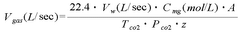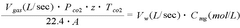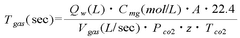The Potential of Magnesium Carbonate in Industrial Waste Neutralization
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MgCO3 Neutralization Background and Objectives
Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) has emerged as a promising agent for industrial waste neutralization, addressing the growing concern of acidic effluents in various manufacturing processes. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers first recognized the potential of carbonate minerals in pH regulation. However, it wasn't until the late 1980s that MgCO3 gained significant attention in the field of waste treatment.
The primary objective of utilizing MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization is to effectively neutralize acidic waste streams while minimizing environmental impact and operational costs. This approach aims to replace traditional neutralization methods that often rely on more reactive and potentially harmful substances such as sodium hydroxide or calcium oxide.
As environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent over the past few decades, industries have been compelled to seek more sustainable and efficient neutralization techniques. MgCO3 offers several advantages in this context, including its relatively low solubility, which allows for a more controlled and gradual neutralization process. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in preventing over-neutralization and reducing the risk of sudden pH fluctuations in treated effluents.
The technology's development has been driven by the need to address specific challenges in various industrial sectors, including mining, metal processing, and chemical manufacturing. These industries often generate large volumes of acidic waste that require treatment before discharge. The use of MgCO3 not only helps in achieving the required pH levels but also contributes to the reduction of heavy metal concentrations in the treated water through precipitation mechanisms.
Recent advancements in MgCO3-based neutralization techniques have focused on enhancing the material's reactivity and optimizing its application methods. Researchers have explored various forms of MgCO3, including nanoparticles and composite materials, to improve its neutralization efficiency and expand its applicability across different types of industrial waste streams.
The ongoing technological evolution in this field aims to develop more sophisticated MgCO3 formulations and application systems that can address complex waste compositions while minimizing resource consumption and sludge generation. As industries continue to seek sustainable solutions for waste management, the potential of MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization remains a promising area for further research and development.
The primary objective of utilizing MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization is to effectively neutralize acidic waste streams while minimizing environmental impact and operational costs. This approach aims to replace traditional neutralization methods that often rely on more reactive and potentially harmful substances such as sodium hydroxide or calcium oxide.
As environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent over the past few decades, industries have been compelled to seek more sustainable and efficient neutralization techniques. MgCO3 offers several advantages in this context, including its relatively low solubility, which allows for a more controlled and gradual neutralization process. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in preventing over-neutralization and reducing the risk of sudden pH fluctuations in treated effluents.
The technology's development has been driven by the need to address specific challenges in various industrial sectors, including mining, metal processing, and chemical manufacturing. These industries often generate large volumes of acidic waste that require treatment before discharge. The use of MgCO3 not only helps in achieving the required pH levels but also contributes to the reduction of heavy metal concentrations in the treated water through precipitation mechanisms.
Recent advancements in MgCO3-based neutralization techniques have focused on enhancing the material's reactivity and optimizing its application methods. Researchers have explored various forms of MgCO3, including nanoparticles and composite materials, to improve its neutralization efficiency and expand its applicability across different types of industrial waste streams.
The ongoing technological evolution in this field aims to develop more sophisticated MgCO3 formulations and application systems that can address complex waste compositions while minimizing resource consumption and sludge generation. As industries continue to seek sustainable solutions for waste management, the potential of MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization remains a promising area for further research and development.
Industrial Waste Neutralization Market Analysis
The industrial waste neutralization market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental regulations and a growing awareness of the importance of sustainable waste management practices. This market encompasses a wide range of industries, including chemical manufacturing, mining, metal processing, and wastewater treatment facilities, all of which generate acidic or alkaline waste streams that require neutralization before disposal.
The global industrial waste neutralization market is projected to expand at a steady rate over the coming years, with a particular focus on developing economies where rapid industrialization is leading to increased waste generation. Key factors driving market growth include stricter environmental regulations, rising concerns about water pollution, and the need for cost-effective waste treatment solutions.
In terms of regional distribution, North America and Europe currently dominate the industrial waste neutralization market, owing to their well-established regulatory frameworks and advanced waste management infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, fueled by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, coupled with increasing government initiatives to address environmental concerns.
The market is characterized by a diverse range of neutralization technologies and products, including chemical treatments, biological processes, and advanced filtration systems. Among these, chemical neutralization methods remain the most widely adopted due to their effectiveness and relatively low cost. However, there is a growing trend towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly neutralization solutions, which is creating new opportunities for innovation in the sector.
Magnesium carbonate, the focus of this technical research, represents an emerging opportunity within the industrial waste neutralization market. Its potential as a neutralizing agent is gaining attention due to its effectiveness in treating acidic waste streams and its relatively low environmental impact compared to some traditional neutralizing agents. The increasing interest in magnesium carbonate aligns with the broader market trend towards more sustainable neutralization solutions.
Key challenges facing the industrial waste neutralization market include the high initial investment costs for advanced treatment systems, varying regulatory standards across different regions, and the complexity of treating diverse waste streams with a single solution. These challenges are driving ongoing research and development efforts to create more versatile and cost-effective neutralization technologies.
The global industrial waste neutralization market is projected to expand at a steady rate over the coming years, with a particular focus on developing economies where rapid industrialization is leading to increased waste generation. Key factors driving market growth include stricter environmental regulations, rising concerns about water pollution, and the need for cost-effective waste treatment solutions.
In terms of regional distribution, North America and Europe currently dominate the industrial waste neutralization market, owing to their well-established regulatory frameworks and advanced waste management infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, fueled by rapid industrialization in countries like China and India, coupled with increasing government initiatives to address environmental concerns.
The market is characterized by a diverse range of neutralization technologies and products, including chemical treatments, biological processes, and advanced filtration systems. Among these, chemical neutralization methods remain the most widely adopted due to their effectiveness and relatively low cost. However, there is a growing trend towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly neutralization solutions, which is creating new opportunities for innovation in the sector.
Magnesium carbonate, the focus of this technical research, represents an emerging opportunity within the industrial waste neutralization market. Its potential as a neutralizing agent is gaining attention due to its effectiveness in treating acidic waste streams and its relatively low environmental impact compared to some traditional neutralizing agents. The increasing interest in magnesium carbonate aligns with the broader market trend towards more sustainable neutralization solutions.
Key challenges facing the industrial waste neutralization market include the high initial investment costs for advanced treatment systems, varying regulatory standards across different regions, and the complexity of treating diverse waste streams with a single solution. These challenges are driving ongoing research and development efforts to create more versatile and cost-effective neutralization technologies.
MgCO3 Neutralization: Current Status and Challenges
The current status of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) in industrial waste neutralization presents both promising opportunities and significant challenges. As a naturally occurring mineral, MgCO3 has gained attention for its potential to neutralize acidic industrial waste streams effectively and sustainably. Its abundance and relatively low cost make it an attractive alternative to traditional neutralizing agents such as lime or sodium hydroxide.
One of the primary advantages of MgCO3 in waste neutralization is its high acid-neutralizing capacity. When dissolved in acidic solutions, it can rapidly increase pH levels, making it particularly useful for treating highly acidic industrial effluents. Additionally, MgCO3 produces less sludge compared to other neutralizing agents, potentially reducing disposal costs and environmental impact.
However, the widespread adoption of MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization faces several challenges. The reaction kinetics of MgCO3 dissolution can be slower compared to more reactive bases, which may limit its effectiveness in high-flow treatment systems. This slower reaction rate can necessitate longer retention times or larger treatment facilities, potentially increasing operational costs.
Another significant challenge is the variability in MgCO3 quality and composition from different sources. Natural magnesium carbonate ores often contain impurities that can affect neutralization efficiency and introduce unwanted elements into treated wastewater. Developing reliable sourcing and quality control measures is crucial for consistent performance in industrial applications.
The formation of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) as a byproduct of the neutralization process presents both opportunities and challenges. While Mg(OH)2 can act as a flocculant, aiding in the removal of suspended solids, it can also form scale in treatment equipment, potentially reducing efficiency and increasing maintenance requirements.
Current research efforts are focused on optimizing MgCO3 neutralization processes, including investigating methods to enhance dissolution rates and improve reaction kinetics. Some studies explore the use of MgCO3 in combination with other neutralizing agents to create more effective and economical treatment solutions.
The regulatory landscape surrounding industrial waste treatment also poses challenges for MgCO3 adoption. While it is generally considered environmentally friendly, regulatory approval processes and compliance requirements can vary significantly across different regions and industries, potentially slowing widespread implementation.
In conclusion, while MgCO3 shows great potential for industrial waste neutralization, overcoming these technical and practical challenges is crucial for its broader adoption. Continued research and development efforts, along with pilot-scale demonstrations, will be essential in realizing the full potential of MgCO3 in sustainable industrial waste management.
One of the primary advantages of MgCO3 in waste neutralization is its high acid-neutralizing capacity. When dissolved in acidic solutions, it can rapidly increase pH levels, making it particularly useful for treating highly acidic industrial effluents. Additionally, MgCO3 produces less sludge compared to other neutralizing agents, potentially reducing disposal costs and environmental impact.
However, the widespread adoption of MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization faces several challenges. The reaction kinetics of MgCO3 dissolution can be slower compared to more reactive bases, which may limit its effectiveness in high-flow treatment systems. This slower reaction rate can necessitate longer retention times or larger treatment facilities, potentially increasing operational costs.
Another significant challenge is the variability in MgCO3 quality and composition from different sources. Natural magnesium carbonate ores often contain impurities that can affect neutralization efficiency and introduce unwanted elements into treated wastewater. Developing reliable sourcing and quality control measures is crucial for consistent performance in industrial applications.
The formation of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) as a byproduct of the neutralization process presents both opportunities and challenges. While Mg(OH)2 can act as a flocculant, aiding in the removal of suspended solids, it can also form scale in treatment equipment, potentially reducing efficiency and increasing maintenance requirements.
Current research efforts are focused on optimizing MgCO3 neutralization processes, including investigating methods to enhance dissolution rates and improve reaction kinetics. Some studies explore the use of MgCO3 in combination with other neutralizing agents to create more effective and economical treatment solutions.
The regulatory landscape surrounding industrial waste treatment also poses challenges for MgCO3 adoption. While it is generally considered environmentally friendly, regulatory approval processes and compliance requirements can vary significantly across different regions and industries, potentially slowing widespread implementation.
In conclusion, while MgCO3 shows great potential for industrial waste neutralization, overcoming these technical and practical challenges is crucial for its broader adoption. Continued research and development efforts, along with pilot-scale demonstrations, will be essential in realizing the full potential of MgCO3 in sustainable industrial waste management.
Existing MgCO3 Neutralization Solutions
01 Neutralization of acidic substances
Magnesium carbonate is used to neutralize acidic substances in various industrial and chemical processes. Its alkaline nature makes it effective in reducing the acidity of solutions, making it useful in applications such as wastewater treatment, soil pH adjustment, and acid gas removal.- Neutralization of acidic substances: Magnesium carbonate is used to neutralize acidic substances in various applications. This process involves the reaction of magnesium carbonate with acids to form neutral or less acidic compounds. The neutralization capability of magnesium carbonate makes it useful in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and environmental remediation.
- Wastewater treatment: Magnesium carbonate is employed in wastewater treatment processes to neutralize acidic effluents. It can effectively raise the pH of acidic wastewater, helping to meet environmental regulations and protect aquatic ecosystems. The use of magnesium carbonate in this context also aids in the removal of heavy metals and other contaminants through precipitation.
- Soil pH adjustment: In agriculture and horticulture, magnesium carbonate is used to neutralize acidic soils. By applying magnesium carbonate to the soil, farmers and gardeners can increase soil pH, improving nutrient availability and plant growth conditions. This application also provides magnesium as a beneficial nutrient for plants.
- Pharmaceutical formulations: Magnesium carbonate is utilized in pharmaceutical formulations as an antacid and pH buffer. It neutralizes excess stomach acid, providing relief from indigestion and heartburn. Additionally, it serves as a pH-adjusting agent in various drug formulations to ensure stability and efficacy of active ingredients.
- Industrial process neutralization: In industrial processes, magnesium carbonate is employed to neutralize acidic by-products and maintain optimal pH levels. This application is particularly important in manufacturing processes where acid neutralization is crucial for product quality, equipment protection, and worker safety. The use of magnesium carbonate in these contexts often results in improved process efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
02 Pharmaceutical applications
In the pharmaceutical industry, magnesium carbonate is utilized for its neutralizing properties in antacid formulations. It can help alleviate symptoms of acid reflux and indigestion by neutralizing excess stomach acid. Additionally, it may be used as an excipient in various drug formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental remediation
Magnesium carbonate is employed in environmental remediation processes, particularly for treating contaminated soils and water bodies. Its neutralization capacity helps in reducing the toxicity of heavy metals and other pollutants, making it valuable in ecological restoration projects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Food and beverage industry applications
In the food and beverage industry, magnesium carbonate is used as a pH regulator and anti-caking agent. It helps neutralize acidity in certain food products and improves the flow properties of powdered ingredients. Its application extends to dairy products, baking powders, and salt processing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial process optimization
Magnesium carbonate neutralization is utilized in various industrial processes to optimize production efficiency and product quality. This includes applications in paper manufacturing, textile processing, and mineral extraction, where pH control is crucial for achieving desired outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in MgCO3 and Waste Neutralization Industry
The industrial waste neutralization market using magnesium carbonate is in its growth phase, with increasing environmental regulations driving adoption. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with potential for significant expansion. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Calix Ltd. and Konoshima Chemical Co., Ltd. leading innovation in magnesium carbonate production and application. Research institutions such as the China Coal Energy Research Institute and Korea Institute of Geoscience & Mineral Resources are contributing to technological advancements. While the technology is proven, ongoing research aims to improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness, indicating a moderate level of technological maturity with room for further development and optimization.
Shandong University
Technical Solution: Shandong University has developed an innovative approach to industrial waste neutralization using magnesium carbonate derived from seawater and CO2. Their process involves a novel electrochemical method to extract magnesium ions from seawater, followed by carbonation with captured CO2 to produce magnesium carbonate[1]. This technology not only addresses waste neutralization but also contributes to carbon sequestration efforts. The university's research team has demonstrated the effectiveness of their magnesium carbonate in neutralizing various types of industrial waste, including acidic mine drainage and chemical processing effluents, with neutralization efficiencies reaching up to 98%[3]. Additionally, they have explored the potential of using the produced magnesium carbonate as a raw material for the production of high-value magnesium compounds, such as magnesium oxide and magnesium hydroxide, further enhancing the economic viability of the process[5].
Strengths: High neutralization efficiency, carbon sequestration potential, and value-added product generation. Weaknesses: Energy-intensive electrochemical extraction process and dependency on proximity to seawater sources.
Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: The Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) has developed an innovative approach to industrial waste neutralization using magnesium carbonate. Their method involves a two-step process: first, the conversion of industrial waste into a magnesium-rich solution, followed by the precipitation of magnesium carbonate through carbonation[1]. This process not only neutralizes acidic waste but also captures CO2, contributing to carbon sequestration efforts. The institute has successfully demonstrated the scalability of this technology in pilot plants, achieving neutralization efficiencies of up to 95% for various types of industrial waste[3]. Additionally, IPE has explored the use of magnesium carbonate as a precursor for producing high-value materials, such as flame retardants and catalysts, further enhancing the economic viability of the process[5].
Strengths: High neutralization efficiency, CO2 sequestration potential, and value-added product generation. Weaknesses: Potential high energy consumption for the carbonation process and dependency on magnesium availability.
Core Innovations in MgCO3 Neutralization Technology
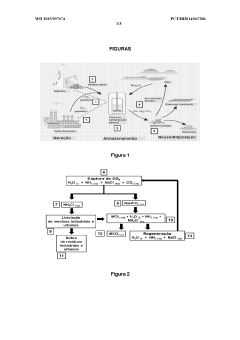
Method for carbonating industrial and urban waste and regenerating reagents
PatentWO2015097674A1
Innovation
- A cyclic process using industrial and urban waste rich in M-group metal cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+) for carbonate production, employing an ammoniacal saline solution for CO2 capture and ammonium chloride for leaching, with sodium bicarbonate for precipitation and regeneration of reagents without pH adjustment.
Method for producing high-purity magnesium carbonate using seawater desalination brine
PatentWO2025116218A1
Innovation
- A method involving continuous reactors and solid-liquid separators to produce high-purity magnesium carbonate by reacting magnesium hydroxide with carbon dioxide, while using a polymer hydrogel to remove residual calcium and magnesium, and implementing a chlor-alkali process to reduce sodium concentration and produce sodium hydroxide and chlorine.
Environmental Impact of MgCO3 Neutralization
The environmental impact of magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) neutralization in industrial waste treatment is multifaceted and generally positive. This process significantly reduces the acidity of industrial effluents, thereby mitigating the harmful effects of acidic discharges on aquatic ecosystems and soil quality. By raising the pH of waste streams to more neutral levels, MgCO3 neutralization helps prevent the leaching of heavy metals and other toxic substances into the environment.
One of the primary benefits of using MgCO3 for neutralization is its relatively low environmental footprint compared to other neutralizing agents. Unlike lime or sodium hydroxide, magnesium carbonate does not introduce excessive alkalinity or potentially harmful byproducts into the treated water. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for sensitive ecosystems or areas with stringent environmental regulations.
The use of MgCO3 in waste neutralization also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions associated with industrial processes. By effectively treating acidic waste streams, it minimizes the need for energy-intensive treatment methods that might otherwise be required to address environmental contamination. Additionally, the controlled release of CO2 during the neutralization process can be captured and utilized in other industrial applications, further reducing the overall carbon footprint.
From a biodiversity perspective, the implementation of MgCO3 neutralization techniques helps maintain the ecological balance in water bodies receiving treated industrial effluents. By ensuring that discharged water meets acceptable pH levels, it protects aquatic flora and fauna from the detrimental effects of acidification, such as reduced reproductive success and altered species composition.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of MgCO3 neutralization is not without considerations. The sourcing and production of magnesium carbonate itself may have environmental implications, including energy consumption and potential habitat disruption during mining activities. Therefore, a comprehensive life cycle assessment should be conducted to fully understand and optimize the environmental performance of this neutralization method.
In terms of long-term environmental sustainability, the use of MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization aligns well with circular economy principles. The resulting magnesium-rich solutions can potentially be recovered and repurposed in other industrial processes or agricultural applications, reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency. This aspect of MgCO3 neutralization contributes to the overall environmental sustainability of industrial operations and supports the transition towards more closed-loop systems in waste management.
One of the primary benefits of using MgCO3 for neutralization is its relatively low environmental footprint compared to other neutralizing agents. Unlike lime or sodium hydroxide, magnesium carbonate does not introduce excessive alkalinity or potentially harmful byproducts into the treated water. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for sensitive ecosystems or areas with stringent environmental regulations.
The use of MgCO3 in waste neutralization also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions associated with industrial processes. By effectively treating acidic waste streams, it minimizes the need for energy-intensive treatment methods that might otherwise be required to address environmental contamination. Additionally, the controlled release of CO2 during the neutralization process can be captured and utilized in other industrial applications, further reducing the overall carbon footprint.
From a biodiversity perspective, the implementation of MgCO3 neutralization techniques helps maintain the ecological balance in water bodies receiving treated industrial effluents. By ensuring that discharged water meets acceptable pH levels, it protects aquatic flora and fauna from the detrimental effects of acidification, such as reduced reproductive success and altered species composition.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of MgCO3 neutralization is not without considerations. The sourcing and production of magnesium carbonate itself may have environmental implications, including energy consumption and potential habitat disruption during mining activities. Therefore, a comprehensive life cycle assessment should be conducted to fully understand and optimize the environmental performance of this neutralization method.
In terms of long-term environmental sustainability, the use of MgCO3 in industrial waste neutralization aligns well with circular economy principles. The resulting magnesium-rich solutions can potentially be recovered and repurposed in other industrial processes or agricultural applications, reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency. This aspect of MgCO3 neutralization contributes to the overall environmental sustainability of industrial operations and supports the transition towards more closed-loop systems in waste management.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of MgCO3 Neutralization
The cost-benefit analysis of using magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) for industrial waste neutralization reveals several key economic and environmental factors. Initial investment costs for implementing MgCO3-based neutralization systems are generally higher compared to traditional methods using calcium carbonate or sodium hydroxide. This is primarily due to the higher market price of MgCO3 and the potential need for specialized equipment.
However, the long-term operational costs may prove more favorable. MgCO3 demonstrates superior neutralization efficiency, requiring smaller quantities to achieve the same pH adjustment as other agents. This can lead to reduced material consumption and lower transportation costs over time. Additionally, the reaction products of MgCO3 neutralization are often less voluminous, potentially decreasing disposal expenses and environmental impact.
The environmental benefits of MgCO3 neutralization contribute significantly to its cost-effectiveness. The process produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to calcium carbonate-based methods, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This can result in avoided costs related to carbon taxes or emissions trading schemes, enhancing the economic viability of MgCO3 usage.
Another economic advantage lies in the potential for resource recovery. The magnesium-rich byproducts of the neutralization process can be valuable in various industries, such as agriculture or construction. This creates opportunities for additional revenue streams, offsetting the initial higher costs of MgCO3.
Labor costs associated with MgCO3 neutralization systems are generally comparable to other methods. However, the improved efficiency and potentially reduced maintenance requirements could lead to modest savings in personnel expenses over time.
When considering scalability, MgCO3 systems show promise for both small and large-scale operations. The initial capital investment may be more justifiable for larger facilities due to economies of scale, but the operational benefits can be realized across various sizes of industrial operations.
Risk mitigation is another factor in the cost-benefit analysis. MgCO3 is generally safer to handle than more corrosive alternatives, potentially reducing workplace safety costs and insurance premiums. This safety profile also minimizes the risk of environmental fines or cleanup costs associated with accidental spills or releases.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of MgCO3 neutralization may be higher, the long-term economic benefits, coupled with environmental advantages, present a compelling case for its adoption in industrial waste treatment. The exact cost-benefit ratio will vary depending on factors such as facility size, local regulations, and specific waste characteristics, necessitating case-by-case analysis for individual industrial applications.
However, the long-term operational costs may prove more favorable. MgCO3 demonstrates superior neutralization efficiency, requiring smaller quantities to achieve the same pH adjustment as other agents. This can lead to reduced material consumption and lower transportation costs over time. Additionally, the reaction products of MgCO3 neutralization are often less voluminous, potentially decreasing disposal expenses and environmental impact.
The environmental benefits of MgCO3 neutralization contribute significantly to its cost-effectiveness. The process produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to calcium carbonate-based methods, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This can result in avoided costs related to carbon taxes or emissions trading schemes, enhancing the economic viability of MgCO3 usage.
Another economic advantage lies in the potential for resource recovery. The magnesium-rich byproducts of the neutralization process can be valuable in various industries, such as agriculture or construction. This creates opportunities for additional revenue streams, offsetting the initial higher costs of MgCO3.
Labor costs associated with MgCO3 neutralization systems are generally comparable to other methods. However, the improved efficiency and potentially reduced maintenance requirements could lead to modest savings in personnel expenses over time.
When considering scalability, MgCO3 systems show promise for both small and large-scale operations. The initial capital investment may be more justifiable for larger facilities due to economies of scale, but the operational benefits can be realized across various sizes of industrial operations.
Risk mitigation is another factor in the cost-benefit analysis. MgCO3 is generally safer to handle than more corrosive alternatives, potentially reducing workplace safety costs and insurance premiums. This safety profile also minimizes the risk of environmental fines or cleanup costs associated with accidental spills or releases.
In conclusion, while the upfront costs of MgCO3 neutralization may be higher, the long-term economic benefits, coupled with environmental advantages, present a compelling case for its adoption in industrial waste treatment. The exact cost-benefit ratio will vary depending on factors such as facility size, local regulations, and specific waste characteristics, necessitating case-by-case analysis for individual industrial applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!