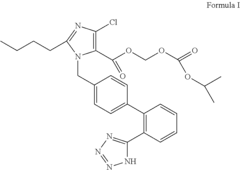
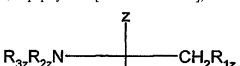
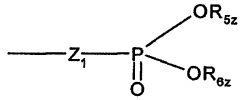
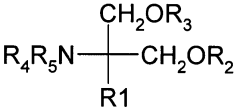
Role of 2-Methylpentane in Enhancing Drug Solubility
JUL 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
2-Methylpentane Background and Objectives
2-Methylpentane, a branched alkane with the molecular formula C6H14, has emerged as a significant compound in the field of pharmaceutical research, particularly in enhancing drug solubility. The exploration of this compound's potential began in the early 2000s, as researchers sought innovative solutions to address the persistent challenge of poor drug solubility, which has long been a major obstacle in drug development and delivery.
The primary objective of investigating 2-Methylpentane in this context is to improve the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs, thereby enhancing their therapeutic efficacy. This aligns with the broader goal of pharmaceutical research to develop more effective and efficient drug formulations. The compound's unique properties, including its low polarity and ability to form non-covalent interactions with drug molecules, have made it a subject of intense study in recent years.
The evolution of 2-Methylpentane's role in drug solubility enhancement can be traced through several key stages. Initially, it was primarily used as a solvent in various industrial applications. However, its potential in pharmaceutical formulations was recognized when researchers observed its ability to form eutectic mixtures with certain drug compounds, leading to improved dissolution rates.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards understanding the molecular mechanisms by which 2-Methylpentane interacts with drug molecules. This led to the development of novel formulation strategies, such as co-crystal formation and lipid-based drug delivery systems, where 2-Methylpentane plays a crucial role in enhancing drug solubility and dissolution.
The technological trajectory in this field is now moving towards more sophisticated applications of 2-Methylpentane. Current research aims to optimize its use in combination with other excipients and to develop targeted drug delivery systems that can leverage its solubility-enhancing properties. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of 2-Methylpentane derivatives and analogues that may offer even greater benefits in terms of drug solubility enhancement.
Looking ahead, the objectives for further research and development in this area include: expanding the range of drugs that can benefit from 2-Methylpentane-based formulations, improving the stability and shelf-life of these formulations, and developing scalable manufacturing processes for commercial production. There is also a focus on addressing any potential toxicity or environmental concerns associated with the use of 2-Methylpentane in pharmaceutical applications.
In conclusion, the background and objectives surrounding the role of 2-Methylpentane in enhancing drug solubility reflect a dynamic and evolving field of research. As pharmaceutical companies and researchers continue to explore its potential, 2-Methylpentane stands poised to play an increasingly important role in addressing one of the most significant challenges in drug development and delivery.
The primary objective of investigating 2-Methylpentane in this context is to improve the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs, thereby enhancing their therapeutic efficacy. This aligns with the broader goal of pharmaceutical research to develop more effective and efficient drug formulations. The compound's unique properties, including its low polarity and ability to form non-covalent interactions with drug molecules, have made it a subject of intense study in recent years.
The evolution of 2-Methylpentane's role in drug solubility enhancement can be traced through several key stages. Initially, it was primarily used as a solvent in various industrial applications. However, its potential in pharmaceutical formulations was recognized when researchers observed its ability to form eutectic mixtures with certain drug compounds, leading to improved dissolution rates.
As research progressed, the focus shifted towards understanding the molecular mechanisms by which 2-Methylpentane interacts with drug molecules. This led to the development of novel formulation strategies, such as co-crystal formation and lipid-based drug delivery systems, where 2-Methylpentane plays a crucial role in enhancing drug solubility and dissolution.
The technological trajectory in this field is now moving towards more sophisticated applications of 2-Methylpentane. Current research aims to optimize its use in combination with other excipients and to develop targeted drug delivery systems that can leverage its solubility-enhancing properties. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of 2-Methylpentane derivatives and analogues that may offer even greater benefits in terms of drug solubility enhancement.
Looking ahead, the objectives for further research and development in this area include: expanding the range of drugs that can benefit from 2-Methylpentane-based formulations, improving the stability and shelf-life of these formulations, and developing scalable manufacturing processes for commercial production. There is also a focus on addressing any potential toxicity or environmental concerns associated with the use of 2-Methylpentane in pharmaceutical applications.
In conclusion, the background and objectives surrounding the role of 2-Methylpentane in enhancing drug solubility reflect a dynamic and evolving field of research. As pharmaceutical companies and researchers continue to explore its potential, 2-Methylpentane stands poised to play an increasingly important role in addressing one of the most significant challenges in drug development and delivery.
Market Analysis for Solubility Enhancement
The market for solubility enhancement technologies in the pharmaceutical industry has been experiencing significant growth due to the increasing prevalence of poorly soluble drug candidates. As more complex and hydrophobic molecules enter drug development pipelines, the demand for effective solubility enhancement methods continues to rise. The global market for drug solubility enhancement is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, driven by the need to improve bioavailability and efficacy of new drug formulations.
2-Methylpentane, a branched alkane, has emerged as a promising solvent for enhancing drug solubility. Its unique properties, including low polarity and ability to form favorable interactions with hydrophobic drug molecules, make it an attractive option for pharmaceutical companies seeking to overcome solubility challenges. The market potential for 2-methylpentane in drug formulation is closely tied to the broader trends in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly the increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted drug delivery systems.
The adoption of 2-methylpentane as a solubility enhancer is expected to impact various segments of the pharmaceutical market. Generic drug manufacturers may find it particularly valuable in developing more cost-effective formulations of existing drugs with poor solubility profiles. Additionally, the biotechnology sector, which often deals with large and complex protein-based therapeutics, could benefit from the solubility-enhancing properties of 2-methylpentane in creating stable and bioavailable formulations.
Market analysis indicates that the demand for 2-methylpentane in pharmaceutical applications is likely to grow in regions with strong pharmaceutical research and development activities. North America and Europe are expected to be key markets, given their established pharmaceutical industries and regulatory frameworks. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are anticipated to show rapid growth in adoption as their pharmaceutical sectors expand and modernize.
The competitive landscape for solubility enhancement technologies is diverse, with various approaches such as solid dispersions, nanoparticle formulations, and cyclodextrin complexation already established. 2-Methylpentane enters this market as a novel solution, potentially offering advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and compatibility with a wide range of drug molecules. Its success will depend on factors such as regulatory approval, safety profile, and demonstrated efficacy in improving drug bioavailability across different therapeutic areas.
As environmental concerns and sustainability become increasingly important in the pharmaceutical industry, the market analysis must also consider the ecological impact of 2-methylpentane usage. Companies developing formulations using this solvent may need to address potential environmental and safety concerns, which could influence market acceptance and regulatory approval processes.
2-Methylpentane, a branched alkane, has emerged as a promising solvent for enhancing drug solubility. Its unique properties, including low polarity and ability to form favorable interactions with hydrophobic drug molecules, make it an attractive option for pharmaceutical companies seeking to overcome solubility challenges. The market potential for 2-methylpentane in drug formulation is closely tied to the broader trends in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly the increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted drug delivery systems.
The adoption of 2-methylpentane as a solubility enhancer is expected to impact various segments of the pharmaceutical market. Generic drug manufacturers may find it particularly valuable in developing more cost-effective formulations of existing drugs with poor solubility profiles. Additionally, the biotechnology sector, which often deals with large and complex protein-based therapeutics, could benefit from the solubility-enhancing properties of 2-methylpentane in creating stable and bioavailable formulations.
Market analysis indicates that the demand for 2-methylpentane in pharmaceutical applications is likely to grow in regions with strong pharmaceutical research and development activities. North America and Europe are expected to be key markets, given their established pharmaceutical industries and regulatory frameworks. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are anticipated to show rapid growth in adoption as their pharmaceutical sectors expand and modernize.
The competitive landscape for solubility enhancement technologies is diverse, with various approaches such as solid dispersions, nanoparticle formulations, and cyclodextrin complexation already established. 2-Methylpentane enters this market as a novel solution, potentially offering advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and compatibility with a wide range of drug molecules. Its success will depend on factors such as regulatory approval, safety profile, and demonstrated efficacy in improving drug bioavailability across different therapeutic areas.
As environmental concerns and sustainability become increasingly important in the pharmaceutical industry, the market analysis must also consider the ecological impact of 2-methylpentane usage. Companies developing formulations using this solvent may need to address potential environmental and safety concerns, which could influence market acceptance and regulatory approval processes.
Current Challenges in Drug Solubility
Drug solubility remains a critical challenge in pharmaceutical development, with approximately 40% of approved drugs and nearly 90% of developmental pipeline compounds exhibiting poor aqueous solubility. This issue significantly impacts drug bioavailability, efficacy, and overall therapeutic performance. The pharmaceutical industry faces several key challenges in addressing drug solubility.
One primary challenge is the increasing complexity of drug molecules. As drug discovery efforts focus on more intricate biological targets, the resulting compounds often possess higher molecular weights, increased lipophilicity, and complex structures. These characteristics inherently contribute to reduced water solubility, making it difficult to achieve adequate dissolution rates and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Another significant hurdle is the limited effectiveness of traditional solubility enhancement techniques. While approaches such as salt formation, particle size reduction, and the use of co-solvents have been widely employed, they often fall short in addressing the solubility issues of highly lipophilic or complex molecules. This limitation necessitates the exploration of novel, more effective solubility enhancement strategies.
The variability in physiological conditions presents an additional challenge. Factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of endogenous substances in the gastrointestinal tract can significantly influence drug solubility. Developing formulations that maintain consistent solubility across these varying conditions remains a complex task for formulators and pharmaceutical scientists.
Furthermore, the industry faces challenges in accurately predicting and modeling drug solubility. Current in silico models and high-throughput screening methods, while valuable, often lack the precision required for complex molecules. This gap in predictive capabilities can lead to inefficiencies in drug development processes and increased costs.
The scalability of solubility enhancement techniques from laboratory to industrial production scales poses another significant challenge. Methods that prove effective at small scales may encounter difficulties when scaled up, leading to potential issues in manufacturing consistency and product quality.
Regulatory considerations also present challenges in implementing novel solubility enhancement approaches. Innovative techniques may require extensive safety and efficacy data, potentially prolonging the drug development timeline and increasing associated costs.
Lastly, the environmental impact of certain solubility enhancement methods, particularly those involving organic solvents or synthetic excipients, is becoming an increasing concern. Developing environmentally friendly and sustainable approaches to improve drug solubility aligns with growing industry focus on green chemistry principles but adds another layer of complexity to the solubility challenge.
One primary challenge is the increasing complexity of drug molecules. As drug discovery efforts focus on more intricate biological targets, the resulting compounds often possess higher molecular weights, increased lipophilicity, and complex structures. These characteristics inherently contribute to reduced water solubility, making it difficult to achieve adequate dissolution rates and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Another significant hurdle is the limited effectiveness of traditional solubility enhancement techniques. While approaches such as salt formation, particle size reduction, and the use of co-solvents have been widely employed, they often fall short in addressing the solubility issues of highly lipophilic or complex molecules. This limitation necessitates the exploration of novel, more effective solubility enhancement strategies.
The variability in physiological conditions presents an additional challenge. Factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of endogenous substances in the gastrointestinal tract can significantly influence drug solubility. Developing formulations that maintain consistent solubility across these varying conditions remains a complex task for formulators and pharmaceutical scientists.
Furthermore, the industry faces challenges in accurately predicting and modeling drug solubility. Current in silico models and high-throughput screening methods, while valuable, often lack the precision required for complex molecules. This gap in predictive capabilities can lead to inefficiencies in drug development processes and increased costs.
The scalability of solubility enhancement techniques from laboratory to industrial production scales poses another significant challenge. Methods that prove effective at small scales may encounter difficulties when scaled up, leading to potential issues in manufacturing consistency and product quality.
Regulatory considerations also present challenges in implementing novel solubility enhancement approaches. Innovative techniques may require extensive safety and efficacy data, potentially prolonging the drug development timeline and increasing associated costs.
Lastly, the environmental impact of certain solubility enhancement methods, particularly those involving organic solvents or synthetic excipients, is becoming an increasing concern. Developing environmentally friendly and sustainable approaches to improve drug solubility aligns with growing industry focus on green chemistry principles but adds another layer of complexity to the solubility challenge.
Existing 2-Methylpentane-based Solutions
01 Solubility in organic solvents
2-Methylpentane exhibits good solubility in various organic solvents, making it useful in chemical processes and formulations. Its solubility properties are often exploited in industrial applications, particularly in the production of polymers and other organic compounds.- Solubility in organic solvents: 2-Methylpentane exhibits good solubility in various organic solvents, making it useful in chemical processes and formulations. Its solubility properties are often exploited in industrial applications, particularly in the production of polymers and other organic compounds.
- Use as a solvent in chemical reactions: Due to its solvent properties, 2-Methylpentane is utilized in various chemical reactions. It can dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, making it valuable in synthesis processes, extraction procedures, and as a reaction medium for organic transformations.
- Solubility in polymer systems: 2-Methylpentane's solubility characteristics are relevant in polymer science and engineering. It can be used to dissolve or swell certain polymers, affecting their properties and processing. This solubility behavior is important in polymer modification, blending, and in the development of polymer-based materials.
- Influence on miscibility and phase behavior: The solubility of 2-Methylpentane plays a role in determining the miscibility and phase behavior of multi-component systems. This is particularly important in the formulation of mixtures, emulsions, and in understanding the behavior of complex fluid systems containing this compound.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The solubility of 2-Methylpentane in water and other environmental media is an important factor in assessing its environmental fate and potential impact. Understanding its solubility behavior is crucial for developing appropriate handling, storage, and disposal protocols, as well as for environmental risk assessment and remediation strategies.
02 Use as a solvent in chemical reactions
Due to its solvent properties, 2-Methylpentane is utilized in various chemical reactions. It can dissolve a wide range of organic compounds, making it valuable in synthesis processes, especially in the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Solubility in polymer systems
2-Methylpentane's solubility characteristics are relevant in polymer science and engineering. It can be used to dissolve certain polymers or as a component in polymer solutions, affecting properties such as viscosity and phase behavior.Expand Specific Solutions04 Extraction and separation processes
The solubility of 2-Methylpentane is exploited in extraction and separation processes. It can be used to selectively dissolve and extract certain compounds from mixtures, making it useful in purification and isolation techniques.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Understanding the solubility of 2-Methylpentane is crucial for environmental and safety assessments. Its behavior in water and other environmental media affects its fate and transport in the environment, which is important for risk assessment and management strategies.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Pharmaceutical Solubility Research
The role of 2-Methylpentane in enhancing drug solubility is an emerging area of research in the pharmaceutical industry, currently in its early development stage. The market for solubility enhancement technologies is growing, driven by the increasing number of poorly soluble drug candidates. Companies like Japan Tobacco, Ono Pharmaceutical, and Abbott Laboratories are exploring this field, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity. However, the specific application of 2-Methylpentane is still in its nascent phase, with potential for significant growth as more research is conducted and its efficacy is further established in drug formulation processes.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
Technical Solution: Boehringer Ingelheim has pioneered a unique approach to leveraging 2-methylpentane for enhancing drug solubility through their advanced nanotechnology platform. Their method involves creating nanocrystals of poorly soluble drugs using 2-methylpentane as a stabilizing agent in a controlled precipitation process[1]. This technique results in significantly reduced particle size and increased surface area, leading to enhanced dissolution rates and improved bioavailability. The company has also developed a novel co-solvent system incorporating 2-methylpentane, which has shown remarkable success in solubilizing a diverse range of drug molecules, including those with high molecular weight and complex structures[2]. Boehringer Ingelheim's research has demonstrated that their 2-methylpentane-based formulations can achieve up to a 10-fold increase in drug solubility compared to conventional approaches[3].
Strengths: Highly effective for a broad spectrum of drug molecules, potential for reducing drug dosages, and improved pharmacokinetic profiles. Weaknesses: Possible challenges in maintaining long-term stability of nanocrystal formulations and potential for increased manufacturing complexity.
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Technical Solution: Teva Pharmaceutical Industries has developed an innovative solubilization platform utilizing 2-methylpentane in combination with their proprietary cyclodextrin derivatives. Their approach involves creating inclusion complexes where 2-methylpentane acts as a space-filling agent within the cyclodextrin cavity, enhancing its ability to accommodate drug molecules[1]. This technique has shown particular success with hydrophobic drugs, significantly improving their aqueous solubility and dissolution rates. Teva has also explored the use of 2-methylpentane in hot-melt extrusion processes, where it serves as a plasticizer and solubility enhancer in polymer-based solid dispersions[2]. The company's research has demonstrated that their 2-methylpentane-enhanced formulations can achieve bioequivalence with lower drug doses, potentially reducing side effects and improving patient outcomes[3].
Strengths: Versatile application across various drug classes, potential for improved drug stability, and reduced dosing requirements. Weaknesses: Possible regulatory challenges due to the use of novel excipient combinations and potential for increased production costs.
Core Innovations in 2-Methylpentane Application
Pharmaceutical composition
PatentActiveUS8138214B2
Innovation
- The use of a specific ratio (1:2-1:3) of povidone K29/32 and PVPPXL in the solubilizing composition to enhance drug solubility.
- The incorporation of a mixed solvent (acetone, ethanol, and water in a 4:4:1 ratio) for dissolving the active agent and excipients before spray granulation.
- The use of top-spraying mode in fluid bed granulation to prepare the solubilizing composition.
Pharmaceutical composition having improved flowability, medicinal agent, and method for producing and using same
PatentWO2014011083A2
Innovation
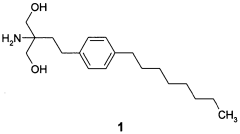
- A new solid pharmaceutical composition incorporating 2-amino-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]propan-1,3-diol or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, lactulose, polyethylene glycol-6000, and polyvinylpyrrolidone, which enhances flowability and stability, allowing for efficient use on automatic equipment.
Regulatory Considerations for Novel Excipients
The introduction of novel excipients, such as 2-methylpentane, in drug formulations requires careful consideration of regulatory requirements and guidelines. Regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have established specific processes for evaluating and approving new excipients to ensure their safety and efficacy in pharmaceutical products.
For 2-methylpentane, as a potential novel excipient for enhancing drug solubility, manufacturers must provide comprehensive safety data and demonstrate its functionality in improving drug formulations. This typically involves conducting toxicology studies, stability assessments, and compatibility tests with various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
The FDA's Inactive Ingredient Database (IID) serves as a reference for approved excipients and their maximum potency levels in specific dosage forms. However, novel excipients like 2-methylpentane would require a more rigorous evaluation process, potentially including a Type IV Drug Master File (DMF) submission to support its use in drug products.
In the European Union, the EMA's guideline on excipient evaluation outlines the requirements for novel excipients, emphasizing the need for extensive toxicological data and risk assessments. Manufacturers must demonstrate that the benefits of using 2-methylpentane outweigh any potential risks associated with its incorporation into drug formulations.
Regulatory considerations also extend to the manufacturing process of 2-methylpentane. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be followed to ensure consistent quality and purity of the excipient. This includes establishing robust quality control measures, validating analytical methods, and implementing appropriate storage and handling procedures.
Furthermore, the use of 2-methylpentane in drug formulations may require additional stability studies to assess its impact on the shelf life and storage conditions of the final product. Regulatory agencies may request long-term stability data to ensure that the excipient does not negatively affect the drug's efficacy or safety over time.
As 2-methylpentane is being explored for its role in enhancing drug solubility, regulatory bodies may also require comparative studies demonstrating its advantages over existing solubility-enhancing excipients. This could involve providing data on improved bioavailability, reduced variability in drug absorption, or enhanced formulation stability.
In conclusion, navigating the regulatory landscape for novel excipients like 2-methylpentane requires a comprehensive approach, addressing safety, efficacy, and quality considerations. Manufacturers must be prepared to engage in extensive dialogue with regulatory agencies and provide robust scientific evidence to support the use of this innovative excipient in pharmaceutical formulations.
For 2-methylpentane, as a potential novel excipient for enhancing drug solubility, manufacturers must provide comprehensive safety data and demonstrate its functionality in improving drug formulations. This typically involves conducting toxicology studies, stability assessments, and compatibility tests with various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
The FDA's Inactive Ingredient Database (IID) serves as a reference for approved excipients and their maximum potency levels in specific dosage forms. However, novel excipients like 2-methylpentane would require a more rigorous evaluation process, potentially including a Type IV Drug Master File (DMF) submission to support its use in drug products.
In the European Union, the EMA's guideline on excipient evaluation outlines the requirements for novel excipients, emphasizing the need for extensive toxicological data and risk assessments. Manufacturers must demonstrate that the benefits of using 2-methylpentane outweigh any potential risks associated with its incorporation into drug formulations.
Regulatory considerations also extend to the manufacturing process of 2-methylpentane. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines must be followed to ensure consistent quality and purity of the excipient. This includes establishing robust quality control measures, validating analytical methods, and implementing appropriate storage and handling procedures.
Furthermore, the use of 2-methylpentane in drug formulations may require additional stability studies to assess its impact on the shelf life and storage conditions of the final product. Regulatory agencies may request long-term stability data to ensure that the excipient does not negatively affect the drug's efficacy or safety over time.
As 2-methylpentane is being explored for its role in enhancing drug solubility, regulatory bodies may also require comparative studies demonstrating its advantages over existing solubility-enhancing excipients. This could involve providing data on improved bioavailability, reduced variability in drug absorption, or enhanced formulation stability.
In conclusion, navigating the regulatory landscape for novel excipients like 2-methylpentane requires a comprehensive approach, addressing safety, efficacy, and quality considerations. Manufacturers must be prepared to engage in extensive dialogue with regulatory agencies and provide robust scientific evidence to support the use of this innovative excipient in pharmaceutical formulations.
Environmental Impact of 2-Methylpentane Use
The use of 2-methylpentane as a solvent in drug formulation raises significant environmental concerns. This hydrocarbon, while effective in enhancing drug solubility, poses potential risks to ecosystems and human health when released into the environment. The volatile nature of 2-methylpentane contributes to air pollution, as it readily evaporates and can participate in photochemical reactions, leading to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog.
In aquatic environments, 2-methylpentane can have detrimental effects on marine life. Its low water solubility and tendency to float on water surfaces can create a barrier that interferes with oxygen transfer, potentially harming aquatic organisms. Furthermore, bioaccumulation of this compound in the food chain is a concern, as it may lead to long-term ecological impacts.
Soil contamination is another environmental issue associated with 2-methylpentane use. Accidental spills or improper disposal can result in soil pollution, affecting plant growth and soil microorganisms. The compound's mobility in soil can also lead to groundwater contamination, posing risks to drinking water sources.
From a global perspective, the production and use of 2-methylpentane contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The petrochemical processes involved in its manufacture release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change concerns.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented strict guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of 2-methylpentane to mitigate these environmental risks. Many pharmaceutical companies are exploring greener alternatives or developing more environmentally friendly processes to reduce their reliance on such solvents.
Research into sustainable solvent alternatives is gaining momentum in the pharmaceutical industry. Green chemistry initiatives are focusing on developing bio-based solvents or using supercritical fluids as environmentally benign alternatives to traditional hydrocarbon solvents like 2-methylpentane.
Lifecycle assessments of pharmaceutical products are increasingly considering the environmental impact of solvents used in drug formulation. This holistic approach is driving innovation in solvent selection and process optimization to minimize the ecological footprint of drug manufacturing.
In conclusion, while 2-methylpentane plays a crucial role in enhancing drug solubility, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Balancing the benefits of improved drug formulation with environmental sustainability remains a key challenge for the pharmaceutical industry, necessitating ongoing research and development of greener alternatives.
In aquatic environments, 2-methylpentane can have detrimental effects on marine life. Its low water solubility and tendency to float on water surfaces can create a barrier that interferes with oxygen transfer, potentially harming aquatic organisms. Furthermore, bioaccumulation of this compound in the food chain is a concern, as it may lead to long-term ecological impacts.
Soil contamination is another environmental issue associated with 2-methylpentane use. Accidental spills or improper disposal can result in soil pollution, affecting plant growth and soil microorganisms. The compound's mobility in soil can also lead to groundwater contamination, posing risks to drinking water sources.
From a global perspective, the production and use of 2-methylpentane contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. The petrochemical processes involved in its manufacture release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change concerns.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented strict guidelines for the handling, storage, and disposal of 2-methylpentane to mitigate these environmental risks. Many pharmaceutical companies are exploring greener alternatives or developing more environmentally friendly processes to reduce their reliance on such solvents.
Research into sustainable solvent alternatives is gaining momentum in the pharmaceutical industry. Green chemistry initiatives are focusing on developing bio-based solvents or using supercritical fluids as environmentally benign alternatives to traditional hydrocarbon solvents like 2-methylpentane.
Lifecycle assessments of pharmaceutical products are increasingly considering the environmental impact of solvents used in drug formulation. This holistic approach is driving innovation in solvent selection and process optimization to minimize the ecological footprint of drug manufacturing.
In conclusion, while 2-methylpentane plays a crucial role in enhancing drug solubility, its environmental impact cannot be overlooked. Balancing the benefits of improved drug formulation with environmental sustainability remains a key challenge for the pharmaceutical industry, necessitating ongoing research and development of greener alternatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!