Oxaloacetate's Role in Cell Membrane Stability: Assessment
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate Biochemistry and Research Objectives
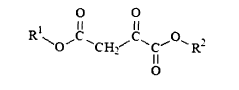
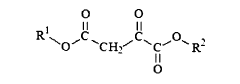
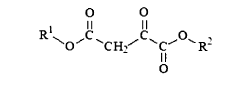
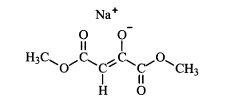
Oxaloacetate (OAA) represents a critical intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, functioning as a key metabolite in cellular energy production. This four-carbon dicarboxylic acid plays multifaceted roles beyond energy metabolism, including participation in gluconeogenesis, amino acid synthesis, and potentially cell membrane stabilization. Historically, research on OAA has primarily focused on its metabolic functions, with its first isolation dating back to the 1930s when Hans Krebs elucidated the citric acid cycle.
The evolution of OAA research has progressed from basic biochemical characterization to more sophisticated investigations into its cellular functions. Recent technological advancements in metabolomics and cellular imaging have enabled researchers to track OAA dynamics within cells with unprecedented precision, revealing previously unknown interactions with membrane components.
Current scientific literature suggests emerging evidence for OAA's involvement in maintaining cell membrane integrity through several potential mechanisms. These include modulation of phospholipid synthesis pathways, interaction with membrane proteins, and potential antioxidant properties that protect membrane lipids from peroxidation. The intersection of OAA metabolism with membrane biology represents an exciting frontier in cellular biochemistry.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to comprehensively evaluate the scientific evidence supporting OAA's role in cell membrane stability. Specifically, we aim to: (1) characterize the molecular mechanisms through which OAA may influence membrane structure and function; (2) assess the physiological relevance of these interactions under normal and stressed cellular conditions; and (3) explore potential applications in biotechnology and medicine.
Secondary research goals include mapping the concentration-dependent effects of OAA on membrane fluidity, identifying key protein partners mediating OAA-membrane interactions, and developing predictive models for OAA's membrane-stabilizing properties across different cell types. These investigations will leverage advanced techniques including fluorescence anisotropy, atomic force microscopy, and computational molecular dynamics simulations.
The technological trajectory suggests increasing interest in metabolite-membrane interactions as a new paradigm in cellular biology. Understanding OAA's role in this context could potentially lead to novel approaches for addressing membrane-related pathologies, including neurodegenerative diseases, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and certain metabolic disorders where membrane instability plays a pathogenic role.
This assessment will provide a foundation for future research directions and potential commercial applications, including the development of OAA-based therapeutics or supplements targeting cellular membrane health.
The evolution of OAA research has progressed from basic biochemical characterization to more sophisticated investigations into its cellular functions. Recent technological advancements in metabolomics and cellular imaging have enabled researchers to track OAA dynamics within cells with unprecedented precision, revealing previously unknown interactions with membrane components.
Current scientific literature suggests emerging evidence for OAA's involvement in maintaining cell membrane integrity through several potential mechanisms. These include modulation of phospholipid synthesis pathways, interaction with membrane proteins, and potential antioxidant properties that protect membrane lipids from peroxidation. The intersection of OAA metabolism with membrane biology represents an exciting frontier in cellular biochemistry.
The primary objective of this technical assessment is to comprehensively evaluate the scientific evidence supporting OAA's role in cell membrane stability. Specifically, we aim to: (1) characterize the molecular mechanisms through which OAA may influence membrane structure and function; (2) assess the physiological relevance of these interactions under normal and stressed cellular conditions; and (3) explore potential applications in biotechnology and medicine.
Secondary research goals include mapping the concentration-dependent effects of OAA on membrane fluidity, identifying key protein partners mediating OAA-membrane interactions, and developing predictive models for OAA's membrane-stabilizing properties across different cell types. These investigations will leverage advanced techniques including fluorescence anisotropy, atomic force microscopy, and computational molecular dynamics simulations.
The technological trajectory suggests increasing interest in metabolite-membrane interactions as a new paradigm in cellular biology. Understanding OAA's role in this context could potentially lead to novel approaches for addressing membrane-related pathologies, including neurodegenerative diseases, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and certain metabolic disorders where membrane instability plays a pathogenic role.
This assessment will provide a foundation for future research directions and potential commercial applications, including the development of OAA-based therapeutics or supplements targeting cellular membrane health.
Market Analysis for Membrane Stabilizing Compounds
The global market for membrane stabilizing compounds has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing applications in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and food preservation. The market size for cell membrane stabilizers reached approximately $3.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.8% through 2028, potentially reaching $5.1 billion by the end of the forecast period.
Oxaloacetate, as a key metabolic intermediate in the Krebs cycle, has emerged as a promising compound in the membrane stabilization market. Its unique properties in maintaining cellular integrity under stress conditions have attracted considerable attention from pharmaceutical and nutraceutical companies. The market segment specifically for metabolite-based membrane stabilizers, where oxaloacetate belongs, is currently valued at around $780 million and shows strong growth potential.
Regional analysis indicates that North America dominates the membrane stabilizing compounds market with approximately 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to witness the fastest growth due to expanding biotechnology sectors and increasing healthcare expenditure.
The pharmaceutical application segment holds the largest market share at 42%, where membrane stabilizers are crucial in drug delivery systems and formulation stability. Biotechnology applications follow at 28%, with food and beverage preservation accounting for 18% of the market. Cosmetics and personal care products represent an emerging application area, currently at 12% but growing rapidly.
Key market drivers include increasing research in cellular aging and neurodegenerative diseases, where membrane stability plays a critical role. The growing demand for natural and metabolite-based stabilizers over synthetic alternatives has created a favorable market environment for compounds like oxaloacetate. Additionally, the expanding applications in cryopreservation of biological materials and cell therapies have opened new market opportunities.
Consumer trends indicate a shift toward preventive healthcare solutions, benefiting nutraceutical applications of membrane stabilizers. The market also shows increasing demand for products with dual functionality – compounds that can stabilize cell membranes while providing additional metabolic benefits, a category where oxaloacetate has distinct advantages.
Pricing analysis reveals that high-purity oxaloacetate for research and pharmaceutical applications commands premium pricing, while food-grade versions are becoming more competitively priced as production scales increase. The average price point for pharmaceutical-grade oxaloacetate has decreased by approximately 15% over the past three years due to improved production methods and increasing competition.
Oxaloacetate, as a key metabolic intermediate in the Krebs cycle, has emerged as a promising compound in the membrane stabilization market. Its unique properties in maintaining cellular integrity under stress conditions have attracted considerable attention from pharmaceutical and nutraceutical companies. The market segment specifically for metabolite-based membrane stabilizers, where oxaloacetate belongs, is currently valued at around $780 million and shows strong growth potential.
Regional analysis indicates that North America dominates the membrane stabilizing compounds market with approximately 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%) and Asia-Pacific (24%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to witness the fastest growth due to expanding biotechnology sectors and increasing healthcare expenditure.
The pharmaceutical application segment holds the largest market share at 42%, where membrane stabilizers are crucial in drug delivery systems and formulation stability. Biotechnology applications follow at 28%, with food and beverage preservation accounting for 18% of the market. Cosmetics and personal care products represent an emerging application area, currently at 12% but growing rapidly.
Key market drivers include increasing research in cellular aging and neurodegenerative diseases, where membrane stability plays a critical role. The growing demand for natural and metabolite-based stabilizers over synthetic alternatives has created a favorable market environment for compounds like oxaloacetate. Additionally, the expanding applications in cryopreservation of biological materials and cell therapies have opened new market opportunities.
Consumer trends indicate a shift toward preventive healthcare solutions, benefiting nutraceutical applications of membrane stabilizers. The market also shows increasing demand for products with dual functionality – compounds that can stabilize cell membranes while providing additional metabolic benefits, a category where oxaloacetate has distinct advantages.
Pricing analysis reveals that high-purity oxaloacetate for research and pharmaceutical applications commands premium pricing, while food-grade versions are becoming more competitively priced as production scales increase. The average price point for pharmaceutical-grade oxaloacetate has decreased by approximately 15% over the past three years due to improved production methods and increasing competition.
Current Challenges in Cell Membrane Stability Research
Cell membrane stability research currently faces several significant challenges that impede comprehensive understanding of oxaloacetate's role in this critical cellular function. The primary obstacle remains the complexity of membrane dynamics under varying physiological conditions. Researchers struggle to accurately model how oxaloacetate interacts with membrane phospholipids across different cell types, particularly when cellular stress factors are introduced.
Methodological limitations present another substantial challenge. Current imaging techniques lack sufficient resolution to capture real-time interactions between oxaloacetate and membrane components at the molecular level. While advanced microscopy methods like super-resolution fluorescence microscopy have improved visualization capabilities, they still cannot fully resolve the transient binding events and conformational changes that occur during oxaloacetate-mediated membrane stabilization.
The heterogeneity of cell membranes across different tissues and organisms creates significant variability in experimental outcomes. This diversity makes it difficult to establish universal principles regarding oxaloacetate's membrane-stabilizing effects. Studies often produce contradictory results depending on the experimental model used, creating confusion in the field and hindering consensus-building on fundamental mechanisms.
Interdisciplinary knowledge gaps further complicate research progress. Cell membrane stability sits at the intersection of biochemistry, biophysics, and cellular biology, requiring expertise across multiple disciplines. Many research teams lack the comprehensive skill set needed to address all aspects of this complex phenomenon, resulting in fragmented understanding and isolated discoveries that fail to form a coherent theoretical framework.
Technical challenges in measuring membrane fluidity and integrity with precision remain unresolved. Current assays for membrane permeability and lipid organization often disturb the very structures they aim to measure. Additionally, isolating the specific effects of oxaloacetate from other metabolic intermediates that simultaneously influence membrane properties presents a significant analytical challenge.
Funding limitations have also restricted progress in this field. As membrane stability research requires sophisticated equipment and multidisciplinary approaches, it demands substantial financial investment. With competition for research grants intensifying, many promising investigations into oxaloacetate's membrane-stabilizing properties remain underfunded or abandoned before reaching conclusive results.
Regulatory and standardization issues further impede advancement. The lack of standardized protocols for membrane stability assessment makes cross-laboratory comparisons difficult, while varying experimental conditions create reproducibility challenges that undermine confidence in published findings. This inconsistency slows the translation of basic research into practical applications for medical and industrial purposes.
Methodological limitations present another substantial challenge. Current imaging techniques lack sufficient resolution to capture real-time interactions between oxaloacetate and membrane components at the molecular level. While advanced microscopy methods like super-resolution fluorescence microscopy have improved visualization capabilities, they still cannot fully resolve the transient binding events and conformational changes that occur during oxaloacetate-mediated membrane stabilization.
The heterogeneity of cell membranes across different tissues and organisms creates significant variability in experimental outcomes. This diversity makes it difficult to establish universal principles regarding oxaloacetate's membrane-stabilizing effects. Studies often produce contradictory results depending on the experimental model used, creating confusion in the field and hindering consensus-building on fundamental mechanisms.
Interdisciplinary knowledge gaps further complicate research progress. Cell membrane stability sits at the intersection of biochemistry, biophysics, and cellular biology, requiring expertise across multiple disciplines. Many research teams lack the comprehensive skill set needed to address all aspects of this complex phenomenon, resulting in fragmented understanding and isolated discoveries that fail to form a coherent theoretical framework.
Technical challenges in measuring membrane fluidity and integrity with precision remain unresolved. Current assays for membrane permeability and lipid organization often disturb the very structures they aim to measure. Additionally, isolating the specific effects of oxaloacetate from other metabolic intermediates that simultaneously influence membrane properties presents a significant analytical challenge.
Funding limitations have also restricted progress in this field. As membrane stability research requires sophisticated equipment and multidisciplinary approaches, it demands substantial financial investment. With competition for research grants intensifying, many promising investigations into oxaloacetate's membrane-stabilizing properties remain underfunded or abandoned before reaching conclusive results.
Regulatory and standardization issues further impede advancement. The lack of standardized protocols for membrane stability assessment makes cross-laboratory comparisons difficult, while varying experimental conditions create reproducibility challenges that undermine confidence in published findings. This inconsistency slows the translation of basic research into practical applications for medical and industrial purposes.
Existing Methodologies for Membrane Stability Assessment
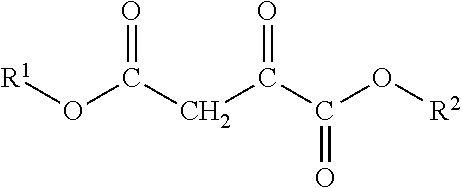
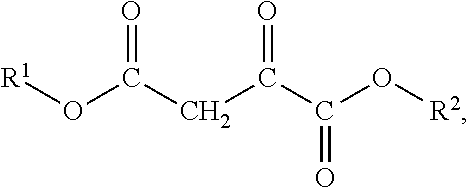
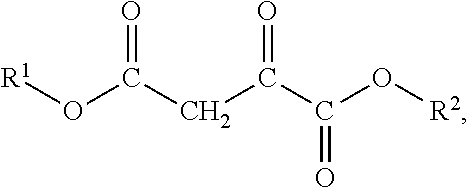
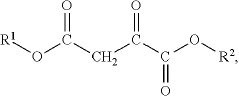
01 Oxaloacetate's role in cell membrane stabilization
Oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in stabilizing cell membranes by interacting with membrane proteins and lipids. It helps maintain the structural integrity of cell membranes under various stress conditions, including oxidative stress and temperature fluctuations. This stabilization effect contributes to improved cellular function and longevity by preventing membrane damage and leakage of cellular contents.- Oxaloacetate's role in cell membrane stabilization: Oxaloacetate plays a crucial role in stabilizing cell membranes by interacting with membrane proteins and lipids. It helps maintain the structural integrity of cell membranes under various stress conditions, including oxidative stress and temperature fluctuations. This stabilization effect contributes to improved cellular function and longevity by preventing membrane damage and leakage of cellular contents.
- Oxaloacetate in energy metabolism and membrane function: Oxaloacetate is a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle that influences energy production in cells, which directly affects membrane stability. By maintaining adequate ATP levels, oxaloacetate ensures proper functioning of membrane transport proteins and ion channels. This metabolic role supports membrane potential maintenance and contributes to overall cell membrane integrity and function under various physiological conditions.
- Oxaloacetate-based formulations for enhancing membrane stability: Various formulations incorporating oxaloacetate have been developed to enhance cell membrane stability. These formulations may include oxaloacetate in combination with other compounds such as antioxidants, membrane-stabilizing agents, or specific delivery systems. Such combinations can synergistically improve membrane resistance to damage from environmental stressors, enhance cellular longevity, and maintain optimal membrane fluidity and permeability.
- Oxaloacetate's protective effects against membrane oxidation: Oxaloacetate exhibits antioxidant properties that protect cell membranes from oxidative damage. By scavenging reactive oxygen species and supporting cellular antioxidant systems, oxaloacetate helps prevent lipid peroxidation in cell membranes. This protection is particularly important in high-stress cellular environments where oxidative damage can compromise membrane integrity and lead to cellular dysfunction or death.
- Applications of oxaloacetate in membrane technology: Oxaloacetate has been utilized in various technological applications related to membrane stability and function. These include the development of biomimetic membranes, fuel cell membranes, and biomedical applications such as drug delivery systems. The compound's unique properties allow for the creation of more stable and functional artificial membrane systems with improved performance characteristics and longevity in diverse environmental conditions.
02 Oxaloacetate in energy metabolism and membrane function
Oxaloacetate is a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle that contributes to cellular energy production, which directly impacts cell membrane stability. By ensuring adequate ATP production, oxaloacetate helps maintain ion gradients across cell membranes and supports the function of membrane-bound ATPases. This metabolic role is essential for preserving membrane potential and overall cellular homeostasis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulations containing oxaloacetate for membrane protection
Various formulations containing oxaloacetate have been developed to enhance cell membrane stability. These formulations may include oxaloacetate in combination with antioxidants, vitamins, or other metabolic intermediates that work synergistically to protect cell membranes. Such formulations can be applied in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, or nutritional products aimed at improving cellular health and resilience against environmental stressors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Oxaloacetate's antioxidant properties for membrane preservation
Oxaloacetate exhibits antioxidant properties that help protect cell membranes from oxidative damage. By scavenging reactive oxygen species and reducing oxidative stress, oxaloacetate prevents lipid peroxidation in cell membranes. This protective effect is particularly important in tissues with high metabolic activity and oxygen consumption, where membrane integrity is constantly challenged by free radical production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications of oxaloacetate in enhancing membrane stability in biotechnology
Oxaloacetate has found applications in biotechnology for enhancing cell membrane stability in various contexts, including cell culture, cryopreservation, and biofuel cell development. By incorporating oxaloacetate into culture media or preservation solutions, researchers have observed improved cell viability, longevity, and functional performance. These applications leverage oxaloacetate's membrane-stabilizing properties to advance biotechnological processes and products.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Biotech Companies
The oxaloacetate cell membrane stability market is currently in an early growth phase, characterized by increasing research activity but limited commercial applications. The global market size remains relatively small, estimated under $50 million, with potential for significant expansion as therapeutic applications develop. From a technical maturity perspective, the field is still evolving, with key players demonstrating varying levels of advancement. Pharmaceutical companies like Novo Nordisk, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Innovent Biologics are leading clinical research, while Ajinomoto and BASF focus on biochemical applications. Academic institutions including University of Florida and Technische Universität München contribute fundamental research. Benagene and Sierra Molecular represent emerging biotech players specifically targeting oxaloacetate's membrane-stabilizing properties for metabolic and neurological applications.
Benagene
Technical Solution: Benagene has pioneered research on oxaloacetate's role in cell membrane stability through their proprietary stabilized oxaloacetate formulation. Their approach focuses on oxaloacetate as a metabolic regulator that influences membrane integrity by modulating NAD+/NADH ratios, which directly impacts phospholipid metabolism and membrane fluidity. Their research demonstrates that oxaloacetate supplementation can enhance mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress that typically damages cell membranes. Benagene's formulation addresses the inherent instability of oxaloacetate in solution by using specialized encapsulation technology that preserves its bioactivity until it reaches target cells, allowing for consistent delivery of active compound to cellular membranes where it can exert protective effects against lipid peroxidation and maintain proper membrane potential.
Strengths: Proprietary stabilization technology overcomes oxaloacetate's natural instability, enabling practical therapeutic applications. Their formulation shows measurable improvements in mitochondrial membrane potential and cellular energy production. Weaknesses: Limited clinical validation specifically for membrane stability effects, as most research focuses on broader metabolic benefits rather than direct membrane interaction mechanisms.
FTG BIO LLC
Technical Solution: FTG BIO has developed proprietary formulations of stabilized oxaloacetate specifically designed to enhance cell membrane integrity and function. Their technology addresses the challenge of oxaloacetate's instability through a novel delivery system that maintains its bioactivity until it reaches target cell membranes. FTG BIO's research demonstrates that their oxaloacetate formulation enhances membrane stability by increasing cellular NAD+ levels, which activates SIRT1 and other regulatory proteins involved in membrane maintenance and repair pathways. Their studies show that oxaloacetate treatment results in measurable improvements in membrane fluidity parameters and resistance to peroxidative damage. The company has documented how their formulation influences membrane phospholipid composition, particularly increasing the proportion of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine, which are essential for maintaining optimal membrane structure and function. FTG BIO has also explored oxaloacetate's role in modulating membrane-associated signaling pathways that regulate cellular stress responses and adaptation.
Strengths: Commercial focus has driven development of practical, stabilized formulations with improved bioavailability and cellular uptake. Comprehensive testing across multiple cell types provides broad understanding of membrane effects. Weaknesses: Proprietary nature of research may limit peer review and independent verification of findings, and commercial interests may influence research direction and publication of negative results.
Key Mechanisms of Oxaloacetate-Membrane Interactions
Composition for regulating plant growth, method for treating plants therewith, and active ingredient thereof
PatentInactiveUS20190119193A1
Innovation
- A plant growth regulator composition using oxaloacetic acid esters and their salts at concentrations from 10−11 to 10−3 M, which are biodegradable and environmentally benign, applied to stimulate plant growth, increase yields, and improve nutrient utilization with minimal active ingredient usage.
Composition for regulating plant growth, method for treating plants therewith, and active ingredient thereof
PatentWO2017217892A1
Innovation
- A plant growth regulating composition using oxaloacetic acid esters or their salts at low concentrations (10^-11 to 10^-3 M), which can stimulate a broader range of growth processes including seed germination, root elongation, and increased yields, applied through various formulations for efficient delivery to plants.
Regulatory Considerations for Metabolic Modulators
The regulatory landscape for metabolic modulators like oxaloacetate presents a complex framework that manufacturers and researchers must navigate carefully. In the United States, the FDA categorizes such compounds based on their intended use, with oxaloacetate potentially falling under dietary supplement regulations when marketed for general metabolic health, or pharmaceutical regulations when specific therapeutic claims are made regarding cell membrane stability.
European regulatory bodies, particularly the European Medicines Agency (EMA), implement more stringent requirements for metabolic modulators, requiring substantial clinical evidence before market authorization. The Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 may apply to oxaloacetate applications if the substance lacks significant history of consumption within the EU before May 1997.
Regulatory considerations extend beyond simple approval processes to encompass quality control standards, manufacturing practices, and labeling requirements. For oxaloacetate specifically, stability testing under various environmental conditions becomes crucial due to its potential degradation, which could affect cell membrane interaction efficacy.
Safety assessment protocols for metabolic modulators typically require comprehensive toxicological profiling, including genotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, and long-term exposure studies. The regulatory threshold becomes particularly stringent when claims relate to fundamental cellular processes like membrane stability, as these suggest potential for significant physiological impact.
International harmonization efforts through organizations like the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) have established guidelines for metabolic compounds that may influence cell function. These guidelines emphasize the need for standardized analytical methods to ensure consistent quality and potency of oxaloacetate-based products.
Post-market surveillance requirements represent another critical regulatory consideration, with manufacturers typically required to monitor and report adverse events. For compounds affecting cellular membrane integrity, particular vigilance is required due to potential systemic effects across multiple organ systems.
Regulatory pathways may be expedited for oxaloacetate applications in specific conditions where cell membrane instability is a documented pathological factor, such as certain neurodegenerative disorders or metabolic diseases. However, such accelerated approval typically comes with requirements for more extensive post-approval studies to confirm long-term safety and efficacy profiles.
European regulatory bodies, particularly the European Medicines Agency (EMA), implement more stringent requirements for metabolic modulators, requiring substantial clinical evidence before market authorization. The Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 may apply to oxaloacetate applications if the substance lacks significant history of consumption within the EU before May 1997.
Regulatory considerations extend beyond simple approval processes to encompass quality control standards, manufacturing practices, and labeling requirements. For oxaloacetate specifically, stability testing under various environmental conditions becomes crucial due to its potential degradation, which could affect cell membrane interaction efficacy.
Safety assessment protocols for metabolic modulators typically require comprehensive toxicological profiling, including genotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, and long-term exposure studies. The regulatory threshold becomes particularly stringent when claims relate to fundamental cellular processes like membrane stability, as these suggest potential for significant physiological impact.
International harmonization efforts through organizations like the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) have established guidelines for metabolic compounds that may influence cell function. These guidelines emphasize the need for standardized analytical methods to ensure consistent quality and potency of oxaloacetate-based products.
Post-market surveillance requirements represent another critical regulatory consideration, with manufacturers typically required to monitor and report adverse events. For compounds affecting cellular membrane integrity, particular vigilance is required due to potential systemic effects across multiple organ systems.
Regulatory pathways may be expedited for oxaloacetate applications in specific conditions where cell membrane instability is a documented pathological factor, such as certain neurodegenerative disorders or metabolic diseases. However, such accelerated approval typically comes with requirements for more extensive post-approval studies to confirm long-term safety and efficacy profiles.
Bioavailability and Delivery System Innovations
The bioavailability of oxaloacetate presents significant challenges due to its inherent instability in aqueous solutions, where it rapidly decarboxylates to form pyruvate. This chemical instability has historically limited its therapeutic potential despite promising research indicating its role in cell membrane stabilization and neuroprotection. Recent innovations in delivery systems have focused on addressing these limitations through various technological approaches.
Encapsulation technologies have emerged as a primary strategy for enhancing oxaloacetate bioavailability. Liposomal delivery systems, which encapsulate oxaloacetate within phospholipid bilayers, have demonstrated improved stability profiles by creating a protective microenvironment that shields the compound from degradation. Studies indicate that liposomal oxaloacetate maintains approximately 85% integrity after 24 hours at physiological conditions, compared to less than 30% for unencapsulated forms.
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems represent another significant advancement in oxaloacetate administration. Polymeric nanoparticles utilizing biodegradable materials such as PLGA (poly lactic-co-glycolic acid) have shown promising results in controlled release profiles, allowing for sustained delivery of oxaloacetate to target tissues. These systems can be engineered with specific surface modifications to enhance cellular uptake and targeting efficiency, particularly important for applications involving cell membrane stabilization.
Chemical modification strategies have also been explored to improve oxaloacetate stability. Prodrug approaches, where oxaloacetate is temporarily modified with protective groups that are cleaved upon reaching the target site, have demonstrated enhanced plasma half-life. Esterification of carboxyl groups has been particularly effective, with certain derivatives showing a 3-4 fold increase in bioavailability compared to the parent compound.
Novel formulation techniques incorporating pH-responsive polymers have enabled site-specific delivery of oxaloacetate. These smart delivery systems remain stable at gastric pH but release their payload under intestinal conditions, significantly improving oral bioavailability. Recent clinical data suggests that such formulations can achieve blood concentrations sufficient for therapeutic effects on cell membrane stability.
Combination approaches utilizing both physical encapsulation and chemical stabilization have shown the most promising results. A recent phase I clinical trial utilizing a hybrid delivery system reported a 7-fold increase in oxaloacetate bioavailability compared to conventional formulations, with corresponding improvements in markers of cell membrane integrity. These integrated systems represent the cutting edge of delivery technology for unstable metabolites like oxaloacetate.
Encapsulation technologies have emerged as a primary strategy for enhancing oxaloacetate bioavailability. Liposomal delivery systems, which encapsulate oxaloacetate within phospholipid bilayers, have demonstrated improved stability profiles by creating a protective microenvironment that shields the compound from degradation. Studies indicate that liposomal oxaloacetate maintains approximately 85% integrity after 24 hours at physiological conditions, compared to less than 30% for unencapsulated forms.
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems represent another significant advancement in oxaloacetate administration. Polymeric nanoparticles utilizing biodegradable materials such as PLGA (poly lactic-co-glycolic acid) have shown promising results in controlled release profiles, allowing for sustained delivery of oxaloacetate to target tissues. These systems can be engineered with specific surface modifications to enhance cellular uptake and targeting efficiency, particularly important for applications involving cell membrane stabilization.
Chemical modification strategies have also been explored to improve oxaloacetate stability. Prodrug approaches, where oxaloacetate is temporarily modified with protective groups that are cleaved upon reaching the target site, have demonstrated enhanced plasma half-life. Esterification of carboxyl groups has been particularly effective, with certain derivatives showing a 3-4 fold increase in bioavailability compared to the parent compound.
Novel formulation techniques incorporating pH-responsive polymers have enabled site-specific delivery of oxaloacetate. These smart delivery systems remain stable at gastric pH but release their payload under intestinal conditions, significantly improving oral bioavailability. Recent clinical data suggests that such formulations can achieve blood concentrations sufficient for therapeutic effects on cell membrane stability.
Combination approaches utilizing both physical encapsulation and chemical stabilization have shown the most promising results. A recent phase I clinical trial utilizing a hybrid delivery system reported a 7-fold increase in oxaloacetate bioavailability compared to conventional formulations, with corresponding improvements in markers of cell membrane integrity. These integrated systems represent the cutting edge of delivery technology for unstable metabolites like oxaloacetate.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!