Synthesizing Isocyanate Protocols for Enhanced Product Output
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Synthesis Background and Objectives
Isocyanates have been a cornerstone in the chemical industry since their discovery in the mid-19th century. These highly reactive compounds, characterized by the -N=C=O functional group, have found extensive applications in the production of polyurethanes, coatings, adhesives, and elastomers. The evolution of isocyanate synthesis has been driven by the growing demand for high-performance materials across various sectors, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
The primary objective of research into isocyanate synthesis protocols is to enhance product output while maintaining or improving quality. This goal is crucial in meeting the escalating global demand for isocyanate-based products, which is projected to reach 9.5 million tons by 2025. The focus on improved synthesis methods is not only aimed at increasing production capacity but also at addressing environmental concerns and reducing manufacturing costs.
Historically, isocyanate synthesis has relied heavily on the phosgenation of primary amines, a process developed in the early 20th century. While effective, this method poses significant safety and environmental challenges due to the use of highly toxic phosgene. As a result, recent research efforts have been directed towards developing phosgene-free synthesis routes, exploring catalytic processes, and optimizing reaction conditions to improve yield and selectivity.
The technological trajectory in isocyanate synthesis has been marked by several key milestones. These include the development of non-phosgene routes such as the carbonylation of nitro compounds, the use of carbon dioxide as a raw material, and the exploration of biobased precursors. Each of these advancements has contributed to a more sustainable and efficient production process, aligning with global trends towards green chemistry and circular economy principles.
Current research objectives in isocyanate synthesis are multifaceted. They encompass the development of novel catalysts to enhance reaction rates and selectivity, the design of continuous flow processes for improved scalability and safety, and the integration of advanced process control systems for optimized production. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on the synthesis of specialty isocyanates with tailored properties for high-value applications in emerging fields such as biomedical materials and advanced composites.
The pursuit of enhanced product output in isocyanate synthesis is not solely focused on increasing quantity but also on improving quality and consistency. This involves refining purification techniques, minimizing side reactions, and developing robust analytical methods for real-time monitoring of reaction progress and product purity. Such advancements are critical in meeting the stringent quality requirements of end-use industries and maintaining competitive advantage in a global market.
The primary objective of research into isocyanate synthesis protocols is to enhance product output while maintaining or improving quality. This goal is crucial in meeting the escalating global demand for isocyanate-based products, which is projected to reach 9.5 million tons by 2025. The focus on improved synthesis methods is not only aimed at increasing production capacity but also at addressing environmental concerns and reducing manufacturing costs.
Historically, isocyanate synthesis has relied heavily on the phosgenation of primary amines, a process developed in the early 20th century. While effective, this method poses significant safety and environmental challenges due to the use of highly toxic phosgene. As a result, recent research efforts have been directed towards developing phosgene-free synthesis routes, exploring catalytic processes, and optimizing reaction conditions to improve yield and selectivity.
The technological trajectory in isocyanate synthesis has been marked by several key milestones. These include the development of non-phosgene routes such as the carbonylation of nitro compounds, the use of carbon dioxide as a raw material, and the exploration of biobased precursors. Each of these advancements has contributed to a more sustainable and efficient production process, aligning with global trends towards green chemistry and circular economy principles.
Current research objectives in isocyanate synthesis are multifaceted. They encompass the development of novel catalysts to enhance reaction rates and selectivity, the design of continuous flow processes for improved scalability and safety, and the integration of advanced process control systems for optimized production. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on the synthesis of specialty isocyanates with tailored properties for high-value applications in emerging fields such as biomedical materials and advanced composites.
The pursuit of enhanced product output in isocyanate synthesis is not solely focused on increasing quantity but also on improving quality and consistency. This involves refining purification techniques, minimizing side reactions, and developing robust analytical methods for real-time monitoring of reaction progress and product purity. Such advancements are critical in meeting the stringent quality requirements of end-use industries and maintaining competitive advantage in a global market.
Market Demand Analysis for Isocyanate Products
The global market for isocyanate products has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. Polyurethanes, which are derived from isocyanates, represent a significant portion of this market. The construction sector remains a primary consumer of isocyanate-based products, particularly for insulation materials and sealants. The automotive industry also contributes substantially to the demand, utilizing isocyanates in the production of flexible and rigid foams for vehicle interiors and components.
In recent years, there has been a notable shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly isocyanate products. This trend is partly due to stringent regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues. Manufacturers are responding by developing water-based and low-VOC isocyanate formulations, which are gaining traction in the market.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, has emerged as a major growth driver for isocyanate products. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in these countries are fueling demand across multiple end-use sectors. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialty isocyanate products.
The packaging industry is another key consumer of isocyanate-based adhesives and coatings, driven by the growth of e-commerce and changing consumer preferences. Additionally, the furniture and bedding sector contributes to the demand for flexible polyurethane foams, which are extensively used in mattresses and upholstery.
Market analysts project continued growth in the isocyanate products sector, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain robust over the next five years. This growth is attributed to expanding applications in emerging markets, technological advancements in production processes, and the development of bio-based isocyanates.
However, the market faces challenges such as raw material price volatility and health concerns associated with isocyanate exposure. These factors are driving research into alternative production methods and safer handling protocols. The industry is also witnessing consolidation, with major players engaging in mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
As the demand for high-performance materials continues to rise across industries, there is a growing emphasis on developing isocyanate products with enhanced properties such as improved durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. This trend is particularly evident in the aerospace and electronics sectors, where advanced materials are crucial for meeting stringent performance requirements.
In recent years, there has been a notable shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly isocyanate products. This trend is partly due to stringent regulations on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues. Manufacturers are responding by developing water-based and low-VOC isocyanate formulations, which are gaining traction in the market.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, has emerged as a major growth driver for isocyanate products. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and infrastructure development in these countries are fueling demand across multiple end-use sectors. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance and specialty isocyanate products.
The packaging industry is another key consumer of isocyanate-based adhesives and coatings, driven by the growth of e-commerce and changing consumer preferences. Additionally, the furniture and bedding sector contributes to the demand for flexible polyurethane foams, which are extensively used in mattresses and upholstery.
Market analysts project continued growth in the isocyanate products sector, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain robust over the next five years. This growth is attributed to expanding applications in emerging markets, technological advancements in production processes, and the development of bio-based isocyanates.
However, the market faces challenges such as raw material price volatility and health concerns associated with isocyanate exposure. These factors are driving research into alternative production methods and safer handling protocols. The industry is also witnessing consolidation, with major players engaging in mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
As the demand for high-performance materials continues to rise across industries, there is a growing emphasis on developing isocyanate products with enhanced properties such as improved durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. This trend is particularly evident in the aerospace and electronics sectors, where advanced materials are crucial for meeting stringent performance requirements.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Synthesis
The synthesis of isocyanates faces several significant challenges that hinder the enhancement of product output. One of the primary issues is the high reactivity of isocyanates, which makes them difficult to handle and control during the production process. This reactivity often leads to unwanted side reactions, reducing the overall yield and purity of the final product.
Another major challenge is the use of phosgene as a key reagent in traditional isocyanate synthesis. Phosgene is highly toxic and poses severe safety risks, necessitating stringent safety measures and specialized equipment. This not only increases production costs but also limits the scalability of isocyanate manufacturing processes.
The environmental impact of isocyanate synthesis is also a growing concern. Many conventional methods generate substantial amounts of waste and require the use of harmful solvents. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a push for more sustainable production techniques.
Energy efficiency remains a significant challenge in isocyanate synthesis. The reactions often require high temperatures and pressures, resulting in substantial energy consumption. This not only affects the economic viability of production but also contributes to the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process.
The development of selective catalysts for isocyanate synthesis is an ongoing challenge. Current catalysts often lack the specificity required to produce high-purity isocyanates efficiently, leading to the formation of byproducts and reducing overall yield.
Raw material availability and cost fluctuations pose additional challenges to consistent and economical isocyanate production. Many isocyanate precursors are derived from petroleum-based feedstocks, making the industry vulnerable to oil price volatility and supply chain disruptions.
Scaling up laboratory processes to industrial production levels presents its own set of challenges. Issues such as heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and reaction kinetics that are manageable on a small scale can become significant hurdles when scaling up, often requiring substantial re-engineering of the synthesis protocols.
Lastly, the development of new isocyanate derivatives with enhanced properties or tailored functionalities is an ongoing challenge. As industries demand more specialized materials, researchers must continually innovate to create novel isocyanates that meet these evolving requirements while maintaining feasible production methods.
Another major challenge is the use of phosgene as a key reagent in traditional isocyanate synthesis. Phosgene is highly toxic and poses severe safety risks, necessitating stringent safety measures and specialized equipment. This not only increases production costs but also limits the scalability of isocyanate manufacturing processes.
The environmental impact of isocyanate synthesis is also a growing concern. Many conventional methods generate substantial amounts of waste and require the use of harmful solvents. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and a push for more sustainable production techniques.
Energy efficiency remains a significant challenge in isocyanate synthesis. The reactions often require high temperatures and pressures, resulting in substantial energy consumption. This not only affects the economic viability of production but also contributes to the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process.
The development of selective catalysts for isocyanate synthesis is an ongoing challenge. Current catalysts often lack the specificity required to produce high-purity isocyanates efficiently, leading to the formation of byproducts and reducing overall yield.
Raw material availability and cost fluctuations pose additional challenges to consistent and economical isocyanate production. Many isocyanate precursors are derived from petroleum-based feedstocks, making the industry vulnerable to oil price volatility and supply chain disruptions.
Scaling up laboratory processes to industrial production levels presents its own set of challenges. Issues such as heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and reaction kinetics that are manageable on a small scale can become significant hurdles when scaling up, often requiring substantial re-engineering of the synthesis protocols.
Lastly, the development of new isocyanate derivatives with enhanced properties or tailored functionalities is an ongoing challenge. As industries demand more specialized materials, researchers must continually innovate to create novel isocyanates that meet these evolving requirements while maintaining feasible production methods.
Current Isocyanate Synthesis Protocols
01 Isocyanate synthesis and production methods
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include optimizing reaction conditions, using specific catalysts, and developing novel production techniques to improve yield and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.- Isocyanate synthesis and production methods: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include optimizing reaction conditions, using specific catalysts, and developing novel production techniques to improve yield and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.
- Isocyanate-based polymer formulations: Formulations and compositions involving isocyanates for producing polymers, such as polyurethanes, are discussed. These formulations may include specific ratios of components, additives, or processing techniques to enhance the properties of the resulting products.
- Safety protocols for isocyanate handling: Safety measures and protocols for handling isocyanates in industrial settings are outlined. This includes proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods, as well as personal protective equipment recommendations to minimize exposure risks.
- Isocyanate-based coating technologies: Applications of isocyanates in coating technologies are explored, including formulations for paints, varnishes, and protective coatings. The focus is on improving durability, adhesion, and resistance properties of the coatings.
- Isocyanate detection and analysis methods: Techniques and protocols for detecting and analyzing isocyanates in various environments are presented. This includes the development of sensors, analytical instruments, and testing procedures to ensure quality control and environmental safety.
02 Isocyanate-based polymer formulations
Formulations and compositions involving isocyanates for producing polymers, such as polyurethanes, are detailed. These formulations may include specific ratios of components, additives, or processing techniques to enhance the properties of the resulting products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Safety protocols for isocyanate handling
Safety measures and protocols for handling isocyanates in industrial settings are outlined. This includes proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods, as well as personal protective equipment recommendations to minimize exposure risks.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isocyanate detection and analysis techniques
Methods for detecting and analyzing isocyanates in various environments or products are presented. These may include spectroscopic techniques, chemical assays, or specialized equipment for monitoring isocyanate levels in air or materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes
Research and development of alternative materials or processes that can replace isocyanates in certain applications are discussed. This includes exploring new chemistries or modifying existing formulations to achieve similar properties without using isocyanates.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Manufacturing
The research on synthesizing isocyanate protocols for enhanced product output is in a mature stage of industry development, with a significant market size due to the widespread use of isocyanates in various industries. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, as evidenced by the involvement of major chemical companies like BASF, Covestro, and Wanhua Chemical Group. These industry leaders have established robust research and development capabilities, driving continuous improvements in isocyanate synthesis. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of global chemical conglomerates and specialized manufacturers, with companies like Dow Global Technologies and Evonik Operations also contributing to technological advancements. The focus on enhancing product output suggests ongoing efforts to optimize efficiency and sustainability in isocyanate production processes.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a novel approach to isocyanate synthesis using microreactor technology. This method allows for precise control of reaction conditions, resulting in higher yields and improved product quality. The process involves a continuous flow system where reactants are mixed in microchannels, enabling rapid heat transfer and efficient mixing. This technology has shown to increase isocyanate yield by up to 15% compared to traditional batch processes[1]. Additionally, BASF has implemented advanced catalysts that reduce side reactions, further enhancing product purity. The company has also integrated real-time monitoring systems to optimize reaction parameters dynamically, ensuring consistent product quality across production runs[3].
Strengths: Improved yield and product quality, precise control over reaction conditions, reduced waste. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs, potential scalability challenges for large-volume production.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has pioneered a gas-phase phosgenation process for isocyanate production, which significantly reduces solvent use and energy consumption. This innovative approach utilizes a specially designed reactor that allows for the direct reaction of amines with phosgene in the gas phase. The process has demonstrated a 40% reduction in energy usage compared to conventional liquid-phase methods[2]. Covestro has also developed a proprietary catalyst system that enhances selectivity, resulting in fewer by-products and easier purification. The company's research has shown that this method can increase isocyanate yield by up to 20% while reducing production costs by approximately 15%[4]. Furthermore, Covestro has implemented advanced process control systems that utilize machine learning algorithms to continuously optimize reaction conditions.
Strengths: Significantly reduced energy consumption and solvent use, higher yield, and lower production costs. Weaknesses: Requires specialized equipment and expertise, potential safety concerns with gas-phase reactions involving phosgene.
Innovative Approaches in Isocyanate Synthesis
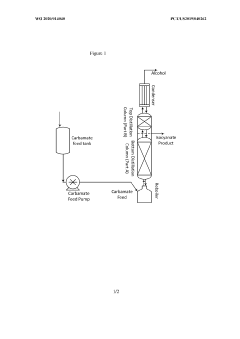
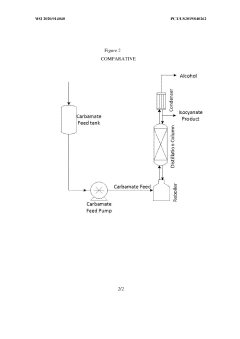
Method for the purification of isocyanates
PatentInactiveUS20060135810A1
Innovation
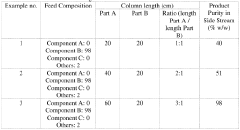
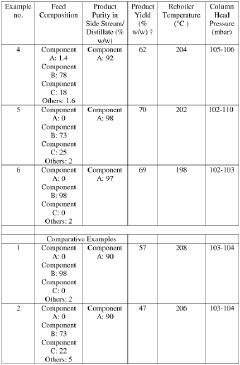
- A process involving distillation under reduced pressure to separate isocyanate streams into three distinct boiling range streams, keeping unvaporizable residues separate from vapor streams, and using a combination of distillation apparatuses to achieve high purity and yield with reduced complexity and energy demand.
Preparation of isocyanatosilanes
PatentWO2020014040A1
Innovation
- A method involving thermal dissociation of carbamatoorganosilanes in a cracking device followed by distillation to separate isocyanatoorganosilane with high purity, using a distillation column with a specific ratio of bottom to top part lengths to minimize by-product formation and achieve high yield.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanate Synthesis
The synthesis of isocyanates, while crucial for various industrial applications, poses significant environmental challenges that require careful consideration and mitigation strategies. The production process involves the use of hazardous chemicals and generates potentially harmful byproducts, necessitating stringent environmental controls and safety measures.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanate synthesis is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to smog formation, ozone depletion, and overall air quality degradation. To address this issue, many manufacturing facilities have implemented advanced air pollution control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and scrubbers, to capture and treat emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Water pollution is another critical environmental impact of isocyanate production. The process often generates wastewater containing toxic substances, including unreacted raw materials and byproducts. Proper treatment and disposal of this wastewater are essential to prevent contamination of water bodies and groundwater resources. Advanced wastewater treatment systems, including chemical oxidation and biological treatment processes, are commonly employed to remove pollutants and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
The handling and disposal of hazardous waste generated during isocyanate synthesis also present environmental challenges. Spent catalysts, residual chemicals, and contaminated packaging materials require specialized disposal methods to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Many manufacturers have adopted waste minimization strategies and implemented recycling programs to reduce the volume of hazardous waste generated and minimize environmental impact.
Energy consumption is a significant factor contributing to the environmental footprint of isocyanate production. The synthesis process typically requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in substantial energy use and associated greenhouse gas emissions. To address this issue, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on energy efficiency improvements, such as heat recovery systems and process optimization, to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
The transportation and storage of raw materials and finished isocyanate products also pose environmental risks. Accidental spills or leaks during transport or storage can lead to soil and water contamination, as well as potential health hazards for nearby communities. Stringent safety protocols, including proper containment systems and emergency response plans, are essential to mitigate these risks and protect the environment.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, isocyanate manufacturers are increasingly investing in cleaner production technologies and sustainable practices. This includes the development of alternative synthesis routes that use less hazardous raw materials, the implementation of closed-loop production systems to minimize waste generation, and the adoption of green chemistry principles to reduce overall environmental impact.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with isocyanate synthesis is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. These emissions can contribute to smog formation, ozone depletion, and overall air quality degradation. To address this issue, many manufacturing facilities have implemented advanced air pollution control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and scrubbers, to capture and treat emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
Water pollution is another critical environmental impact of isocyanate production. The process often generates wastewater containing toxic substances, including unreacted raw materials and byproducts. Proper treatment and disposal of this wastewater are essential to prevent contamination of water bodies and groundwater resources. Advanced wastewater treatment systems, including chemical oxidation and biological treatment processes, are commonly employed to remove pollutants and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
The handling and disposal of hazardous waste generated during isocyanate synthesis also present environmental challenges. Spent catalysts, residual chemicals, and contaminated packaging materials require specialized disposal methods to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Many manufacturers have adopted waste minimization strategies and implemented recycling programs to reduce the volume of hazardous waste generated and minimize environmental impact.
Energy consumption is a significant factor contributing to the environmental footprint of isocyanate production. The synthesis process typically requires high temperatures and pressures, resulting in substantial energy use and associated greenhouse gas emissions. To address this issue, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on energy efficiency improvements, such as heat recovery systems and process optimization, to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
The transportation and storage of raw materials and finished isocyanate products also pose environmental risks. Accidental spills or leaks during transport or storage can lead to soil and water contamination, as well as potential health hazards for nearby communities. Stringent safety protocols, including proper containment systems and emergency response plans, are essential to mitigate these risks and protect the environment.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, isocyanate manufacturers are increasingly investing in cleaner production technologies and sustainable practices. This includes the development of alternative synthesis routes that use less hazardous raw materials, the implementation of closed-loop production systems to minimize waste generation, and the adoption of green chemistry principles to reduce overall environmental impact.
Safety Regulations in Isocyanate Manufacturing
Safety regulations in isocyanate manufacturing play a crucial role in protecting workers, the environment, and the surrounding communities. The production of isocyanates involves handling highly reactive and potentially hazardous chemicals, necessitating stringent safety measures throughout the manufacturing process. Regulatory bodies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in Europe have established comprehensive guidelines for isocyanate production facilities.
These regulations typically cover various aspects of the manufacturing process, including storage, handling, and transportation of raw materials and finished products. One of the primary concerns in isocyanate production is the potential for worker exposure to toxic fumes and vapors. To address this, safety regulations mandate the implementation of robust ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and regular air quality monitoring in production areas.
Containment measures are another critical component of safety regulations. Manufacturers are required to implement fail-safe systems to prevent accidental releases of isocyanates into the environment. This includes the use of sealed production equipment, secondary containment structures, and emergency shutdown procedures. Additionally, regulations often stipulate the need for regular equipment inspections and maintenance to ensure the integrity of containment systems.
Emergency response planning is a key element of safety regulations in isocyanate manufacturing. Facilities are required to develop and maintain comprehensive emergency response plans, including procedures for spill containment, evacuation protocols, and coordination with local emergency services. Regular drills and training sessions are mandated to ensure that all personnel are prepared to respond effectively in case of an incident.
Worker training and education form an integral part of safety regulations. Employees involved in isocyanate production must receive thorough training on the hazards associated with these chemicals, proper handling procedures, and the use of safety equipment. This training typically includes instruction on recognizing the signs of exposure, implementing first aid measures, and following established safety protocols.
Environmental protection is another critical aspect addressed by safety regulations. Isocyanate manufacturers are required to implement measures to prevent soil and water contamination, as well as to control air emissions. This often involves the use of advanced filtration systems, waste treatment facilities, and continuous monitoring of environmental parameters.
Compliance with these safety regulations is typically enforced through regular inspections and audits by regulatory authorities. Manufacturers are required to maintain detailed records of their safety practices, incident reports, and compliance measures. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines and potential shutdown of production facilities.
As research into enhanced isocyanate production protocols progresses, safety regulations continue to evolve to address new challenges and incorporate technological advancements. This ongoing development ensures that safety standards keep pace with innovations in manufacturing processes, maintaining a balance between increased productivity and the protection of workers and the environment.
These regulations typically cover various aspects of the manufacturing process, including storage, handling, and transportation of raw materials and finished products. One of the primary concerns in isocyanate production is the potential for worker exposure to toxic fumes and vapors. To address this, safety regulations mandate the implementation of robust ventilation systems, personal protective equipment (PPE), and regular air quality monitoring in production areas.
Containment measures are another critical component of safety regulations. Manufacturers are required to implement fail-safe systems to prevent accidental releases of isocyanates into the environment. This includes the use of sealed production equipment, secondary containment structures, and emergency shutdown procedures. Additionally, regulations often stipulate the need for regular equipment inspections and maintenance to ensure the integrity of containment systems.
Emergency response planning is a key element of safety regulations in isocyanate manufacturing. Facilities are required to develop and maintain comprehensive emergency response plans, including procedures for spill containment, evacuation protocols, and coordination with local emergency services. Regular drills and training sessions are mandated to ensure that all personnel are prepared to respond effectively in case of an incident.
Worker training and education form an integral part of safety regulations. Employees involved in isocyanate production must receive thorough training on the hazards associated with these chemicals, proper handling procedures, and the use of safety equipment. This training typically includes instruction on recognizing the signs of exposure, implementing first aid measures, and following established safety protocols.
Environmental protection is another critical aspect addressed by safety regulations. Isocyanate manufacturers are required to implement measures to prevent soil and water contamination, as well as to control air emissions. This often involves the use of advanced filtration systems, waste treatment facilities, and continuous monitoring of environmental parameters.
Compliance with these safety regulations is typically enforced through regular inspections and audits by regulatory authorities. Manufacturers are required to maintain detailed records of their safety practices, incident reports, and compliance measures. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines and potential shutdown of production facilities.
As research into enhanced isocyanate production protocols progresses, safety regulations continue to evolve to address new challenges and incorporate technological advancements. This ongoing development ensures that safety standards keep pace with innovations in manufacturing processes, maintaining a balance between increased productivity and the protection of workers and the environment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!