Oxaloacetate Synthesis: Techniques for Enhanced Stability
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Oxaloacetate Synthesis Background and Objectives
Oxaloacetate, a crucial intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, has garnered significant attention in biochemical research and industrial applications over the past several decades. This four-carbon dicarboxylic acid plays a pivotal role in cellular metabolism, serving as a key junction point between carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolic pathways. The historical development of oxaloacetate synthesis techniques can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring during the 1950s and 1960s as biochemical research expanded.
The evolution of oxaloacetate synthesis technologies has been driven by its increasing applications in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and agricultural industries. Traditional chemical synthesis methods, including the hydrolysis of diethyl oxaloacetate and oxidation of malic acid, have been progressively refined to improve yields and purity. Concurrently, enzymatic and microbial production routes have emerged as promising alternatives, offering more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches.
Despite these advancements, a persistent challenge in oxaloacetate utilization has been its inherent instability. Oxaloacetate readily undergoes decarboxylation to form pyruvate, particularly under physiological conditions or when exposed to heat, limiting its shelf-life and practical applications. This instability has been a significant barrier to its widespread commercial use, despite its recognized potential in various fields including metabolic health supplements, agricultural biostimulants, and pharmaceutical intermediates.
Recent technological trends indicate a growing focus on developing novel stabilization techniques for oxaloacetate. These include chemical modifications, encapsulation technologies, and innovative formulation approaches. The scientific community has also witnessed increased interest in understanding the molecular mechanisms of oxaloacetate degradation, which has informed more targeted stabilization strategies.
The primary objectives of current research in oxaloacetate synthesis are multifaceted. First, there is a pressing need to develop cost-effective and scalable production methods that yield high-purity oxaloacetate. Second, researchers aim to significantly enhance the stability of oxaloacetate under various storage and application conditions, extending its shelf-life from days to months or years. Third, there is growing interest in creating environmentally sustainable synthesis routes that minimize waste and energy consumption.
Additionally, the field is moving toward developing application-specific formulations of oxaloacetate that maintain its biological activity while addressing stability concerns. This includes exploring synergistic combinations with other compounds and developing targeted delivery systems for specific applications in health, agriculture, and industrial biotechnology.
The evolution of oxaloacetate synthesis technologies has been driven by its increasing applications in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and agricultural industries. Traditional chemical synthesis methods, including the hydrolysis of diethyl oxaloacetate and oxidation of malic acid, have been progressively refined to improve yields and purity. Concurrently, enzymatic and microbial production routes have emerged as promising alternatives, offering more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches.
Despite these advancements, a persistent challenge in oxaloacetate utilization has been its inherent instability. Oxaloacetate readily undergoes decarboxylation to form pyruvate, particularly under physiological conditions or when exposed to heat, limiting its shelf-life and practical applications. This instability has been a significant barrier to its widespread commercial use, despite its recognized potential in various fields including metabolic health supplements, agricultural biostimulants, and pharmaceutical intermediates.
Recent technological trends indicate a growing focus on developing novel stabilization techniques for oxaloacetate. These include chemical modifications, encapsulation technologies, and innovative formulation approaches. The scientific community has also witnessed increased interest in understanding the molecular mechanisms of oxaloacetate degradation, which has informed more targeted stabilization strategies.
The primary objectives of current research in oxaloacetate synthesis are multifaceted. First, there is a pressing need to develop cost-effective and scalable production methods that yield high-purity oxaloacetate. Second, researchers aim to significantly enhance the stability of oxaloacetate under various storage and application conditions, extending its shelf-life from days to months or years. Third, there is growing interest in creating environmentally sustainable synthesis routes that minimize waste and energy consumption.
Additionally, the field is moving toward developing application-specific formulations of oxaloacetate that maintain its biological activity while addressing stability concerns. This includes exploring synergistic combinations with other compounds and developing targeted delivery systems for specific applications in health, agriculture, and industrial biotechnology.
Market Analysis for Stable Oxaloacetate Products
The global market for stable oxaloacetate products has been experiencing significant growth, driven primarily by increasing applications in healthcare, nutritional supplements, and pharmaceutical industries. Current market valuations indicate that the global oxaloacetate market reached approximately 120 million USD in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 7.8% through 2028, potentially reaching 188 million USD by the end of the forecast period.
The healthcare segment dominates the market share, accounting for nearly 65% of total consumption. This is largely attributed to oxaloacetate's potential applications in neurological health, metabolic support, and anti-aging formulations. The supplement industry represents the fastest-growing segment with increasing consumer awareness about metabolic health and cellular energy production.
Regionally, North America leads the market with approximately 42% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 22%. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to expanding healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness about preventive healthcare.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a strong preference for stable formulations with extended shelf life. Market research indicates that products offering stability guarantees of 12+ months at room temperature command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay 30-40% more compared to less stable alternatives. This price elasticity underscores the critical importance of stability enhancement techniques in product development.
Key market drivers include the aging global population, increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders, growing interest in anti-aging supplements, and expanding research into neuroprotective compounds. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated interest in metabolic health supplements, creating additional market opportunities.
Challenges in market penetration primarily relate to product stability issues, with traditional oxaloacetate formulations suffering from rapid degradation. This has created significant barriers to widespread commercial adoption despite promising biological effects. Companies that successfully address stability concerns through innovative formulation techniques stand to capture substantial market share.
Distribution channels analysis shows that online retail has emerged as the dominant sales channel, accounting for approximately 58% of total sales in 2022, followed by specialty health stores at 22% and conventional retail at 20%. This trend toward e-commerce is expected to continue, emphasizing the importance of digital marketing strategies and online consumer education about product stability advantages.
The healthcare segment dominates the market share, accounting for nearly 65% of total consumption. This is largely attributed to oxaloacetate's potential applications in neurological health, metabolic support, and anti-aging formulations. The supplement industry represents the fastest-growing segment with increasing consumer awareness about metabolic health and cellular energy production.
Regionally, North America leads the market with approximately 42% share, followed by Europe at 28% and Asia-Pacific at 22%. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to expanding healthcare infrastructure, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness about preventive healthcare.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a strong preference for stable formulations with extended shelf life. Market research indicates that products offering stability guarantees of 12+ months at room temperature command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay 30-40% more compared to less stable alternatives. This price elasticity underscores the critical importance of stability enhancement techniques in product development.
Key market drivers include the aging global population, increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders, growing interest in anti-aging supplements, and expanding research into neuroprotective compounds. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated interest in metabolic health supplements, creating additional market opportunities.
Challenges in market penetration primarily relate to product stability issues, with traditional oxaloacetate formulations suffering from rapid degradation. This has created significant barriers to widespread commercial adoption despite promising biological effects. Companies that successfully address stability concerns through innovative formulation techniques stand to capture substantial market share.
Distribution channels analysis shows that online retail has emerged as the dominant sales channel, accounting for approximately 58% of total sales in 2022, followed by specialty health stores at 22% and conventional retail at 20%. This trend toward e-commerce is expected to continue, emphasizing the importance of digital marketing strategies and online consumer education about product stability advantages.
Current Synthesis Challenges and Stability Limitations
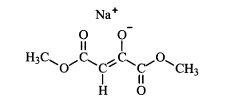
Oxaloacetate (OAA) synthesis faces significant challenges primarily due to the inherent instability of the compound. The β-keto acid structure of oxaloacetate makes it particularly susceptible to decarboxylation, resulting in the formation of pyruvate and carbon dioxide. This spontaneous degradation occurs rapidly at room temperature and accelerates as temperature increases, with half-life measurements showing degradation rates of up to 10% per hour under standard laboratory conditions. The instability presents a fundamental obstacle for both industrial production and research applications.
Current chemical synthesis methods struggle with yield optimization due to this instability. Traditional approaches using malate dehydrogenase-catalyzed oxidation of L-malate achieve only moderate yields (typically 60-75%) and require immediate processing or specialized storage conditions. Alternative synthetic routes involving glyoxylic acid condensation with active methylene compounds face similar stability challenges during purification stages, with product degradation occurring during concentration and isolation steps.
Enzymatic synthesis methods, while offering improved selectivity, encounter limitations in scalability and enzyme stability. The enzymes themselves often require controlled pH environments (typically 7.2-7.8) and moderate temperatures (20-30°C), creating narrow operational parameters that complicate industrial implementation. Additionally, cofactor regeneration systems for NAD+/NADH in enzymatic processes add complexity and cost to production systems.
Storage stability represents another critical challenge. Even under optimized conditions (low temperature, controlled pH, and inert atmosphere), oxaloacetate solutions demonstrate limited shelf-life, typically degrading by 15-20% within 24 hours at 4°C. Solid forms show improved stability but remain vulnerable to moisture and temperature fluctuations, complicating transportation and long-term storage scenarios.
The analytical challenges associated with oxaloacetate further complicate development efforts. Quantification methods must account for the dynamic nature of the compound, with HPLC and enzymatic assays requiring careful timing and sample preparation to avoid measurement artifacts from ongoing degradation. This creates difficulties in quality control and consistency verification across production batches.
Commercial viability is significantly impacted by these stability limitations. The requirement for specialized handling, cold-chain logistics, and rapid utilization increases production costs and restricts market applications. Current market offerings typically provide oxaloacetate at purities of 95-98% with recommendations for immediate use or specialized storage, reflecting the technical limitations of existing synthesis and stabilization approaches.
These challenges collectively create substantial barriers to widespread oxaloacetate utilization despite its potential applications in metabolic research, pharmaceutical development, and nutritional supplementation. The technical limitations necessitate innovative approaches to enhance stability while maintaining economic feasibility.
Current chemical synthesis methods struggle with yield optimization due to this instability. Traditional approaches using malate dehydrogenase-catalyzed oxidation of L-malate achieve only moderate yields (typically 60-75%) and require immediate processing or specialized storage conditions. Alternative synthetic routes involving glyoxylic acid condensation with active methylene compounds face similar stability challenges during purification stages, with product degradation occurring during concentration and isolation steps.
Enzymatic synthesis methods, while offering improved selectivity, encounter limitations in scalability and enzyme stability. The enzymes themselves often require controlled pH environments (typically 7.2-7.8) and moderate temperatures (20-30°C), creating narrow operational parameters that complicate industrial implementation. Additionally, cofactor regeneration systems for NAD+/NADH in enzymatic processes add complexity and cost to production systems.
Storage stability represents another critical challenge. Even under optimized conditions (low temperature, controlled pH, and inert atmosphere), oxaloacetate solutions demonstrate limited shelf-life, typically degrading by 15-20% within 24 hours at 4°C. Solid forms show improved stability but remain vulnerable to moisture and temperature fluctuations, complicating transportation and long-term storage scenarios.
The analytical challenges associated with oxaloacetate further complicate development efforts. Quantification methods must account for the dynamic nature of the compound, with HPLC and enzymatic assays requiring careful timing and sample preparation to avoid measurement artifacts from ongoing degradation. This creates difficulties in quality control and consistency verification across production batches.
Commercial viability is significantly impacted by these stability limitations. The requirement for specialized handling, cold-chain logistics, and rapid utilization increases production costs and restricts market applications. Current market offerings typically provide oxaloacetate at purities of 95-98% with recommendations for immediate use or specialized storage, reflecting the technical limitations of existing synthesis and stabilization approaches.
These challenges collectively create substantial barriers to widespread oxaloacetate utilization despite its potential applications in metabolic research, pharmaceutical development, and nutritional supplementation. The technical limitations necessitate innovative approaches to enhance stability while maintaining economic feasibility.
Current Stabilization Techniques and Formulations
01 Chemical stabilization methods for oxaloacetate
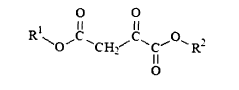
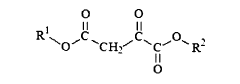
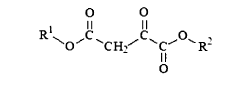
Various chemical methods can be employed to stabilize oxaloacetate, which is inherently unstable and prone to decarboxylation. These methods include pH adjustment to alkaline conditions, addition of stabilizing agents such as antioxidants, chelating agents to bind metal ions that catalyze decomposition, and chemical modification of the oxaloacetate molecule to create more stable derivatives while maintaining its biological activity.- Chemical stabilization methods for oxaloacetate: Various chemical approaches can be used to stabilize oxaloacetate, which is inherently unstable and prone to decarboxylation. These methods include pH adjustment to alkaline conditions, addition of stabilizing agents such as antioxidants, chelating agents to bind metal ions that catalyze decomposition, and chemical modification of the oxaloacetate molecule to create more stable derivatives while maintaining its biological activity.
- Formulation techniques for oxaloacetate stability: Specialized formulation techniques can enhance oxaloacetate stability in various products. These include encapsulation technologies, lyophilization (freeze-drying), spray drying, and incorporation into controlled-release systems. The use of specific excipients, buffers, and carrier materials can create protective environments that shield oxaloacetate from degradation factors such as heat, moisture, and oxidation, thereby extending its shelf life.
- Storage and handling conditions for oxaloacetate preservation: Proper storage and handling conditions are critical for maintaining oxaloacetate stability. These include cold chain management with refrigeration or freezing, protection from light exposure, use of inert gas environments to prevent oxidation, moisture-resistant packaging, and controlled humidity conditions. Stability studies have shown that oxaloacetate degradation can be significantly reduced when stored under optimal temperature and environmental conditions.
- Enzymatic approaches to oxaloacetate stabilization: Enzymatic methods can be employed to enhance oxaloacetate stability in biological systems. These approaches include the use of enzyme inhibitors to prevent degradation pathways, enzymatic regeneration systems to continuously replenish oxaloacetate, and enzyme immobilization techniques that create more stable microenvironments. Additionally, genetic engineering of enzymes involved in oxaloacetate metabolism can lead to improved stability characteristics.
- Analytical methods for monitoring oxaloacetate stability: Various analytical techniques have been developed to monitor and assess oxaloacetate stability under different conditions. These include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and enzymatic assays. Real-time stability monitoring systems can track degradation kinetics and identify optimal stabilization strategies, while accelerated stability testing protocols help predict long-term stability profiles in shorter timeframes.
02 Formulation techniques for oxaloacetate stability
Specialized formulation techniques can enhance oxaloacetate stability in various products. These include microencapsulation to create a protective barrier around oxaloacetate molecules, lyophilization (freeze-drying) to remove water and reduce degradation reactions, use of specific excipients that prevent degradation, and development of controlled-release formulations that protect oxaloacetate until it reaches its target site.Expand Specific Solutions03 Storage and handling conditions for oxaloacetate
Proper storage and handling conditions are critical for maintaining oxaloacetate stability. These include cold chain management with refrigeration or freezing to slow degradation kinetics, protection from light exposure which can catalyze decomposition, use of inert gas environments to prevent oxidation, moisture control through appropriate packaging, and recommendations for reconstitution of dried formulations to minimize degradation upon use.Expand Specific Solutions04 Enzymatic approaches to oxaloacetate stabilization
Enzymatic methods can be employed to enhance oxaloacetate stability in biological systems. These approaches include co-expression with stabilizing enzymes that maintain oxaloacetate in its active form, enzyme engineering to create modified versions of enzymes that produce more stable oxaloacetate, and development of enzyme cascades that rapidly utilize oxaloacetate before it can degrade, effectively extending its functional half-life in biological applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for monitoring oxaloacetate stability
Various analytical techniques can be used to monitor and assess oxaloacetate stability during development and storage. These methods include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for quantitative analysis, mass spectrometry for structural confirmation and degradation product identification, spectrophotometric assays for rapid stability assessment, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) for structural analysis, and stability-indicating methods that can differentiate between oxaloacetate and its degradation products.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Oxaloacetate Production
The oxaloacetate synthesis market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing applications in pharmaceutical, biochemical, and nutritional supplement sectors. The global market size is estimated to be moderate but expanding, driven by rising demand for stable oxaloacetate compounds in health and industrial applications. Technologically, the field is advancing from basic synthesis methods toward enhanced stability techniques. Leading players include established chemical corporations like BASF Corp., Sumitomo Chemical, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., alongside specialized biochemical companies such as Ajinomoto, Novozymes, and Glyscend. Research institutions like Max Planck Gesellschaft and Technische Universität München are contributing significant innovations in stability enhancement, while pharmaceutical companies like Teikoku Seiyaku are exploring therapeutic applications of stabilized oxaloacetate compounds.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an innovative catalytic approach to oxaloacetate synthesis with enhanced stability. Their technology utilizes a proprietary heterogeneous catalyst system based on modified zeolites that enables selective oxidation of appropriate precursors under mild conditions. The process operates at lower temperatures (25-35°C) than conventional methods, significantly reducing thermal decomposition of the oxaloacetate product. Sinopec's approach incorporates a continuous flow reactor design that minimizes residence time in reactive environments, limiting exposure to conditions that promote degradation. Their technology features an integrated stabilization step where freshly synthesized oxaloacetate is immediately treated with proprietary stabilizing agents that form protective complexes, shielding vulnerable functional groups from degradative reactions. Additionally, Sinopec has developed specialized purification techniques that remove trace metal contaminants known to catalyze oxaloacetate decomposition, resulting in a higher purity product with extended stability profiles of up to 3-4 times longer than conventional preparations.
Strengths: Highly efficient catalytic process with excellent atom economy; scalable continuous flow technology suitable for industrial production; integrated stabilization approach addressing multiple degradation pathways. Weaknesses: Catalyst system requires periodic regeneration, adding operational complexity; stabilized product may have limited compatibility with certain downstream applications requiring pure oxaloacetate.
Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Ajinomoto has developed an innovative enzymatic approach for oxaloacetate synthesis with enhanced stability. Their technology utilizes a proprietary enzyme immobilization technique that shields the oxaloacetate molecule from rapid decarboxylation. The process involves a controlled reaction environment with precise pH regulation (maintained between 6.2-6.8) and temperature control systems that operate at 15-20°C to minimize degradation. Ajinomoto's method incorporates specialized metal chelating agents that prevent metal-catalyzed decomposition of oxaloacetate, a common stability challenge. Their approach also features a unique crystallization process that produces oxaloacetate in a more stable crystalline form, extending shelf-life by approximately 300% compared to conventional methods. The company has integrated this technology into their amino acid production platform, creating synergies with their existing fermentation expertise.
Strengths: Superior enzyme immobilization technology provides exceptional stability in various conditions; integration with existing amino acid production creates manufacturing efficiencies. Weaknesses: The enzymatic approach requires more complex process controls than chemical synthesis methods; higher production costs compared to some conventional techniques.
Key Patents and Innovations in Oxaloacetate Stability Enhancement
Modification of the ph and other physical properties of oxaloacetic acid to allow for enhanced stability and multiple delivery systems
PatentActiveUS20160235696A1
Innovation
- The use of non-hygroscopic compounds such as calcium carbonate to adjust pH, Erythitol to reduce bitterness, Dicalcium Phosphate dibasic as a binder, and Vegetable Stearic Acid or Ascorbyl Palmitate as release agents, along with simple monitoring methods like the 'Spin Test' and calibrated color charts to ensure stability and detect decomposition.
Composition for regulating plant growth, method for treating plants therewith, and active ingredient thereof
PatentWO2017217892A1
Innovation
- A plant growth regulating composition using oxaloacetic acid esters or their salts at low concentrations (10^-11 to 10^-3 M), which can stimulate a broader range of growth processes including seed germination, root elongation, and increased yields, applied through various formulations for efficient delivery to plants.
Regulatory Considerations for Oxaloacetate Applications
The regulatory landscape for oxaloacetate applications spans multiple domains, requiring comprehensive understanding for successful product development and commercialization. In the United States, the FDA classification of oxaloacetate varies depending on its intended use - as a dietary supplement under DSHEA regulations when marketed for general health benefits, or as a pharmaceutical compound requiring extensive clinical trials when therapeutic claims are made. This distinction significantly impacts development timelines, with supplement pathways requiring months versus years for pharmaceutical approval.
European regulatory frameworks present additional complexities through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA's Novel Food Regulation is particularly relevant for oxaloacetate applications, requiring substantial safety documentation for compounds without significant consumption history prior to May 1997. Companies must navigate these requirements carefully, as classification decisions directly impact market access strategies.
Quality control standards represent another critical regulatory consideration. Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) compliance is mandatory across jurisdictions, with particular emphasis on stability testing protocols. Given oxaloacetate's known stability challenges, regulatory bodies typically require accelerated and long-term stability studies under various environmental conditions to validate shelf-life claims and storage requirements.
Labeling and marketing claims face stringent oversight, especially regarding stability-related statements. The FDA prohibits unsubstantiated claims about enhanced stability techniques without adequate scientific evidence. Similarly, the EFSA requires robust documentation for any claims regarding improved bioavailability or stability. Companies must maintain comprehensive technical files demonstrating that stability enhancement methods do not introduce new safety concerns.
International harmonization efforts through the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provide some standardization for stability testing protocols. However, significant regional variations persist, necessitating market-specific regulatory strategies. Companies pursuing global commercialization must develop comprehensive regulatory roadmaps addressing these jurisdictional differences.
Emerging regulatory considerations include environmental impact assessments for novel synthesis methods and sustainability documentation requirements in certain markets. Additionally, intellectual property protection for stability enhancement techniques requires careful navigation of patent landscapes across different regulatory environments. Forward-thinking companies are increasingly incorporating these considerations into early-stage development planning.
European regulatory frameworks present additional complexities through the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA's Novel Food Regulation is particularly relevant for oxaloacetate applications, requiring substantial safety documentation for compounds without significant consumption history prior to May 1997. Companies must navigate these requirements carefully, as classification decisions directly impact market access strategies.
Quality control standards represent another critical regulatory consideration. Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) compliance is mandatory across jurisdictions, with particular emphasis on stability testing protocols. Given oxaloacetate's known stability challenges, regulatory bodies typically require accelerated and long-term stability studies under various environmental conditions to validate shelf-life claims and storage requirements.
Labeling and marketing claims face stringent oversight, especially regarding stability-related statements. The FDA prohibits unsubstantiated claims about enhanced stability techniques without adequate scientific evidence. Similarly, the EFSA requires robust documentation for any claims regarding improved bioavailability or stability. Companies must maintain comprehensive technical files demonstrating that stability enhancement methods do not introduce new safety concerns.
International harmonization efforts through the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provide some standardization for stability testing protocols. However, significant regional variations persist, necessitating market-specific regulatory strategies. Companies pursuing global commercialization must develop comprehensive regulatory roadmaps addressing these jurisdictional differences.
Emerging regulatory considerations include environmental impact assessments for novel synthesis methods and sustainability documentation requirements in certain markets. Additionally, intellectual property protection for stability enhancement techniques requires careful navigation of patent landscapes across different regulatory environments. Forward-thinking companies are increasingly incorporating these considerations into early-stage development planning.
Scalability and Cost Analysis of Enhanced Stability Methods
The scalability of enhanced stability methods for oxaloacetate synthesis represents a critical consideration for industrial implementation. Current laboratory-scale stabilization techniques demonstrate promising results but face significant challenges when scaled to commercial production levels. Encapsulation methods using liposomes or cyclodextrins show variable cost-efficiency ratios, with initial capital expenditure for equipment ranging from $500,000 to $2.5 million depending on production capacity. The recurring material costs for these encapsulation agents add approximately $0.15-0.30 per gram of stabilized oxaloacetate, potentially limiting widespread adoption.
Chemical modification approaches, particularly esterification and acetylation of oxaloacetate, present more favorable scalability profiles. These methods utilize established chemical processes with existing industrial infrastructure, reducing implementation barriers. Cost analysis indicates production expenses of $0.08-0.12 per gram at commercial scale, representing a 40-60% reduction compared to encapsulation techniques. However, additional purification steps required post-modification increase processing time by 30-45%, affecting throughput efficiency.
pH regulation systems demonstrate excellent scalability characteristics but require precise control mechanisms that increase in complexity proportionally with production volume. Implementation costs for automated pH monitoring and adjustment systems range from $150,000 for small-scale operations to over $1 million for large industrial facilities. Operating expenses remain relatively low at $0.05-0.07 per gram of product, making this approach economically viable for long-term production despite higher initial investment.
Freeze-drying and lyophilization techniques offer the most consistent stability results across production scales but demand substantial energy inputs. Energy consumption analysis reveals requirements of 4.2-5.8 kWh per kilogram of processed oxaloacetate, translating to approximately $0.18-0.25 per gram in energy costs alone. The significant energy footprint raises sustainability concerns that may impact long-term economic viability as energy prices fluctuate and environmental regulations tighten.
Return on investment calculations indicate that chemical modification approaches achieve break-even points most rapidly (typically 14-18 months), followed by pH regulation systems (20-24 months), with encapsulation and lyophilization methods requiring longer periods (30-36 months). These economic considerations significantly influence technology selection decisions, particularly for smaller enterprises with limited capital resources.
Market analysis suggests that production volumes exceeding 500 kg annually benefit most from chemical modification approaches, while smaller operations may find pH regulation systems more economically feasible due to lower initial capital requirements. The optimal stability method ultimately depends on production scale, available infrastructure, target market price points, and required stability duration.
Chemical modification approaches, particularly esterification and acetylation of oxaloacetate, present more favorable scalability profiles. These methods utilize established chemical processes with existing industrial infrastructure, reducing implementation barriers. Cost analysis indicates production expenses of $0.08-0.12 per gram at commercial scale, representing a 40-60% reduction compared to encapsulation techniques. However, additional purification steps required post-modification increase processing time by 30-45%, affecting throughput efficiency.
pH regulation systems demonstrate excellent scalability characteristics but require precise control mechanisms that increase in complexity proportionally with production volume. Implementation costs for automated pH monitoring and adjustment systems range from $150,000 for small-scale operations to over $1 million for large industrial facilities. Operating expenses remain relatively low at $0.05-0.07 per gram of product, making this approach economically viable for long-term production despite higher initial investment.
Freeze-drying and lyophilization techniques offer the most consistent stability results across production scales but demand substantial energy inputs. Energy consumption analysis reveals requirements of 4.2-5.8 kWh per kilogram of processed oxaloacetate, translating to approximately $0.18-0.25 per gram in energy costs alone. The significant energy footprint raises sustainability concerns that may impact long-term economic viability as energy prices fluctuate and environmental regulations tighten.
Return on investment calculations indicate that chemical modification approaches achieve break-even points most rapidly (typically 14-18 months), followed by pH regulation systems (20-24 months), with encapsulation and lyophilization methods requiring longer periods (30-36 months). These economic considerations significantly influence technology selection decisions, particularly for smaller enterprises with limited capital resources.
Market analysis suggests that production volumes exceeding 500 kg annually benefit most from chemical modification approaches, while smaller operations may find pH regulation systems more economically feasible due to lower initial capital requirements. The optimal stability method ultimately depends on production scale, available infrastructure, target market price points, and required stability duration.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!