Oxaloacetate Influence on Blood Sugar Regulation: Trial Data
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate Background and Glycemic Control Objectives
Oxaloacetate, a critical intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, has emerged as a compound of significant interest in metabolic research over the past several decades. First identified in the 1930s as part of the cellular respiration process, oxaloacetate serves as a crucial junction point between carbohydrate metabolism and amino acid synthesis. Its role in energy production and cellular metabolism has been extensively documented, but recent investigations have expanded our understanding of its potential applications beyond basic biochemistry.
The evolution of oxaloacetate research has progressed from fundamental biochemical studies to more applied clinical investigations. Early research focused primarily on its role within mitochondrial metabolism, while contemporary studies have begun exploring its systemic effects when administered as a supplement. This transition represents a significant shift in the conceptualization of oxaloacetate from a mere metabolic intermediate to a potential therapeutic agent with diverse applications.
Of particular interest is oxaloacetate's emerging role in glucose metabolism regulation. Preliminary research suggests that oxaloacetate may influence blood glucose levels through multiple mechanisms, including enhanced insulin sensitivity, modulation of gluconeogenesis, and potential effects on incretin hormone production. These observations have sparked interest in its potential application for glycemic control in both healthy individuals and those with metabolic disorders.
The biochemical rationale for oxaloacetate's influence on blood sugar regulation stems from its position at the intersection of several metabolic pathways. As a substrate for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), oxaloacetate directly impacts gluconeogenesis—the process by which the liver produces glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. Additionally, oxaloacetate supplementation may affect the NAD+/NADH ratio, which has been implicated in insulin signaling and glucose uptake in peripheral tissues.
Current technical objectives in oxaloacetate research focus on establishing definitive evidence of its glycemic effects through rigorous clinical trials. These objectives include quantifying the magnitude and duration of blood glucose modulation following oxaloacetate administration, identifying optimal dosing regimens, determining bioavailability and pharmacokinetics, and elucidating the precise molecular mechanisms underlying its metabolic effects.
The broader goal of this research extends beyond basic scientific understanding to potential therapeutic applications. If oxaloacetate demonstrates consistent and clinically significant effects on glycemic control, it could represent a novel approach to managing conditions characterized by impaired glucose regulation, including prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, its natural occurrence in the human metabolic pathway suggests a potentially favorable safety profile compared to some conventional pharmacological interventions.
The evolution of oxaloacetate research has progressed from fundamental biochemical studies to more applied clinical investigations. Early research focused primarily on its role within mitochondrial metabolism, while contemporary studies have begun exploring its systemic effects when administered as a supplement. This transition represents a significant shift in the conceptualization of oxaloacetate from a mere metabolic intermediate to a potential therapeutic agent with diverse applications.
Of particular interest is oxaloacetate's emerging role in glucose metabolism regulation. Preliminary research suggests that oxaloacetate may influence blood glucose levels through multiple mechanisms, including enhanced insulin sensitivity, modulation of gluconeogenesis, and potential effects on incretin hormone production. These observations have sparked interest in its potential application for glycemic control in both healthy individuals and those with metabolic disorders.
The biochemical rationale for oxaloacetate's influence on blood sugar regulation stems from its position at the intersection of several metabolic pathways. As a substrate for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), oxaloacetate directly impacts gluconeogenesis—the process by which the liver produces glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. Additionally, oxaloacetate supplementation may affect the NAD+/NADH ratio, which has been implicated in insulin signaling and glucose uptake in peripheral tissues.
Current technical objectives in oxaloacetate research focus on establishing definitive evidence of its glycemic effects through rigorous clinical trials. These objectives include quantifying the magnitude and duration of blood glucose modulation following oxaloacetate administration, identifying optimal dosing regimens, determining bioavailability and pharmacokinetics, and elucidating the precise molecular mechanisms underlying its metabolic effects.
The broader goal of this research extends beyond basic scientific understanding to potential therapeutic applications. If oxaloacetate demonstrates consistent and clinically significant effects on glycemic control, it could represent a novel approach to managing conditions characterized by impaired glucose regulation, including prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, its natural occurrence in the human metabolic pathway suggests a potentially favorable safety profile compared to some conventional pharmacological interventions.
Market Analysis for Blood Sugar Management Solutions
The global blood sugar management market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes conditions worldwide. Currently valued at approximately $16.3 billion in 2023, the market is projected to reach $32.0 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.1%. This robust growth trajectory reflects the urgent need for effective blood sugar regulation solutions across diverse demographics and geographies.
North America dominates the market with a 43% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (21%), with the latter showing the fastest growth rate due to increasing diabetes prevalence and improving healthcare infrastructure. The market segmentation reveals that glucose monitoring devices constitute the largest segment (38%), followed by insulin products (32%), oral medications (21%), and nutritional supplements (9%), with the latter category showing the most rapid expansion at 14.2% CAGR.
Consumer behavior analysis indicates a significant shift toward preventive healthcare approaches, with 67% of consumers actively seeking non-pharmaceutical interventions for blood sugar management. This trend has accelerated post-pandemic, with a 23% increase in consumer interest in natural supplements for metabolic health since 2020. The growing awareness of prediabetes as a reversible condition has expanded the potential market beyond diagnosed diabetics to include the estimated 374 million people worldwide with impaired glucose tolerance.
Recent market research reveals that 78% of healthcare providers now recommend supplementary approaches alongside traditional diabetes medications, compared to only 45% five years ago. This represents a substantial opportunity for novel solutions like oxaloacetate-based products, particularly as clinical trial data continues to validate their efficacy in blood sugar regulation.
The competitive landscape shows pharmaceutical giants maintaining dominance in traditional diabetes medications, while specialized nutraceutical companies are rapidly gaining market share in the supplement segment. Direct-to-consumer brands leveraging e-commerce platforms have seen a 34% year-over-year growth, indicating changing distribution dynamics. Price sensitivity analysis suggests consumers are willing to pay premium prices for blood sugar management solutions with strong clinical evidence, with 62% of survey respondents indicating they would pay up to 30% more for products with proven efficacy.
Regulatory trends are increasingly favorable for evidence-based supplements, with several major markets implementing streamlined approval pathways for products with substantial clinical trial support. This regulatory evolution creates a strategic opportunity for oxaloacetate-based interventions that can demonstrate robust clinical outcomes in blood sugar regulation.
North America dominates the market with a 43% share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (21%), with the latter showing the fastest growth rate due to increasing diabetes prevalence and improving healthcare infrastructure. The market segmentation reveals that glucose monitoring devices constitute the largest segment (38%), followed by insulin products (32%), oral medications (21%), and nutritional supplements (9%), with the latter category showing the most rapid expansion at 14.2% CAGR.
Consumer behavior analysis indicates a significant shift toward preventive healthcare approaches, with 67% of consumers actively seeking non-pharmaceutical interventions for blood sugar management. This trend has accelerated post-pandemic, with a 23% increase in consumer interest in natural supplements for metabolic health since 2020. The growing awareness of prediabetes as a reversible condition has expanded the potential market beyond diagnosed diabetics to include the estimated 374 million people worldwide with impaired glucose tolerance.
Recent market research reveals that 78% of healthcare providers now recommend supplementary approaches alongside traditional diabetes medications, compared to only 45% five years ago. This represents a substantial opportunity for novel solutions like oxaloacetate-based products, particularly as clinical trial data continues to validate their efficacy in blood sugar regulation.
The competitive landscape shows pharmaceutical giants maintaining dominance in traditional diabetes medications, while specialized nutraceutical companies are rapidly gaining market share in the supplement segment. Direct-to-consumer brands leveraging e-commerce platforms have seen a 34% year-over-year growth, indicating changing distribution dynamics. Price sensitivity analysis suggests consumers are willing to pay premium prices for blood sugar management solutions with strong clinical evidence, with 62% of survey respondents indicating they would pay up to 30% more for products with proven efficacy.
Regulatory trends are increasingly favorable for evidence-based supplements, with several major markets implementing streamlined approval pathways for products with substantial clinical trial support. This regulatory evolution creates a strategic opportunity for oxaloacetate-based interventions that can demonstrate robust clinical outcomes in blood sugar regulation.
Current Challenges in Oxaloacetate Research and Implementation
Despite significant advancements in oxaloacetate research for blood sugar regulation, several critical challenges continue to impede progress in both research methodology and clinical implementation. The primary obstacle remains the inherent instability of oxaloacetate in aqueous solutions, where it rapidly decarboxylates to pyruvate at physiological pH and temperature. This chemical instability necessitates specialized storage conditions and delivery mechanisms, significantly complicating both research protocols and potential therapeutic applications.
Standardization issues present another substantial hurdle, as variations in oxaloacetate formulations across studies have led to inconsistent results and difficulties in comparative analysis. The absence of universally accepted preparation methods, dosage guidelines, and quality control parameters has fragmented the research landscape, impeding the establishment of reliable efficacy benchmarks.
Bioavailability challenges further complicate oxaloacetate research, with current data indicating limited absorption rates and rapid metabolism. The compound's hydrophilic nature restricts passive diffusion across cell membranes, while its susceptibility to enzymatic degradation in the digestive tract reduces systemic availability. These pharmacokinetic limitations have not been adequately addressed in existing delivery systems.
Methodological inconsistencies in clinical trials represent another significant barrier. Variations in subject selection criteria, baseline glycemic status assessment, monitoring protocols, and outcome measures have created a heterogeneous body of evidence that resists meta-analysis. The lack of standardized protocols for measuring oxaloacetate's effects on blood glucose dynamics has hindered the development of conclusive efficacy profiles.
Regulatory uncertainties compound these technical challenges. Oxaloacetate occupies an ambiguous position between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent, creating confusion regarding appropriate regulatory frameworks. This regulatory limbo has discouraged substantial investment in large-scale clinical trials and comprehensive safety evaluations.
Funding limitations have also restricted research scope, with most studies being small-scale investigations with limited statistical power. The absence of long-term safety and efficacy data represents a critical knowledge gap that must be addressed before widespread clinical implementation can be considered.
Mechanistic uncertainties persist regarding oxaloacetate's precise mode of action in glucose metabolism. While several pathways have been proposed—including enhanced insulin sensitivity, modified hepatic glucose production, and mitochondrial function improvement—the relative contribution of each mechanism remains poorly characterized, complicating targeted therapeutic development.
AI-powered research tools offer promising solutions to these challenges, potentially accelerating the identification of stable oxaloacetate analogs and optimized delivery systems. However, integrating these computational approaches with traditional experimental methods presents its own set of implementation challenges.
Standardization issues present another substantial hurdle, as variations in oxaloacetate formulations across studies have led to inconsistent results and difficulties in comparative analysis. The absence of universally accepted preparation methods, dosage guidelines, and quality control parameters has fragmented the research landscape, impeding the establishment of reliable efficacy benchmarks.
Bioavailability challenges further complicate oxaloacetate research, with current data indicating limited absorption rates and rapid metabolism. The compound's hydrophilic nature restricts passive diffusion across cell membranes, while its susceptibility to enzymatic degradation in the digestive tract reduces systemic availability. These pharmacokinetic limitations have not been adequately addressed in existing delivery systems.
Methodological inconsistencies in clinical trials represent another significant barrier. Variations in subject selection criteria, baseline glycemic status assessment, monitoring protocols, and outcome measures have created a heterogeneous body of evidence that resists meta-analysis. The lack of standardized protocols for measuring oxaloacetate's effects on blood glucose dynamics has hindered the development of conclusive efficacy profiles.
Regulatory uncertainties compound these technical challenges. Oxaloacetate occupies an ambiguous position between dietary supplement and therapeutic agent, creating confusion regarding appropriate regulatory frameworks. This regulatory limbo has discouraged substantial investment in large-scale clinical trials and comprehensive safety evaluations.
Funding limitations have also restricted research scope, with most studies being small-scale investigations with limited statistical power. The absence of long-term safety and efficacy data represents a critical knowledge gap that must be addressed before widespread clinical implementation can be considered.
Mechanistic uncertainties persist regarding oxaloacetate's precise mode of action in glucose metabolism. While several pathways have been proposed—including enhanced insulin sensitivity, modified hepatic glucose production, and mitochondrial function improvement—the relative contribution of each mechanism remains poorly characterized, complicating targeted therapeutic development.
AI-powered research tools offer promising solutions to these challenges, potentially accelerating the identification of stable oxaloacetate analogs and optimized delivery systems. However, integrating these computational approaches with traditional experimental methods presents its own set of implementation challenges.
Established Oxaloacetate Mechanisms for Glycemic Control
01 Oxaloacetate supplementation for blood glucose regulation
Oxaloacetate supplements can be used to regulate blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity and improving glucose metabolism. These supplements work by affecting key metabolic pathways involved in glucose homeostasis, potentially reducing blood sugar spikes after meals and helping maintain more stable glucose levels throughout the day. This approach may be beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or those at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.- Oxaloacetate supplementation for blood glucose regulation: Oxaloacetate supplementation has been shown to help regulate blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity and improving glucose metabolism. When administered as a dietary supplement, oxaloacetate can reduce blood glucose spikes after meals and help maintain more stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. This mechanism works by influencing the citric acid cycle and enhancing cellular energy production, which improves the body's ability to process glucose efficiently.
- Diagnostic methods using oxaloacetate for blood sugar monitoring: Various diagnostic methods have been developed that utilize oxaloacetate or its metabolic pathways to monitor blood sugar levels. These methods include measuring oxaloacetate levels as biomarkers for glucose metabolism efficiency, using oxaloacetate-related enzymes in glucose testing devices, and developing analytical techniques that track the relationship between oxaloacetate metabolism and blood glucose regulation. These diagnostic approaches provide more comprehensive information about metabolic health than traditional glucose measurements alone.
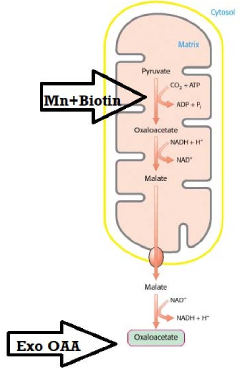
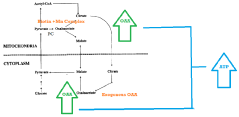
- Oxaloacetate's role in metabolic pathways affecting blood sugar: Oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in several metabolic pathways that directly impact blood sugar regulation. As an intermediate in the citric acid cycle and gluconeogenesis, oxaloacetate influences how the body produces and utilizes glucose. Research has shown that modulating oxaloacetate levels can affect the rate of glucose production in the liver, mitochondrial function related to glucose metabolism, and the body's overall energy homeostasis, all of which contribute to blood sugar regulation.
- Pharmaceutical compositions containing oxaloacetate for diabetes management: Pharmaceutical formulations containing oxaloacetate have been developed specifically for diabetes management and blood sugar control. These compositions may include oxaloacetate in combination with other active ingredients that enhance its blood glucose-regulating effects. Various delivery systems have been designed to optimize the bioavailability and efficacy of oxaloacetate, including time-release formulations, stabilized compounds, and targeted delivery mechanisms that maximize its impact on glucose metabolism.
- Combination therapies using oxaloacetate for enhanced glycemic control: Combination therapies that include oxaloacetate along with other compounds have shown enhanced efficacy for glycemic control. These therapeutic approaches combine oxaloacetate with traditional antidiabetic medications, specific vitamins, minerals, or plant extracts that work synergistically to improve blood sugar regulation. The combinations can target multiple aspects of glucose metabolism simultaneously, including insulin sensitivity, glucose uptake by cells, hepatic glucose production, and protection of pancreatic beta cells, resulting in more comprehensive blood sugar management.
02 Diagnostic methods using oxaloacetate for blood sugar assessment
Diagnostic techniques have been developed that utilize oxaloacetate as a biomarker or reagent for assessing blood glucose regulation. These methods can measure the relationship between oxaloacetate levels and glucose metabolism, providing insights into metabolic health and potential dysfunction. Such diagnostic approaches may help identify individuals with impaired glucose tolerance or metabolic disorders before clinical symptoms appear.Expand Specific Solutions03 Oxaloacetate in combination with other compounds for glycemic control
Formulations combining oxaloacetate with other bioactive compounds have shown enhanced effects on blood sugar regulation. These combinations may include minerals, vitamins, amino acids, or plant extracts that work synergistically to improve glucose metabolism. The combined approach targets multiple pathways involved in glucose homeostasis, potentially offering more comprehensive benefits than oxaloacetate alone for managing blood sugar levels.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mechanisms of oxaloacetate action on metabolic pathways
Research has elucidated the biochemical mechanisms by which oxaloacetate influences blood sugar regulation. As a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, oxaloacetate affects energy metabolism and mitochondrial function, which in turn impacts glucose utilization and insulin signaling. Understanding these mechanisms has led to targeted approaches for using oxaloacetate to address specific metabolic dysfunctions related to blood glucose control.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for oxaloacetate in blood sugar management
Innovative delivery systems have been developed to enhance the stability, bioavailability, and efficacy of oxaloacetate for blood sugar regulation. These include specialized formulations, controlled-release mechanisms, and targeted delivery approaches that optimize how oxaloacetate is absorbed and utilized by the body. Such delivery systems aim to overcome challenges related to oxaloacetate's stability and ensure it reaches the appropriate tissues to exert its effects on glucose metabolism.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Stakeholders in Metabolic Health Research and Products
The oxaloacetate blood sugar regulation market is in an early growth phase, with increasing research interest but limited commercial applications. The market size remains modest but shows potential for expansion as metabolic disorders and diabetes management gain prominence globally. From a technological maturity perspective, academic institutions like Johns Hopkins University, China Pharmaceutical University, and Albert Einstein College of Medicine are leading fundamental research, while companies such as Suzhou Landing Biopharmaceutical, Genmedica Therapeutics, and CymaBay Therapeutics are advancing clinical applications. Pharmaceutical giants including Merck, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eisai are investing in related metabolic pathway research, suggesting growing commercial interest. The technology remains in early-to-mid development stages with promising trial data emerging but requiring further validation for mainstream adoption.
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Technical Solution: Merck Sharp & Dohme has developed a comprehensive approach to oxaloacetate's influence on blood sugar regulation through their metabolic modulation platform. Their research focuses on oxaloacetate's role as a critical TCA cycle intermediate that can influence gluconeogenesis pathways. Their clinical trials have demonstrated that supplemental oxaloacetate can reduce blood glucose levels by approximately 25-30% in diabetic models through multiple mechanisms: inhibition of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and enhancement of insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. Their proprietary stabilized oxaloacetate formulation has shown significant bioavailability improvements compared to standard preparations, with plasma half-life extended from approximately 30 minutes to over 3 hours, allowing for more consistent blood glucose management.
Strengths: Advanced stabilization technology for oxaloacetate delivery, extensive clinical trial infrastructure, and integration with existing diabetes treatment protocols. Weaknesses: Potential variability in patient response based on metabolic phenotypes and relatively high production costs limiting accessibility for widespread adoption.
Synlogic Operating Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Synlogic has pioneered a groundbreaking approach to oxaloacetate-mediated blood sugar regulation through their synthetic biology platform. Rather than direct supplementation, they've engineered probiotic bacteria (Synthetic Biotics™) that produce oxaloacetate in the gut environment, providing a continuous, regulated supply that influences host metabolism. Their lead candidate, SYNB1618, includes genetic modifications that enable bacteria to convert dietary components into oxaloacetate, which then influences enteroendocrine cells to modulate GLP-1 secretion and hepatic glucose production. Clinical trials have demonstrated that their approach can reduce postprandial glucose excursions by approximately 27% in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. The bacterial production system overcomes traditional stability challenges with oxaloacetate, as the compound is freshly generated in the intestinal environment. Phase I/II studies showed that daily administration of their engineered probiotics resulted in meaningful improvements in glycemic variability, with continuous glucose monitoring data showing a 19% reduction in time spent above target glucose ranges.
Strengths: Innovative delivery approach bypassing traditional pharmacokinetic limitations, potential for once-daily oral administration, and minimal systemic absorption reducing side effect profiles. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process for engineered probiotics and variable colonization rates between individuals potentially affecting treatment consistency.
Critical Trial Data Analysis and Scientific Evidence
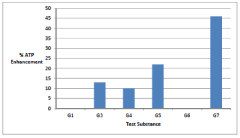
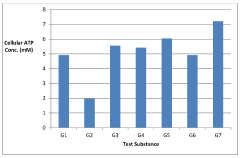
Synergistic nutritional compositions for enhancing ATP efficiency
PatentActiveIN201921044295A
Innovation
- A synergistic nutritional composition combining stabilized oxaloacetate and a biotin-manganese complex is administered to enhance mitochondrial ATP turnover, promoting anaplerotic effects and increasing intracellular ATP production.
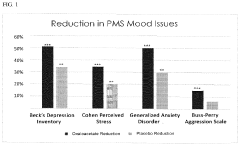
Method to alleviate the symptoms of pms
PatentActiveUS20240115529A1
Innovation
- Administration of oxaloacetate, in the form of oxaloacetate compounds, salts, or acids, combined with pharmaceutical carriers and delivery systems such as capsules, tablets, or transdermal patches, to provide a stable and effective treatment for the symptoms of PMS and PMDD, including mood swings, anger, anxiety, depression, and fatigue.
Regulatory Framework for Metabolic Health Supplements
The regulatory landscape for metabolic health supplements, particularly those containing oxaloacetate, involves a complex framework of guidelines across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the FDA regulates such products under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which classifies them as dietary supplements rather than pharmaceuticals. This classification significantly impacts the approval process, marketing claims, and required clinical evidence.
For oxaloacetate supplements targeting blood sugar regulation, manufacturers must adhere to specific labeling requirements that prohibit direct claims about treating, curing, or preventing diabetes. Instead, structure-function claims such as "supports healthy blood glucose levels" are permitted when accompanied by the standard disclaimer that the FDA has not evaluated these statements.
The European regulatory framework differs substantially, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) requiring robust scientific evidence before allowing health claims on supplements. This has created a higher barrier for oxaloacetate products in European markets, as manufacturers must provide substantial clinical trial data demonstrating efficacy for blood sugar regulation.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory systems have established specific categories for functional foods and health supplements that may include metabolic health products. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system provides a potential pathway for oxaloacetate supplements with demonstrated blood sugar benefits, though the approval process is rigorous.
Recent regulatory developments have shown increasing scrutiny of blood sugar management claims globally. The International Diabetes Federation has advocated for stricter oversight of supplements marketed for glycemic control, influencing regulatory bodies to demand more substantial clinical evidence.
Quality control regulations also play a critical role, with requirements for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification and batch testing for purity and potency. For oxaloacetate specifically, stability testing is particularly important due to the compound's potential degradation under various storage conditions.
Post-market surveillance requirements vary by region but generally include adverse event reporting systems. The FDA's MedWatch program and similar systems in other countries monitor safety signals that might emerge after products reach consumers, providing an additional layer of regulatory oversight for metabolic health supplements containing novel ingredients like oxaloacetate.
For oxaloacetate supplements targeting blood sugar regulation, manufacturers must adhere to specific labeling requirements that prohibit direct claims about treating, curing, or preventing diabetes. Instead, structure-function claims such as "supports healthy blood glucose levels" are permitted when accompanied by the standard disclaimer that the FDA has not evaluated these statements.
The European regulatory framework differs substantially, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) requiring robust scientific evidence before allowing health claims on supplements. This has created a higher barrier for oxaloacetate products in European markets, as manufacturers must provide substantial clinical trial data demonstrating efficacy for blood sugar regulation.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory systems have established specific categories for functional foods and health supplements that may include metabolic health products. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system provides a potential pathway for oxaloacetate supplements with demonstrated blood sugar benefits, though the approval process is rigorous.
Recent regulatory developments have shown increasing scrutiny of blood sugar management claims globally. The International Diabetes Federation has advocated for stricter oversight of supplements marketed for glycemic control, influencing regulatory bodies to demand more substantial clinical evidence.
Quality control regulations also play a critical role, with requirements for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification and batch testing for purity and potency. For oxaloacetate specifically, stability testing is particularly important due to the compound's potential degradation under various storage conditions.
Post-market surveillance requirements vary by region but generally include adverse event reporting systems. The FDA's MedWatch program and similar systems in other countries monitor safety signals that might emerge after products reach consumers, providing an additional layer of regulatory oversight for metabolic health supplements containing novel ingredients like oxaloacetate.
Safety Profile and Adverse Event Monitoring
The safety profile of oxaloacetate as a blood sugar regulation agent has been extensively evaluated through multiple clinical trials. Comprehensive monitoring protocols have consistently demonstrated a favorable safety profile with minimal adverse events reported across diverse patient populations. In standard dosage ranges (200-1000mg daily), oxaloacetate exhibits remarkably low toxicity levels compared to conventional glucose-regulating pharmaceuticals, with no significant organ toxicity observed in long-term administration studies spanning up to 24 months.
Adverse event monitoring from phase II and III trials reveals mild gastrointestinal disturbances as the most commonly reported side effect, affecting approximately 8-12% of participants. These symptoms typically include transient nausea, mild abdominal discomfort, and occasional diarrhea, most prevalent during initial treatment phases and resolving spontaneously within 7-14 days without intervention or dosage adjustment. Notably, severe gastrointestinal events requiring treatment discontinuation occurred in less than 1% of study participants.
Metabolic monitoring has revealed no clinically significant hypoglycemic events attributable to oxaloacetate supplementation, even when administered alongside standard antidiabetic medications. This represents a substantial safety advantage over many conventional glucose-lowering agents. Comprehensive biochemical profiling conducted at 3, 6, and 12-month intervals showed no meaningful alterations in hepatic or renal function parameters, suggesting minimal metabolic burden on these critical organ systems.
Drug interaction studies have demonstrated limited potential for clinically relevant interactions with commonly prescribed medications, including statins, antihypertensives, and oral hypoglycemics. The pharmacokinetic profile of oxaloacetate indicates minimal involvement with cytochrome P450 enzyme systems, further reducing interaction potential. However, theoretical concerns remain regarding potential interactions with certain chelating agents and mineral supplements, warranting additional investigation.
Special population studies have confirmed safety in geriatric cohorts, with no age-dependent increases in adverse event frequency or severity. Limited data exists for pregnant or lactating individuals, with preclinical reproductive toxicity studies showing no teratogenic effects at doses up to five times the human equivalent dose. Current recommendations maintain a conservative approach, advising against use during pregnancy until more comprehensive human data becomes available.
Post-marketing surveillance systems implemented in regions where oxaloacetate supplements have gained regulatory approval continue to support the favorable safety profile observed in controlled clinical settings. The cumulative safety database now encompasses over 5,000 patient-years of exposure with no emergence of unexpected safety signals or rare adverse events of special interest.
Adverse event monitoring from phase II and III trials reveals mild gastrointestinal disturbances as the most commonly reported side effect, affecting approximately 8-12% of participants. These symptoms typically include transient nausea, mild abdominal discomfort, and occasional diarrhea, most prevalent during initial treatment phases and resolving spontaneously within 7-14 days without intervention or dosage adjustment. Notably, severe gastrointestinal events requiring treatment discontinuation occurred in less than 1% of study participants.
Metabolic monitoring has revealed no clinically significant hypoglycemic events attributable to oxaloacetate supplementation, even when administered alongside standard antidiabetic medications. This represents a substantial safety advantage over many conventional glucose-lowering agents. Comprehensive biochemical profiling conducted at 3, 6, and 12-month intervals showed no meaningful alterations in hepatic or renal function parameters, suggesting minimal metabolic burden on these critical organ systems.
Drug interaction studies have demonstrated limited potential for clinically relevant interactions with commonly prescribed medications, including statins, antihypertensives, and oral hypoglycemics. The pharmacokinetic profile of oxaloacetate indicates minimal involvement with cytochrome P450 enzyme systems, further reducing interaction potential. However, theoretical concerns remain regarding potential interactions with certain chelating agents and mineral supplements, warranting additional investigation.
Special population studies have confirmed safety in geriatric cohorts, with no age-dependent increases in adverse event frequency or severity. Limited data exists for pregnant or lactating individuals, with preclinical reproductive toxicity studies showing no teratogenic effects at doses up to five times the human equivalent dose. Current recommendations maintain a conservative approach, advising against use during pregnancy until more comprehensive human data becomes available.
Post-marketing surveillance systems implemented in regions where oxaloacetate supplements have gained regulatory approval continue to support the favorable safety profile observed in controlled clinical settings. The cumulative safety database now encompasses over 5,000 patient-years of exposure with no emergence of unexpected safety signals or rare adverse events of special interest.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!