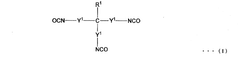
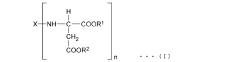
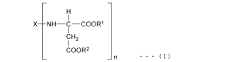
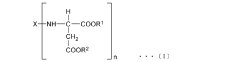
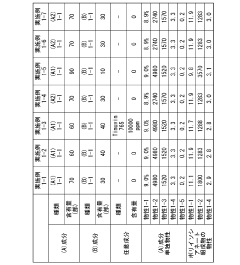
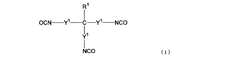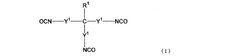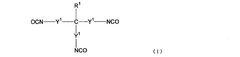Isocyanate Formulations for Improved Weather Resistance
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Formulation Background and Objectives
Isocyanate formulations have been a cornerstone in the development of high-performance coatings and adhesives for decades. These versatile compounds, characterized by their reactive -N=C=O functional group, have revolutionized various industries due to their exceptional bonding properties and chemical resistance. The evolution of isocyanate technology can be traced back to the 1930s, with significant advancements occurring in the post-World War II era.
The primary objective of researching isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance is to address the long-standing challenge of environmental degradation in polyurethane-based products. While isocyanates offer excellent initial performance, their susceptibility to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations has been a persistent issue. This vulnerability often leads to discoloration, chalking, and loss of mechanical properties in outdoor applications.
Recent technological trends in isocyanate formulations have focused on enhancing the durability and longevity of coatings and adhesives exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Researchers are exploring novel approaches such as incorporating UV stabilizers, developing hybrid systems with other polymer technologies, and modifying the chemical structure of isocyanates to improve their inherent weather resistance.
The market demand for weather-resistant isocyanate formulations has been driven by several factors, including the growing construction industry, automotive sector, and renewable energy installations. These applications require materials that can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight, rain, and temperature variations while maintaining their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is also a push towards developing eco-friendly isocyanate formulations. This includes reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived isocyanates. The challenge lies in maintaining the superior performance characteristics of isocyanates while addressing environmental concerns.
The technological goals for improving weather resistance in isocyanate formulations are multifaceted. They include extending the service life of coated surfaces, reducing maintenance costs, and expanding the application range of isocyanate-based products in outdoor environments. Additionally, there is a focus on developing formulations that offer rapid curing and improved adhesion to various substrates under diverse weather conditions.
In conclusion, the research on isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance represents a critical area of innovation in polymer science. It aims to overcome the limitations of current technologies while meeting the increasing demands for durable, sustainable, and high-performance materials across multiple industries.
The primary objective of researching isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance is to address the long-standing challenge of environmental degradation in polyurethane-based products. While isocyanates offer excellent initial performance, their susceptibility to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations has been a persistent issue. This vulnerability often leads to discoloration, chalking, and loss of mechanical properties in outdoor applications.
Recent technological trends in isocyanate formulations have focused on enhancing the durability and longevity of coatings and adhesives exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Researchers are exploring novel approaches such as incorporating UV stabilizers, developing hybrid systems with other polymer technologies, and modifying the chemical structure of isocyanates to improve their inherent weather resistance.
The market demand for weather-resistant isocyanate formulations has been driven by several factors, including the growing construction industry, automotive sector, and renewable energy installations. These applications require materials that can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight, rain, and temperature variations while maintaining their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, there is also a push towards developing eco-friendly isocyanate formulations. This includes reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived isocyanates. The challenge lies in maintaining the superior performance characteristics of isocyanates while addressing environmental concerns.
The technological goals for improving weather resistance in isocyanate formulations are multifaceted. They include extending the service life of coated surfaces, reducing maintenance costs, and expanding the application range of isocyanate-based products in outdoor environments. Additionally, there is a focus on developing formulations that offer rapid curing and improved adhesion to various substrates under diverse weather conditions.
In conclusion, the research on isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance represents a critical area of innovation in polymer science. It aims to overcome the limitations of current technologies while meeting the increasing demands for durable, sustainable, and high-performance materials across multiple industries.
Market Analysis for Weather-Resistant Coatings
The global market for weather-resistant coatings has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and marine. This surge is primarily attributed to the growing awareness of the importance of protecting surfaces from harsh environmental conditions, including UV radiation, moisture, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure.
In the construction sector, the rise in infrastructure development and the need for long-lasting protective coatings have been key drivers. The automotive industry has also shown a strong demand for weather-resistant coatings to enhance the durability and appearance of vehicles. Similarly, the aerospace and marine sectors require high-performance coatings to withstand extreme weather conditions and corrosive environments.
The market for weather-resistant coatings based on isocyanate formulations has shown particular promise. These coatings offer superior durability, chemical resistance, and weatherability compared to traditional alternatives. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations has also led to the development of low-VOC and water-based isocyanate formulations, further expanding market opportunities.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the fastest-growing market for weather-resistant coatings, fueled by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by renovation activities and stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of advanced coating technologies.
The competitive landscape of the weather-resistant coatings market is characterized by the presence of both global players and regional manufacturers. Key market players have been investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products with enhanced performance characteristics. Collaborations between coating manufacturers and raw material suppliers have become increasingly common to develop tailored solutions for specific applications.
Looking ahead, the market for weather-resistant coatings is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing need for durable and long-lasting coatings, growing environmental concerns, and the development of smart coatings with self-healing properties are likely to shape the future of this market. The ongoing research on isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance is poised to play a crucial role in meeting these evolving market demands and driving innovation in the coatings industry.
In the construction sector, the rise in infrastructure development and the need for long-lasting protective coatings have been key drivers. The automotive industry has also shown a strong demand for weather-resistant coatings to enhance the durability and appearance of vehicles. Similarly, the aerospace and marine sectors require high-performance coatings to withstand extreme weather conditions and corrosive environments.
The market for weather-resistant coatings based on isocyanate formulations has shown particular promise. These coatings offer superior durability, chemical resistance, and weatherability compared to traditional alternatives. The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations has also led to the development of low-VOC and water-based isocyanate formulations, further expanding market opportunities.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the fastest-growing market for weather-resistant coatings, fueled by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, driven by renovation activities and stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of advanced coating technologies.
The competitive landscape of the weather-resistant coatings market is characterized by the presence of both global players and regional manufacturers. Key market players have been investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products with enhanced performance characteristics. Collaborations between coating manufacturers and raw material suppliers have become increasingly common to develop tailored solutions for specific applications.
Looking ahead, the market for weather-resistant coatings is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing need for durable and long-lasting coatings, growing environmental concerns, and the development of smart coatings with self-healing properties are likely to shape the future of this market. The ongoing research on isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance is poised to play a crucial role in meeting these evolving market demands and driving innovation in the coatings industry.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate-Based Weather Resistance
Despite significant advancements in isocyanate-based coatings for weather resistance, several challenges persist in achieving optimal performance and durability. One of the primary issues is the susceptibility of isocyanate-based coatings to UV degradation. Prolonged exposure to sunlight can lead to discoloration, chalking, and loss of gloss, compromising both the aesthetic and protective properties of the coating.
Moisture sensitivity remains another critical challenge. While isocyanates react with water to form polyurea linkages, excessive moisture during application or curing can result in foaming, blistering, or inadequate crosslinking. This can significantly impair the coating's barrier properties and overall weather resistance.
The reactivity of isocyanates also poses difficulties in formulation and application. Their high reactivity with various functional groups can lead to premature curing or unwanted side reactions, affecting pot life and application window. Balancing reactivity for optimal curing while maintaining workability is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Environmental and health concerns associated with isocyanates present additional hurdles. Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and potential respiratory sensitization have led to increased regulatory scrutiny. Developing low-VOC or VOC-free formulations that maintain high performance standards is a significant challenge facing the industry.
Adhesion to diverse substrates, particularly in extreme weather conditions, remains problematic. Thermal cycling and freeze-thaw cycles can stress the coating-substrate interface, leading to delamination or loss of protective properties. Enhancing adhesion across a wide range of materials and environmental conditions is crucial for improving overall weather resistance.
Cost-effectiveness is another persistent challenge. While high-performance isocyanate formulations can offer superior weather resistance, their higher cost compared to conventional alternatives can limit widespread adoption. Striking a balance between performance and affordability is essential for market penetration.
Lastly, the development of bio-based or sustainable isocyanate alternatives that match or exceed the performance of traditional petrochemical-derived isocyanates is an ongoing challenge. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, finding eco-friendly solutions that do not compromise on weather resistance is a key focus for research and development efforts in the field.
Moisture sensitivity remains another critical challenge. While isocyanates react with water to form polyurea linkages, excessive moisture during application or curing can result in foaming, blistering, or inadequate crosslinking. This can significantly impair the coating's barrier properties and overall weather resistance.
The reactivity of isocyanates also poses difficulties in formulation and application. Their high reactivity with various functional groups can lead to premature curing or unwanted side reactions, affecting pot life and application window. Balancing reactivity for optimal curing while maintaining workability is an ongoing challenge for formulators.
Environmental and health concerns associated with isocyanates present additional hurdles. Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and potential respiratory sensitization have led to increased regulatory scrutiny. Developing low-VOC or VOC-free formulations that maintain high performance standards is a significant challenge facing the industry.
Adhesion to diverse substrates, particularly in extreme weather conditions, remains problematic. Thermal cycling and freeze-thaw cycles can stress the coating-substrate interface, leading to delamination or loss of protective properties. Enhancing adhesion across a wide range of materials and environmental conditions is crucial for improving overall weather resistance.
Cost-effectiveness is another persistent challenge. While high-performance isocyanate formulations can offer superior weather resistance, their higher cost compared to conventional alternatives can limit widespread adoption. Striking a balance between performance and affordability is essential for market penetration.
Lastly, the development of bio-based or sustainable isocyanate alternatives that match or exceed the performance of traditional petrochemical-derived isocyanates is an ongoing challenge. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, finding eco-friendly solutions that do not compromise on weather resistance is a key focus for research and development efforts in the field.
Existing Weather-Resistant Isocyanate Solutions
01 Use of polyisocyanate compositions
Polyisocyanate compositions are utilized to enhance weather resistance in various applications. These formulations often include specific isocyanate compounds and additives that improve durability and resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.- Use of polyisocyanate compositions: Polyisocyanate compositions are utilized to enhance weather resistance in various applications. These formulations often include specific types of isocyanates or combinations thereof, which contribute to improved durability and protection against environmental factors. The compositions may be optimized for different substrates and exposure conditions.
- Incorporation of UV stabilizers: UV stabilizers are added to isocyanate formulations to improve their resistance to degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation. These additives help maintain the integrity of the coating or material over time, preventing discoloration, cracking, and loss of physical properties when exposed to sunlight and other weather conditions.
- Moisture-curing systems: Moisture-curing isocyanate systems are developed to provide enhanced weather resistance. These formulations react with atmospheric moisture to form durable, cross-linked structures that offer excellent protection against various environmental factors. The curing process and resulting properties can be tailored for specific applications and exposure conditions.
- Blending with other polymers: Isocyanate formulations are often blended with other polymers to create hybrid systems with improved weather resistance. These combinations can leverage the strengths of different materials to achieve superior performance in outdoor applications. The selection and ratio of polymers are optimized based on the desired properties and environmental conditions.
- Surface treatment and additives: Various surface treatments and additives are employed to enhance the weather resistance of isocyanate-based coatings and materials. These may include specialized primers, topcoats, or incorporation of nanoparticles or other functional additives. Such treatments can improve adhesion, barrier properties, and overall durability under harsh environmental conditions.
02 Incorporation of UV stabilizers
UV stabilizers are added to isocyanate formulations to improve their resistance to degradation caused by sunlight exposure. These additives help maintain the integrity of the coating or material over time, preventing discoloration, cracking, and loss of physical properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Moisture-curing isocyanate systems
Moisture-curing isocyanate systems are developed to provide excellent weather resistance. These formulations react with atmospheric moisture to form durable, cross-linked coatings that offer superior protection against various environmental factors, including rain, humidity, and temperature changes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Blending with other polymers
Isocyanate formulations are often blended with other polymers to enhance weather resistance. This approach combines the beneficial properties of different materials, resulting in improved overall performance and durability in outdoor applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surface treatment and coating techniques
Specialized surface treatment and coating techniques are employed to improve the weather resistance of isocyanate-based materials. These methods may include the application of protective topcoats, surface modification, or the use of specific application processes to enhance the material's resistance to environmental factors.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Formulation Industry
The research on isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance is in a mature stage of development, with a significant market size driven by growing demand in construction, automotive, and industrial applications. The global market for weather-resistant coatings is expanding, with key players like Wanhua Chemical Group, Asahi Kasei, BASF, and Covestro leading the way. These companies have established strong research and development capabilities, focusing on innovative formulations to enhance durability and performance. The technology's maturity is evident in the diverse range of products offered by major manufacturers, including specialized polyurethane systems and advanced coating solutions. However, there is still room for improvement and innovation, particularly in areas such as eco-friendly formulations and extreme weather resistance.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed advanced isocyanate formulations for improved weather resistance, focusing on aliphatic isocyanates. Their approach involves synthesizing novel polyisocyanates with enhanced UV stability and hydrolysis resistance. The company has introduced a series of hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) based products, including HDI trimers and biurets, which offer superior durability in exterior coatings[1]. Wanhua's formulations incorporate specialized additives and cross-linking agents to further improve weather resistance, resulting in coatings that maintain gloss and color stability under prolonged exposure to sunlight and moisture[2].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, wide range of isocyanate products, and strong market presence. Weaknesses: Higher production costs for specialized formulations and potential regulatory challenges in some markets.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed innovative isocyanate formulations focusing on polyurethane dispersions (PUDs) for enhanced weather resistance. Their approach combines aliphatic isocyanates with novel polyols and chain extenders to create high-performance coatings. Dow's technology incorporates UV-absorbing monomers and HALS (Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers) directly into the polymer backbone, providing long-lasting protection against weathering[3]. The company has also introduced water-based formulations that offer excellent adhesion and flexibility while maintaining superior weather resistance, addressing both performance and environmental concerns[4].
Strengths: Strong focus on sustainability, extensive global research facilities, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Complex formulations may lead to higher costs and potential scalability issues for some applications.
Innovative Approaches in Isocyanate Chemistry
Polyisocyanate mixture, coating composition, and coating film
PatentWO2018070531A1
Innovation
- A polyisocyanate mixture comprising a triisocyanate compound and specific diisocyanates, such as aliphatic, cycloaliphatic, or aromatic diisocyanates, with a controlled molecular weight and isocyanate group content, is developed to enhance coating film properties, including recoat adhesion and weather resistance.
Polyisocyanate composition, coating material composition, and coating film
PatentWO2024147294A1
Innovation
- A polyisocyanate composition comprising specific diisocyanates and polyester polyols with controlled functional groups and molecular weights, along with an allophanate and isocyanurate group ratio, is used as a curing agent, which enhances elongation and transparency, preventing clouding and improving weather resistance.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanate-Based Coatings
The environmental impact of isocyanate-based coatings has become a significant concern in recent years, particularly as the demand for weather-resistant coatings continues to grow. These coatings, while effective in providing protection against harsh environmental conditions, pose several challenges to ecological systems and human health.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanate-based coatings is their potential for releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application and curing processes. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This not only affects air quality but also impacts plant life and ecosystems in the surrounding areas.
Furthermore, the production of isocyanates involves the use of hazardous chemicals, including phosgene and chlorine, which can have severe environmental consequences if not properly managed. The manufacturing process generates waste products that require careful disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
When exposed to moisture, isocyanate-based coatings can release small amounts of carbon dioxide and potentially harmful byproducts. This slow degradation process can lead to the accumulation of microplastics in aquatic environments, posing risks to marine life and potentially entering the food chain.
The disposal of products coated with isocyanate-based materials presents another environmental challenge. As these coatings are designed for durability, they do not readily biodegrade, contributing to long-term waste management issues. Incineration of such materials can release toxic fumes, including hydrogen cyanide and other hazardous substances.
However, it is important to note that advancements in isocyanate chemistry have led to the development of more environmentally friendly formulations. Water-based polyurethane dispersions and high-solids formulations have been introduced to reduce VOC emissions. Additionally, bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are being explored as sustainable alternatives.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stricter guidelines for the use and disposal of isocyanate-based coatings. These regulations aim to minimize environmental impact by setting limits on VOC content, enforcing proper handling and disposal procedures, and encouraging the development of greener alternatives.
As research continues in the field of weather-resistant coatings, there is a growing focus on balancing performance with environmental sustainability. This includes exploring novel curing mechanisms, developing hybrid systems that reduce isocyanate content, and investigating entirely new classes of weather-resistant materials that offer comparable performance with reduced ecological footprint.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanate-based coatings is their potential for releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application and curing processes. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. This not only affects air quality but also impacts plant life and ecosystems in the surrounding areas.
Furthermore, the production of isocyanates involves the use of hazardous chemicals, including phosgene and chlorine, which can have severe environmental consequences if not properly managed. The manufacturing process generates waste products that require careful disposal to prevent soil and water contamination.
When exposed to moisture, isocyanate-based coatings can release small amounts of carbon dioxide and potentially harmful byproducts. This slow degradation process can lead to the accumulation of microplastics in aquatic environments, posing risks to marine life and potentially entering the food chain.
The disposal of products coated with isocyanate-based materials presents another environmental challenge. As these coatings are designed for durability, they do not readily biodegrade, contributing to long-term waste management issues. Incineration of such materials can release toxic fumes, including hydrogen cyanide and other hazardous substances.
However, it is important to note that advancements in isocyanate chemistry have led to the development of more environmentally friendly formulations. Water-based polyurethane dispersions and high-solids formulations have been introduced to reduce VOC emissions. Additionally, bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are being explored as sustainable alternatives.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented stricter guidelines for the use and disposal of isocyanate-based coatings. These regulations aim to minimize environmental impact by setting limits on VOC content, enforcing proper handling and disposal procedures, and encouraging the development of greener alternatives.
As research continues in the field of weather-resistant coatings, there is a growing focus on balancing performance with environmental sustainability. This includes exploring novel curing mechanisms, developing hybrid systems that reduce isocyanate content, and investigating entirely new classes of weather-resistant materials that offer comparable performance with reduced ecological footprint.
Regulatory Framework for Isocyanate Use in Coatings
The regulatory framework for isocyanate use in coatings has become increasingly stringent in recent years, reflecting growing concerns about the potential health and environmental impacts of these chemicals. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established strict guidelines for the handling and use of isocyanates in industrial settings, including mandatory exposure limits and personal protective equipment requirements.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a crucial role in regulating isocyanates through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Under this act, manufacturers and importers of isocyanate-containing products must comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. Additionally, the EPA has implemented restrictions on certain isocyanates, such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI), due to their potential carcinogenic properties.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of isocyanates in coatings. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety data, with specific provisions for substances of very high concern (SVHCs). Some isocyanates, particularly those classified as respiratory sensitizers, fall under this category and are subject to more stringent controls.
Japan has implemented its own regulatory framework through the Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL), which mandates the evaluation and regulation of new and existing chemical substances, including isocyanates used in coatings. The law requires manufacturers and importers to submit safety data and conduct risk assessments for these chemicals.
Many countries have also introduced labeling requirements for products containing isocyanates. For instance, the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) has been widely adopted, ensuring consistent hazard communication across different regions. This system mandates specific pictograms, hazard statements, and precautionary information on product labels and safety data sheets.
As research on the long-term effects of isocyanate exposure continues, regulatory bodies are likely to update their frameworks. There is a growing trend towards promoting safer alternatives and encouraging the development of low-isocyanate or isocyanate-free formulations for coatings. This shift is driven by both regulatory pressure and market demand for more environmentally friendly and worker-safe products.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a crucial role in regulating isocyanates through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Under this act, manufacturers and importers of isocyanate-containing products must comply with reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements. Additionally, the EPA has implemented restrictions on certain isocyanates, such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI), due to their potential carcinogenic properties.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of isocyanates in coatings. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety data, with specific provisions for substances of very high concern (SVHCs). Some isocyanates, particularly those classified as respiratory sensitizers, fall under this category and are subject to more stringent controls.
Japan has implemented its own regulatory framework through the Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL), which mandates the evaluation and regulation of new and existing chemical substances, including isocyanates used in coatings. The law requires manufacturers and importers to submit safety data and conduct risk assessments for these chemicals.
Many countries have also introduced labeling requirements for products containing isocyanates. For instance, the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) has been widely adopted, ensuring consistent hazard communication across different regions. This system mandates specific pictograms, hazard statements, and precautionary information on product labels and safety data sheets.
As research on the long-term effects of isocyanate exposure continues, regulatory bodies are likely to update their frameworks. There is a growing trend towards promoting safer alternatives and encouraging the development of low-isocyanate or isocyanate-free formulations for coatings. This shift is driven by both regulatory pressure and market demand for more environmentally friendly and worker-safe products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!