Magnesium Carbonate in Pulp and Paper Industry Applications
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Magnesium Carbonate in Pulp and Paper: Overview and Objectives
Magnesium carbonate has emerged as a significant material in the pulp and paper industry, playing a crucial role in various applications. This research aims to explore the current state, potential benefits, and future prospects of magnesium carbonate utilization in this sector. The pulp and paper industry, being one of the largest industrial sectors globally, constantly seeks innovative solutions to enhance product quality, reduce environmental impact, and improve operational efficiency.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate applications in this industry can be traced back to the mid-20th century when its potential as a filler and coating material was first recognized. Since then, continuous advancements in material science and processing technologies have expanded its use across different stages of paper production. Today, magnesium carbonate is utilized in various forms, including precipitated magnesium carbonate (PMC) and ground magnesium carbonate (GMC), each offering unique properties and benefits.
One of the primary objectives of this research is to comprehensively analyze the current applications of magnesium carbonate in pulp and paper manufacturing. This includes its role in improving paper brightness, opacity, and printability, as well as its potential to enhance the mechanical properties of paper products. Additionally, the study aims to investigate the environmental implications of magnesium carbonate usage, particularly in terms of reducing the carbon footprint of paper production processes.
The research also seeks to explore emerging trends and innovative applications of magnesium carbonate in the industry. This includes its potential use in advanced coating technologies, sustainable packaging solutions, and specialty paper products. By examining these areas, the study aims to identify new opportunities for magnesium carbonate to address evolving industry challenges and consumer demands.
Furthermore, this research intends to evaluate the economic aspects of magnesium carbonate utilization in pulp and paper production. This involves analyzing cost-effectiveness, supply chain considerations, and potential market growth for magnesium carbonate-based products and technologies. Understanding these factors is crucial for assessing the long-term viability and adoption of magnesium carbonate solutions in the industry.
Lastly, the study aims to provide insights into the technological advancements and research directions that could further enhance the applications of magnesium carbonate in pulp and paper manufacturing. This includes exploring potential synergies with other materials, innovative processing techniques, and novel product development opportunities. By identifying these future research avenues, the study seeks to contribute to the ongoing evolution of magnesium carbonate applications in the pulp and paper industry.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate applications in this industry can be traced back to the mid-20th century when its potential as a filler and coating material was first recognized. Since then, continuous advancements in material science and processing technologies have expanded its use across different stages of paper production. Today, magnesium carbonate is utilized in various forms, including precipitated magnesium carbonate (PMC) and ground magnesium carbonate (GMC), each offering unique properties and benefits.
One of the primary objectives of this research is to comprehensively analyze the current applications of magnesium carbonate in pulp and paper manufacturing. This includes its role in improving paper brightness, opacity, and printability, as well as its potential to enhance the mechanical properties of paper products. Additionally, the study aims to investigate the environmental implications of magnesium carbonate usage, particularly in terms of reducing the carbon footprint of paper production processes.
The research also seeks to explore emerging trends and innovative applications of magnesium carbonate in the industry. This includes its potential use in advanced coating technologies, sustainable packaging solutions, and specialty paper products. By examining these areas, the study aims to identify new opportunities for magnesium carbonate to address evolving industry challenges and consumer demands.
Furthermore, this research intends to evaluate the economic aspects of magnesium carbonate utilization in pulp and paper production. This involves analyzing cost-effectiveness, supply chain considerations, and potential market growth for magnesium carbonate-based products and technologies. Understanding these factors is crucial for assessing the long-term viability and adoption of magnesium carbonate solutions in the industry.
Lastly, the study aims to provide insights into the technological advancements and research directions that could further enhance the applications of magnesium carbonate in pulp and paper manufacturing. This includes exploring potential synergies with other materials, innovative processing techniques, and novel product development opportunities. By identifying these future research avenues, the study seeks to contribute to the ongoing evolution of magnesium carbonate applications in the pulp and paper industry.
Market Analysis for Magnesium Carbonate in Paper Industry
The global market for magnesium carbonate in the pulp and paper industry has shown steady growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for high-quality paper products and the material's unique properties. Magnesium carbonate serves multiple functions in paper manufacturing, including as a filler, coating agent, and pH regulator, contributing to improved paper quality and production efficiency.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the market, with China and India leading in consumption due to their rapidly expanding paper industries. North America and Europe follow, maintaining significant market shares owing to their established paper manufacturing sectors and focus on specialty paper products. Latin America and the Middle East are emerging as promising markets, showing increased adoption of magnesium carbonate in paper production.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising demand for packaging materials, especially in e-commerce and food industries, and the increasing use of specialty papers in various applications. The shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly paper production methods has also boosted the demand for magnesium carbonate, as it helps reduce the use of harmful chemicals in the papermaking process.
The market is segmented based on product type, with basic magnesium carbonate and precipitated magnesium carbonate being the primary forms used in the paper industry. Basic magnesium carbonate is widely used as a filler and coating agent, while precipitated magnesium carbonate finds applications in specialty papers and high-end products.
Market challenges include fluctuations in raw material prices and competition from alternative materials such as calcium carbonate. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the properties of magnesium carbonate for paper applications, potentially opening new market opportunities.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially disrupted the market due to supply chain issues and reduced demand for certain paper products. However, the increased use of packaging materials for e-commerce and healthcare products has partially offset these negative impacts. As economies recover, the market is expected to regain momentum, driven by the growing emphasis on sustainable packaging solutions and the revival of commercial printing activities.
Looking ahead, the market for magnesium carbonate in the pulp and paper industry is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as technological advancements in paper manufacturing, increasing environmental regulations favoring eco-friendly materials, and the expanding packaging industry in developing countries are expected to fuel this growth. Additionally, the trend towards lightweight and high-performance paper products is likely to create new opportunities for magnesium carbonate applications in the industry.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the market, with China and India leading in consumption due to their rapidly expanding paper industries. North America and Europe follow, maintaining significant market shares owing to their established paper manufacturing sectors and focus on specialty paper products. Latin America and the Middle East are emerging as promising markets, showing increased adoption of magnesium carbonate in paper production.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising demand for packaging materials, especially in e-commerce and food industries, and the increasing use of specialty papers in various applications. The shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly paper production methods has also boosted the demand for magnesium carbonate, as it helps reduce the use of harmful chemicals in the papermaking process.
The market is segmented based on product type, with basic magnesium carbonate and precipitated magnesium carbonate being the primary forms used in the paper industry. Basic magnesium carbonate is widely used as a filler and coating agent, while precipitated magnesium carbonate finds applications in specialty papers and high-end products.
Market challenges include fluctuations in raw material prices and competition from alternative materials such as calcium carbonate. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the properties of magnesium carbonate for paper applications, potentially opening new market opportunities.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially disrupted the market due to supply chain issues and reduced demand for certain paper products. However, the increased use of packaging materials for e-commerce and healthcare products has partially offset these negative impacts. As economies recover, the market is expected to regain momentum, driven by the growing emphasis on sustainable packaging solutions and the revival of commercial printing activities.
Looking ahead, the market for magnesium carbonate in the pulp and paper industry is projected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as technological advancements in paper manufacturing, increasing environmental regulations favoring eco-friendly materials, and the expanding packaging industry in developing countries are expected to fuel this growth. Additionally, the trend towards lightweight and high-performance paper products is likely to create new opportunities for magnesium carbonate applications in the industry.
Technical Challenges in Magnesium Carbonate Application
The application of magnesium carbonate in the pulp and paper industry faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance and efficiency. One of the primary obstacles is achieving uniform dispersion of magnesium carbonate particles throughout the paper matrix. The tendency of these particles to agglomerate can lead to inconsistent distribution, affecting the final product's quality and properties.
Another significant challenge lies in maintaining the stability of magnesium carbonate suspensions during the papermaking process. The high-speed and turbulent environment of paper machines can cause settling or separation of the particles, potentially leading to uneven application and reduced effectiveness. This issue is particularly pronounced when dealing with different paper grades and production speeds.
The interaction between magnesium carbonate and other additives in the papermaking process presents a complex challenge. Compatibility issues may arise, affecting the overall performance of the paper's functional properties. For instance, the presence of magnesium carbonate can influence the retention of other chemicals, such as sizing agents or optical brighteners, potentially altering the intended characteristics of the final product.
Controlling the particle size of magnesium carbonate is crucial for its effectiveness in various applications within the pulp and paper industry. However, achieving and maintaining the desired particle size distribution throughout the production process remains a technical hurdle. Variations in particle size can impact factors such as opacity, brightness, and printability of the paper.
The alkaline nature of magnesium carbonate poses challenges in pH control during papermaking. Fluctuations in pH can affect the performance of other additives and the overall chemistry of the paper machine system. Balancing the benefits of magnesium carbonate with the need for precise pH management requires sophisticated control mechanisms and careful formulation.
Environmental considerations also present technical challenges in the application of magnesium carbonate. As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a need to optimize the use of magnesium carbonate to minimize its environmental footprint. This includes reducing water consumption, improving recyclability, and ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Lastly, the integration of magnesium carbonate into existing paper production processes without significant modifications to equipment or procedures remains a challenge. Developing application methods that are both effective and compatible with current manufacturing setups is essential for widespread adoption in the industry.
Another significant challenge lies in maintaining the stability of magnesium carbonate suspensions during the papermaking process. The high-speed and turbulent environment of paper machines can cause settling or separation of the particles, potentially leading to uneven application and reduced effectiveness. This issue is particularly pronounced when dealing with different paper grades and production speeds.
The interaction between magnesium carbonate and other additives in the papermaking process presents a complex challenge. Compatibility issues may arise, affecting the overall performance of the paper's functional properties. For instance, the presence of magnesium carbonate can influence the retention of other chemicals, such as sizing agents or optical brighteners, potentially altering the intended characteristics of the final product.
Controlling the particle size of magnesium carbonate is crucial for its effectiveness in various applications within the pulp and paper industry. However, achieving and maintaining the desired particle size distribution throughout the production process remains a technical hurdle. Variations in particle size can impact factors such as opacity, brightness, and printability of the paper.
The alkaline nature of magnesium carbonate poses challenges in pH control during papermaking. Fluctuations in pH can affect the performance of other additives and the overall chemistry of the paper machine system. Balancing the benefits of magnesium carbonate with the need for precise pH management requires sophisticated control mechanisms and careful formulation.
Environmental considerations also present technical challenges in the application of magnesium carbonate. As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a need to optimize the use of magnesium carbonate to minimize its environmental footprint. This includes reducing water consumption, improving recyclability, and ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Lastly, the integration of magnesium carbonate into existing paper production processes without significant modifications to equipment or procedures remains a challenge. Developing application methods that are both effective and compatible with current manufacturing setups is essential for widespread adoption in the industry.
Current Applications in Pulp and Paper Manufacturing
01 Magnesium carbonate in pharmaceutical compositions
Magnesium carbonate is used in various pharmaceutical compositions as an excipient or active ingredient. It can be utilized in antacid formulations, oral care products, and as a filler or binder in tablets and capsules. Its properties make it suitable for improving drug stability, controlling release rates, and enhancing bioavailability of certain medications.- Magnesium carbonate in pharmaceutical compositions: Magnesium carbonate is used in various pharmaceutical formulations as an excipient or active ingredient. It can be employed in antacid preparations, oral care products, and as a filler or diluent in tablets and capsules. Its properties make it useful for improving drug stability, controlling release rates, and enhancing bioavailability of certain medications.
- Industrial applications of magnesium carbonate: Magnesium carbonate finds extensive use in industrial processes. It is utilized as a raw material in the production of magnesium oxide, as a filler in rubber and plastic manufacturing, and as a component in fireproofing materials. Additionally, it serves as a drying agent, a color retention additive in foods, and a reinforcing agent in various composite materials.
- Magnesium carbonate in personal care products: In personal care and cosmetic products, magnesium carbonate is employed for its absorbent and mattifying properties. It is used in deodorants, body powders, and makeup products to control moisture and oil. Its gentle nature makes it suitable for sensitive skin formulations, and it can also act as a bulking agent in various cosmetic preparations.
- Environmental and agricultural applications: Magnesium carbonate has applications in environmental remediation and agriculture. It is used in soil treatment to adjust pH levels and improve soil structure. In wastewater treatment, it can help remove heavy metals and other contaminants. Additionally, it finds use in animal feed supplements and as a component in fertilizers to provide magnesium to plants.
- Magnesium carbonate in sports and recreation: In sports and recreational activities, magnesium carbonate is widely used as a drying agent. It is commonly employed by gymnasts, rock climbers, and weightlifters to improve grip by absorbing sweat and reducing slippage. Its non-toxic nature and ability to absorb moisture make it a preferred choice in these applications.
02 Magnesium carbonate in industrial applications
Magnesium carbonate finds extensive use in industrial processes and products. It is employed as a filler in rubber and plastic manufacturing, a whitening agent in paper production, and a component in fireproofing materials. Its heat-resistant properties make it valuable in refractory applications, while its ability to absorb oils and moisture makes it useful in various chemical processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Magnesium carbonate in food and beverage industry
In the food and beverage industry, magnesium carbonate serves multiple purposes. It is used as an anticaking agent in powdered products, a pH regulator in certain food preparations, and a color retention agent. Its application extends to fortifying foods with magnesium and as a processing aid in the production of some beverages.Expand Specific Solutions04 Magnesium carbonate in personal care and cosmetics
Magnesium carbonate is incorporated into various personal care and cosmetic products. It functions as an absorbent in deodorants and antiperspirants, a bulking agent in powders, and a mild abrasive in toothpaste formulations. Its oil-absorbing properties make it useful in face powders and other cosmetic applications to control shine and improve texture.Expand Specific Solutions05 Magnesium carbonate in environmental applications
Magnesium carbonate plays a role in environmental applications, particularly in carbon capture and sequestration technologies. It can be used to absorb carbon dioxide from industrial emissions, potentially helping to mitigate greenhouse gas effects. Additionally, it finds use in water treatment processes and as a component in certain types of air purification systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Magnesium Carbonate Production and Supply
The research on magnesium carbonate in pulp and paper industry applications is in a growth phase, with increasing market potential due to the industry's focus on sustainable and efficient processes. The global pulp and paper chemicals market, which includes magnesium carbonate applications, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Nippon Paper Industries, UPM-Kymmene Oyj, and FPInnovations leading innovation. These firms are developing new applications and improving existing processes, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity with room for further advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring both established paper industry giants and specialized chemical companies, fostering a dynamic environment for research and development in this area.
Omya International AG
Technical Solution: Omya has developed advanced magnesium carbonate-based solutions for the pulp and paper industry. Their technology focuses on using ultrafine precipitated magnesium carbonate (PCC) as a functional filler and coating pigment. This innovative approach enhances paper properties such as brightness, opacity, and printability while reducing overall production costs[1]. Omya's process involves the controlled precipitation of magnesium carbonate under specific conditions to achieve optimal particle size and morphology. The company has also invested in research to improve the dispersion and retention of magnesium carbonate in paper matrices, leading to more efficient use of the material[2].
Strengths: High-quality PCC production, improved paper properties, cost-effective solution. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for implementation, potential limitations in certain paper grades.
Voith Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Voith has developed a novel approach to utilizing magnesium carbonate in pulp and paper production, focusing on its application in the deinking process. Their technology involves the use of magnesium carbonate as a pH regulator and flotation aid during the recycling of waste paper. By carefully controlling the addition of magnesium carbonate, Voith's process enhances the removal of ink particles and other contaminants from recycled fibers[3]. The company has also explored the use of magnesium carbonate in combination with enzymes to improve the efficiency of the deinking process, resulting in higher quality recycled pulp with reduced chemical consumption[4].
Strengths: Improved deinking efficiency, reduced chemical usage, applicable to various waste paper grades. Weaknesses: May require modifications to existing recycling systems, potential increased complexity in process control.
Innovative Research on Magnesium Carbonate Properties
Basic magnesium carbonate, production method and use of the same
PatentInactiveUS7922991B2
Innovation
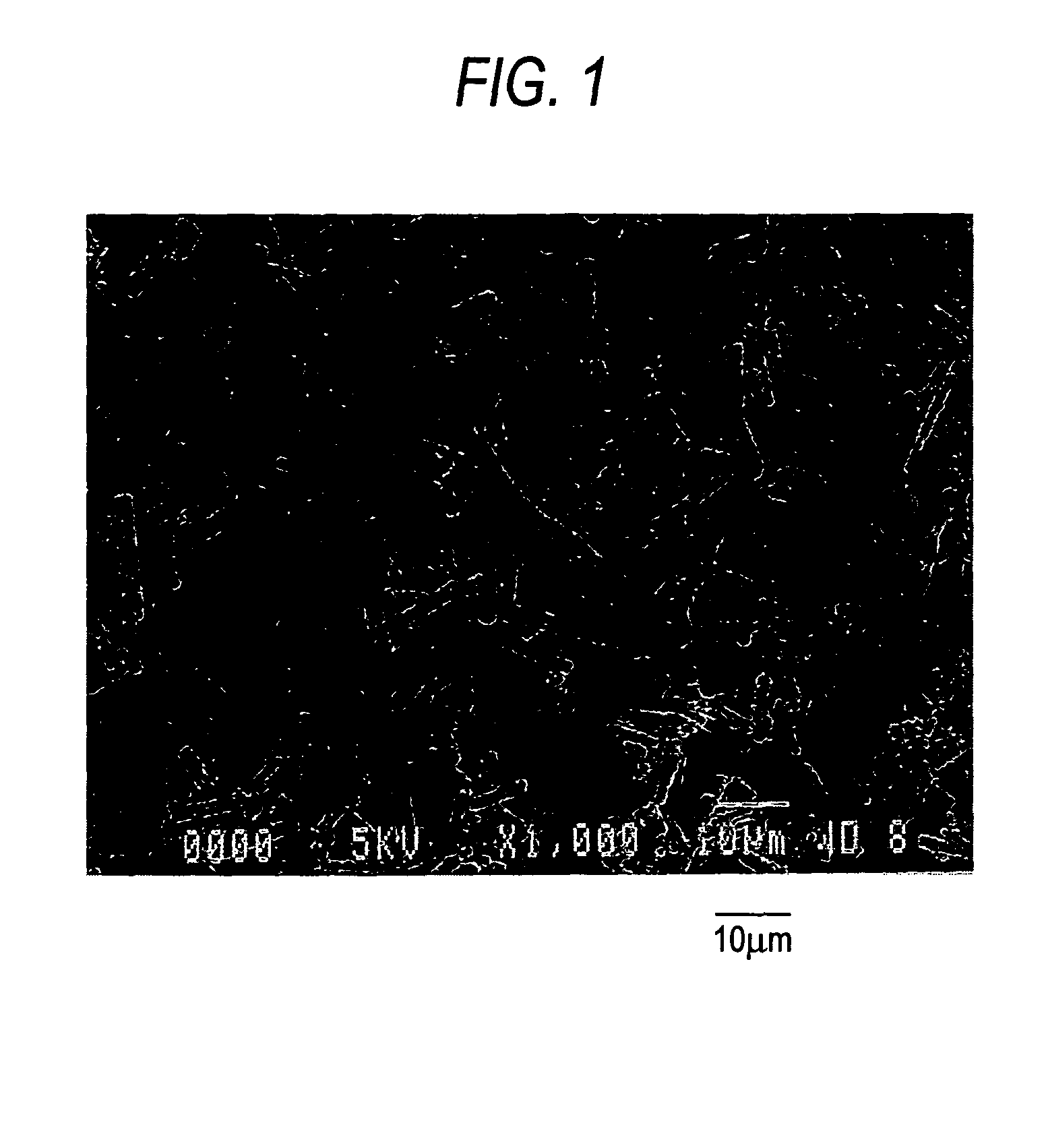
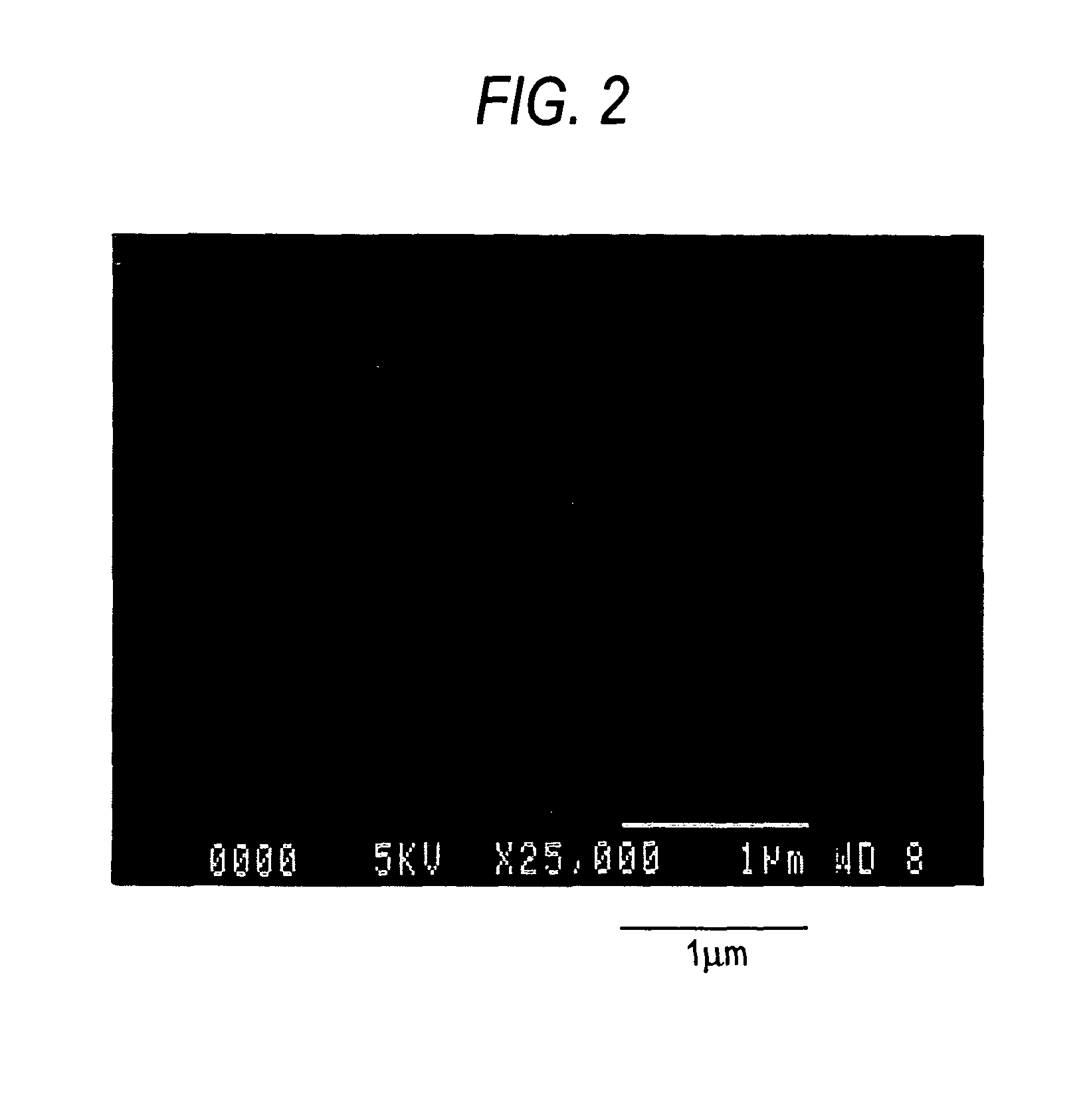
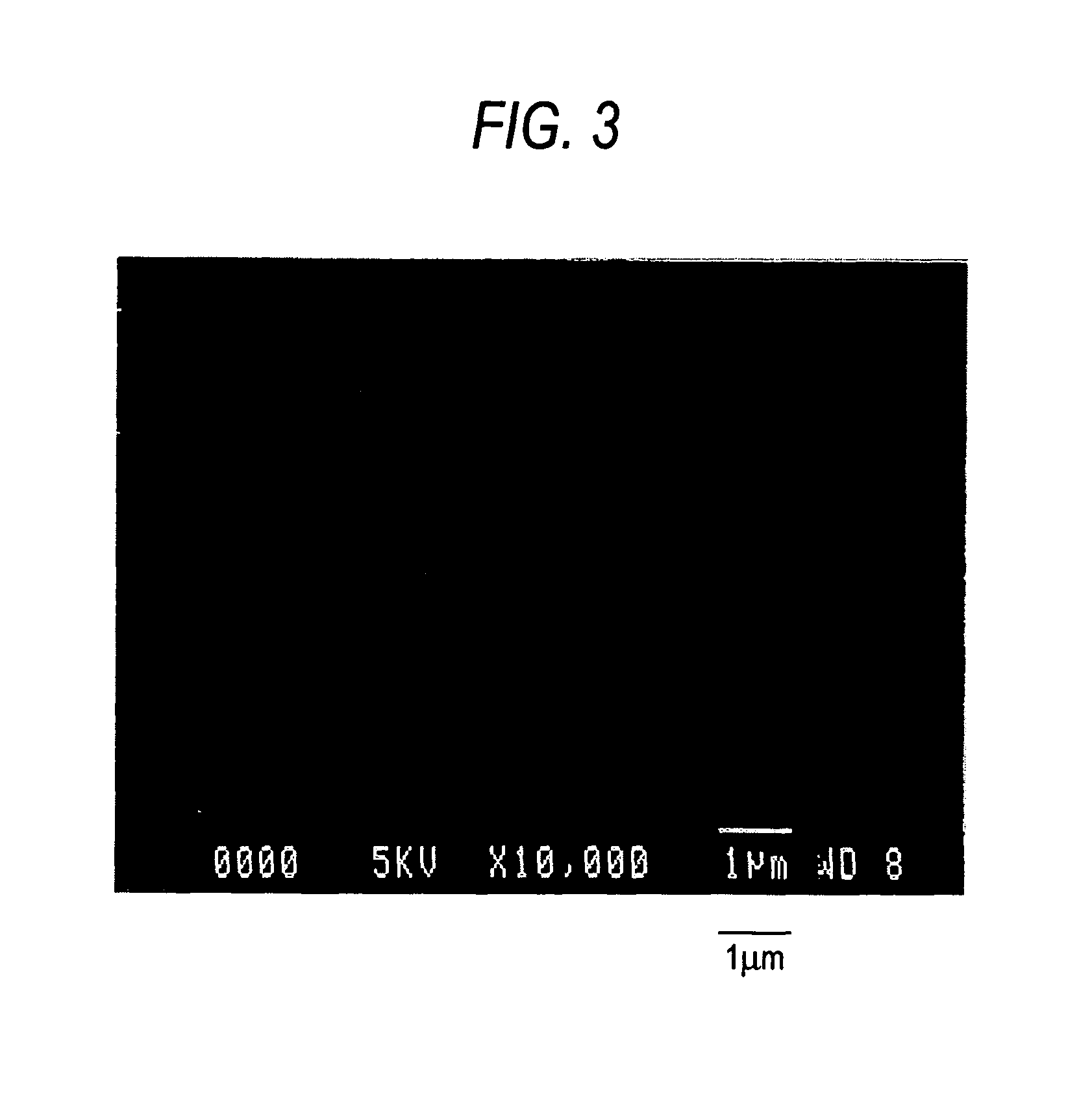
- Development of a basic magnesium carbonate with a novel tubular aggregated particle shape of flaky fine crystals, achieved through specific temperature and pH control methods, enhancing its specific surface area, pore volume, and oil/water absorption properties.
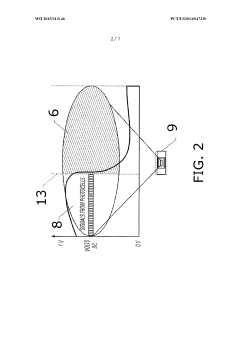
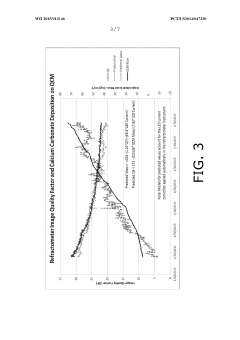
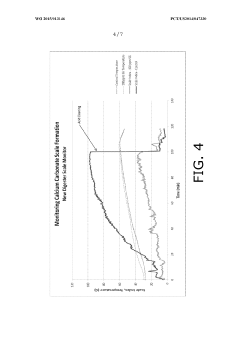
Method of deposition monitoring
PatentWO2015013146A1
Innovation
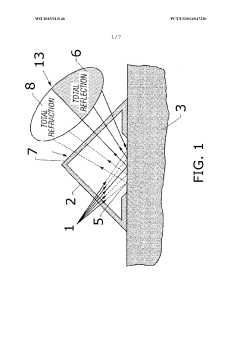
- A refractometer-based method using photon emission, a prism, and an optical sensor to measure the cell fouling factor by determining the critical angle of refraction, allowing for the detection and calculation of scale formation and the effectiveness of scale control agents under harsh conditions.
Environmental Impact of Magnesium Carbonate Usage
The use of magnesium carbonate in the pulp and paper industry has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. One of the primary environmental benefits is the reduction of chlorine-based bleaching agents, which are known to produce harmful byproducts such as dioxins and furans. By incorporating magnesium carbonate into the pulping process, mills can achieve comparable brightness levels with reduced chemical usage, thereby minimizing the release of these toxic compounds into the environment.
However, the extraction and processing of magnesium carbonate itself can have environmental impacts. Mining operations for magnesium carbonate can lead to habitat disruption, soil erosion, and potential groundwater contamination if not managed properly. The energy-intensive nature of processing raw magnesium carbonate into a usable form for the paper industry also contributes to carbon emissions, although this may be offset by the reduced energy requirements in the bleaching process.
In terms of water usage, magnesium carbonate can play a dual role. On one hand, it can help in water treatment processes within paper mills, potentially reducing the overall water consumption. On the other hand, the increased use of fillers like magnesium carbonate may require additional water for proper dispersion and retention in the paper-making process.
The impact on waste management is another crucial aspect to consider. While magnesium carbonate can improve the recyclability of paper products by enhancing their brightness without relying on optical brighteners, it may complicate the de-inking process during recycling. This could potentially lead to increased energy consumption and chemical usage in recycling facilities.
From a lifecycle perspective, the use of magnesium carbonate in paper production can contribute to lighter-weight papers, which in turn reduces transportation-related emissions. However, this benefit must be weighed against the environmental costs of magnesium carbonate production and transportation to paper mills.
Lastly, the alkaline nature of magnesium carbonate can have both positive and negative environmental effects. It can help neutralize acidic effluents from paper mills, potentially reducing the need for additional wastewater treatment chemicals. However, if not properly managed, it could also lead to changes in the pH balance of local water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems.
However, the extraction and processing of magnesium carbonate itself can have environmental impacts. Mining operations for magnesium carbonate can lead to habitat disruption, soil erosion, and potential groundwater contamination if not managed properly. The energy-intensive nature of processing raw magnesium carbonate into a usable form for the paper industry also contributes to carbon emissions, although this may be offset by the reduced energy requirements in the bleaching process.
In terms of water usage, magnesium carbonate can play a dual role. On one hand, it can help in water treatment processes within paper mills, potentially reducing the overall water consumption. On the other hand, the increased use of fillers like magnesium carbonate may require additional water for proper dispersion and retention in the paper-making process.
The impact on waste management is another crucial aspect to consider. While magnesium carbonate can improve the recyclability of paper products by enhancing their brightness without relying on optical brighteners, it may complicate the de-inking process during recycling. This could potentially lead to increased energy consumption and chemical usage in recycling facilities.
From a lifecycle perspective, the use of magnesium carbonate in paper production can contribute to lighter-weight papers, which in turn reduces transportation-related emissions. However, this benefit must be weighed against the environmental costs of magnesium carbonate production and transportation to paper mills.
Lastly, the alkaline nature of magnesium carbonate can have both positive and negative environmental effects. It can help neutralize acidic effluents from paper mills, potentially reducing the need for additional wastewater treatment chemicals. However, if not properly managed, it could also lead to changes in the pH balance of local water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems.
Quality Control Measures for Magnesium Carbonate in Paper
Quality control measures for magnesium carbonate in paper production are crucial to ensure consistent product quality and optimal performance. These measures typically involve a combination of raw material testing, in-process monitoring, and final product evaluation.
Raw material testing is the first line of defense in quality control. Incoming magnesium carbonate should be thoroughly analyzed for purity, particle size distribution, and moisture content. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) techniques are commonly employed to verify the chemical composition and crystalline structure of the material. Particle size analysis using laser diffraction or sieve methods helps ensure the magnesium carbonate meets the required specifications for paper applications.
During the paper production process, continuous monitoring of magnesium carbonate addition rates and dispersion is essential. Online sensors and automated control systems can be implemented to maintain consistent dosage levels. Regular sampling and testing of the paper stock can help detect any variations in magnesium carbonate concentration or distribution throughout the production run.
The finished paper product undergoes rigorous testing to verify the effectiveness of magnesium carbonate incorporation. Key parameters include opacity, brightness, smoothness, and printability. Standardized test methods, such as those outlined by TAPPI (Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry), are typically used to evaluate these properties. Ash content analysis is also performed to determine the overall mineral content, including magnesium carbonate, in the final paper.
Statistical process control (SPC) techniques are often employed to track quality trends over time and identify potential issues before they become significant problems. This involves collecting and analyzing data from various stages of production to establish control limits and detect deviations from normal operating conditions.
To ensure the long-term stability of paper containing magnesium carbonate, accelerated aging tests may be conducted. These tests simulate extended storage conditions to assess potential changes in paper properties over time, such as yellowing or brittleness.
Implementing a comprehensive quality management system, such as ISO 9001, can help standardize and improve quality control processes for magnesium carbonate in paper production. This system emphasizes continuous improvement and documentation of quality procedures, ensuring consistent adherence to established standards and facilitating traceability in case of quality issues.
Raw material testing is the first line of defense in quality control. Incoming magnesium carbonate should be thoroughly analyzed for purity, particle size distribution, and moisture content. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray fluorescence (XRF) techniques are commonly employed to verify the chemical composition and crystalline structure of the material. Particle size analysis using laser diffraction or sieve methods helps ensure the magnesium carbonate meets the required specifications for paper applications.
During the paper production process, continuous monitoring of magnesium carbonate addition rates and dispersion is essential. Online sensors and automated control systems can be implemented to maintain consistent dosage levels. Regular sampling and testing of the paper stock can help detect any variations in magnesium carbonate concentration or distribution throughout the production run.
The finished paper product undergoes rigorous testing to verify the effectiveness of magnesium carbonate incorporation. Key parameters include opacity, brightness, smoothness, and printability. Standardized test methods, such as those outlined by TAPPI (Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry), are typically used to evaluate these properties. Ash content analysis is also performed to determine the overall mineral content, including magnesium carbonate, in the final paper.
Statistical process control (SPC) techniques are often employed to track quality trends over time and identify potential issues before they become significant problems. This involves collecting and analyzing data from various stages of production to establish control limits and detect deviations from normal operating conditions.
To ensure the long-term stability of paper containing magnesium carbonate, accelerated aging tests may be conducted. These tests simulate extended storage conditions to assess potential changes in paper properties over time, such as yellowing or brittleness.
Implementing a comprehensive quality management system, such as ISO 9001, can help standardize and improve quality control processes for magnesium carbonate in paper production. This system emphasizes continuous improvement and documentation of quality procedures, ensuring consistent adherence to established standards and facilitating traceability in case of quality issues.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!