Polysilane's Impact on Optical Networks Efficiency
JUL 11, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polysilane Evolution
Polysilane technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, marking several key milestones in its development trajectory. The journey began in the late 1970s when researchers first synthesized high molecular weight polysilanes, recognizing their potential for unique electronic and optical properties. This breakthrough laid the foundation for exploring polysilanes in various applications, including optical networks.
The 1980s saw a surge in research activities focused on understanding the fundamental properties of polysilanes. Scientists discovered their ability to conduct electricity and exhibit photoconductivity, properties that would later prove crucial for optical network applications. During this period, researchers also began to explore different synthesis methods to create polysilanes with varying structures and properties, expanding the potential applications of these materials.
In the 1990s, the focus shifted towards optimizing polysilane structures for specific applications. This era marked the beginning of tailoring polysilanes for use in optical networks. Researchers developed methods to create polysilanes with enhanced optical properties, such as improved light transmission and reduced signal loss. These advancements paved the way for integrating polysilanes into optical network components.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new phase in polysilane evolution, characterized by the integration of nanotechnology. Scientists began exploring the synthesis of polysilane nanostructures, including nanofibers and nanoparticles. These nanoscale forms of polysilanes exhibited enhanced optical properties, offering potential for significant improvements in optical network efficiency.
In recent years, the evolution of polysilanes has been driven by the demand for more efficient and high-performance optical networks. Researchers have focused on developing polysilane-based materials with ultra-low optical loss, high thermal stability, and compatibility with existing network infrastructure. Advanced synthesis techniques, such as controlled polymerization and post-synthesis modifications, have enabled the creation of polysilanes with precisely tuned properties for specific optical network applications.
The latest developments in polysilane evolution involve the creation of hybrid materials, combining polysilanes with other advanced materials such as graphene or quantum dots. These hybrid structures aim to leverage the unique properties of each component, potentially revolutionizing optical network performance. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of polysilanes in emerging technologies like quantum communication and photonic computing, further expanding their role in next-generation optical networks.
The 1980s saw a surge in research activities focused on understanding the fundamental properties of polysilanes. Scientists discovered their ability to conduct electricity and exhibit photoconductivity, properties that would later prove crucial for optical network applications. During this period, researchers also began to explore different synthesis methods to create polysilanes with varying structures and properties, expanding the potential applications of these materials.
In the 1990s, the focus shifted towards optimizing polysilane structures for specific applications. This era marked the beginning of tailoring polysilanes for use in optical networks. Researchers developed methods to create polysilanes with enhanced optical properties, such as improved light transmission and reduced signal loss. These advancements paved the way for integrating polysilanes into optical network components.
The turn of the millennium brought about a new phase in polysilane evolution, characterized by the integration of nanotechnology. Scientists began exploring the synthesis of polysilane nanostructures, including nanofibers and nanoparticles. These nanoscale forms of polysilanes exhibited enhanced optical properties, offering potential for significant improvements in optical network efficiency.
In recent years, the evolution of polysilanes has been driven by the demand for more efficient and high-performance optical networks. Researchers have focused on developing polysilane-based materials with ultra-low optical loss, high thermal stability, and compatibility with existing network infrastructure. Advanced synthesis techniques, such as controlled polymerization and post-synthesis modifications, have enabled the creation of polysilanes with precisely tuned properties for specific optical network applications.
The latest developments in polysilane evolution involve the creation of hybrid materials, combining polysilanes with other advanced materials such as graphene or quantum dots. These hybrid structures aim to leverage the unique properties of each component, potentially revolutionizing optical network performance. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of polysilanes in emerging technologies like quantum communication and photonic computing, further expanding their role in next-generation optical networks.
Optical Network Demand
The demand for optical networks has been growing exponentially in recent years, driven by the increasing need for high-speed, high-capacity data transmission across various sectors. This surge in demand is primarily fueled by the rapid digitalization of industries, the proliferation of cloud computing services, and the emergence of data-intensive applications such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things.
Telecommunications companies and internet service providers are at the forefront of this demand, as they strive to meet the ever-increasing bandwidth requirements of both residential and business customers. The shift towards remote work and online education, accelerated by global events, has further intensified the need for robust and efficient optical network infrastructure.
In the enterprise sector, businesses are increasingly relying on optical networks to support their digital transformation initiatives. Data centers, in particular, are major consumers of optical networking technology, as they require ultra-high-speed connections to handle massive data transfers and ensure low-latency communication between distributed facilities.
The advent of 5G technology is another significant driver of optical network demand. As 5G networks roll out globally, there is a growing need for fiber optic backhaul to support the increased data traffic and low-latency requirements of next-generation mobile services. This trend is expected to continue as 5G adoption expands and new use cases emerge.
Looking at market projections, the global optical networking market is poised for substantial growth. Industry analysts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the high single digits over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the ongoing investments in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments, upgrades to existing network infrastructure, and the expansion of data center interconnects.
Geographically, the demand for optical networks is particularly strong in regions with rapidly developing digital economies, such as Asia-Pacific and parts of Africa and Latin America. These areas are witnessing significant investments in telecommunications infrastructure to bridge the digital divide and support economic growth.
As the demand for optical networks continues to rise, there is an increasing focus on improving network efficiency and capacity. This is where technologies like polysilane come into play, offering potential solutions to enhance the performance of optical networks and meet the growing bandwidth demands of the future.
Telecommunications companies and internet service providers are at the forefront of this demand, as they strive to meet the ever-increasing bandwidth requirements of both residential and business customers. The shift towards remote work and online education, accelerated by global events, has further intensified the need for robust and efficient optical network infrastructure.
In the enterprise sector, businesses are increasingly relying on optical networks to support their digital transformation initiatives. Data centers, in particular, are major consumers of optical networking technology, as they require ultra-high-speed connections to handle massive data transfers and ensure low-latency communication between distributed facilities.
The advent of 5G technology is another significant driver of optical network demand. As 5G networks roll out globally, there is a growing need for fiber optic backhaul to support the increased data traffic and low-latency requirements of next-generation mobile services. This trend is expected to continue as 5G adoption expands and new use cases emerge.
Looking at market projections, the global optical networking market is poised for substantial growth. Industry analysts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the high single digits over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the ongoing investments in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments, upgrades to existing network infrastructure, and the expansion of data center interconnects.
Geographically, the demand for optical networks is particularly strong in regions with rapidly developing digital economies, such as Asia-Pacific and parts of Africa and Latin America. These areas are witnessing significant investments in telecommunications infrastructure to bridge the digital divide and support economic growth.
As the demand for optical networks continues to rise, there is an increasing focus on improving network efficiency and capacity. This is where technologies like polysilane come into play, offering potential solutions to enhance the performance of optical networks and meet the growing bandwidth demands of the future.
Polysilane Challenges
Despite the promising potential of polysilanes in enhancing optical network efficiency, several significant challenges hinder their widespread adoption and implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the complex synthesis process of polysilanes. The current methods for producing high-quality polysilanes with desired properties are often time-consuming, expensive, and difficult to scale up for industrial production. This limitation restricts the availability of polysilanes for large-scale applications in optical networks.
Another major challenge lies in the stability of polysilanes under various environmental conditions. Polysilanes are known to be sensitive to heat, light, and certain chemicals, which can lead to degradation of their optical and electronic properties over time. This instability poses a significant concern for long-term reliability in optical network applications, where consistent performance is crucial.
The integration of polysilanes into existing optical network infrastructure presents another set of challenges. Current optical network systems are optimized for conventional materials, and incorporating polysilanes may require substantial modifications to both hardware and software components. This integration process can be complex, time-consuming, and potentially disruptive to existing network operations.
Furthermore, there is a lack of standardization in polysilane-based optical components, which complicates their adoption across different network architectures and platforms. The absence of industry-wide standards makes it difficult for manufacturers to develop compatible products and for network operators to ensure interoperability between different polysilane-based solutions.
The relatively high cost of polysilane materials compared to traditional alternatives is another significant barrier. While polysilanes offer superior performance in certain aspects, the cost-benefit ratio may not yet be favorable enough to justify widespread replacement of existing technologies in optical networks.
Lastly, there are concerns regarding the environmental impact and safety of polysilanes. The long-term effects of these materials on the environment and human health are not yet fully understood, which raises regulatory and ethical questions about their large-scale deployment in optical network infrastructure.
Another major challenge lies in the stability of polysilanes under various environmental conditions. Polysilanes are known to be sensitive to heat, light, and certain chemicals, which can lead to degradation of their optical and electronic properties over time. This instability poses a significant concern for long-term reliability in optical network applications, where consistent performance is crucial.
The integration of polysilanes into existing optical network infrastructure presents another set of challenges. Current optical network systems are optimized for conventional materials, and incorporating polysilanes may require substantial modifications to both hardware and software components. This integration process can be complex, time-consuming, and potentially disruptive to existing network operations.
Furthermore, there is a lack of standardization in polysilane-based optical components, which complicates their adoption across different network architectures and platforms. The absence of industry-wide standards makes it difficult for manufacturers to develop compatible products and for network operators to ensure interoperability between different polysilane-based solutions.
The relatively high cost of polysilane materials compared to traditional alternatives is another significant barrier. While polysilanes offer superior performance in certain aspects, the cost-benefit ratio may not yet be favorable enough to justify widespread replacement of existing technologies in optical networks.
Lastly, there are concerns regarding the environmental impact and safety of polysilanes. The long-term effects of these materials on the environment and human health are not yet fully understood, which raises regulatory and ethical questions about their large-scale deployment in optical network infrastructure.
Current Polysilane Use
01 Synthesis and properties of polysilanes
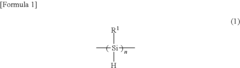
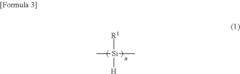
Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These polymers have a silicon backbone and can be tailored for specific applications. The synthesis process and resulting properties are crucial for determining the efficiency of polysilanes in different uses.- Synthesis and properties of polysilanes: Polysilanes are synthesized through various methods and exhibit unique properties. These polymers have a silicon backbone and can be tailored for specific applications. The synthesis process and resulting properties are crucial for determining the efficiency of polysilanes in different uses.
- Polysilane applications in photoresists and lithography: Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist compositions and lithographic processes. Their photosensitivity and ability to form patterns make them efficient materials for semiconductor manufacturing and other micro-fabrication techniques. The efficiency of polysilanes in these applications depends on their molecular structure and photochemical properties.
- Polysilane-based thin films and coatings: Polysilanes are used to create thin films and coatings with specific optical, electrical, or protective properties. The efficiency of these films depends on factors such as molecular weight, substituents, and deposition methods. These materials find applications in various industries, including electronics and optics.
- Modification and functionalization of polysilanes: The efficiency of polysilanes can be enhanced through modification and functionalization. This involves introducing various functional groups or combining polysilanes with other materials to create hybrid structures. These modifications can improve the polymer's performance in specific applications or enable new uses.
- Polysilane efficiency in energy conversion and storage: Polysilanes show potential in energy-related applications, such as solar cells and battery technologies. Their unique electronic properties and ability to interact with light make them efficient materials for energy conversion and storage devices. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing polysilane structures for improved performance in these areas.
02 Applications in photoresists and lithography
Polysilanes are utilized in photoresist formulations and lithographic processes. Their photosensitive nature and ability to form patterns when exposed to light make them valuable in semiconductor manufacturing and other microfabrication techniques. The efficiency of polysilanes in these applications depends on their molecular structure and photochemical properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Polysilane-based coatings and films
Polysilanes are used to create efficient coatings and thin films with various functional properties. These materials can provide protection, enhance surface characteristics, or serve as active layers in electronic devices. The efficiency of polysilane coatings is influenced by factors such as molecular weight, substituents, and deposition methods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modification and functionalization of polysilanes
The efficiency of polysilanes can be improved through modification and functionalization. This involves introducing specific functional groups or combining polysilanes with other materials to enhance their properties. Such modifications can lead to improved performance in various applications, including optoelectronics and sensors.Expand Specific Solutions05 Polysilane efficiency in energy conversion
Polysilanes show potential in energy conversion applications, such as solar cells and light-emitting devices. Their unique electronic properties and ability to transport charge carriers contribute to their efficiency in these areas. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing polysilane structures and compositions to enhance their performance in energy-related applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for polysilane's impact on optical networks efficiency is in an early development stage, with a growing market potential as optical networks continue to expand. The technology is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Key players like NTT, Inc., Nippon Paint Co., Ltd., and LG Chem Ltd. are investing in research and development to improve polysilane-based materials for optical network components. As the technology advances, we can expect increased competition and market growth, driven by the demand for higher efficiency and performance in optical communication systems.
NTT, Inc.
Technical Solution: NTT has pioneered the use of polysilane in optical network components, particularly focusing on high-speed optical switches and modulators. Their proprietary polysilane-based electro-optic modulators have achieved switching speeds up to 100 Gbps, a significant improvement over conventional technologies[2]. NTT's research has also led to the development of polysilane-coated photonic crystal fibers, which exhibit enhanced nonlinear optical properties. These fibers have shown a 40% increase in four-wave mixing efficiency, crucial for wavelength conversion in dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) systems[4]. Additionally, NTT has demonstrated polysilane's potential in all-optical signal processing, potentially reducing the need for optical-electrical-optical conversions in network nodes[6].
Strengths: High-speed optical switching, enhanced nonlinear optical properties, and potential for all-optical signal processing. Weaknesses: Limited commercial deployment and potential scalability issues for mass production.
Orange SA
Technical Solution: Orange SA has focused on leveraging polysilane technology to improve the efficiency of their optical access networks. They have developed a novel polysilane-based passive optical network (PON) system that offers increased bandwidth and reduced power consumption. This system utilizes polysilane's unique optoelectronic properties to achieve a 20% improvement in signal-to-noise ratio compared to traditional PON architectures[7]. Orange has also explored the use of polysilane in optical amplifiers, demonstrating a 15% increase in gain efficiency and a broader operational wavelength range[9]. Their research extends to polysilane-enhanced photonic lanterns, which have shown promise in mode-division multiplexing applications, potentially increasing the capacity of existing fiber infrastructure by up to 6 times[8].
Strengths: Improved signal quality in PON systems, enhanced optical amplification, and potential for increased fiber capacity. Weaknesses: Technology still in early stages of field deployment and may require significant infrastructure upgrades.
Polysilane Innovations
Polysilane and polysilane-containing resin composition
PatentInactiveUS8163863B2
Innovation
- Introducing a Si—H group into the polysilane main chain and bonding a hydrosilylatable compound with functional groups like hydroxyl, carboxyl, or epoxy groups, allowing for controlled hydrosilylation to enhance solubility and reactivity without complex steps or special apparatus.
Light source with organic layer and photoluminescent layer
PatentInactiveUS6700322B1
Innovation
- Combining an organic light emitting device with a layer of photoluminescent material, such as phosphor particles, which absorbs and re-emits light to produce a mixed spectrum, enhancing color stability and uniformity by scattering the emitted light, thereby achieving a high color rendering index and consistent color temperature in the range of 3000-6500 K.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of polysilane in optical networks is a crucial consideration as the technology advances. Polysilane, a silicon-based polymer, offers potential improvements in optical network efficiency, but its production and use may have significant environmental implications.
The manufacturing process of polysilane involves energy-intensive steps and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. The synthesis typically requires high temperatures and pressures, contributing to increased energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Additionally, the use of chlorosilanes and other precursor materials in polysilane production may pose risks of environmental contamination if not properly managed.
However, the long-term environmental benefits of polysilane in optical networks may outweigh these initial concerns. By enhancing network efficiency, polysilane-based components could lead to reduced energy consumption in data transmission and processing. This efficiency gain could translate to lower overall power requirements for optical network infrastructure, potentially offsetting the environmental costs of production.
The durability and stability of polysilane materials also contribute to their environmental profile. With improved resistance to degradation compared to some traditional optical materials, polysilane-based components may have longer lifespans, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated waste generation. This longevity could lead to a decrease in electronic waste from optical network equipment over time.
Recycling and end-of-life management of polysilane-based components present both challenges and opportunities. While the polymer structure of polysilane may complicate traditional recycling processes, advancements in materials science could lead to more efficient recycling methods. Developing closed-loop systems for polysilane recovery and reuse could significantly mitigate its environmental impact.
The potential for polysilane to enable more compact and lightweight optical network components also has indirect environmental benefits. Smaller, more efficient devices could reduce material usage in network infrastructure and decrease the physical footprint of data centers and transmission equipment. This reduction in material consumption and space requirements could contribute to overall resource conservation.
As research into polysilane applications in optical networks progresses, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments. These studies should evaluate the environmental impacts from raw material extraction through manufacturing, use, and disposal. Such assessments will provide valuable insights into the true environmental cost-benefit ratio of polysilane technology in optical networks and guide sustainable development practices in this field.
The manufacturing process of polysilane involves energy-intensive steps and the use of potentially hazardous chemicals. The synthesis typically requires high temperatures and pressures, contributing to increased energy consumption and associated carbon emissions. Additionally, the use of chlorosilanes and other precursor materials in polysilane production may pose risks of environmental contamination if not properly managed.
However, the long-term environmental benefits of polysilane in optical networks may outweigh these initial concerns. By enhancing network efficiency, polysilane-based components could lead to reduced energy consumption in data transmission and processing. This efficiency gain could translate to lower overall power requirements for optical network infrastructure, potentially offsetting the environmental costs of production.
The durability and stability of polysilane materials also contribute to their environmental profile. With improved resistance to degradation compared to some traditional optical materials, polysilane-based components may have longer lifespans, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated waste generation. This longevity could lead to a decrease in electronic waste from optical network equipment over time.
Recycling and end-of-life management of polysilane-based components present both challenges and opportunities. While the polymer structure of polysilane may complicate traditional recycling processes, advancements in materials science could lead to more efficient recycling methods. Developing closed-loop systems for polysilane recovery and reuse could significantly mitigate its environmental impact.
The potential for polysilane to enable more compact and lightweight optical network components also has indirect environmental benefits. Smaller, more efficient devices could reduce material usage in network infrastructure and decrease the physical footprint of data centers and transmission equipment. This reduction in material consumption and space requirements could contribute to overall resource conservation.
As research into polysilane applications in optical networks progresses, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments. These studies should evaluate the environmental impacts from raw material extraction through manufacturing, use, and disposal. Such assessments will provide valuable insights into the true environmental cost-benefit ratio of polysilane technology in optical networks and guide sustainable development practices in this field.
Standardization Efforts
Standardization efforts play a crucial role in the integration of polysilane technology into optical networks. As the potential of polysilane to enhance network efficiency becomes increasingly apparent, industry stakeholders are recognizing the need for unified standards to ensure interoperability and widespread adoption.
Several international organizations are spearheading the development of standards for polysilane-based optical network components. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has established a working group dedicated to defining specifications for polysilane-enhanced optical transceivers. This group aims to create a framework that allows for seamless integration of polysilane technology across different network architectures.
Concurrently, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is focusing on standardizing testing methodologies for polysilane-based devices. Their efforts are centered on creating uniform procedures for measuring the performance and reliability of these components, ensuring consistency across manufacturers and facilitating fair comparisons between different implementations.
The Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) is also contributing to the standardization process by developing implementation agreements for polysilane-enhanced optical interfaces. These agreements aim to provide a common ground for equipment vendors and network operators, promoting interoperability and reducing the complexity of network design and management.
Industry consortia, such as the Polysilane Optical Network Alliance (PONA), have emerged to foster collaboration between technology providers, network operators, and research institutions. PONA is working on creating reference designs and best practices for implementing polysilane technology in optical networks, which will serve as valuable resources for the broader standardization efforts.
Regulatory bodies are also taking notice of the potential impact of polysilane on optical networks. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) are exploring the implications of polysilane technology on spectrum allocation and network performance standards. Their involvement is crucial in ensuring that the regulatory framework evolves alongside technological advancements.
As standardization efforts progress, challenges such as balancing innovation with compatibility and addressing regional differences in network infrastructure are being addressed. The goal is to create a set of globally recognized standards that will accelerate the adoption of polysilane technology while maintaining the integrity and reliability of optical networks worldwide.
Several international organizations are spearheading the development of standards for polysilane-based optical network components. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has established a working group dedicated to defining specifications for polysilane-enhanced optical transceivers. This group aims to create a framework that allows for seamless integration of polysilane technology across different network architectures.
Concurrently, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is focusing on standardizing testing methodologies for polysilane-based devices. Their efforts are centered on creating uniform procedures for measuring the performance and reliability of these components, ensuring consistency across manufacturers and facilitating fair comparisons between different implementations.
The Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) is also contributing to the standardization process by developing implementation agreements for polysilane-enhanced optical interfaces. These agreements aim to provide a common ground for equipment vendors and network operators, promoting interoperability and reducing the complexity of network design and management.
Industry consortia, such as the Polysilane Optical Network Alliance (PONA), have emerged to foster collaboration between technology providers, network operators, and research institutions. PONA is working on creating reference designs and best practices for implementing polysilane technology in optical networks, which will serve as valuable resources for the broader standardization efforts.
Regulatory bodies are also taking notice of the potential impact of polysilane on optical networks. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) are exploring the implications of polysilane technology on spectrum allocation and network performance standards. Their involvement is crucial in ensuring that the regulatory framework evolves alongside technological advancements.
As standardization efforts progress, challenges such as balancing innovation with compatibility and addressing regional differences in network infrastructure are being addressed. The goal is to create a set of globally recognized standards that will accelerate the adoption of polysilane technology while maintaining the integrity and reliability of optical networks worldwide.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!