The Role of Magnesium Carbonate in Dietary Magnesium Supplements
JUL 31, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Magnesium Carbonate Supplement Background
Magnesium carbonate has been a significant component in dietary magnesium supplements for several decades. Its history as a supplement dates back to the early 20th century when researchers began to recognize the importance of magnesium in human health. Initially, magnesium carbonate was primarily used in industrial applications, but its potential as a dietary supplement was soon realized due to its high magnesium content and relatively low cost of production.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate as a supplement has been closely tied to advancements in nutritional science and our understanding of magnesium's role in the body. As research progressed, it became clear that magnesium was essential for numerous physiological processes, including energy production, muscle function, and bone health. This led to increased interest in magnesium supplementation, with magnesium carbonate emerging as a popular choice.
In the 1960s and 1970s, studies began to focus on the bioavailability of different magnesium compounds. While magnesium carbonate was found to have lower bioavailability compared to some other forms, its stability and ease of formulation made it a practical option for supplement manufacturers. This period also saw the development of various processing techniques to improve the absorption of magnesium carbonate in the body.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a surge in consumer awareness about the importance of mineral supplementation. Magnesium carbonate supplements gained popularity as part of this trend, often marketed for their potential benefits in areas such as stress reduction, sleep improvement, and muscle recovery. During this time, researchers also began to explore the potential of magnesium carbonate in combination with other nutrients to enhance its effectiveness.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards understanding the specific mechanisms by which magnesium carbonate is absorbed and utilized in the body. Advanced imaging techniques and molecular studies have provided new insights into how this compound interacts with the digestive system and enters the bloodstream. This research has led to the development of more sophisticated formulations, including slow-release and enhanced-absorption versions of magnesium carbonate supplements.
The current landscape of magnesium carbonate supplementation is characterized by a diverse range of products catering to various health needs and preferences. From traditional tablets and capsules to effervescent powders and liquid formulations, magnesium carbonate continues to be a versatile ingredient in the dietary supplement industry. Its role in supporting overall health and addressing specific conditions, such as magnesium deficiency and certain metabolic disorders, remains a subject of ongoing research and clinical interest.
The evolution of magnesium carbonate as a supplement has been closely tied to advancements in nutritional science and our understanding of magnesium's role in the body. As research progressed, it became clear that magnesium was essential for numerous physiological processes, including energy production, muscle function, and bone health. This led to increased interest in magnesium supplementation, with magnesium carbonate emerging as a popular choice.
In the 1960s and 1970s, studies began to focus on the bioavailability of different magnesium compounds. While magnesium carbonate was found to have lower bioavailability compared to some other forms, its stability and ease of formulation made it a practical option for supplement manufacturers. This period also saw the development of various processing techniques to improve the absorption of magnesium carbonate in the body.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a surge in consumer awareness about the importance of mineral supplementation. Magnesium carbonate supplements gained popularity as part of this trend, often marketed for their potential benefits in areas such as stress reduction, sleep improvement, and muscle recovery. During this time, researchers also began to explore the potential of magnesium carbonate in combination with other nutrients to enhance its effectiveness.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards understanding the specific mechanisms by which magnesium carbonate is absorbed and utilized in the body. Advanced imaging techniques and molecular studies have provided new insights into how this compound interacts with the digestive system and enters the bloodstream. This research has led to the development of more sophisticated formulations, including slow-release and enhanced-absorption versions of magnesium carbonate supplements.
The current landscape of magnesium carbonate supplementation is characterized by a diverse range of products catering to various health needs and preferences. From traditional tablets and capsules to effervescent powders and liquid formulations, magnesium carbonate continues to be a versatile ingredient in the dietary supplement industry. Its role in supporting overall health and addressing specific conditions, such as magnesium deficiency and certain metabolic disorders, remains a subject of ongoing research and clinical interest.
Market Analysis of Magnesium Supplements
The global market for magnesium supplements has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of the essential role magnesium plays in human health. The market size for magnesium supplements reached $1.43 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of magnesium deficiency, growing health consciousness among consumers, and the expanding elderly population.
Magnesium carbonate, as a key ingredient in dietary magnesium supplements, has gained traction due to its high magnesium content and bioavailability. The demand for magnesium carbonate-based supplements has been particularly strong in North America and Europe, where consumers are increasingly seeking natural and organic supplement options.
The market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including tablets, capsules, powders, and liquid formulations. Tablets and capsules remain the most popular forms, accounting for over 60% of the market share. However, powdered and liquid magnesium supplements are gaining popularity, especially among younger consumers and athletes.
Key market players in the magnesium supplement industry include Nature's Bounty, NOW Foods, Doctor's Best, and Life Extension. These companies have been investing in research and development to improve the bioavailability and efficacy of their magnesium carbonate-based products. Additionally, there has been a trend towards the development of combination supplements that pair magnesium with other nutrients like vitamin D and calcium.
The retail landscape for magnesium supplements is evolving, with e-commerce channels experiencing rapid growth. Online sales of magnesium supplements increased by 32% in 2020, partly due to the COVID-19 pandemic's impact on consumer shopping habits. Traditional brick-and-mortar pharmacies and health food stores continue to be important distribution channels, but their market share is gradually declining.
Consumer demographics play a crucial role in shaping the magnesium supplement market. While older adults remain a key consumer group due to age-related magnesium deficiency risks, there is growing demand among younger adults, particularly those aged 25-40, who are increasingly health-conscious and proactive about nutritional supplementation.
Regionally, North America dominates the magnesium supplement market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing disposable incomes, growing health awareness, and the adoption of Western dietary habits in countries like China and India.
Magnesium carbonate, as a key ingredient in dietary magnesium supplements, has gained traction due to its high magnesium content and bioavailability. The demand for magnesium carbonate-based supplements has been particularly strong in North America and Europe, where consumers are increasingly seeking natural and organic supplement options.
The market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including tablets, capsules, powders, and liquid formulations. Tablets and capsules remain the most popular forms, accounting for over 60% of the market share. However, powdered and liquid magnesium supplements are gaining popularity, especially among younger consumers and athletes.
Key market players in the magnesium supplement industry include Nature's Bounty, NOW Foods, Doctor's Best, and Life Extension. These companies have been investing in research and development to improve the bioavailability and efficacy of their magnesium carbonate-based products. Additionally, there has been a trend towards the development of combination supplements that pair magnesium with other nutrients like vitamin D and calcium.
The retail landscape for magnesium supplements is evolving, with e-commerce channels experiencing rapid growth. Online sales of magnesium supplements increased by 32% in 2020, partly due to the COVID-19 pandemic's impact on consumer shopping habits. Traditional brick-and-mortar pharmacies and health food stores continue to be important distribution channels, but their market share is gradually declining.
Consumer demographics play a crucial role in shaping the magnesium supplement market. While older adults remain a key consumer group due to age-related magnesium deficiency risks, there is growing demand among younger adults, particularly those aged 25-40, who are increasingly health-conscious and proactive about nutritional supplementation.
Regionally, North America dominates the magnesium supplement market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing disposable incomes, growing health awareness, and the adoption of Western dietary habits in countries like China and India.
Current Challenges in Magnesium Supplementation
Despite the widespread recognition of magnesium's importance in human health, several challenges persist in the field of magnesium supplementation. One of the primary issues is the bioavailability of different magnesium compounds, including magnesium carbonate. While magnesium carbonate is a common form used in dietary supplements, its absorption rate in the human body remains a subject of debate among researchers.
The variability in absorption rates across different magnesium compounds poses a significant challenge for both manufacturers and consumers. This variability makes it difficult to determine the optimal dosage and form of magnesium supplementation for individual needs. Furthermore, the interaction between magnesium carbonate and other nutrients or medications in the digestive system is not fully understood, potentially affecting its efficacy.
Another challenge lies in the potential side effects associated with magnesium supplementation, particularly when using magnesium carbonate. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, including diarrhea or nausea, when taking high doses of magnesium supplements. This can lead to poor compliance and discontinuation of supplementation, even when it may be beneficial for overall health.
The lack of standardized testing methods for magnesium status in the body further complicates the assessment of supplementation efficacy. Current methods, such as serum magnesium levels, may not accurately reflect the body's total magnesium stores, making it challenging to determine the true impact of magnesium carbonate supplementation on an individual's magnesium status.
Additionally, there is a growing concern about the environmental impact of magnesium carbonate production for dietary supplements. The extraction and processing of magnesium carbonate can have significant ecological consequences, raising questions about the sustainability of its widespread use in supplementation.
Regulatory challenges also play a role in the current landscape of magnesium supplementation. The varying regulations across different countries regarding the permissible forms and dosages of magnesium supplements, including magnesium carbonate, create obstacles for global distribution and standardization of supplementation practices.
Lastly, the ongoing debate about the necessity of magnesium supplementation for the general population versus targeted supplementation for specific health conditions or deficiencies adds another layer of complexity to the field. This uncertainty can lead to confusion among healthcare providers and consumers alike, potentially resulting in either over-supplementation or under-utilization of magnesium carbonate and other magnesium compounds in dietary supplements.
The variability in absorption rates across different magnesium compounds poses a significant challenge for both manufacturers and consumers. This variability makes it difficult to determine the optimal dosage and form of magnesium supplementation for individual needs. Furthermore, the interaction between magnesium carbonate and other nutrients or medications in the digestive system is not fully understood, potentially affecting its efficacy.
Another challenge lies in the potential side effects associated with magnesium supplementation, particularly when using magnesium carbonate. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, including diarrhea or nausea, when taking high doses of magnesium supplements. This can lead to poor compliance and discontinuation of supplementation, even when it may be beneficial for overall health.
The lack of standardized testing methods for magnesium status in the body further complicates the assessment of supplementation efficacy. Current methods, such as serum magnesium levels, may not accurately reflect the body's total magnesium stores, making it challenging to determine the true impact of magnesium carbonate supplementation on an individual's magnesium status.
Additionally, there is a growing concern about the environmental impact of magnesium carbonate production for dietary supplements. The extraction and processing of magnesium carbonate can have significant ecological consequences, raising questions about the sustainability of its widespread use in supplementation.
Regulatory challenges also play a role in the current landscape of magnesium supplementation. The varying regulations across different countries regarding the permissible forms and dosages of magnesium supplements, including magnesium carbonate, create obstacles for global distribution and standardization of supplementation practices.
Lastly, the ongoing debate about the necessity of magnesium supplementation for the general population versus targeted supplementation for specific health conditions or deficiencies adds another layer of complexity to the field. This uncertainty can lead to confusion among healthcare providers and consumers alike, potentially resulting in either over-supplementation or under-utilization of magnesium carbonate and other magnesium compounds in dietary supplements.
Magnesium Carbonate Formulation Techniques
01 Enhancing magnesium carbonate bioavailability through particle size reduction
Reducing the particle size of magnesium carbonate can significantly improve its bioavailability. This can be achieved through various methods such as micronization or nanoparticle formulation. Smaller particles have a larger surface area, which allows for better dissolution and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.- Enhancing magnesium carbonate bioavailability through particle size reduction: Reducing the particle size of magnesium carbonate can significantly improve its bioavailability. Techniques such as micronization or nanoparticle formulation can increase the surface area of the compound, leading to better absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. This approach can be particularly effective for improving the efficacy of magnesium carbonate in nutritional supplements and pharmaceutical applications.
- Combining magnesium carbonate with organic acids for improved absorption: The bioavailability of magnesium carbonate can be enhanced by combining it with organic acids such as citric acid or malic acid. This combination creates more soluble magnesium salts, which are more readily absorbed by the body. The resulting formulations can be used in various applications, including dietary supplements and fortified food products.
- Developing controlled-release formulations of magnesium carbonate: Controlled-release formulations can improve the bioavailability of magnesium carbonate by gradually releasing the compound over an extended period. This approach can help maintain consistent magnesium levels in the body and reduce potential gastrointestinal side effects associated with high doses. Various technologies, such as matrix systems or coated pellets, can be employed to achieve controlled release.
- Utilizing magnesium carbonate in combination with other minerals: Combining magnesium carbonate with other minerals, such as calcium or zinc, can potentially enhance its bioavailability through synergistic effects. This approach can be particularly useful in developing multi-mineral supplements or fortified food products. The specific mineral combinations and ratios can be optimized to maximize absorption and overall nutritional benefits.
- Incorporating magnesium carbonate into novel delivery systems: Novel delivery systems, such as liposomes, microemulsions, or transdermal patches, can be used to improve the bioavailability of magnesium carbonate. These advanced formulations can enhance absorption by bypassing traditional gastrointestinal routes or by protecting the compound from degradation. Such innovative approaches may lead to more efficient magnesium supplementation methods.
02 Combining magnesium carbonate with organic acids
The bioavailability of magnesium carbonate can be enhanced by combining it with organic acids such as citric acid or malic acid. These acids can help to increase the solubility of magnesium carbonate and improve its absorption in the body.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulating magnesium carbonate in sustained-release preparations
Developing sustained-release formulations of magnesium carbonate can improve its bioavailability by providing a steady release of the mineral over an extended period. This approach can help maintain consistent magnesium levels in the body and potentially reduce gastrointestinal side effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Utilizing magnesium carbonate in combination with other minerals
Combining magnesium carbonate with other minerals, such as calcium or zinc, can potentially enhance its bioavailability through synergistic effects. This approach may also provide additional nutritional benefits and improve overall mineral absorption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Enhancing magnesium carbonate absorption through dietary factors
Certain dietary factors can influence the bioavailability of magnesium carbonate. For example, consuming magnesium carbonate with a meal containing protein or healthy fats may improve its absorption. Additionally, avoiding substances that can interfere with magnesium absorption, such as high doses of calcium or certain types of fiber, can help optimize bioavailability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Magnesium Supplement Industry
The market for magnesium carbonate in dietary supplements is in a growth phase, driven by increasing consumer awareness of magnesium's health benefits. The global magnesium supplements market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a projected CAGR of around 6% from 2021 to 2026. While the technology for producing magnesium carbonate supplements is relatively mature, companies like Balchem Corp., Abiogen Pharma, and Maruo Calcium Co. are continually innovating to improve bioavailability and efficacy. Research institutions such as Zhejiang University and Chongqing University are contributing to the advancement of magnesium supplement technology, potentially leading to new formulations and applications in the near future.
Balchem Corp.
Technical Solution: Balchem Corp. has developed a proprietary technology for magnesium carbonate-based dietary supplements. Their approach involves microencapsulation of magnesium carbonate particles, which enhances bioavailability and controlled release of magnesium in the digestive system[1]. This technology allows for a higher absorption rate of magnesium compared to traditional supplements. The company has also formulated a unique blend of magnesium carbonate with other minerals to optimize its effectiveness as a dietary supplement[2]. Their research has shown that this formulation can maintain stable blood magnesium levels over an extended period, potentially reducing the frequency of supplement intake[3].
Strengths: Enhanced bioavailability, controlled release, and potential for reduced dosing frequency. Weaknesses: May be more expensive to produce than conventional magnesium supplements.
Naveh Pharma (1996) Ltd.
Technical Solution: Naveh Pharma has developed an innovative magnesium carbonate supplement called MAG-C+. This formulation combines magnesium carbonate with vitamin C to enhance absorption and provide additional health benefits[1]. The company's research indicates that this combination can improve magnesium uptake by up to 30% compared to standard magnesium carbonate supplements[2]. Naveh Pharma has also implemented a unique granulation process that results in a more stable and palatable product, addressing common issues with magnesium carbonate such as poor taste and rapid degradation[3]. Their formulation is designed to have a neutral effect on stomach pH, potentially reducing gastrointestinal side effects associated with some magnesium supplements[4].
Strengths: Improved absorption, added vitamin C benefits, and reduced gastrointestinal side effects. Weaknesses: May not be suitable for individuals who need to limit vitamin C intake.
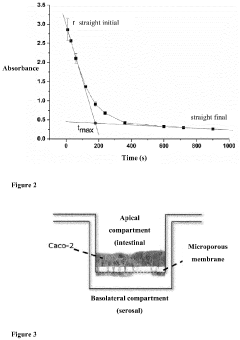
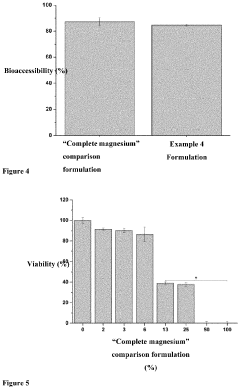
Bioavailability Studies of Magnesium Carbonate
Calcium compositions
PatentActiveUS20070264329A1
Innovation
- A granulation process using ground calcium carbonate with a porosity increasing agent like polyethylene glycol or hydrophilic surfactants, allowing for high-density, low-volume tablets with reduced excipient content, enabling easier swallowing and rapid disintegration.
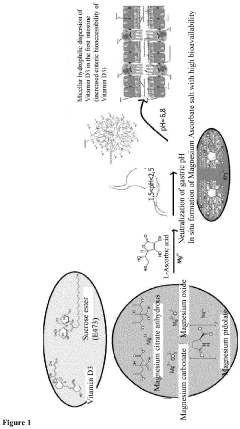
Oral formulation based on vitamin d3, ascorbic acid, and magnesium salts for use as a dietary supplement
PatentActiveEP3928764A1
Innovation
- An oral formulation comprising ascorbic acid, vitamin D3 in micellar dispersion, and magnesium salts including magnesium carbonate and oxide, with a specific weight ratio, forming magnesium ascorbate in situ in the gastric tract to enhance bioavailability, and incorporating additional magnesium sources like magnesium pidolate and citrate to improve absorption.
Regulatory Framework for Dietary Supplements
The regulatory framework for dietary supplements, including magnesium carbonate-based products, is primarily governed by the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994 in the United States. This act defines dietary supplements as products intended to supplement the diet, containing vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, or other dietary substances. Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing dietary supplements. While the FDA does not approve dietary supplements before they enter the market, it has the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded products. Manufacturers must register their facilities with the FDA and follow current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) to ensure product quality and safety.
Labeling requirements for magnesium carbonate supplements are stringent. Labels must include a Supplement Facts panel, listing the amount of elemental magnesium per serving, along with other ingredients. Any claims made on the label must be truthful and not misleading. Structure-function claims, which describe the role of magnesium in the body, are permitted but must be accompanied by a disclaimer stating that the FDA has not evaluated the claim.
Internationally, regulations vary. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) sets guidelines for dietary supplements in the European Union. EFSA has established a tolerable upper intake level for magnesium from supplements, which manufacturers must consider when formulating their products. In Canada, Natural Health Products Regulations govern dietary supplements, requiring pre-market approval and licensing.
Quality control measures are essential in the production of magnesium carbonate supplements. Manufacturers must implement systems to prevent contamination and ensure consistent potency. Third-party testing and certification programs, such as USP verification, provide additional assurance of product quality and adherence to regulatory standards.
The regulatory landscape for dietary supplements is dynamic, with ongoing discussions about potential reforms. There are calls for increased FDA oversight and more stringent safety evaluations before products reach the market. As research on magnesium supplementation evolves, regulations may adapt to reflect new scientific understanding of its benefits and potential risks.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for manufacturers of magnesium carbonate supplements. Failure to adhere to regulatory requirements can result in product recalls, legal action, and damage to brand reputation. As such, staying informed about regulatory changes and maintaining robust quality assurance processes are essential for success in the dietary supplement industry.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing dietary supplements. While the FDA does not approve dietary supplements before they enter the market, it has the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded products. Manufacturers must register their facilities with the FDA and follow current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) to ensure product quality and safety.
Labeling requirements for magnesium carbonate supplements are stringent. Labels must include a Supplement Facts panel, listing the amount of elemental magnesium per serving, along with other ingredients. Any claims made on the label must be truthful and not misleading. Structure-function claims, which describe the role of magnesium in the body, are permitted but must be accompanied by a disclaimer stating that the FDA has not evaluated the claim.
Internationally, regulations vary. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) sets guidelines for dietary supplements in the European Union. EFSA has established a tolerable upper intake level for magnesium from supplements, which manufacturers must consider when formulating their products. In Canada, Natural Health Products Regulations govern dietary supplements, requiring pre-market approval and licensing.
Quality control measures are essential in the production of magnesium carbonate supplements. Manufacturers must implement systems to prevent contamination and ensure consistent potency. Third-party testing and certification programs, such as USP verification, provide additional assurance of product quality and adherence to regulatory standards.
The regulatory landscape for dietary supplements is dynamic, with ongoing discussions about potential reforms. There are calls for increased FDA oversight and more stringent safety evaluations before products reach the market. As research on magnesium supplementation evolves, regulations may adapt to reflect new scientific understanding of its benefits and potential risks.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for manufacturers of magnesium carbonate supplements. Failure to adhere to regulatory requirements can result in product recalls, legal action, and damage to brand reputation. As such, staying informed about regulatory changes and maintaining robust quality assurance processes are essential for success in the dietary supplement industry.
Environmental Impact of Magnesium Carbonate Production
The production of magnesium carbonate for dietary supplements has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The extraction and processing of raw materials, primarily magnesite or dolomite, involve energy-intensive mining operations and chemical treatments. These activities can lead to habitat disruption, soil erosion, and potential water pollution if not properly managed.
The manufacturing process of magnesium carbonate typically requires high temperatures, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The calcination of magnesite, a common method for producing magnesium carbonate, releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct. This process not only impacts air quality but also contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the supplement industry.
Water usage is another critical environmental factor in magnesium carbonate production. The purification and crystallization stages often require substantial amounts of water, potentially straining local water resources in areas where production facilities are located. Proper water management and recycling systems are essential to mitigate these impacts.
Chemical waste generated during the production process poses additional environmental challenges. Residual acids, bases, and other chemical agents used in the refinement of magnesium carbonate must be carefully handled and disposed of to prevent soil and water contamination. Implementing advanced waste treatment technologies and adhering to strict environmental regulations are crucial for minimizing these risks.
Transportation of raw materials and finished products also contributes to the environmental footprint of magnesium carbonate supplements. The global nature of the supplement industry often involves long-distance shipping, resulting in increased fuel consumption and associated emissions. Optimizing supply chain logistics and exploring more sustainable transportation methods can help reduce this impact.
On a positive note, the increasing demand for environmentally friendly production methods has led to innovations in the magnesium carbonate industry. Some manufacturers are exploring alternative production techniques that reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. These include the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities and the development of closed-loop systems that recycle water and chemicals.
The environmental impact of magnesium carbonate production extends beyond the manufacturing process to packaging and disposal considerations. The use of sustainable packaging materials and the implementation of recycling programs for supplement containers can further reduce the overall environmental footprint of these products.
The manufacturing process of magnesium carbonate typically requires high temperatures, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The calcination of magnesite, a common method for producing magnesium carbonate, releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct. This process not only impacts air quality but also contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the supplement industry.
Water usage is another critical environmental factor in magnesium carbonate production. The purification and crystallization stages often require substantial amounts of water, potentially straining local water resources in areas where production facilities are located. Proper water management and recycling systems are essential to mitigate these impacts.
Chemical waste generated during the production process poses additional environmental challenges. Residual acids, bases, and other chemical agents used in the refinement of magnesium carbonate must be carefully handled and disposed of to prevent soil and water contamination. Implementing advanced waste treatment technologies and adhering to strict environmental regulations are crucial for minimizing these risks.
Transportation of raw materials and finished products also contributes to the environmental footprint of magnesium carbonate supplements. The global nature of the supplement industry often involves long-distance shipping, resulting in increased fuel consumption and associated emissions. Optimizing supply chain logistics and exploring more sustainable transportation methods can help reduce this impact.
On a positive note, the increasing demand for environmentally friendly production methods has led to innovations in the magnesium carbonate industry. Some manufacturers are exploring alternative production techniques that reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. These include the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities and the development of closed-loop systems that recycle water and chemicals.
The environmental impact of magnesium carbonate production extends beyond the manufacturing process to packaging and disposal considerations. The use of sustainable packaging materials and the implementation of recycling programs for supplement containers can further reduce the overall environmental footprint of these products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!