Microcrystalline Cellulose in Oral Care Products: Abrasive and Texturizing Effects
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MCC in Oral Care: Background and Objectives
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) has emerged as a versatile ingredient in oral care products, offering both abrasive and texturizing properties. The evolution of MCC in this field can be traced back to the mid-20th century when cellulose-based materials were first explored for dental applications. As dental hygiene practices advanced, the demand for effective yet gentle oral care products grew, prompting researchers to investigate novel ingredients.
The development of MCC technology has been driven by the need for multifunctional components in oral care formulations. Initially, the focus was primarily on its abrasive qualities, which aid in the removal of plaque and stains from teeth. However, as formulation science progressed, the texturizing capabilities of MCC became increasingly valuable, allowing for the creation of more appealing and stable product consistencies.
The technical objectives surrounding MCC in oral care products are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a continuous effort to optimize the balance between effective cleaning and minimal enamel wear. This involves fine-tuning the particle size, shape, and hardness of MCC to achieve optimal abrasiveness without causing damage to tooth surfaces or soft tissues in the mouth.
Another key objective is to enhance the texturizing effects of MCC to improve the overall sensory experience of oral care products. This includes achieving the desired viscosity, smoothness, and mouthfeel in toothpastes, gels, and other dental formulations. The goal is to create products that are not only effective but also pleasant to use, thereby encouraging regular oral hygiene practices.
Furthermore, researchers aim to expand the functionality of MCC in oral care applications. This includes exploring its potential as a carrier for active ingredients, its role in controlled release systems, and its ability to stabilize formulations. The development of modified MCC variants with enhanced properties is also an area of active research, seeking to tailor the material's characteristics to specific oral care needs.
As environmental concerns gain prominence, there is a growing focus on the sustainability aspects of MCC production and use in oral care products. Objectives in this area include developing more eco-friendly extraction and processing methods, as well as investigating the biodegradability and environmental impact of MCC-containing formulations.
The technological trajectory of MCC in oral care is closely aligned with broader trends in the industry, such as the shift towards natural and biocompatible materials, the demand for multifunctional ingredients, and the pursuit of personalized oral care solutions. As such, the ongoing research and development in this field aim to position MCC as a key component in the next generation of oral care products, meeting both consumer expectations and regulatory standards.
The development of MCC technology has been driven by the need for multifunctional components in oral care formulations. Initially, the focus was primarily on its abrasive qualities, which aid in the removal of plaque and stains from teeth. However, as formulation science progressed, the texturizing capabilities of MCC became increasingly valuable, allowing for the creation of more appealing and stable product consistencies.
The technical objectives surrounding MCC in oral care products are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a continuous effort to optimize the balance between effective cleaning and minimal enamel wear. This involves fine-tuning the particle size, shape, and hardness of MCC to achieve optimal abrasiveness without causing damage to tooth surfaces or soft tissues in the mouth.
Another key objective is to enhance the texturizing effects of MCC to improve the overall sensory experience of oral care products. This includes achieving the desired viscosity, smoothness, and mouthfeel in toothpastes, gels, and other dental formulations. The goal is to create products that are not only effective but also pleasant to use, thereby encouraging regular oral hygiene practices.
Furthermore, researchers aim to expand the functionality of MCC in oral care applications. This includes exploring its potential as a carrier for active ingredients, its role in controlled release systems, and its ability to stabilize formulations. The development of modified MCC variants with enhanced properties is also an area of active research, seeking to tailor the material's characteristics to specific oral care needs.
As environmental concerns gain prominence, there is a growing focus on the sustainability aspects of MCC production and use in oral care products. Objectives in this area include developing more eco-friendly extraction and processing methods, as well as investigating the biodegradability and environmental impact of MCC-containing formulations.
The technological trajectory of MCC in oral care is closely aligned with broader trends in the industry, such as the shift towards natural and biocompatible materials, the demand for multifunctional ingredients, and the pursuit of personalized oral care solutions. As such, the ongoing research and development in this field aim to position MCC as a key component in the next generation of oral care products, meeting both consumer expectations and regulatory standards.
Market Analysis: MCC in Oral Care Products
The global oral care market has been experiencing steady growth, with a significant portion attributed to the increasing adoption of advanced ingredients like Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC). The market for MCC in oral care products is projected to expand substantially over the next five years, driven by consumer demand for more effective and natural dental hygiene solutions.
MCC's unique properties as both an abrasive and texturizing agent have positioned it as a versatile ingredient in various oral care products. Toothpaste remains the primary application, where MCC serves as a gentle abrasive that effectively removes plaque and stains without damaging tooth enamel. The market for MCC in toothpaste formulations has seen robust growth, particularly in premium and natural product segments.
Mouthwashes and oral rinses represent another rapidly growing segment for MCC usage. As consumers seek alcohol-free alternatives, MCC's ability to provide texture and suspension properties without compromising efficacy has led to increased incorporation in these products. This trend is expected to continue, with MCC-containing mouthwashes gaining market share from traditional formulations.
The dental floss and interdental cleaning products sector has also begun to leverage MCC's properties. Manufacturers are exploring MCC-coated flosses that offer improved plaque removal and a smoother glide between teeth. While this application is still in its early stages, it shows promise for future market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the MCC oral care market, owing to higher consumer awareness and willingness to pay for premium oral care products. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years. This is attributed to rising disposable incomes, increasing oral health awareness, and the growing popularity of natural ingredients in personal care products across countries like China and India.
Consumer trends driving the MCC oral care market include a shift towards natural and sustainable products, increased focus on preventive dental care, and demand for multifunctional oral care solutions. These trends have led to the development of innovative products such as whitening toothpastes with MCC as a key ingredient, capitalizing on its gentle abrasive properties.
The competitive landscape of the MCC oral care market is characterized by a mix of established oral care giants and emerging natural product companies. Major players are investing in research and development to enhance MCC's functionality and explore new applications within oral care. This is expected to result in a wave of product innovations and further market expansion in the near future.
MCC's unique properties as both an abrasive and texturizing agent have positioned it as a versatile ingredient in various oral care products. Toothpaste remains the primary application, where MCC serves as a gentle abrasive that effectively removes plaque and stains without damaging tooth enamel. The market for MCC in toothpaste formulations has seen robust growth, particularly in premium and natural product segments.
Mouthwashes and oral rinses represent another rapidly growing segment for MCC usage. As consumers seek alcohol-free alternatives, MCC's ability to provide texture and suspension properties without compromising efficacy has led to increased incorporation in these products. This trend is expected to continue, with MCC-containing mouthwashes gaining market share from traditional formulations.
The dental floss and interdental cleaning products sector has also begun to leverage MCC's properties. Manufacturers are exploring MCC-coated flosses that offer improved plaque removal and a smoother glide between teeth. While this application is still in its early stages, it shows promise for future market expansion.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the MCC oral care market, owing to higher consumer awareness and willingness to pay for premium oral care products. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years. This is attributed to rising disposable incomes, increasing oral health awareness, and the growing popularity of natural ingredients in personal care products across countries like China and India.
Consumer trends driving the MCC oral care market include a shift towards natural and sustainable products, increased focus on preventive dental care, and demand for multifunctional oral care solutions. These trends have led to the development of innovative products such as whitening toothpastes with MCC as a key ingredient, capitalizing on its gentle abrasive properties.
The competitive landscape of the MCC oral care market is characterized by a mix of established oral care giants and emerging natural product companies. Major players are investing in research and development to enhance MCC's functionality and explore new applications within oral care. This is expected to result in a wave of product innovations and further market expansion in the near future.
Technical Challenges in MCC Application
The application of Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) in oral care products presents several technical challenges that researchers and manufacturers must address to optimize its performance as an abrasive and texturizing agent. One primary challenge is achieving the ideal particle size distribution for MCC. The abrasive efficiency and texture-enhancing properties of MCC are highly dependent on particle size, with smaller particles generally providing better cleaning action but potentially increasing the risk of enamel erosion.
Another significant challenge lies in maintaining the stability of MCC in oral care formulations. MCC particles have a tendency to agglomerate over time, which can lead to inconsistent product performance and reduced shelf life. This agglomeration can affect the product's texture, flow properties, and abrasive efficacy. Developing strategies to prevent or minimize particle agglomeration without compromising the overall formulation stability is crucial.
The interaction between MCC and other ingredients in oral care products poses additional challenges. MCC may compete with or interfere with active ingredients such as fluoride, potentially reducing their effectiveness. Ensuring compatibility and synergy between MCC and other components while maintaining the desired abrasive and texturizing effects requires careful formulation and extensive testing.
Controlling the hardness and abrasiveness of MCC particles is another technical hurdle. While effective cleaning is desired, excessive abrasiveness can lead to tooth enamel wear and gum irritation. Striking the right balance between cleaning efficacy and gentleness on oral tissues demands precise control over MCC properties and concentration in the formulation.
The moisture sensitivity of MCC presents challenges in maintaining product consistency across various environmental conditions. MCC can absorb moisture from the environment, potentially altering its physical properties and affecting the overall product performance. Developing moisture-resistant MCC or implementing effective packaging solutions to protect the product from humidity is essential.
Achieving uniform dispersion of MCC throughout the oral care product is critical for consistent performance. Inadequate dispersion can result in areas of high concentration, leading to localized abrasiveness or textural inconsistencies. Developing effective mixing and dispersion techniques that work across different product viscosities and formulations is an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, scaling up MCC production and maintaining consistent quality for large-scale manufacturing of oral care products presents significant technical challenges. Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in terms of particle size, morphology, and purity is crucial for product reliability and regulatory compliance. Developing robust quality control measures and potentially exploring continuous manufacturing processes for MCC production are areas requiring further research and development.
Another significant challenge lies in maintaining the stability of MCC in oral care formulations. MCC particles have a tendency to agglomerate over time, which can lead to inconsistent product performance and reduced shelf life. This agglomeration can affect the product's texture, flow properties, and abrasive efficacy. Developing strategies to prevent or minimize particle agglomeration without compromising the overall formulation stability is crucial.
The interaction between MCC and other ingredients in oral care products poses additional challenges. MCC may compete with or interfere with active ingredients such as fluoride, potentially reducing their effectiveness. Ensuring compatibility and synergy between MCC and other components while maintaining the desired abrasive and texturizing effects requires careful formulation and extensive testing.
Controlling the hardness and abrasiveness of MCC particles is another technical hurdle. While effective cleaning is desired, excessive abrasiveness can lead to tooth enamel wear and gum irritation. Striking the right balance between cleaning efficacy and gentleness on oral tissues demands precise control over MCC properties and concentration in the formulation.
The moisture sensitivity of MCC presents challenges in maintaining product consistency across various environmental conditions. MCC can absorb moisture from the environment, potentially altering its physical properties and affecting the overall product performance. Developing moisture-resistant MCC or implementing effective packaging solutions to protect the product from humidity is essential.
Achieving uniform dispersion of MCC throughout the oral care product is critical for consistent performance. Inadequate dispersion can result in areas of high concentration, leading to localized abrasiveness or textural inconsistencies. Developing effective mixing and dispersion techniques that work across different product viscosities and formulations is an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, scaling up MCC production and maintaining consistent quality for large-scale manufacturing of oral care products presents significant technical challenges. Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in terms of particle size, morphology, and purity is crucial for product reliability and regulatory compliance. Developing robust quality control measures and potentially exploring continuous manufacturing processes for MCC production are areas requiring further research and development.
Current MCC Formulations in Oral Care
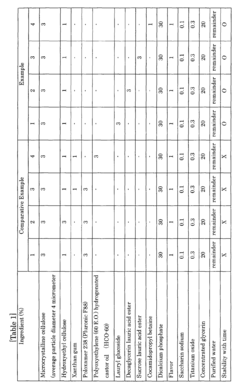
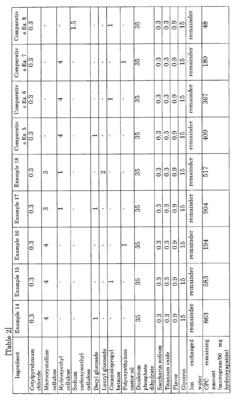
01 Abrasive properties of microcrystalline cellulose
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) exhibits abrasive properties, making it suitable for use in various applications such as toothpaste, cosmetics, and cleaning products. Its fine particle size and hardness contribute to its effectiveness as a mild abrasive agent, capable of removing surface debris and providing gentle exfoliation without causing excessive damage to the underlying substrate.- Abrasive properties of microcrystalline cellulose: Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) exhibits abrasive properties, making it suitable for use in various applications such as toothpaste, cosmetics, and cleaning products. Its fine particle size and hardness contribute to its effectiveness as a mild abrasive agent, capable of removing surface debris and providing gentle exfoliation without causing excessive damage to the underlying substrate.
- Texturizing effects in food and pharmaceutical products: Microcrystalline cellulose is widely used as a texturizing agent in food and pharmaceutical formulations. It can improve the texture, mouthfeel, and stability of various products, including creams, gels, and tablets. MCC's ability to form stable suspensions and its thixotropic properties contribute to its effectiveness in enhancing product consistency and overall sensory experience.
- Surface modification and functionalization of MCC: Microcrystalline cellulose can be modified or functionalized to enhance its properties for specific applications. Surface treatments can alter its hydrophobicity, improve its dispersibility, or introduce new functional groups. These modifications can lead to improved performance in areas such as drug delivery, composite materials, and advanced coatings.
- MCC in personal care and cosmetic formulations: Microcrystalline cellulose is utilized in various personal care and cosmetic products for its multifunctional properties. It can serve as a gentle abrasive, texturizer, and stabilizer in formulations such as scrubs, lotions, and makeup. MCC's natural origin and biocompatibility make it an attractive ingredient for consumers seeking eco-friendly and skin-friendly products.
- MCC in paper and packaging applications: Microcrystalline cellulose finds applications in the paper and packaging industry, where it can enhance the strength, texture, and printability of paper products. It can be used as a coating additive or filler to improve surface properties and overall product performance. MCC's renewable nature aligns with the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions.
02 Texturizing effects in food and pharmaceutical products
Microcrystalline cellulose is widely used as a texturizing agent in food and pharmaceutical products. It can improve the texture, mouthfeel, and stability of various formulations. MCC's ability to form stable suspensions and its thixotropic properties make it valuable for enhancing the consistency and sensory attributes of products such as sauces, dressings, and oral suspensions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface modification and functionalization of MCC
Microcrystalline cellulose can be modified or functionalized to enhance its properties for specific applications. Surface treatments or chemical modifications can alter its hydrophobicity, improve its dispersibility, or introduce new functional groups. These modifications can expand the range of applications for MCC in areas such as composite materials, drug delivery systems, and advanced coatings.Expand Specific Solutions04 MCC in personal care and cosmetic formulations
Microcrystalline cellulose is utilized in personal care and cosmetic products for its multifunctional properties. It can serve as a gentle abrasive, texturizing agent, and stabilizer in formulations such as scrubs, lotions, and creams. MCC's natural origin and skin-friendly characteristics make it an attractive ingredient for products aimed at providing both functional and sensory benefits.Expand Specific Solutions05 MCC in paper and packaging applications
Microcrystalline cellulose finds applications in the paper and packaging industry. It can be used to improve the strength, smoothness, and printability of paper products. In packaging materials, MCC can enhance barrier properties and provide texturizing effects. Its biodegradability and renewable nature make it an environmentally friendly option for various paper-based products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in MCC Oral Care Market
The microcrystalline cellulose market in oral care products is in a growth phase, driven by increasing consumer demand for natural and effective oral hygiene solutions. The global market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 7.2% from 2021 to 2028. Technologically, the use of microcrystalline cellulose as an abrasive and texturizing agent is well-established, with ongoing research focused on optimizing its performance and sustainability. Key players like Colgate-Palmolive, Unilever, and J.M. Huber Corporation are investing in R&D to enhance product formulations and manufacturing processes. Regional companies such as LG H&H and Nice Group are also contributing to market growth and innovation, particularly in Asian markets.
Colgate-Palmolive Co.
Technical Solution: Colgate-Palmolive has developed advanced formulations incorporating microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) in their oral care products. Their approach focuses on optimizing the particle size and concentration of MCC to achieve a balance between effective cleaning and gentle abrasion. The company has implemented a proprietary processing technique that enhances the dispersion of MCC particles in toothpaste formulations, resulting in improved texture and mouthfeel[1]. Additionally, Colgate-Palmolive has conducted extensive research on the synergistic effects of MCC with other abrasive agents, such as silica, to create multi-functional oral care products that offer both cleaning and polishing benefits[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global market presence, and established brand recognition. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs due to specialized processing techniques.
FMC Corp.
Technical Solution: FMC Corporation has pioneered the development of highly refined microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) specifically tailored for oral care applications. Their technology focuses on producing MCC with controlled particle size distribution and surface characteristics to optimize abrasive performance while minimizing enamel wear. FMC's MCC products for oral care are designed to provide effective plaque removal and stain reduction without compromising tooth enamel integrity[2]. The company has also developed innovative co-processing techniques that combine MCC with other ingredients to create multifunctional excipients that enhance both the abrasive and texturizing properties of oral care formulations[4].
Strengths: Specialized expertise in cellulose-based materials, strong intellectual property portfolio. Weaknesses: Limited direct consumer brand recognition in the oral care market.
Key Patents and Literature on MCC in Oral Care
Compositions for oral cavity
PatentInactiveEP1532971A1
Innovation
- Incorporating microcrystalline cellulose and specific surface active agents like alkyl glucoside, polyglycerin fatty acid ester, and betaine to enhance shape-holding and dispersibility, while using cationic antimicrobial agents like quaternary ammonium salts to improve residence on the tooth surface and prevent oral diseases.
High water content oral compositions comprising microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose
PatentActiveZA201601554A
Innovation
- Combining microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose in high water content oral compositions to maintain stability and texture.
- Incorporating silica abrasive with the cellulose components to create a balanced oral care formulation with both cleaning and texturizing properties.
- Developing high water content dentifrice compositions that can effectively deliver oral care benefits while maintaining desired consistency.
Regulatory Framework for MCC in Oral Care
The regulatory framework for microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) in oral care products is a complex and evolving landscape that encompasses various international and national standards. At the global level, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines for the safe use of food additives, which include MCC. These guidelines often serve as a reference point for national regulatory bodies when establishing their own standards for oral care products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates MCC under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. MCC is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food and pharmaceutical applications, including oral care products. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the use of MCC in toothpaste and other oral care formulations, focusing on purity standards, particle size, and maximum allowable concentrations.
The European Union (EU) regulates MCC through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 provides the framework for the use of MCC in oral care products within the EU market. This regulation emphasizes safety assessments, labeling requirements, and restrictions on certain substances in cosmetic products, including those used for oral care.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare oversees the regulation of MCC in oral care products. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia and the Standards for Cosmetics set forth specific requirements for the use of MCC in these applications, including purity standards and permitted concentrations.
Many other countries have their own regulatory frameworks for MCC in oral care products, often drawing from international standards while adapting them to local requirements. For instance, China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has established guidelines for the use of MCC in oral care products, focusing on safety and efficacy.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the particle size of MCC used in oral care products, due to concerns about potential abrasiveness. As a result, manufacturers must adhere to strict specifications regarding the physical properties of MCC to ensure product safety and efficacy.
The regulatory landscape for MCC in oral care products is subject to ongoing review and updates as new scientific evidence emerges. Manufacturers and formulators must stay abreast of these changes to ensure compliance across different markets and to maintain consumer trust in their products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates MCC under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. MCC is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food and pharmaceutical applications, including oral care products. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the use of MCC in toothpaste and other oral care formulations, focusing on purity standards, particle size, and maximum allowable concentrations.
The European Union (EU) regulates MCC through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 provides the framework for the use of MCC in oral care products within the EU market. This regulation emphasizes safety assessments, labeling requirements, and restrictions on certain substances in cosmetic products, including those used for oral care.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare oversees the regulation of MCC in oral care products. The Japanese Pharmacopoeia and the Standards for Cosmetics set forth specific requirements for the use of MCC in these applications, including purity standards and permitted concentrations.
Many other countries have their own regulatory frameworks for MCC in oral care products, often drawing from international standards while adapting them to local requirements. For instance, China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has established guidelines for the use of MCC in oral care products, focusing on safety and efficacy.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the particle size of MCC used in oral care products, due to concerns about potential abrasiveness. As a result, manufacturers must adhere to strict specifications regarding the physical properties of MCC to ensure product safety and efficacy.
The regulatory landscape for MCC in oral care products is subject to ongoing review and updates as new scientific evidence emerges. Manufacturers and formulators must stay abreast of these changes to ensure compliance across different markets and to maintain consumer trust in their products.
Environmental Impact of MCC in Oral Care
The environmental impact of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) in oral care products is an important consideration as the industry moves towards more sustainable practices. MCC, derived from natural cellulose sources, is generally considered a biodegradable and eco-friendly ingredient. However, its widespread use in oral care products necessitates a closer examination of its environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental benefits of MCC is its renewable nature. As a plant-based material, it can be sourced from sustainable forestry practices, reducing the reliance on non-renewable resources. This aligns with the growing consumer demand for natural and environmentally responsible products in the oral care sector.
The production process of MCC involves the hydrolysis of cellulose, which can be energy-intensive. However, advancements in manufacturing technologies have led to more efficient production methods, reducing the overall energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Some manufacturers have implemented closed-loop systems to minimize waste and recycle water and chemicals used in the production process.
In terms of disposal, MCC's biodegradability offers an advantage over synthetic alternatives. When oral care products containing MCC are disposed of, they are less likely to persist in the environment or contribute to microplastic pollution, a growing concern in aquatic ecosystems. This biodegradability also reduces the burden on waste management systems and landfills.
However, the environmental impact of MCC is not entirely benign. The sourcing of cellulose, if not managed responsibly, can contribute to deforestation and habitat loss. This underscores the importance of sustainable sourcing practices and third-party certifications to ensure that the raw materials are obtained from well-managed forests.
Water usage in MCC production is another environmental consideration. The manufacturing process requires significant amounts of water, which can strain local water resources if not managed properly. Industry leaders are investing in water-efficient technologies and water recycling systems to mitigate this impact.
The use of MCC in oral care products may also have indirect environmental benefits. Its effectiveness as an abrasive and texturizing agent can reduce the need for synthetic alternatives, which often have a higher environmental impact. Additionally, the multifunctional nature of MCC can potentially simplify product formulations, reducing the overall number of ingredients and, consequently, the environmental footprint of the final product.
As the oral care industry continues to evolve, there is ongoing research into further improving the environmental profile of MCC. This includes exploring alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste, to reduce pressure on forest resources. Additionally, innovations in green chemistry are being applied to MCC production to minimize the use of harsh chemicals and further reduce environmental impacts.
One of the primary environmental benefits of MCC is its renewable nature. As a plant-based material, it can be sourced from sustainable forestry practices, reducing the reliance on non-renewable resources. This aligns with the growing consumer demand for natural and environmentally responsible products in the oral care sector.
The production process of MCC involves the hydrolysis of cellulose, which can be energy-intensive. However, advancements in manufacturing technologies have led to more efficient production methods, reducing the overall energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Some manufacturers have implemented closed-loop systems to minimize waste and recycle water and chemicals used in the production process.
In terms of disposal, MCC's biodegradability offers an advantage over synthetic alternatives. When oral care products containing MCC are disposed of, they are less likely to persist in the environment or contribute to microplastic pollution, a growing concern in aquatic ecosystems. This biodegradability also reduces the burden on waste management systems and landfills.
However, the environmental impact of MCC is not entirely benign. The sourcing of cellulose, if not managed responsibly, can contribute to deforestation and habitat loss. This underscores the importance of sustainable sourcing practices and third-party certifications to ensure that the raw materials are obtained from well-managed forests.
Water usage in MCC production is another environmental consideration. The manufacturing process requires significant amounts of water, which can strain local water resources if not managed properly. Industry leaders are investing in water-efficient technologies and water recycling systems to mitigate this impact.
The use of MCC in oral care products may also have indirect environmental benefits. Its effectiveness as an abrasive and texturizing agent can reduce the need for synthetic alternatives, which often have a higher environmental impact. Additionally, the multifunctional nature of MCC can potentially simplify product formulations, reducing the overall number of ingredients and, consequently, the environmental footprint of the final product.
As the oral care industry continues to evolve, there is ongoing research into further improving the environmental profile of MCC. This includes exploring alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste, to reduce pressure on forest resources. Additionally, innovations in green chemistry are being applied to MCC production to minimize the use of harsh chemicals and further reduce environmental impacts.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!