Ammonium Hydroxide in the Development of Sustainable Agrochemicals
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide in Agrochemicals: Background and Objectives
Ammonium hydroxide has played a significant role in the development of agrochemicals, serving as a crucial component in various agricultural applications. The use of this compound in agriculture dates back to the early 20th century when the Haber-Bosch process revolutionized the production of ammonia, making it more accessible and cost-effective for agricultural use. Since then, ammonium hydroxide has been widely utilized in fertilizers, pesticides, and other agrochemical formulations.
The primary objective of researching ammonium hydroxide in the context of sustainable agrochemicals is to address the growing demand for environmentally friendly and efficient agricultural solutions. As global population continues to rise, there is an increasing need for enhanced crop yields and food production. Simultaneously, there is a pressing requirement to minimize the environmental impact of agricultural practices, particularly in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preserving soil health.
Ammonium hydroxide's versatility in agrochemical applications stems from its ability to provide readily available nitrogen to plants, which is essential for growth and development. It can be used directly as a fertilizer or as a precursor in the production of other nitrogen-based fertilizers. Additionally, its alkaline properties make it useful in pH adjustment of soil and in the formulation of certain pesticides.
The evolution of ammonium hydroxide usage in agrochemicals has been marked by continuous efforts to improve its efficiency and reduce potential negative environmental impacts. Research has focused on optimizing application methods, developing slow-release formulations, and exploring synergistic effects with other agrochemical components. These advancements aim to enhance nutrient uptake by plants while minimizing nitrogen losses through volatilization, leaching, and runoff.
Recent technological trends in the field of sustainable agrochemicals have emphasized the importance of precision agriculture and smart delivery systems. This has led to increased interest in developing novel formulations of ammonium hydroxide-based products that can be more precisely targeted and controlled in their release. Such innovations aim to maximize the benefits of ammonium hydroxide while minimizing its potential drawbacks, such as ammonia volatilization and nitrate leaching.
The ongoing research on ammonium hydroxide in sustainable agrochemicals is driven by the need to balance agricultural productivity with environmental stewardship. Key objectives include improving nitrogen use efficiency, reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with fertilizer production and application, and developing more sustainable manufacturing processes for ammonium hydroxide-based products. These goals align with broader initiatives in sustainable agriculture and the circular economy, emphasizing the importance of resource conservation and environmental protection in modern agricultural practices.
The primary objective of researching ammonium hydroxide in the context of sustainable agrochemicals is to address the growing demand for environmentally friendly and efficient agricultural solutions. As global population continues to rise, there is an increasing need for enhanced crop yields and food production. Simultaneously, there is a pressing requirement to minimize the environmental impact of agricultural practices, particularly in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preserving soil health.
Ammonium hydroxide's versatility in agrochemical applications stems from its ability to provide readily available nitrogen to plants, which is essential for growth and development. It can be used directly as a fertilizer or as a precursor in the production of other nitrogen-based fertilizers. Additionally, its alkaline properties make it useful in pH adjustment of soil and in the formulation of certain pesticides.
The evolution of ammonium hydroxide usage in agrochemicals has been marked by continuous efforts to improve its efficiency and reduce potential negative environmental impacts. Research has focused on optimizing application methods, developing slow-release formulations, and exploring synergistic effects with other agrochemical components. These advancements aim to enhance nutrient uptake by plants while minimizing nitrogen losses through volatilization, leaching, and runoff.
Recent technological trends in the field of sustainable agrochemicals have emphasized the importance of precision agriculture and smart delivery systems. This has led to increased interest in developing novel formulations of ammonium hydroxide-based products that can be more precisely targeted and controlled in their release. Such innovations aim to maximize the benefits of ammonium hydroxide while minimizing its potential drawbacks, such as ammonia volatilization and nitrate leaching.
The ongoing research on ammonium hydroxide in sustainable agrochemicals is driven by the need to balance agricultural productivity with environmental stewardship. Key objectives include improving nitrogen use efficiency, reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with fertilizer production and application, and developing more sustainable manufacturing processes for ammonium hydroxide-based products. These goals align with broader initiatives in sustainable agriculture and the circular economy, emphasizing the importance of resource conservation and environmental protection in modern agricultural practices.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Agrochemical Solutions
The sustainable agrochemical market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing environmental concerns and the demand for eco-friendly farming practices. This sector encompasses a wide range of products, including bio-based pesticides, organic fertilizers, and sustainable crop protection solutions. The global market for sustainable agrochemicals is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of over 7% in the coming years, with a particular focus on products that reduce environmental impact while maintaining crop yields.
Ammonium hydroxide, as a potential component in sustainable agrochemical formulations, is gaining attention due to its versatility and relatively low environmental footprint compared to traditional chemical alternatives. The market for ammonium hydroxide-based agrochemicals is still in its nascent stages but shows promising growth potential, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Key market drivers include the rising adoption of precision agriculture techniques, increasing organic farming practices, and growing consumer awareness about food safety and environmental sustainability. Government initiatives promoting sustainable agriculture and restrictions on harmful chemical pesticides are also contributing to market expansion. Developing economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are emerging as lucrative markets for sustainable agrochemicals, driven by the need to increase agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental degradation.
However, the market faces challenges such as higher production costs compared to conventional agrochemicals, which can impact affordability for small-scale farmers. Additionally, the efficacy of some sustainable solutions is still being debated, leading to slower adoption rates in certain regions. Despite these challenges, the long-term outlook for sustainable agrochemicals remains positive, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving product performance and cost-effectiveness.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established agrochemical companies diversifying into sustainable solutions and innovative startups specializing in eco-friendly products. Strategic partnerships between research institutions and industry players are becoming increasingly common, accelerating the development and commercialization of novel sustainable agrochemical solutions.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards organic and sustainably produced food products, creating a ripple effect throughout the agricultural supply chain. This trend is expected to further boost the demand for sustainable agrochemicals, including those potentially incorporating ammonium hydroxide, in the coming years. As the market matures, we anticipate increased investment in research and development, leading to more advanced and efficient sustainable agrochemical formulations that can compete effectively with traditional chemical alternatives.
Ammonium hydroxide, as a potential component in sustainable agrochemical formulations, is gaining attention due to its versatility and relatively low environmental footprint compared to traditional chemical alternatives. The market for ammonium hydroxide-based agrochemicals is still in its nascent stages but shows promising growth potential, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Key market drivers include the rising adoption of precision agriculture techniques, increasing organic farming practices, and growing consumer awareness about food safety and environmental sustainability. Government initiatives promoting sustainable agriculture and restrictions on harmful chemical pesticides are also contributing to market expansion. Developing economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are emerging as lucrative markets for sustainable agrochemicals, driven by the need to increase agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental degradation.
However, the market faces challenges such as higher production costs compared to conventional agrochemicals, which can impact affordability for small-scale farmers. Additionally, the efficacy of some sustainable solutions is still being debated, leading to slower adoption rates in certain regions. Despite these challenges, the long-term outlook for sustainable agrochemicals remains positive, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving product performance and cost-effectiveness.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established agrochemical companies diversifying into sustainable solutions and innovative startups specializing in eco-friendly products. Strategic partnerships between research institutions and industry players are becoming increasingly common, accelerating the development and commercialization of novel sustainable agrochemical solutions.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards organic and sustainably produced food products, creating a ripple effect throughout the agricultural supply chain. This trend is expected to further boost the demand for sustainable agrochemicals, including those potentially incorporating ammonium hydroxide, in the coming years. As the market matures, we anticipate increased investment in research and development, leading to more advanced and efficient sustainable agrochemical formulations that can compete effectively with traditional chemical alternatives.
Current Status and Challenges in Ammonium Hydroxide Application
The application of ammonium hydroxide in sustainable agrochemicals has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by the growing demand for environmentally friendly agricultural practices. Currently, ammonium hydroxide is widely used as a nitrogen source in fertilizers, playing a crucial role in crop nutrition and soil management. Its popularity stems from its high nitrogen content and ease of application, making it an attractive option for farmers seeking to optimize crop yields.
However, the widespread use of ammonium hydroxide in agriculture faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for ammonia volatilization, which can lead to significant nitrogen losses and reduced fertilizer efficiency. This not only impacts crop productivity but also contributes to environmental issues such as air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Researchers and agrochemical companies are actively working on developing formulations and application techniques to mitigate these losses and improve nitrogen use efficiency.
Another challenge lies in the production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide. The manufacturing process is energy-intensive, often relying on fossil fuels, which raises questions about its long-term sustainability. Additionally, the corrosive nature of ammonium hydroxide poses safety risks during handling and storage, necessitating strict safety protocols and specialized equipment.
The agricultural sector is also grappling with the need to balance the benefits of ammonium hydroxide use with potential environmental impacts. Excessive application can lead to soil acidification and nutrient imbalances, affecting long-term soil health and biodiversity. This has prompted research into precision agriculture techniques and smart fertilizer formulations that optimize nutrient delivery while minimizing environmental footprint.
Regulatory pressures present another hurdle in the widespread adoption of ammonium hydroxide-based agrochemicals. As environmental regulations become more stringent, manufacturers and farmers must adapt to new guidelines governing the use and disposal of nitrogen-based fertilizers. This has spurred innovation in controlled-release formulations and enhanced efficiency fertilizers that aim to comply with regulatory standards while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Despite these challenges, the field of sustainable agrochemicals continues to evolve, with ammonium hydroxide playing a central role. Researchers are exploring novel approaches such as nanotechnology-enhanced delivery systems and bio-based alternatives to traditional ammonium hydroxide formulations. These innovations aim to address current limitations and pave the way for more sustainable agricultural practices.
However, the widespread use of ammonium hydroxide in agriculture faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for ammonia volatilization, which can lead to significant nitrogen losses and reduced fertilizer efficiency. This not only impacts crop productivity but also contributes to environmental issues such as air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Researchers and agrochemical companies are actively working on developing formulations and application techniques to mitigate these losses and improve nitrogen use efficiency.
Another challenge lies in the production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide. The manufacturing process is energy-intensive, often relying on fossil fuels, which raises questions about its long-term sustainability. Additionally, the corrosive nature of ammonium hydroxide poses safety risks during handling and storage, necessitating strict safety protocols and specialized equipment.
The agricultural sector is also grappling with the need to balance the benefits of ammonium hydroxide use with potential environmental impacts. Excessive application can lead to soil acidification and nutrient imbalances, affecting long-term soil health and biodiversity. This has prompted research into precision agriculture techniques and smart fertilizer formulations that optimize nutrient delivery while minimizing environmental footprint.
Regulatory pressures present another hurdle in the widespread adoption of ammonium hydroxide-based agrochemicals. As environmental regulations become more stringent, manufacturers and farmers must adapt to new guidelines governing the use and disposal of nitrogen-based fertilizers. This has spurred innovation in controlled-release formulations and enhanced efficiency fertilizers that aim to comply with regulatory standards while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Despite these challenges, the field of sustainable agrochemicals continues to evolve, with ammonium hydroxide playing a central role. Researchers are exploring novel approaches such as nanotechnology-enhanced delivery systems and bio-based alternatives to traditional ammonium hydroxide formulations. These innovations aim to address current limitations and pave the way for more sustainable agricultural practices.
Existing Ammonium Hydroxide-based Agrochemical Solutions
01 Use in chemical processes
Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes, including as a reactant, catalyst, or pH regulator. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of organic compounds, production of fertilizers, and treatment of industrial waste streams. Its alkaline properties make it useful for neutralizing acids and controlling pH levels in different applications.- Use in chemical processes: Ammonium hydroxide is widely used in various chemical processes, including as a reactant, catalyst, or pH adjuster. It plays a crucial role in the synthesis of organic compounds, production of fertilizers, and treatment of industrial waste streams. Its alkaline properties make it useful for neutralizing acids and controlling pH in chemical reactions.
- Application in cleaning and surface treatment: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in cleaning formulations and surface treatment processes. It is effective in removing grease, oils, and other contaminants from various surfaces. In the semiconductor industry, it is used for etching and cleaning silicon wafers. It also finds applications in the textile industry for fabric treatment and in the leather industry for dehairing hides.
- Role in environmental applications: Ammonium hydroxide is employed in environmental applications, particularly in air pollution control and water treatment. It is used to neutralize acidic gases in flue gas desulfurization processes and to remove nitrogen oxides from exhaust gases. In water treatment, it helps in adjusting pH levels and removing heavy metals through precipitation reactions.
- Use in agricultural and food industries: Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in agriculture and food processing. It is used as a nitrogen source in fertilizers and as a pH regulator in soil treatment. In the food industry, it serves as a leavening agent in baked goods and as a processing aid in the production of certain foods. It is also used in the extraction of vegetable oils and in the production of gelatin.
- Applications in personal care and pharmaceuticals: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in personal care products and pharmaceutical formulations. It acts as a pH adjuster in cosmetics and hair care products, helping to maintain the stability and effectiveness of the formulations. In pharmaceuticals, it is used in the synthesis of certain drugs and as an excipient in some medications. It also finds applications in the production of vaccines and biological products.
02 Application in cleaning and surface treatment
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in cleaning formulations and surface treatment processes. It is effective in removing grease, oils, and other contaminants from various surfaces. In the semiconductor industry, it is used for etching and cleaning silicon wafers. Additionally, it finds applications in the textile industry for fabric treatment and in the leather industry for dehairing and tanning processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Role in environmental applications
Ammonium hydroxide plays a significant role in environmental applications, particularly in air pollution control and wastewater treatment. It is used in flue gas desulfurization processes to remove sulfur dioxide from industrial emissions. In wastewater treatment, it helps in pH adjustment, nitrogen removal, and precipitation of heavy metals.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use in agricultural and horticultural products
Ammonium hydroxide is an important component in the production of agricultural and horticultural products. It is used in the manufacture of nitrogen-based fertilizers, providing a source of readily available nitrogen for plant growth. Additionally, it is utilized in the formulation of pesticides and herbicides, contributing to crop protection and yield improvement.Expand Specific Solutions05 Applications in personal care and cosmetic products
Ammonium hydroxide finds applications in personal care and cosmetic products. It is used as a pH adjuster in various formulations, including hair dyes, shampoos, and skin care products. In hair coloring products, it helps to open the hair cuticle, allowing the dye to penetrate more effectively. Its alkaline properties also make it useful in certain depilatory formulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Agrochemical Industry
The research on ammonium hydroxide in sustainable agrochemicals development is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and evolving technological maturity. The global agrochemical market, valued at over $200 billion, is seeing a shift towards sustainable solutions. Major players like Bayer CropScience, BASF, and Syngenta are investing heavily in R&D for eco-friendly alternatives. Companies such as Clariant, Rhodia, and Stepan are focusing on specialty chemicals and formulations to enhance the efficacy of ammonium hydroxide-based products. Academic institutions like Nanjing Agricultural University and research organizations like CSIRO are contributing to technological advancements, indicating a collaborative ecosystem. The involvement of diverse players suggests a competitive landscape with opportunities for innovation and market expansion in sustainable agrochemicals.
Bayer CropScience LP
Technical Solution: Bayer CropScience LP has developed a sustainable agrochemical formulation utilizing ammonium hydroxide as a key component. Their approach involves using ammonium hydroxide as a pH regulator and stabilizer in water-based pesticide formulations[1]. This method enhances the efficacy of active ingredients while reducing environmental impact. The company has also explored the use of ammonium hydroxide in controlled-release fertilizers, where it acts as a nitrogen source and helps in maintaining soil pH[3]. Additionally, Bayer has invested in research to optimize the concentration of ammonium hydroxide in their formulations to maximize crop yield while minimizing potential phytotoxicity[5].
Strengths: Improved efficacy of pesticides, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced nutrient delivery. Weaknesses: Potential for ammonia volatilization and the need for precise application techniques.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has pioneered the use of ammonium hydroxide in their sustainable agrochemical solutions. They have developed a novel approach that incorporates ammonium hydroxide into microencapsulation technology for controlled release of pesticides[2]. This method allows for a gradual release of active ingredients, reducing the overall amount of chemicals needed. BASF has also explored the use of ammonium hydroxide as a catalyst in the production of bio-based pesticides, promoting greener manufacturing processes[4]. Furthermore, the company has conducted extensive research on the interaction between ammonium hydroxide and various soil types, optimizing their formulations for different agricultural environments[6].
Strengths: Innovative microencapsulation technology, promotion of bio-based pesticides, and tailored solutions for various soil types. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potential complexity in application for farmers.
Innovative Approaches in Ammonium Hydroxide Utilization
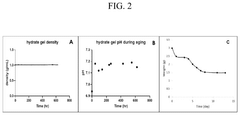
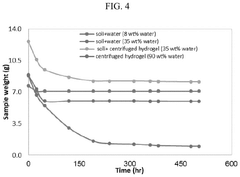
Aluminium hydroxide hydrogel for agriculture
PatentPendingUS20250212739A1
Innovation
- A biodegradable aluminium hydroxide hydrogel is developed through a simple chemical reaction, comprising aluminium polyhydrate and water, which is pH-neutral and non-toxic, and can be prepared at low cost without complex equipment, absorbing and retaining water effectively for extended periods.
Process for removal of waste waters with a high concentration of ammoniacal nitrogen
PatentInactiveEP0363612A1
Innovation
- A multi-stage process involving the addition of magnesium compounds and phosphoric acid to precipitate ammonium as magnesium ammonium phosphate, followed by flocculation and aerobic-biological treatment, optimizing chemical usage and reducing acid capacity through CO₂ blowout stages, and subsequent flocculation with iron-3 chloride to achieve effective pollutant removal.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of ammonium hydroxide in sustainable agrochemical development is a critical aspect that requires thorough examination. Ammonium hydroxide, while beneficial for agricultural productivity, poses potential risks to ecosystems and human health if not managed properly.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ammonium hydroxide is its potential to contribute to soil acidification. When applied to soil, ammonium hydroxide can undergo nitrification, a process that releases hydrogen ions and lowers soil pH. This acidification can negatively impact soil microbial communities, alter nutrient availability, and affect plant growth. Long-term use of ammonium hydroxide-based fertilizers may lead to decreased soil fertility and reduced crop yields if not balanced with appropriate soil management practices.
Water pollution is another significant environmental issue related to ammonium hydroxide use in agriculture. Excess ammonia can leach into groundwater or run off into surface water bodies, leading to eutrophication. This process causes algal blooms, depletes oxygen levels, and disrupts aquatic ecosystems. The contamination of drinking water sources with high levels of ammonia can also pose health risks to humans and livestock.
Atmospheric emissions are a concern when using ammonium hydroxide in agrochemical applications. Volatilization of ammonia from soil and water surfaces contributes to air pollution and can lead to the formation of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) through chemical reactions in the atmosphere. These emissions can have adverse effects on air quality, human respiratory health, and contribute to the formation of acid rain.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also have environmental implications. The manufacturing process typically involves the Haber-Bosch process, which is energy-intensive and relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the transportation and storage of ammonium hydroxide present risks of accidental spills or releases, which can have immediate and severe impacts on local ecosystems.
To mitigate these environmental risks, sustainable agrochemical development must focus on optimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide and exploring alternative formulations. Precision agriculture techniques, such as variable rate application and soil testing, can help minimize excess application. The development of slow-release formulations and nitrification inhibitors can reduce leaching and volatilization, thereby decreasing environmental impact.
Furthermore, integrating ammonium hydroxide use with other sustainable agricultural practices, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic matter management, can enhance soil health and reduce the need for synthetic inputs. Research into bio-based alternatives and the use of waste-derived ammonia sources may also contribute to more environmentally friendly agrochemical solutions.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with ammonium hydroxide is its potential to contribute to soil acidification. When applied to soil, ammonium hydroxide can undergo nitrification, a process that releases hydrogen ions and lowers soil pH. This acidification can negatively impact soil microbial communities, alter nutrient availability, and affect plant growth. Long-term use of ammonium hydroxide-based fertilizers may lead to decreased soil fertility and reduced crop yields if not balanced with appropriate soil management practices.
Water pollution is another significant environmental issue related to ammonium hydroxide use in agriculture. Excess ammonia can leach into groundwater or run off into surface water bodies, leading to eutrophication. This process causes algal blooms, depletes oxygen levels, and disrupts aquatic ecosystems. The contamination of drinking water sources with high levels of ammonia can also pose health risks to humans and livestock.
Atmospheric emissions are a concern when using ammonium hydroxide in agrochemical applications. Volatilization of ammonia from soil and water surfaces contributes to air pollution and can lead to the formation of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) through chemical reactions in the atmosphere. These emissions can have adverse effects on air quality, human respiratory health, and contribute to the formation of acid rain.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also have environmental implications. The manufacturing process typically involves the Haber-Bosch process, which is energy-intensive and relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the transportation and storage of ammonium hydroxide present risks of accidental spills or releases, which can have immediate and severe impacts on local ecosystems.
To mitigate these environmental risks, sustainable agrochemical development must focus on optimizing the use of ammonium hydroxide and exploring alternative formulations. Precision agriculture techniques, such as variable rate application and soil testing, can help minimize excess application. The development of slow-release formulations and nitrification inhibitors can reduce leaching and volatilization, thereby decreasing environmental impact.
Furthermore, integrating ammonium hydroxide use with other sustainable agricultural practices, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic matter management, can enhance soil health and reduce the need for synthetic inputs. Research into bio-based alternatives and the use of waste-derived ammonia sources may also contribute to more environmentally friendly agrochemical solutions.
Regulatory Framework for Sustainable Agrochemicals
The regulatory framework for sustainable agrochemicals plays a crucial role in shaping the development and use of ammonium hydroxide in the agricultural sector. As governments and international organizations increasingly prioritize environmental protection and sustainable practices, the regulations surrounding agrochemicals have become more stringent and comprehensive.
At the global level, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have established the International Code of Conduct on Pesticide Management. This code provides guidelines for the development, distribution, and use of pesticides, including those containing ammonium hydroxide. It emphasizes the importance of risk assessment, proper labeling, and responsible use of agrochemicals to minimize environmental impact and protect human health.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates agrochemicals under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA requires extensive testing and documentation before approving new agrochemicals, including those utilizing ammonium hydroxide. The agency also mandates periodic reviews of registered products to ensure ongoing safety and efficacy.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to all chemical substances, including those used in agriculture. REACH aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment through better and earlier identification of the intrinsic properties of chemical substances. This regulation has significant implications for the development and use of ammonium hydroxide-based agrochemicals in the EU market.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. This system is particularly relevant for ammonium hydroxide, as it ensures consistent safety information across different markets and facilitates international trade in agrochemicals.
The regulatory landscape also includes specific provisions for organic farming. For instance, the USDA National Organic Program sets standards for organic crop production, which may impact the use of ammonium hydroxide-based products in organic agriculture. Similarly, the EU Organic Regulation outlines permitted substances and practices for organic farming within the European Union.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulators are focusing on the lifecycle assessment of agrochemicals. This approach considers the environmental impact of a product from its production to its disposal, encouraging the development of more sustainable formulations and application methods for ammonium hydroxide and other agrochemicals.
At the global level, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have established the International Code of Conduct on Pesticide Management. This code provides guidelines for the development, distribution, and use of pesticides, including those containing ammonium hydroxide. It emphasizes the importance of risk assessment, proper labeling, and responsible use of agrochemicals to minimize environmental impact and protect human health.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates agrochemicals under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA requires extensive testing and documentation before approving new agrochemicals, including those utilizing ammonium hydroxide. The agency also mandates periodic reviews of registered products to ensure ongoing safety and efficacy.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to all chemical substances, including those used in agriculture. REACH aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment through better and earlier identification of the intrinsic properties of chemical substances. This regulation has significant implications for the development and use of ammonium hydroxide-based agrochemicals in the EU market.
Many countries have adopted the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. This system is particularly relevant for ammonium hydroxide, as it ensures consistent safety information across different markets and facilitates international trade in agrochemicals.
The regulatory landscape also includes specific provisions for organic farming. For instance, the USDA National Organic Program sets standards for organic crop production, which may impact the use of ammonium hydroxide-based products in organic agriculture. Similarly, the EU Organic Regulation outlines permitted substances and practices for organic farming within the European Union.
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulators are focusing on the lifecycle assessment of agrochemicals. This approach considers the environmental impact of a product from its production to its disposal, encouraging the development of more sustainable formulations and application methods for ammonium hydroxide and other agrochemicals.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!