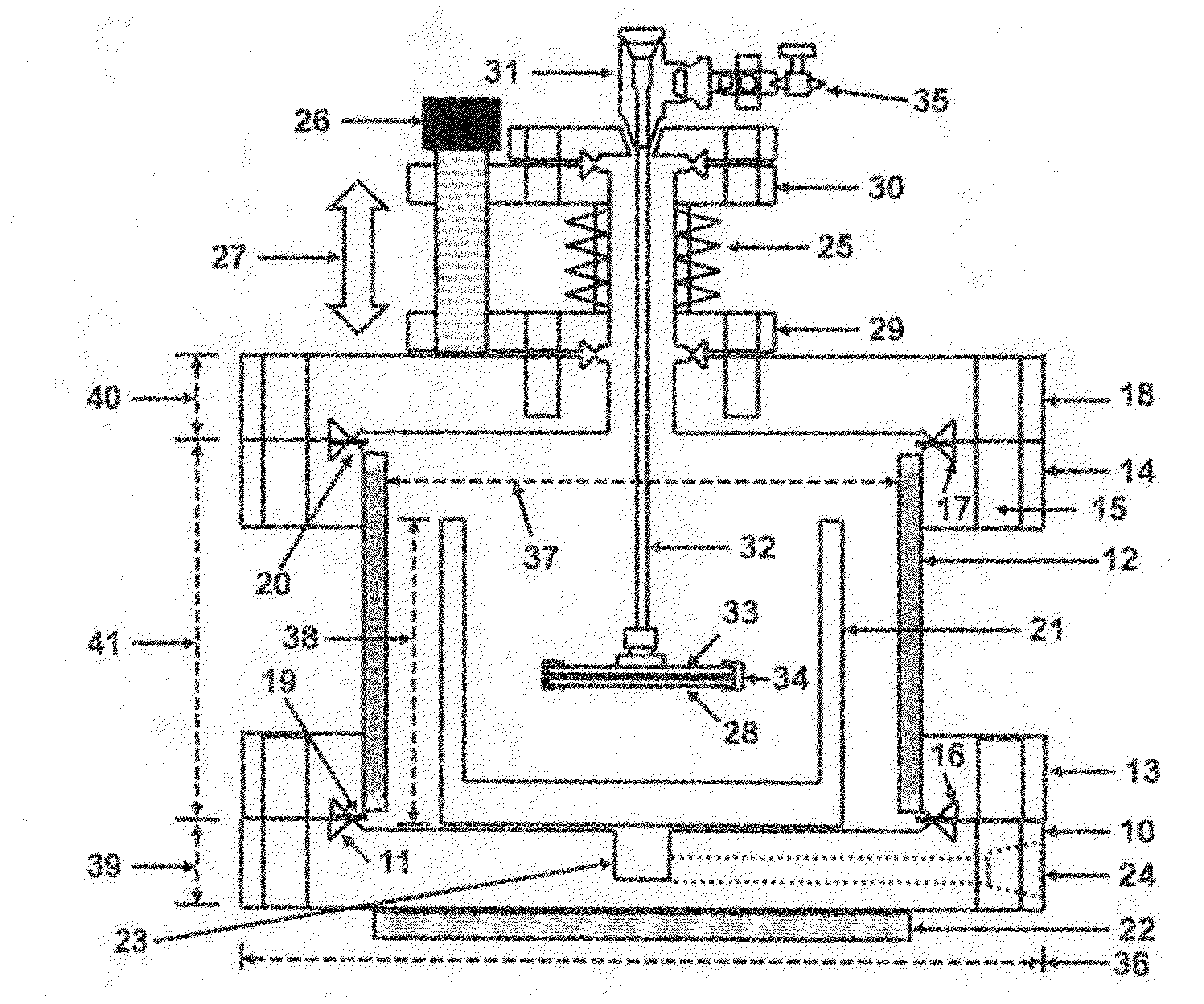
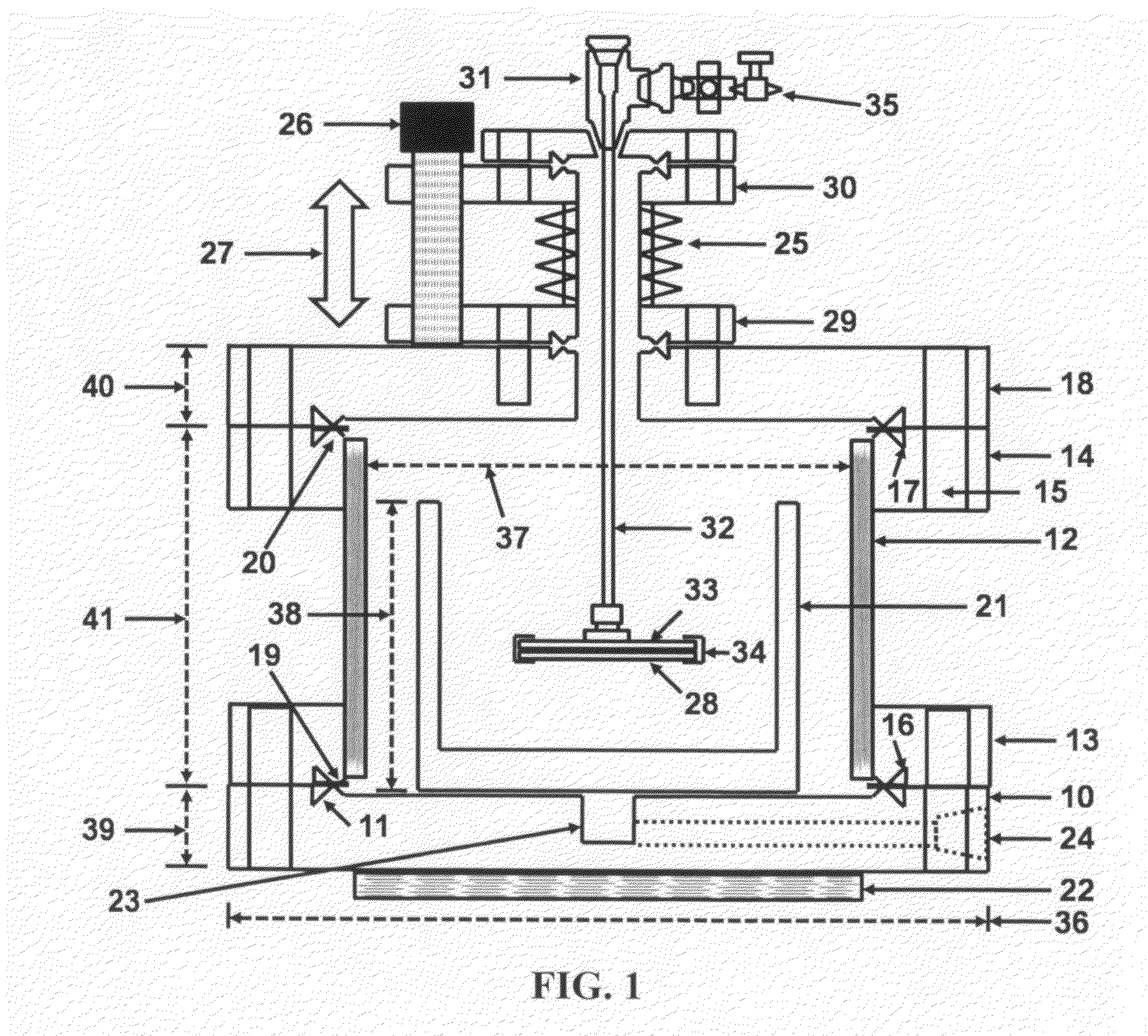
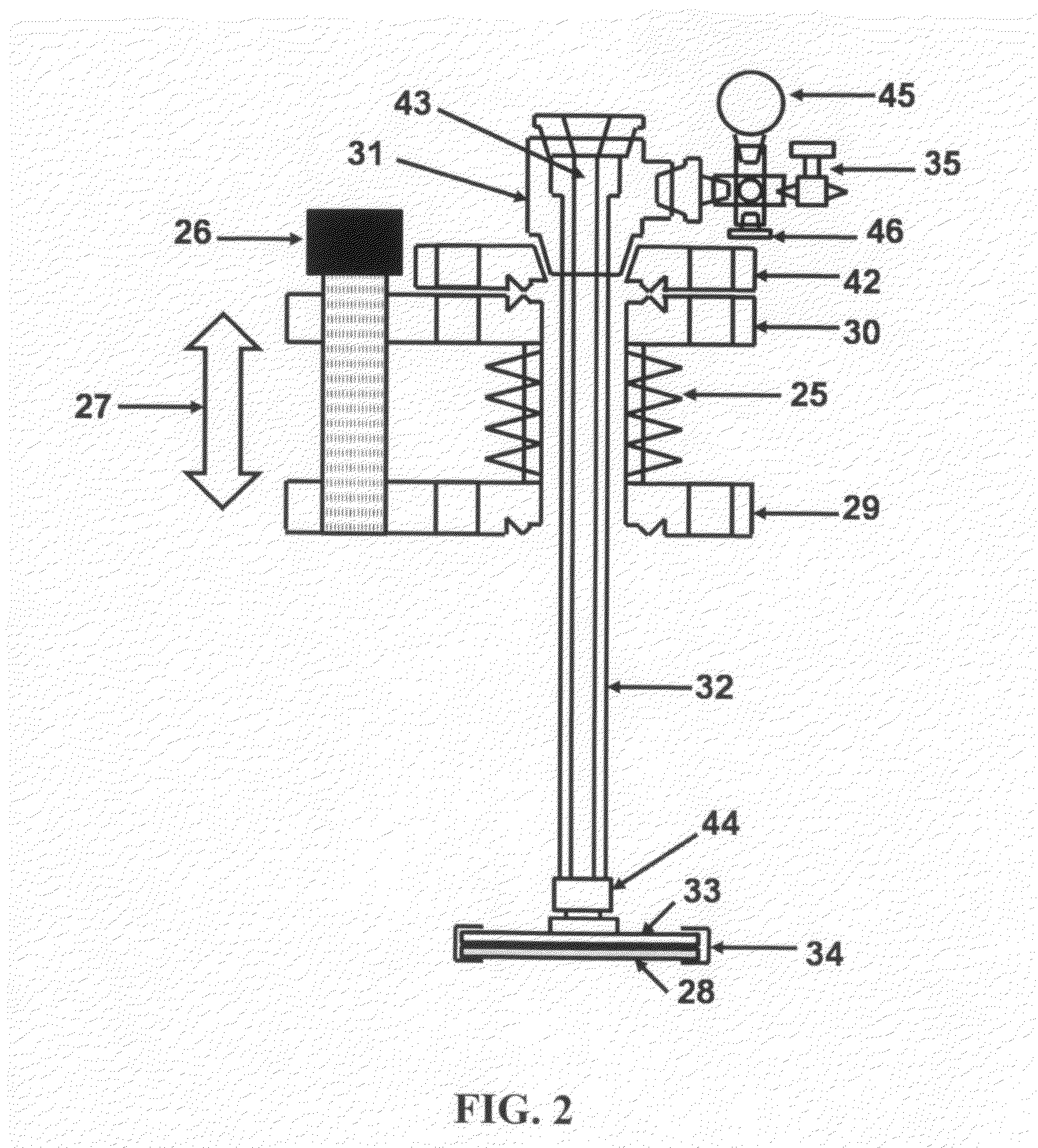
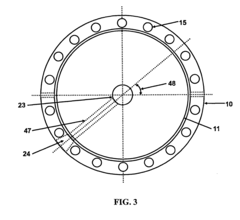
The Application of Ammonium Hydroxide in Precision Texturing of Metals
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ammonium Hydroxide Texturing Background
The application of ammonium hydroxide in precision texturing of metals represents a significant advancement in surface modification techniques. This process has its roots in the broader field of chemical etching, which has been utilized for decades in various industrial applications. The use of ammonium hydroxide specifically for metal texturing emerged as a refined approach to achieve more precise and controlled surface alterations.
Historically, metal texturing techniques have evolved from mechanical methods such as grinding and sandblasting to more sophisticated chemical and electrochemical processes. The introduction of ammonium hydroxide as a texturing agent marked a pivotal point in this evolution, offering a unique combination of effectiveness and selectivity in surface modification.
Ammonium hydroxide, a solution of ammonia in water, possesses properties that make it particularly suitable for metal texturing. Its alkaline nature allows for controlled etching of metal surfaces, while its volatility enables precise manipulation of the etching process. This characteristic has made it an attractive option for industries requiring high-precision surface treatments, such as semiconductor manufacturing and advanced materials engineering.
The development of ammonium hydroxide texturing techniques has been driven by the increasing demand for enhanced surface properties in various technological applications. These include improved adhesion for coatings, optimized light reflection or absorption, and enhanced tribological characteristics. The ability to create specific surface topographies at the micro and nanoscale has opened up new possibilities in fields ranging from optics to biomedical implants.
Research into the mechanisms of ammonium hydroxide texturing has revealed its complex interaction with different metal surfaces. The process typically involves the formation of metal-ammonia complexes, which can be selectively removed from the surface, resulting in controlled etching patterns. This understanding has led to the development of more refined texturing protocols, allowing for unprecedented control over surface morphology.
The adoption of ammonium hydroxide texturing has been further propelled by environmental considerations. Compared to some traditional etching agents, ammonium hydroxide is relatively less harmful and easier to handle, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing processes. This aspect has contributed to its increasing popularity in industries striving to balance technological advancement with environmental responsibility.
As the field continues to evolve, researchers and engineers are exploring new ways to enhance the precision and versatility of ammonium hydroxide texturing. This includes combining it with other techniques such as electrochemical processes or integrating it into advanced manufacturing systems for automated, high-precision surface treatments.
Historically, metal texturing techniques have evolved from mechanical methods such as grinding and sandblasting to more sophisticated chemical and electrochemical processes. The introduction of ammonium hydroxide as a texturing agent marked a pivotal point in this evolution, offering a unique combination of effectiveness and selectivity in surface modification.
Ammonium hydroxide, a solution of ammonia in water, possesses properties that make it particularly suitable for metal texturing. Its alkaline nature allows for controlled etching of metal surfaces, while its volatility enables precise manipulation of the etching process. This characteristic has made it an attractive option for industries requiring high-precision surface treatments, such as semiconductor manufacturing and advanced materials engineering.
The development of ammonium hydroxide texturing techniques has been driven by the increasing demand for enhanced surface properties in various technological applications. These include improved adhesion for coatings, optimized light reflection or absorption, and enhanced tribological characteristics. The ability to create specific surface topographies at the micro and nanoscale has opened up new possibilities in fields ranging from optics to biomedical implants.
Research into the mechanisms of ammonium hydroxide texturing has revealed its complex interaction with different metal surfaces. The process typically involves the formation of metal-ammonia complexes, which can be selectively removed from the surface, resulting in controlled etching patterns. This understanding has led to the development of more refined texturing protocols, allowing for unprecedented control over surface morphology.
The adoption of ammonium hydroxide texturing has been further propelled by environmental considerations. Compared to some traditional etching agents, ammonium hydroxide is relatively less harmful and easier to handle, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing processes. This aspect has contributed to its increasing popularity in industries striving to balance technological advancement with environmental responsibility.
As the field continues to evolve, researchers and engineers are exploring new ways to enhance the precision and versatility of ammonium hydroxide texturing. This includes combining it with other techniques such as electrochemical processes or integrating it into advanced manufacturing systems for automated, high-precision surface treatments.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for precision texturing of metals using ammonium hydroxide has been steadily growing across various industries. This innovative technique offers significant advantages in surface modification, enhancing the performance and functionality of metal components in diverse applications.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for precisely textured metal surfaces to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Ammonium hydroxide-based texturing can create micro-patterns on engine components, reducing friction and improving overall engine performance. This aligns with the industry's push towards more environmentally friendly and efficient vehicles.
The aerospace industry also shows a strong interest in this technology. Precision texturing of turbine blades and other critical components can enhance their aerodynamic properties and heat resistance. As the aerospace sector continues to seek ways to improve fuel efficiency and extend the lifespan of aircraft parts, the demand for advanced texturing techniques is expected to grow.
In the field of medical devices, there is an increasing need for precisely textured implants and surgical instruments. Ammonium hydroxide-based texturing can create biocompatible surfaces that promote better integration with human tissue and reduce the risk of infections. This is particularly relevant in orthopedic and dental implants, where surface properties play a crucial role in long-term success.
The electronics industry is another significant market for this technology. As devices become smaller and more powerful, the need for effective heat dissipation grows. Precision texturing of heat sinks and other thermal management components can significantly improve their efficiency, meeting the demands of next-generation electronic devices.
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in solar panel manufacturing, there is a growing interest in texturing metal surfaces to enhance light absorption and improve overall panel efficiency. This aligns with the global push towards more sustainable energy solutions and the continuous efforts to increase the performance of solar technologies.
The market for precision metal texturing is also expanding in the consumer goods sector. From high-end appliances to luxury products, manufacturers are looking for ways to differentiate their products through unique surface finishes that not only enhance aesthetics but also improve functionality, such as fingerprint resistance or improved grip.
As industries continue to seek more efficient, durable, and high-performance materials, the demand for precision texturing using ammonium hydroxide is expected to grow. This technology offers a versatile solution that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various sectors, driving innovation and opening new possibilities in product design and manufacturing.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for precisely textured metal surfaces to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Ammonium hydroxide-based texturing can create micro-patterns on engine components, reducing friction and improving overall engine performance. This aligns with the industry's push towards more environmentally friendly and efficient vehicles.
The aerospace industry also shows a strong interest in this technology. Precision texturing of turbine blades and other critical components can enhance their aerodynamic properties and heat resistance. As the aerospace sector continues to seek ways to improve fuel efficiency and extend the lifespan of aircraft parts, the demand for advanced texturing techniques is expected to grow.
In the field of medical devices, there is an increasing need for precisely textured implants and surgical instruments. Ammonium hydroxide-based texturing can create biocompatible surfaces that promote better integration with human tissue and reduce the risk of infections. This is particularly relevant in orthopedic and dental implants, where surface properties play a crucial role in long-term success.
The electronics industry is another significant market for this technology. As devices become smaller and more powerful, the need for effective heat dissipation grows. Precision texturing of heat sinks and other thermal management components can significantly improve their efficiency, meeting the demands of next-generation electronic devices.
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in solar panel manufacturing, there is a growing interest in texturing metal surfaces to enhance light absorption and improve overall panel efficiency. This aligns with the global push towards more sustainable energy solutions and the continuous efforts to increase the performance of solar technologies.
The market for precision metal texturing is also expanding in the consumer goods sector. From high-end appliances to luxury products, manufacturers are looking for ways to differentiate their products through unique surface finishes that not only enhance aesthetics but also improve functionality, such as fingerprint resistance or improved grip.
As industries continue to seek more efficient, durable, and high-performance materials, the demand for precision texturing using ammonium hydroxide is expected to grow. This technology offers a versatile solution that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various sectors, driving innovation and opening new possibilities in product design and manufacturing.
Current Challenges
The application of ammonium hydroxide in precision texturing of metals faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary obstacles is the precise control of the etching process. The reaction between ammonium hydroxide and metal surfaces is highly sensitive to concentration, temperature, and exposure time. Achieving consistent and uniform texturing across large surface areas remains a formidable task, as even slight variations in these parameters can lead to uneven etching patterns and compromised surface quality.
Another challenge lies in the environmental and safety concerns associated with the use of ammonium hydroxide. As a corrosive substance, it poses potential risks to workers and requires stringent safety protocols. The disposal of waste products from the etching process also presents environmental challenges, necessitating the development of efficient recycling and treatment methods to minimize ecological impact.
The scalability of ammonium hydroxide-based texturing processes for industrial applications is yet another hurdle. While the technique shows promise in laboratory settings, translating these results to large-scale manufacturing environments proves difficult. Issues such as maintaining uniform chemical distribution, managing heat dissipation, and ensuring consistent surface contact across complex geometries become more pronounced at industrial scales.
Furthermore, the compatibility of ammonium hydroxide with different metal alloys and composites presents a significant challenge. The etching behavior can vary dramatically depending on the specific composition of the metal substrate, requiring extensive research and optimization for each material type. This variability complicates the development of standardized processes and limits the technique's versatility across diverse manufacturing applications.
The long-term stability and durability of textured surfaces produced using ammonium hydroxide also remain areas of concern. The potential for continued chemical reactions or degradation of the textured surface over time under various environmental conditions needs thorough investigation. Ensuring that the textured surfaces maintain their desired properties and performance characteristics throughout the product lifecycle is crucial for many applications, particularly in industries such as aerospace and automotive where long-term reliability is paramount.
Lastly, the integration of ammonium hydroxide-based texturing processes into existing manufacturing workflows presents logistical and technical challenges. Adapting current production lines to accommodate this new technique may require significant modifications to equipment and processes, potentially leading to high implementation costs and production disruptions. Overcoming these integration challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of this texturing method in industrial settings.
Another challenge lies in the environmental and safety concerns associated with the use of ammonium hydroxide. As a corrosive substance, it poses potential risks to workers and requires stringent safety protocols. The disposal of waste products from the etching process also presents environmental challenges, necessitating the development of efficient recycling and treatment methods to minimize ecological impact.
The scalability of ammonium hydroxide-based texturing processes for industrial applications is yet another hurdle. While the technique shows promise in laboratory settings, translating these results to large-scale manufacturing environments proves difficult. Issues such as maintaining uniform chemical distribution, managing heat dissipation, and ensuring consistent surface contact across complex geometries become more pronounced at industrial scales.
Furthermore, the compatibility of ammonium hydroxide with different metal alloys and composites presents a significant challenge. The etching behavior can vary dramatically depending on the specific composition of the metal substrate, requiring extensive research and optimization for each material type. This variability complicates the development of standardized processes and limits the technique's versatility across diverse manufacturing applications.
The long-term stability and durability of textured surfaces produced using ammonium hydroxide also remain areas of concern. The potential for continued chemical reactions or degradation of the textured surface over time under various environmental conditions needs thorough investigation. Ensuring that the textured surfaces maintain their desired properties and performance characteristics throughout the product lifecycle is crucial for many applications, particularly in industries such as aerospace and automotive where long-term reliability is paramount.
Lastly, the integration of ammonium hydroxide-based texturing processes into existing manufacturing workflows presents logistical and technical challenges. Adapting current production lines to accommodate this new technique may require significant modifications to equipment and processes, potentially leading to high implementation costs and production disruptions. Overcoming these integration challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of this texturing method in industrial settings.
Existing Texturing Methods
01 Ammonium hydroxide in textile processing
Ammonium hydroxide is used in textile processing for precision texturing. It can help in modifying the surface properties of fibers, improving their texture and appearance. The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide aids in swelling and softening fibers, making them more receptive to dyes and finishes.- Ammonium hydroxide in textile processing: Ammonium hydroxide is used in textile processing for precision texturing. It can be applied to modify fiber properties, improve dye uptake, and enhance fabric finish. The alkaline nature of ammonium hydroxide helps in swelling fibers, which allows for better penetration of dyes and finishing agents.
- Ammonium hydroxide in chemical synthesis: Ammonium hydroxide plays a role in various chemical synthesis processes. It can be used as a reactant or catalyst in the production of certain compounds. The precise control of ammonium hydroxide concentration and application can lead to improved product quality and yield in chemical manufacturing.
- Ammonium hydroxide in surface treatment: Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in surface treatment applications for precision texturing. It can be employed to etch or modify surfaces of materials such as metals, semiconductors, or ceramics. The controlled use of ammonium hydroxide can create specific surface textures or patterns at a microscopic level.
- Ammonium hydroxide in cleaning and degreasing: Ammonium hydroxide is effective in cleaning and degreasing applications. Its alkaline properties make it suitable for removing oils, greases, and other contaminants from surfaces. Precise application of ammonium hydroxide can result in thorough cleaning without damaging the underlying material.
- Ammonium hydroxide in hair and cosmetic treatments: Ammonium hydroxide is used in hair and cosmetic treatments for precision texturing. It can alter the structure of hair proteins, allowing for various styling and coloring processes. In cosmetics, it may be used to adjust pH or as a buffering agent in certain formulations.
02 Ammonium hydroxide in chemical synthesis
Ammonium hydroxide plays a role in various chemical synthesis processes, particularly in the production of organic compounds. It can act as a pH regulator, a neutralizing agent, or a source of ammonia in reactions. Its precision in adjusting pH levels makes it valuable for controlling reaction conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Ammonium hydroxide in surface treatment
Ammonium hydroxide is utilized in surface treatment processes, including etching and cleaning of materials. Its alkaline properties make it effective in removing contaminants and modifying surface characteristics. This application is particularly relevant in semiconductor manufacturing and metal surface preparation.Expand Specific Solutions04 Ammonium hydroxide in hair and cosmetic products
In the cosmetic industry, ammonium hydroxide is used in hair products and other cosmetic formulations. It can help in adjusting the pH of products, assist in the penetration of active ingredients, and contribute to the texturing of hair. Its alkaline nature aids in opening hair cuticles for better absorption of dyes and treatments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Ammonium hydroxide in cleaning and degreasing
Ammonium hydroxide is employed in cleaning and degreasing applications. Its ability to break down oils and fats makes it effective in removing stubborn stains and grease. This property is utilized in industrial cleaning processes, as well as in household cleaning products for precision cleaning of various surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The application of ammonium hydroxide in precision texturing of metals is an emerging field within surface treatment technologies. The market is in its early growth stage, with increasing demand driven by advancements in manufacturing processes across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. While the global market size is still relatively small, it is expected to expand rapidly due to the growing need for high-precision metal surfaces. Companies like Chemetall GmbH, Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., and Wacker Chemie AG are at the forefront of developing and refining this technology, leveraging their expertise in chemical engineering and surface treatment solutions. The technology's maturity is progressing, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving efficiency, environmental sustainability, and applicability across various metal types and industrial applications.
Chemetall GmbH
Technical Solution: Chemetall GmbH has developed an advanced ammonium hydroxide-based texturing process for precision metal surface treatment. Their technique involves a controlled application of ammonium hydroxide solution to create micro-scale surface patterns on various metal substrates. The process utilizes a proprietary combination of concentration, temperature, and exposure time to achieve optimal surface texturing[1]. This method allows for enhanced adhesion properties and improved corrosion resistance in treated metals. Chemetall's approach also incorporates a post-treatment neutralization step to ensure environmental compliance and worker safety[3].
Strengths: Precise control over surface texture, improved adhesion properties, and enhanced corrosion resistance. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and careful handling of chemicals.
Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Chemical has innovated a novel ammonium hydroxide-based metal texturing process for semiconductor applications. Their method employs a highly purified ammonium hydroxide solution in conjunction with proprietary additives to achieve nanoscale surface modifications on metal substrates used in chip manufacturing[2]. The process is particularly effective for creating uniform and controlled surface roughness on copper interconnects, enhancing their electrical performance and reliability. Sumitomo's technique also incorporates in-situ monitoring systems to ensure precise control over the texturing process, resulting in highly reproducible surface characteristics[4].
Strengths: Nanoscale precision, uniformity in surface modification, and enhanced electrical performance of treated metals. Weaknesses: Potentially high cost due to the need for ultra-pure chemicals and specialized equipment.
Ammonium Hydroxide Innovations
High purity, environmentally clean method and apparatus, for high rate, liquid anisotropic etching of single crystal silicon or etching of polycrystalline silicon, using an overpressure of ammonia gas above aqueous ammonium hydroxide
PatentInactiveUS8790531B2
Innovation
- The use of high purity aqueous ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) solution generated at the point of use from semiconductor-grade ammonia gas dissolved in deionized water, maintained in a hermetically enclosed chamber with an overpressure of ammonia, preventing evaporation and allowing high anisotropic etching rates between 70-90°C, within a corrosion-resistant nickel alloy apparatus.
Method of anodizing metallic surfaces and compositions therefore
PatentWO2005078164A2
Innovation
- An alkaline aqueous anodizing solution comprising phosphorus and oxygen-containing anions, surfactants, water-soluble inorganic hydroxides, and alkaline radicals is used, generating a non-conductive polymer layer that transforms into a gel layer, preventing pore formation and enhancing corrosion and wear resistance through controlled micro-sparking.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The application of ammonium hydroxide in precision texturing of metals raises important environmental considerations that require thorough assessment. The process involves the use of chemicals and generates waste products, necessitating a comprehensive evaluation of its environmental impact.
Ammonium hydroxide, while effective for metal texturing, can pose risks to aquatic ecosystems if released untreated into water bodies. Its high pH and ammonia content can disrupt aquatic life and potentially lead to eutrophication. Therefore, proper wastewater treatment and disposal methods are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Air quality is another concern, as the process may release ammonia vapors. These emissions can contribute to the formation of particulate matter and potentially impact local air quality. Implementing appropriate ventilation systems and air scrubbers can help minimize these emissions and protect both workers and the surrounding environment.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of the texturing process. Considering the lifecycle impact, from raw material extraction to final disposal, is essential for a comprehensive assessment. This includes evaluating energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion associated with the entire supply chain.
Waste management is a critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment. The texturing process generates metal-containing waste solutions that require proper handling and disposal. Implementing recycling and recovery systems for both the ammonium hydroxide and metal byproducts can significantly reduce waste generation and promote resource efficiency.
Water consumption is another factor to consider, as the texturing process may require substantial amounts of water for rinsing and cleaning. Implementing water-saving technologies and closed-loop systems can help minimize water usage and reduce the strain on local water resources.
The potential for accidental spills or leaks during storage and handling of ammonium hydroxide must also be addressed. Proper containment measures, emergency response plans, and staff training are essential to prevent and mitigate any environmental contamination in case of incidents.
Considering alternative, more environmentally friendly texturing methods is an important part of the assessment. Comparing the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide-based texturing with other techniques, such as laser texturing or mechanical methods, can provide valuable insights into the most sustainable approach for precision metal texturing.
Ammonium hydroxide, while effective for metal texturing, can pose risks to aquatic ecosystems if released untreated into water bodies. Its high pH and ammonia content can disrupt aquatic life and potentially lead to eutrophication. Therefore, proper wastewater treatment and disposal methods are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Air quality is another concern, as the process may release ammonia vapors. These emissions can contribute to the formation of particulate matter and potentially impact local air quality. Implementing appropriate ventilation systems and air scrubbers can help minimize these emissions and protect both workers and the surrounding environment.
The production and transportation of ammonium hydroxide also contribute to the overall environmental footprint of the texturing process. Considering the lifecycle impact, from raw material extraction to final disposal, is essential for a comprehensive assessment. This includes evaluating energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion associated with the entire supply chain.
Waste management is a critical aspect of the environmental impact assessment. The texturing process generates metal-containing waste solutions that require proper handling and disposal. Implementing recycling and recovery systems for both the ammonium hydroxide and metal byproducts can significantly reduce waste generation and promote resource efficiency.
Water consumption is another factor to consider, as the texturing process may require substantial amounts of water for rinsing and cleaning. Implementing water-saving technologies and closed-loop systems can help minimize water usage and reduce the strain on local water resources.
The potential for accidental spills or leaks during storage and handling of ammonium hydroxide must also be addressed. Proper containment measures, emergency response plans, and staff training are essential to prevent and mitigate any environmental contamination in case of incidents.
Considering alternative, more environmentally friendly texturing methods is an important part of the assessment. Comparing the environmental impact of ammonium hydroxide-based texturing with other techniques, such as laser texturing or mechanical methods, can provide valuable insights into the most sustainable approach for precision metal texturing.
Safety Regulations Compliance
The application of ammonium hydroxide in precision texturing of metals requires strict adherence to safety regulations to protect workers, the environment, and ensure product quality. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for the successful implementation of this technology in industrial settings.
Occupational safety and health regulations play a primary role in governing the use of ammonium hydroxide. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for ammonia, the primary component of ammonium hydroxide. These limits are set at 50 parts per million (ppm) for an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) and a short-term exposure limit (STEL) of 35 ppm for 15 minutes. Employers must ensure that workplace exposure levels do not exceed these limits through proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and regular monitoring.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of ammonium hydroxide in metal texturing processes. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the release of ammonia under the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act. Facilities using ammonium hydroxide must comply with air emission standards and wastewater discharge limits. This may require the implementation of air scrubbers, wastewater treatment systems, and proper disposal methods for any hazardous waste generated during the texturing process.
Storage and handling of ammonium hydroxide are subject to specific safety requirements. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) mandates proper labeling and safety data sheets (SDS) for ammonium hydroxide. Facilities must ensure that storage areas are well-ventilated, equipped with secondary containment, and protected from heat sources. Transportation of ammonium hydroxide is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States, which classifies it as a hazardous material and requires specific packaging, labeling, and documentation.
Emergency response planning is another critical aspect of regulatory compliance. Facilities using ammonium hydroxide must develop and maintain emergency action plans, including procedures for spill containment, evacuation, and first aid. Regular training of personnel in these procedures is essential to ensure preparedness in case of accidents or releases.
Product safety regulations also apply to the use of ammonium hydroxide in metal texturing. The finished products must comply with relevant industry standards and consumer safety regulations. This may include testing for residual ammonia content and ensuring that the textured metal surfaces meet specifications for intended applications, such as food contact surfaces or medical devices.
Compliance with these safety regulations requires ongoing monitoring, documentation, and reporting. Facilities must maintain records of chemical inventories, exposure assessments, training sessions, and incident reports. Regular audits and inspections, both internal and by regulatory agencies, are necessary to ensure continued compliance and identify areas for improvement in safety practices.
Occupational safety and health regulations play a primary role in governing the use of ammonium hydroxide. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for ammonia, the primary component of ammonium hydroxide. These limits are set at 50 parts per million (ppm) for an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) and a short-term exposure limit (STEL) of 35 ppm for 15 minutes. Employers must ensure that workplace exposure levels do not exceed these limits through proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and regular monitoring.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of ammonium hydroxide in metal texturing processes. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the release of ammonia under the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act. Facilities using ammonium hydroxide must comply with air emission standards and wastewater discharge limits. This may require the implementation of air scrubbers, wastewater treatment systems, and proper disposal methods for any hazardous waste generated during the texturing process.
Storage and handling of ammonium hydroxide are subject to specific safety requirements. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) mandates proper labeling and safety data sheets (SDS) for ammonium hydroxide. Facilities must ensure that storage areas are well-ventilated, equipped with secondary containment, and protected from heat sources. Transportation of ammonium hydroxide is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States, which classifies it as a hazardous material and requires specific packaging, labeling, and documentation.
Emergency response planning is another critical aspect of regulatory compliance. Facilities using ammonium hydroxide must develop and maintain emergency action plans, including procedures for spill containment, evacuation, and first aid. Regular training of personnel in these procedures is essential to ensure preparedness in case of accidents or releases.
Product safety regulations also apply to the use of ammonium hydroxide in metal texturing. The finished products must comply with relevant industry standards and consumer safety regulations. This may include testing for residual ammonia content and ensuring that the textured metal surfaces meet specifications for intended applications, such as food contact surfaces or medical devices.
Compliance with these safety regulations requires ongoing monitoring, documentation, and reporting. Facilities must maintain records of chemical inventories, exposure assessments, training sessions, and incident reports. Regular audits and inspections, both internal and by regulatory agencies, are necessary to ensure continued compliance and identify areas for improvement in safety practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!