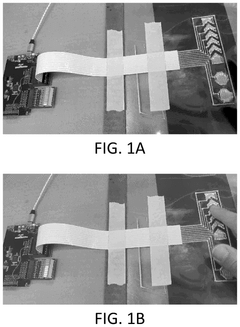
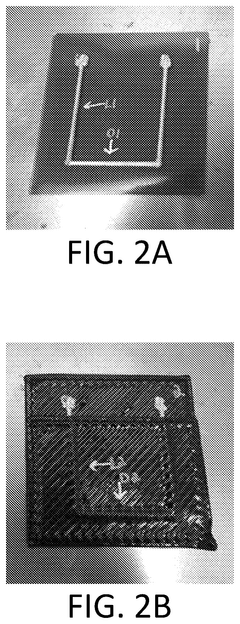
Regulatory And Compliance Considerations For MAP-Produced Materials
AUG 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MAP Technology Background and Objectives
Microwave-Assisted Processing (MAP) technology has evolved significantly over the past several decades, transforming from a simple heating method to a sophisticated materials processing technique. Initially developed in the 1940s for radar systems during World War II, microwave technology found its way into domestic applications in the 1950s. However, its application in materials processing began gaining traction only in the 1980s when researchers recognized its potential for efficient and selective heating capabilities.
The fundamental principle behind MAP involves the interaction between electromagnetic waves and materials, where polar molecules attempt to align with the oscillating electric field, generating heat through molecular friction. This volumetric heating mechanism differentiates MAP from conventional heating methods, offering advantages such as rapid processing times, reduced energy consumption, and the potential for unique material properties.
In recent years, MAP technology has expanded beyond simple heating applications to include sintering, synthesis, extraction, and modification of various materials. The technology has demonstrated particular promise in ceramic processing, polymer curing, pharmaceutical production, and food processing industries. The ability to achieve precise temperature control and selective heating has positioned MAP as a versatile tool in advanced materials manufacturing.
The regulatory landscape surrounding MAP-produced materials has become increasingly complex as applications diversify. Regulatory bodies worldwide have begun developing frameworks to address the unique characteristics and potential risks associated with microwave-processed materials. These considerations span from product safety and quality control to environmental impact and worker safety protocols.
The primary objective of exploring regulatory and compliance considerations for MAP-produced materials is to establish a comprehensive understanding of current regulatory frameworks across different regions and industries. This includes identifying gaps in existing regulations, anticipating future regulatory developments, and developing strategies for ensuring compliance while maintaining innovation and competitiveness.
Additionally, this technical research aims to evaluate how different material categories processed using MAP technology may require distinct regulatory approaches. For instance, MAP-produced pharmaceuticals face different compliance challenges compared to food products or construction materials processed using the same technology.
Understanding the intersection between technological capabilities and regulatory requirements is crucial for sustainable development of MAP applications. This involves not only compliance with current standards but also proactive engagement with regulatory bodies to shape future frameworks that appropriately address the unique aspects of microwave processing while ensuring public safety and environmental protection.
The fundamental principle behind MAP involves the interaction between electromagnetic waves and materials, where polar molecules attempt to align with the oscillating electric field, generating heat through molecular friction. This volumetric heating mechanism differentiates MAP from conventional heating methods, offering advantages such as rapid processing times, reduced energy consumption, and the potential for unique material properties.
In recent years, MAP technology has expanded beyond simple heating applications to include sintering, synthesis, extraction, and modification of various materials. The technology has demonstrated particular promise in ceramic processing, polymer curing, pharmaceutical production, and food processing industries. The ability to achieve precise temperature control and selective heating has positioned MAP as a versatile tool in advanced materials manufacturing.
The regulatory landscape surrounding MAP-produced materials has become increasingly complex as applications diversify. Regulatory bodies worldwide have begun developing frameworks to address the unique characteristics and potential risks associated with microwave-processed materials. These considerations span from product safety and quality control to environmental impact and worker safety protocols.
The primary objective of exploring regulatory and compliance considerations for MAP-produced materials is to establish a comprehensive understanding of current regulatory frameworks across different regions and industries. This includes identifying gaps in existing regulations, anticipating future regulatory developments, and developing strategies for ensuring compliance while maintaining innovation and competitiveness.
Additionally, this technical research aims to evaluate how different material categories processed using MAP technology may require distinct regulatory approaches. For instance, MAP-produced pharmaceuticals face different compliance challenges compared to food products or construction materials processed using the same technology.
Understanding the intersection between technological capabilities and regulatory requirements is crucial for sustainable development of MAP applications. This involves not only compliance with current standards but also proactive engagement with regulatory bodies to shape future frameworks that appropriately address the unique aspects of microwave processing while ensuring public safety and environmental protection.
Market Demand Analysis for MAP-Produced Materials
The market for MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) produced materials has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing consumer demand for fresh, minimally processed foods with extended shelf life. The global MAP market was valued at approximately 13.8 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 21.4 billion USD by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 7.6% during the forecast period.
Food and beverage industries constitute the largest application segment for MAP-produced materials, accounting for over 65% of the total market share. Within this segment, meat and poultry products represent the highest demand, followed by fruits and vegetables, bakery products, and dairy items. The pharmaceutical sector is emerging as another significant consumer of MAP technologies, particularly for oxygen-sensitive medications and medical devices.
Regionally, North America and Europe dominate the MAP materials market due to stringent food safety regulations, advanced retail infrastructure, and high consumer awareness regarding food quality and safety. However, Asia-Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth rate, attributed to rapid urbanization, changing dietary preferences, increasing disposable incomes, and expanding organized retail sectors in countries like China, India, and Japan.
Consumer trends significantly influencing market demand include the growing preference for convenience foods, increasing awareness about food waste reduction, and rising concerns about chemical preservatives. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated these trends, with heightened consumer focus on food safety and extended shelf life of packaged products, driving additional demand for MAP solutions.
From a regulatory perspective, market demand is being shaped by evolving compliance requirements across different regions. Manufacturers are increasingly seeking MAP materials that not only extend product shelf life but also comply with food contact regulations, sustainability mandates, and recyclability requirements. This has created a growing sub-segment for eco-friendly MAP solutions that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Industry surveys indicate that 78% of food manufacturers consider regulatory compliance as a "very important" factor when selecting MAP materials, highlighting the critical intersection between market demand and regulatory considerations. Additionally, 63% of consumers report willingness to pay premium prices for products with extended freshness that utilize environmentally responsible packaging technologies.
The competitive landscape features both established packaging giants and innovative startups focusing on novel MAP technologies. Market differentiation increasingly centers on developing materials that address both regulatory compliance and sustainability concerns while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
Food and beverage industries constitute the largest application segment for MAP-produced materials, accounting for over 65% of the total market share. Within this segment, meat and poultry products represent the highest demand, followed by fruits and vegetables, bakery products, and dairy items. The pharmaceutical sector is emerging as another significant consumer of MAP technologies, particularly for oxygen-sensitive medications and medical devices.
Regionally, North America and Europe dominate the MAP materials market due to stringent food safety regulations, advanced retail infrastructure, and high consumer awareness regarding food quality and safety. However, Asia-Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth rate, attributed to rapid urbanization, changing dietary preferences, increasing disposable incomes, and expanding organized retail sectors in countries like China, India, and Japan.
Consumer trends significantly influencing market demand include the growing preference for convenience foods, increasing awareness about food waste reduction, and rising concerns about chemical preservatives. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated these trends, with heightened consumer focus on food safety and extended shelf life of packaged products, driving additional demand for MAP solutions.
From a regulatory perspective, market demand is being shaped by evolving compliance requirements across different regions. Manufacturers are increasingly seeking MAP materials that not only extend product shelf life but also comply with food contact regulations, sustainability mandates, and recyclability requirements. This has created a growing sub-segment for eco-friendly MAP solutions that maintain performance while reducing environmental impact.
Industry surveys indicate that 78% of food manufacturers consider regulatory compliance as a "very important" factor when selecting MAP materials, highlighting the critical intersection between market demand and regulatory considerations. Additionally, 63% of consumers report willingness to pay premium prices for products with extended freshness that utilize environmentally responsible packaging technologies.
The competitive landscape features both established packaging giants and innovative startups focusing on novel MAP technologies. Market differentiation increasingly centers on developing materials that address both regulatory compliance and sustainability concerns while maintaining or improving performance characteristics.
Current Regulatory Landscape and Challenges
The regulatory landscape for Microwave-Assisted Processing (MAP) produced materials remains fragmented globally, with significant variations across jurisdictions. In the United States, the FDA has established guidelines for food products processed using novel technologies, including MAP, but specific regulations tailored to MAP-produced materials are still evolving. The European Union, through its Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283, requires safety assessments for foods produced using new processing methods, potentially encompassing MAP technologies when they substantially alter food composition or structure.
Japan and South Korea have implemented more progressive regulatory frameworks that explicitly address advanced processing technologies, including provisions that may apply to MAP-produced materials. However, these frameworks primarily focus on food safety rather than comprehensive material characterization and standardization.
A significant challenge in the current regulatory environment is the lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for MAP-produced materials. Conventional testing methods may not adequately capture the unique characteristics and potential risks associated with materials processed through microwave technology. This gap creates uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially delays market entry for innovative products.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the rapid pace of technological advancement in material processing. The inherent complexity of MAP technology—which can produce materials with novel properties through non-conventional heating mechanisms—presents unique challenges for traditional regulatory approaches that were developed for conventional processing methods.
Cross-border trade of MAP-produced materials faces additional complications due to regulatory inconsistencies. Materials approved in one jurisdiction may face barriers in others, creating market fragmentation and increasing compliance costs for global manufacturers. This regulatory divergence particularly impacts small and medium enterprises that lack resources for multiple compliance processes.
Industry stakeholders have highlighted the need for harmonized international standards and mutual recognition agreements to streamline regulatory processes. Several industry associations have formed working groups to develop consensus-based standards that could inform future regulatory frameworks, though these efforts remain in preliminary stages.
Emerging concerns about the long-term environmental and health impacts of MAP-produced materials have prompted some regulatory bodies to adopt precautionary approaches, requiring extensive safety data before granting approvals. This cautious stance, while protective of public interests, may inadvertently slow innovation in the field.
Japan and South Korea have implemented more progressive regulatory frameworks that explicitly address advanced processing technologies, including provisions that may apply to MAP-produced materials. However, these frameworks primarily focus on food safety rather than comprehensive material characterization and standardization.
A significant challenge in the current regulatory environment is the lack of standardized testing protocols specifically designed for MAP-produced materials. Conventional testing methods may not adequately capture the unique characteristics and potential risks associated with materials processed through microwave technology. This gap creates uncertainty for manufacturers and potentially delays market entry for innovative products.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the rapid pace of technological advancement in material processing. The inherent complexity of MAP technology—which can produce materials with novel properties through non-conventional heating mechanisms—presents unique challenges for traditional regulatory approaches that were developed for conventional processing methods.
Cross-border trade of MAP-produced materials faces additional complications due to regulatory inconsistencies. Materials approved in one jurisdiction may face barriers in others, creating market fragmentation and increasing compliance costs for global manufacturers. This regulatory divergence particularly impacts small and medium enterprises that lack resources for multiple compliance processes.
Industry stakeholders have highlighted the need for harmonized international standards and mutual recognition agreements to streamline regulatory processes. Several industry associations have formed working groups to develop consensus-based standards that could inform future regulatory frameworks, though these efforts remain in preliminary stages.
Emerging concerns about the long-term environmental and health impacts of MAP-produced materials have prompted some regulatory bodies to adopt precautionary approaches, requiring extensive safety data before granting approvals. This cautious stance, while protective of public interests, may inadvertently slow innovation in the field.
Current Compliance Frameworks and Solutions
01 Regulatory compliance management systems for MAP-produced materials
Systems designed to manage regulatory compliance for materials produced through MAP (Manufacturing Automation Protocol) processes. These systems include automated tracking of regulatory requirements, documentation management, and verification processes to ensure that MAP-produced materials meet applicable standards and regulations. The systems can identify regulatory gaps, manage compliance workflows, and provide audit trails for regulatory submissions.- Regulatory compliance management systems for MAP materials: Systems designed to manage regulatory compliance for MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging) produced materials. These systems track and ensure adherence to various regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions. They include features for monitoring changes in regulations, documenting compliance efforts, and generating compliance reports. These systems help manufacturers maintain compliance with food safety regulations, packaging standards, and other relevant requirements for MAP materials.
- Data management for MAP regulatory documentation: Solutions focused on managing the extensive documentation required for regulatory compliance of MAP-produced materials. These systems organize, store, and retrieve regulatory documents efficiently, ensuring that all necessary documentation is available during audits or inspections. They include features for document version control, approval workflows, and secure storage of sensitive regulatory information related to modified atmosphere packaging materials.
- Supply chain compliance tracking for MAP products: Systems that monitor and verify regulatory compliance throughout the supply chain for MAP-produced materials. These solutions track materials from raw components to finished packaging products, ensuring that all stages meet regulatory requirements. They provide visibility into supplier compliance, material certifications, and chain of custody documentation, helping companies manage risk and ensure that their MAP materials meet all applicable regulations across different markets.
- Automated compliance verification for packaging materials: Automated systems that verify compliance of MAP materials with relevant regulations and standards. These systems use algorithms and databases to check material specifications against regulatory requirements, flagging potential compliance issues. They can automatically generate compliance certificates, perform gap analyses, and provide recommendations for addressing non-compliance. This automation reduces human error and ensures consistent application of regulatory standards to MAP materials.
- Cross-border regulatory management for MAP technologies: Solutions specifically designed to handle the complexity of cross-border regulatory requirements for MAP-produced materials. These systems help companies navigate different regulatory frameworks across multiple countries, ensuring that packaging materials comply with all relevant international standards. They include features for managing country-specific documentation, tracking regulatory changes in different jurisdictions, and facilitating customs clearance for MAP materials in international trade.
02 Data management and documentation for regulatory compliance
Solutions for managing data and documentation required for regulatory compliance of MAP-produced materials. These include systems for organizing, storing, and retrieving compliance-related documents, maintaining records of material specifications, production processes, and quality control measures. The solutions enable efficient handling of regulatory submissions, facilitate data exchange between stakeholders, and ensure the integrity and security of compliance-related information.Expand Specific Solutions03 Risk assessment and mitigation for MAP-produced materials
Methodologies and systems for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with MAP-produced materials in regulatory contexts. These approaches include risk analysis frameworks, predictive modeling for compliance issues, and automated risk scoring mechanisms. The systems help organizations prioritize compliance efforts, allocate resources effectively, and implement preventive measures to address potential regulatory challenges before they become problematic.Expand Specific Solutions04 Blockchain and distributed ledger technology for regulatory compliance
Implementation of blockchain and distributed ledger technologies to enhance transparency, traceability, and trust in regulatory compliance for MAP-produced materials. These solutions create immutable records of material origins, production processes, testing results, and compliance certifications. The technology enables secure sharing of compliance information across supply chains, facilitates verification by regulatory authorities, and reduces fraud risks in compliance documentation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Automated compliance monitoring and reporting systems
Advanced systems that automate the monitoring and reporting of regulatory compliance for MAP-produced materials. These systems continuously track compliance status, automatically generate required regulatory reports, and provide real-time alerts for potential compliance issues. They incorporate machine learning algorithms to adapt to changing regulatory requirements, analyze compliance trends, and suggest proactive measures to maintain compliance with evolving standards and regulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Regulatory Bodies and Industry Players
The regulatory landscape for MAP-produced materials is evolving within a competitive market characterized by early-stage development but rapid growth potential. Currently, the market is fragmented with key players including BASF Corp., Dow Global Technologies, and Stora Enso Oyj focusing on establishing compliance frameworks. Academic institutions like Northwestern University are collaborating with industry to develop standardized testing protocols, while companies such as GLOBALFOUNDRIES and Micron Technology are addressing semiconductor-specific compliance challenges. The regulatory maturity varies significantly across sectors, with pharmaceutical applications (represented by Zhejiang Raybow Pharmaceutical) facing stricter oversight compared to packaging applications (Huhtamaki Molded Fiber Technology). As the technology matures, we anticipate consolidation of compliance standards and increased regulatory clarity across diverse material applications.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM has implemented an advanced regulatory compliance strategy for MAP materials focused on sustainable solutions that meet stringent global standards. Their Arnitel® VT breathable film technology for MAP applications incorporates a regulatory-by-design approach where compliance considerations are integrated from the earliest R&D stages. DSM's compliance framework includes specialized testing protocols for oxygen and moisture transmission rates that align with FDA, EU, and Asian regulatory requirements. The company has developed a proprietary Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology specifically for MAP materials that evaluates environmental impact while ensuring regulatory compliance across the product lifecycle. DSM provides customers with detailed Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and regulatory compliance documentation packages tailored to specific market entry requirements, facilitating faster approval processes in multiple jurisdictions.
Strengths: Strong integration of sustainability with compliance; specialized testing protocols for MAP-specific performance characteristics; comprehensive documentation support for customers. Weaknesses: Focus on high-performance materials may result in higher costs; balancing innovation with established regulatory frameworks can slow time-to-market.
Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Bakelite has developed a specialized regulatory compliance system for their MAP materials that focuses particularly on food contact applications. Their SUMILITE™ MAP films incorporate a multi-tier compliance verification process that addresses both material composition and performance characteristics under various environmental conditions. The company maintains dedicated regulatory affairs teams in Asia, Europe, and North America to ensure regional compliance with local regulations including Japan's JHOSPA standards, EU 10/2011, and FDA requirements. Sumitomo's approach includes comprehensive migration testing for both intentionally added substances and non-intentionally added substances (NIAS), with specialized protocols for different food types and storage conditions. Their regulatory documentation system provides full material traceability from raw material sourcing through manufacturing, with particular attention to additives and processing aids that may impact regulatory status.
Strengths: Strong expertise in Asian regulatory frameworks; comprehensive migration testing protocols; excellent traceability systems. Weaknesses: May face challenges harmonizing approaches between Asian and Western regulatory frameworks; potentially higher compliance costs due to comprehensive testing requirements.
Critical Regulatory Standards and Guidelines
Systems and methods for compliance mapping of a local feature for additive manufacturing applications
PatentWO2025014536A1
Innovation
- The system divides a model into a submodel of interest and a remaining section, meshes the remaining section with a coarse mesh, calculates compliance matrices, and then finely meshes and analyzes the submodel, allowing for faster resolution of residual stresses by considering the effect of the remaining section on the submodel.
Conductive articles and methods for additive manufacturing thereof
PatentPendingUS20250163278A1
Innovation
- The development of a coreactive composition comprising reactive chemical components that form a conductive portion of an article, achieving a tensile modulus of at least 5 MPa and electrical conductivity of at least 2 S/m within 48 hours, with a solvent content less than 5 wt% and effective conductive filler content.
International Regulatory Harmonization Opportunities
The global nature of advanced manufacturing technologies like MAP (Material Acceleration Platforms) necessitates coordinated international regulatory approaches. Currently, significant disparities exist between regulatory frameworks across major manufacturing regions, creating barriers to the global adoption and commercialization of MAP-produced materials. These inconsistencies increase compliance costs and delay market entry for innovative materials.
Harmonization efforts present substantial opportunities to streamline regulatory processes while maintaining safety and quality standards. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have established working groups specifically addressing advanced manufacturing technologies, providing foundations for global standardization of MAP methodologies and outputs.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between regulatory bodies represent another promising avenue for harmonization. The existing MRAs between the FDA and European Medicines Agency could serve as templates for similar arrangements specific to MAP-produced materials, potentially reducing redundant testing requirements and accelerating approval processes across multiple jurisdictions.
Regional regulatory clusters are emerging as intermediate steps toward global harmonization. The European Union's harmonized approach through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) demonstrates how regional alignment can facilitate broader international cooperation. Similar regional frameworks are developing in the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) region and among BRICS nations.
Data standardization presents a critical opportunity for regulatory alignment. Establishing common data formats, reporting requirements, and validation methodologies for MAP-generated materials would enable more efficient regulatory reviews across borders. The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) model from pharmaceutical regulation offers valuable lessons for implementing such data standardization initiatives.
Industry consortia are increasingly driving pre-competitive collaboration on regulatory harmonization. Organizations like the International Council on Nanotechnology and the Materials Genome Initiative International Alliance are developing shared approaches to characterization, testing protocols, and risk assessment methodologies that could inform unified regulatory frameworks.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and distributed ledger systems offer promising tools for creating transparent, immutable records of material development, testing, and compliance across international boundaries, potentially facilitating regulatory trust and reciprocity between jurisdictions while maintaining appropriate oversight of MAP-produced materials.
Harmonization efforts present substantial opportunities to streamline regulatory processes while maintaining safety and quality standards. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have established working groups specifically addressing advanced manufacturing technologies, providing foundations for global standardization of MAP methodologies and outputs.
Mutual recognition agreements (MRAs) between regulatory bodies represent another promising avenue for harmonization. The existing MRAs between the FDA and European Medicines Agency could serve as templates for similar arrangements specific to MAP-produced materials, potentially reducing redundant testing requirements and accelerating approval processes across multiple jurisdictions.
Regional regulatory clusters are emerging as intermediate steps toward global harmonization. The European Union's harmonized approach through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) demonstrates how regional alignment can facilitate broader international cooperation. Similar regional frameworks are developing in the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) region and among BRICS nations.
Data standardization presents a critical opportunity for regulatory alignment. Establishing common data formats, reporting requirements, and validation methodologies for MAP-generated materials would enable more efficient regulatory reviews across borders. The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) model from pharmaceutical regulation offers valuable lessons for implementing such data standardization initiatives.
Industry consortia are increasingly driving pre-competitive collaboration on regulatory harmonization. Organizations like the International Council on Nanotechnology and the Materials Genome Initiative International Alliance are developing shared approaches to characterization, testing protocols, and risk assessment methodologies that could inform unified regulatory frameworks.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and distributed ledger systems offer promising tools for creating transparent, immutable records of material development, testing, and compliance across international boundaries, potentially facilitating regulatory trust and reciprocity between jurisdictions while maintaining appropriate oversight of MAP-produced materials.
Risk Management Strategies for MAP Compliance
Effective risk management is essential for organizations implementing Microwave-Assisted Processing (MAP) technologies to ensure regulatory compliance. A comprehensive risk management framework should begin with thorough risk identification, cataloging all potential compliance risks across jurisdictions where MAP-produced materials will be marketed. This includes identifying regulatory gaps, as many regions lack specific guidelines for novel processing technologies like MAP.
Risk assessment methodologies must be quantitative where possible, evaluating both the likelihood and potential impact of compliance failures. Organizations should develop risk matrices specifically tailored to MAP applications, considering factors such as material type, processing parameters, and intended use of final products. Particular attention should be paid to food safety risks when MAP is used in food processing applications.
Preventive control measures form the cornerstone of effective compliance risk management. These include implementing robust documentation systems that track all processing parameters, conducting regular validation studies to verify that MAP processes consistently meet regulatory requirements, and establishing clear standard operating procedures (SOPs) for MAP equipment operation and maintenance. Organizations should also consider implementing automated compliance monitoring systems that can alert operators to potential regulatory violations in real-time.
Contingency planning represents another critical component of MAP compliance risk management. Companies should develop detailed response protocols for potential compliance failures, including communication strategies for regulatory authorities, customers, and other stakeholders. These plans should outline specific remediation steps based on the nature and severity of compliance issues.
Regular compliance audits and reviews should be conducted by independent third parties familiar with both MAP technology and relevant regulatory frameworks. These audits should evaluate not only current compliance status but also assess the organization's preparedness for emerging regulatory changes that may impact MAP applications.
Staff training programs must be developed specifically for MAP compliance, ensuring that all personnel understand the unique regulatory considerations associated with microwave processing technologies. This training should be regularly updated to reflect evolving regulatory landscapes and technological advancements in MAP applications.
Finally, organizations should establish cross-functional compliance teams that include representatives from R&D, quality assurance, legal, and regulatory affairs departments. These teams should meet regularly to review compliance status, discuss emerging regulatory trends, and update risk management strategies accordingly. By implementing these comprehensive risk management approaches, organizations can navigate the complex regulatory landscape surrounding MAP technologies while minimizing compliance risks.
Risk assessment methodologies must be quantitative where possible, evaluating both the likelihood and potential impact of compliance failures. Organizations should develop risk matrices specifically tailored to MAP applications, considering factors such as material type, processing parameters, and intended use of final products. Particular attention should be paid to food safety risks when MAP is used in food processing applications.
Preventive control measures form the cornerstone of effective compliance risk management. These include implementing robust documentation systems that track all processing parameters, conducting regular validation studies to verify that MAP processes consistently meet regulatory requirements, and establishing clear standard operating procedures (SOPs) for MAP equipment operation and maintenance. Organizations should also consider implementing automated compliance monitoring systems that can alert operators to potential regulatory violations in real-time.
Contingency planning represents another critical component of MAP compliance risk management. Companies should develop detailed response protocols for potential compliance failures, including communication strategies for regulatory authorities, customers, and other stakeholders. These plans should outline specific remediation steps based on the nature and severity of compliance issues.
Regular compliance audits and reviews should be conducted by independent third parties familiar with both MAP technology and relevant regulatory frameworks. These audits should evaluate not only current compliance status but also assess the organization's preparedness for emerging regulatory changes that may impact MAP applications.
Staff training programs must be developed specifically for MAP compliance, ensuring that all personnel understand the unique regulatory considerations associated with microwave processing technologies. This training should be regularly updated to reflect evolving regulatory landscapes and technological advancements in MAP applications.
Finally, organizations should establish cross-functional compliance teams that include representatives from R&D, quality assurance, legal, and regulatory affairs departments. These teams should meet regularly to review compliance status, discuss emerging regulatory trends, and update risk management strategies accordingly. By implementing these comprehensive risk management approaches, organizations can navigate the complex regulatory landscape surrounding MAP technologies while minimizing compliance risks.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!