the structural fragments present in both the solute and solvent. While less accurate than quantum methods for ionic compounds, these techniques provide rapid estimations that can guide initial solvent selection for lithium acetate dissolution studies.
The integration of these computational approaches into a multi-scale modeling framework represents the current state-of-the-art for solubility prediction. By combining quantum calculations for accurate energetics with MD simulations for dynamic behavior and machine learning for pattern recognition, researchers can now predict lithium acetate solubility across diverse solvent systems with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations represent one of the most established computational methods for solubility prediction. For lithium acetate, these simulations can model the interactions between Li+ and CH3COO- ions with different solvent molecules, accounting for factors such as hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions, and solvation shell formation. Recent advancements in force field parameters have significantly improved the accuracy of these simulations for ionic compounds in polar solvents.
Quantum mechanical calculations, particularly those based on density functional theory (DFT), provide another valuable approach for predicting lithium acetate solubility. These methods can accurately calculate solvation free energies by modeling electronic structures and interactions at the molecular level. The COSMO-RS (Conductor-like Screening Model for Real Solvents) method has shown particular promise for ionic compounds like lithium acetate, as it effectively accounts for the strong electrostatic interactions between ions and solvent molecules.
Machine learning algorithms have recently revolutionized solubility prediction by leveraging existing experimental data to develop predictive models. For lithium acetate, these models correlate solvent properties (dielectric constant, hydrogen bonding capacity, polarity) with observed solubility values to generate accurate predictions for untested solvents. Neural networks and gradient boosting algorithms have demonstrated exceptional predictive power in this domain, achieving correlation coefficients above 0.9 in recent studies.
Group contribution methods offer a more accessible computational approach, where solubility is estimated based on the structural fragments present in both the solute and solvent. While less accurate than quantum methods for ionic compounds, these techniques provide rapid estimations that can guide initial solvent selection for lithium acetate dissolution studies.
The integration of these computational approaches into a multi-scale modeling framework represents the current state-of-the-art for solubility prediction. By combining quantum calculations for accurate energetics with MD simulations for dynamic behavior and machine learning for pattern recognition, researchers can now predict lithium acetate solubility across diverse solvent systems with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!