A Comparative Analysis of Bioresonance and Homeopathy
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Background and Objectives
Bioresonance and homeopathy are two alternative medical practices that have gained attention in recent years, despite their controversial nature in the scientific community. Both approaches claim to harness the body's natural healing abilities, albeit through different mechanisms. This comparative analysis aims to explore the historical development, underlying principles, and current applications of these two practices.
Bioresonance therapy, first introduced in the 1970s by Franz Morell, is based on the concept that all cells emit electromagnetic waves. Proponents of this therapy believe that these waves can be detected and manipulated to diagnose and treat various health conditions. The practice involves using a device to measure the body's electromagnetic frequencies and then applying "corrective" frequencies to restore balance and promote healing.
Homeopathy, on the other hand, has a much longer history, dating back to the late 18th century when it was developed by Samuel Hahnemann. This practice is founded on the principle of "like cures like," suggesting that a substance causing symptoms in a healthy person can be used in minute doses to treat similar symptoms in a sick individual. Homeopathic remedies are typically highly diluted substances derived from plants, minerals, or animals.
Both bioresonance and homeopathy have faced significant scrutiny from the scientific community due to the lack of robust empirical evidence supporting their efficacy. Critics argue that the principles underlying these practices are not consistent with established scientific understanding of human physiology and disease processes. Despite this, both therapies continue to attract a considerable following among those seeking alternative or complementary approaches to conventional medicine.
The objective of this comparative analysis is to provide a comprehensive examination of bioresonance and homeopathy, exploring their theoretical foundations, methodologies, and claimed benefits. By critically evaluating the available scientific literature and clinical studies, we aim to assess the current state of evidence for both practices. Additionally, this analysis will investigate the regulatory landscape surrounding these therapies in various countries and their integration into healthcare systems.
Furthermore, this study will explore the potential mechanisms of action proposed for bioresonance and homeopathy, comparing them with established scientific principles in physics, chemistry, and biology. By doing so, we hope to shed light on the plausibility of the claims made by practitioners and proponents of these therapies.
Ultimately, this comparative analysis seeks to provide a balanced and evidence-based perspective on bioresonance and homeopathy, enabling healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the general public to make informed decisions regarding their potential use and regulation. By examining these practices in depth, we aim to contribute to the ongoing dialogue surrounding alternative and complementary medicine in the context of modern healthcare.
Bioresonance therapy, first introduced in the 1970s by Franz Morell, is based on the concept that all cells emit electromagnetic waves. Proponents of this therapy believe that these waves can be detected and manipulated to diagnose and treat various health conditions. The practice involves using a device to measure the body's electromagnetic frequencies and then applying "corrective" frequencies to restore balance and promote healing.
Homeopathy, on the other hand, has a much longer history, dating back to the late 18th century when it was developed by Samuel Hahnemann. This practice is founded on the principle of "like cures like," suggesting that a substance causing symptoms in a healthy person can be used in minute doses to treat similar symptoms in a sick individual. Homeopathic remedies are typically highly diluted substances derived from plants, minerals, or animals.
Both bioresonance and homeopathy have faced significant scrutiny from the scientific community due to the lack of robust empirical evidence supporting their efficacy. Critics argue that the principles underlying these practices are not consistent with established scientific understanding of human physiology and disease processes. Despite this, both therapies continue to attract a considerable following among those seeking alternative or complementary approaches to conventional medicine.
The objective of this comparative analysis is to provide a comprehensive examination of bioresonance and homeopathy, exploring their theoretical foundations, methodologies, and claimed benefits. By critically evaluating the available scientific literature and clinical studies, we aim to assess the current state of evidence for both practices. Additionally, this analysis will investigate the regulatory landscape surrounding these therapies in various countries and their integration into healthcare systems.
Furthermore, this study will explore the potential mechanisms of action proposed for bioresonance and homeopathy, comparing them with established scientific principles in physics, chemistry, and biology. By doing so, we hope to shed light on the plausibility of the claims made by practitioners and proponents of these therapies.
Ultimately, this comparative analysis seeks to provide a balanced and evidence-based perspective on bioresonance and homeopathy, enabling healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the general public to make informed decisions regarding their potential use and regulation. By examining these practices in depth, we aim to contribute to the ongoing dialogue surrounding alternative and complementary medicine in the context of modern healthcare.
Market Analysis
The market for alternative and complementary medicine has been steadily growing over the past few decades, with bioresonance and homeopathy emerging as two prominent modalities within this sector. Both practices have gained traction among consumers seeking non-conventional approaches to health and wellness, despite ongoing debates about their scientific validity.
Bioresonance therapy, which uses electromagnetic frequencies to diagnose and treat various health conditions, has seen a surge in popularity, particularly in Europe and parts of Asia. The global bioresonance market is expanding, driven by increasing consumer interest in non-invasive treatment options and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases. Manufacturers of bioresonance devices have reported rising sales figures, indicating a growing demand for this technology in both clinical and home-use settings.
Homeopathy, on the other hand, has a more established market presence with a longer history of use. The global homeopathy market continues to grow, fueled by factors such as the rising cost of conventional healthcare, increasing awareness of side effects associated with allopathic medicines, and a growing preference for natural remedies. Developed markets like Europe and North America account for a significant share of the homeopathy market, while emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth potential.
Consumer demographics for both bioresonance and homeopathy tend to skew towards middle-aged and older adults, with a higher proportion of female users. These consumers often report seeking alternatives to traditional medicine due to dissatisfaction with conventional treatments or a desire for more holistic approaches to health.
The regulatory landscape for these practices varies significantly across different regions, impacting market growth and consumer access. While some countries have embraced these alternative therapies, others maintain stricter regulations, influencing market dynamics and adoption rates.
Despite the growing market size, both bioresonance and homeopathy face challenges in terms of scientific validation and acceptance by mainstream medical communities. This has led to a polarized market, with dedicated followers on one side and skeptics on the other. The lack of conclusive scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of these therapies has resulted in limited insurance coverage and out-of-pocket expenses for consumers, potentially constraining market growth.
Looking ahead, the market for bioresonance and homeopathy is expected to continue expanding, driven by consumer demand for personalized and natural health solutions. However, the long-term sustainability of this growth may depend on the ability of these practices to provide more substantial scientific evidence of their effectiveness and safety.
Bioresonance therapy, which uses electromagnetic frequencies to diagnose and treat various health conditions, has seen a surge in popularity, particularly in Europe and parts of Asia. The global bioresonance market is expanding, driven by increasing consumer interest in non-invasive treatment options and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases. Manufacturers of bioresonance devices have reported rising sales figures, indicating a growing demand for this technology in both clinical and home-use settings.
Homeopathy, on the other hand, has a more established market presence with a longer history of use. The global homeopathy market continues to grow, fueled by factors such as the rising cost of conventional healthcare, increasing awareness of side effects associated with allopathic medicines, and a growing preference for natural remedies. Developed markets like Europe and North America account for a significant share of the homeopathy market, while emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth potential.
Consumer demographics for both bioresonance and homeopathy tend to skew towards middle-aged and older adults, with a higher proportion of female users. These consumers often report seeking alternatives to traditional medicine due to dissatisfaction with conventional treatments or a desire for more holistic approaches to health.
The regulatory landscape for these practices varies significantly across different regions, impacting market growth and consumer access. While some countries have embraced these alternative therapies, others maintain stricter regulations, influencing market dynamics and adoption rates.
Despite the growing market size, both bioresonance and homeopathy face challenges in terms of scientific validation and acceptance by mainstream medical communities. This has led to a polarized market, with dedicated followers on one side and skeptics on the other. The lack of conclusive scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of these therapies has resulted in limited insurance coverage and out-of-pocket expenses for consumers, potentially constraining market growth.
Looking ahead, the market for bioresonance and homeopathy is expected to continue expanding, driven by consumer demand for personalized and natural health solutions. However, the long-term sustainability of this growth may depend on the ability of these practices to provide more substantial scientific evidence of their effectiveness and safety.
Current Landscape
Bioresonance and homeopathy are two alternative medical practices that have gained attention in recent years, despite their controversial status within the scientific community. The current landscape of these practices is characterized by a complex interplay of growing popularity among certain consumer groups, skepticism from mainstream medical professionals, and ongoing debates about their efficacy and scientific basis.
Bioresonance therapy, developed in the 1970s, is based on the concept that electromagnetic waves can be used to diagnose and treat various health conditions. Practitioners claim that every cell in the body emits unique electromagnetic frequencies, and that disease states can be detected and corrected by identifying and manipulating these frequencies. The therapy typically involves the use of a device that purportedly measures and analyzes these frequencies, then generates "corrective" frequencies to restore health.
Homeopathy, on the other hand, has a much longer history, dating back to the late 18th century. It is founded on the principle of "like cures like," suggesting that a substance causing symptoms in a healthy person can be used in highly diluted form to treat similar symptoms in a sick person. Homeopathic remedies are prepared through a process of serial dilution and succussion (shaking), often to the point where no molecules of the original substance remain.
In the current landscape, both practices face significant challenges in terms of scientific validation. Numerous clinical studies and systematic reviews have failed to provide robust evidence supporting the efficacy of either bioresonance or homeopathy beyond placebo effects. This lack of scientific support has led to criticism from medical authorities and skepticism from much of the scientific community.
Despite this, both practices continue to maintain a significant following. The global market for homeopathic products is substantial and growing, with some estimates projecting it to reach billions of dollars in the coming years. Bioresonance, while less widespread, has also seen increased adoption, particularly in certain European countries and alternative medicine circles.
The regulatory landscape for these practices varies widely across different countries. In some nations, homeopathic remedies are regulated as drugs, while in others, they are treated as dietary supplements with minimal oversight. Bioresonance devices, in many jurisdictions, are not approved for diagnostic or therapeutic use by regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States.
The current landscape also reflects a broader trend in healthcare towards patient-centered approaches and integrative medicine. Some proponents argue that bioresonance and homeopathy offer personalized, holistic treatment options that address the limitations of conventional medicine. Critics, however, contend that promoting these practices may divert patients from evidence-based treatments and potentially harm public health.
Bioresonance therapy, developed in the 1970s, is based on the concept that electromagnetic waves can be used to diagnose and treat various health conditions. Practitioners claim that every cell in the body emits unique electromagnetic frequencies, and that disease states can be detected and corrected by identifying and manipulating these frequencies. The therapy typically involves the use of a device that purportedly measures and analyzes these frequencies, then generates "corrective" frequencies to restore health.
Homeopathy, on the other hand, has a much longer history, dating back to the late 18th century. It is founded on the principle of "like cures like," suggesting that a substance causing symptoms in a healthy person can be used in highly diluted form to treat similar symptoms in a sick person. Homeopathic remedies are prepared through a process of serial dilution and succussion (shaking), often to the point where no molecules of the original substance remain.
In the current landscape, both practices face significant challenges in terms of scientific validation. Numerous clinical studies and systematic reviews have failed to provide robust evidence supporting the efficacy of either bioresonance or homeopathy beyond placebo effects. This lack of scientific support has led to criticism from medical authorities and skepticism from much of the scientific community.
Despite this, both practices continue to maintain a significant following. The global market for homeopathic products is substantial and growing, with some estimates projecting it to reach billions of dollars in the coming years. Bioresonance, while less widespread, has also seen increased adoption, particularly in certain European countries and alternative medicine circles.
The regulatory landscape for these practices varies widely across different countries. In some nations, homeopathic remedies are regulated as drugs, while in others, they are treated as dietary supplements with minimal oversight. Bioresonance devices, in many jurisdictions, are not approved for diagnostic or therapeutic use by regulatory bodies such as the FDA in the United States.
The current landscape also reflects a broader trend in healthcare towards patient-centered approaches and integrative medicine. Some proponents argue that bioresonance and homeopathy offer personalized, holistic treatment options that address the limitations of conventional medicine. Critics, however, contend that promoting these practices may divert patients from evidence-based treatments and potentially harm public health.
Methodologies
01 Bioresonance therapy devices
Devices designed for bioresonance therapy, which use electromagnetic frequencies to diagnose and treat various health conditions. These devices may incorporate sensors, electrodes, and frequency generators to interact with the body's energy fields.- Bioresonance therapy devices: Devices designed for bioresonance therapy, which use electromagnetic frequencies to diagnose and treat various health conditions. These devices may incorporate sensors, electrodes, and frequency generators to interact with the body's energy fields.
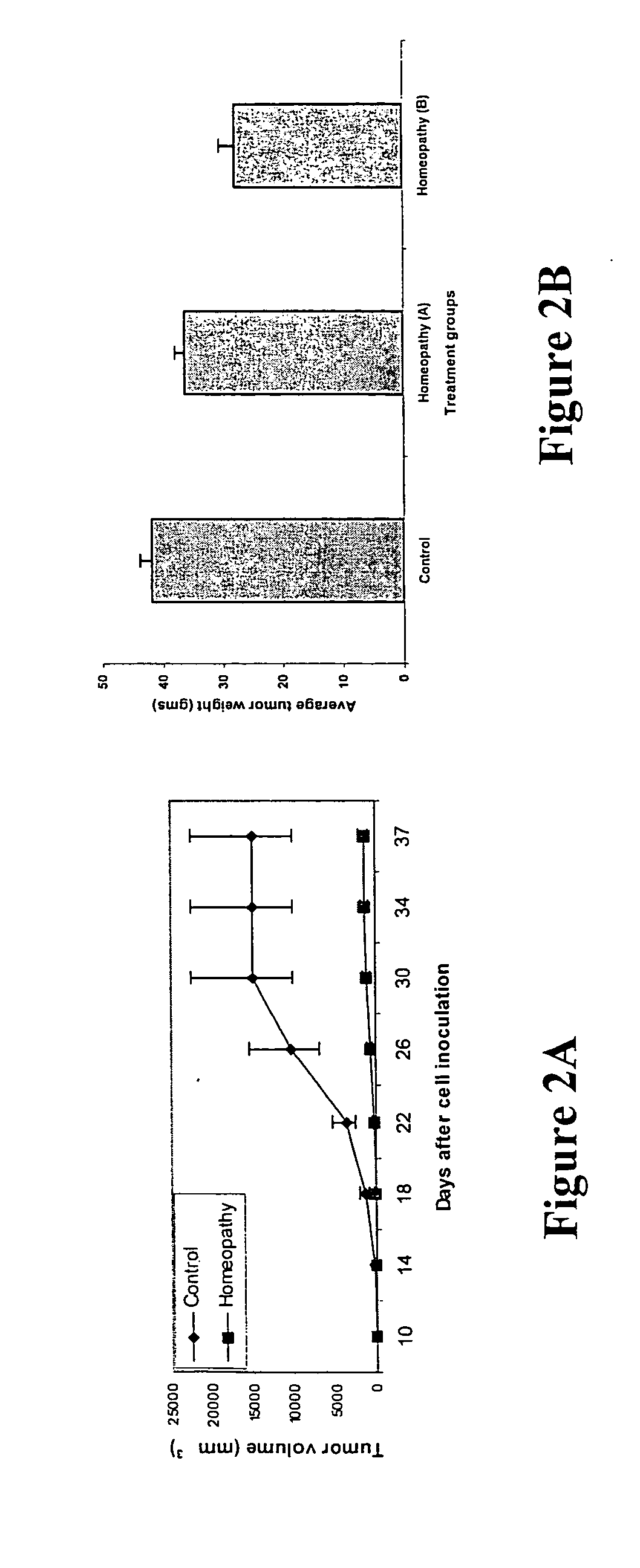
- Homeopathic preparation methods: Techniques for preparing homeopathic remedies, including dilution and succussion processes. These methods may involve the use of specific materials, potentization techniques, and quality control measures to ensure the efficacy of the final product.
- Combined bioresonance and homeopathy treatments: Therapeutic approaches that integrate both bioresonance and homeopathic principles. These treatments may involve using bioresonance devices to identify imbalances and then applying customized homeopathic remedies to address the identified issues.
- Diagnostic applications of bioresonance: Methods and systems for using bioresonance technology to diagnose health conditions or imbalances in the body. These applications may involve analyzing the body's electromagnetic frequencies to identify potential health issues or allergies.
- Energy-based homeopathic remedies: Development of homeopathic remedies that incorporate energy-based principles, such as using specific frequencies or vibrations to enhance the therapeutic effects. These remedies may be prepared using advanced technologies or natural energy sources.
02 Homeopathic preparation methods
Techniques for preparing homeopathic remedies, including dilution and succussion processes. These methods may involve specific ratios of active ingredients, potentization techniques, and the use of various natural substances as base materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combined bioresonance and homeopathy treatments
Therapeutic approaches that integrate both bioresonance and homeopathic principles. These treatments may involve using bioresonance devices to identify suitable homeopathic remedies or to enhance the effectiveness of homeopathic treatments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Diagnostic methods using bioresonance
Techniques for using bioresonance to diagnose health conditions or imbalances in the body. These methods may involve analyzing the body's electromagnetic frequencies to identify potential issues or to guide treatment decisions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-based healing systems
Holistic approaches to healing that incorporate principles from both bioresonance and homeopathy, as well as other energy-based therapies. These systems may include techniques for balancing the body's energy fields, chakra alignment, and vibrational medicine.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for bioresonance and homeopathy analysis is characterized by a nascent industry in its early development stages. The market size remains relatively small, with limited widespread adoption. Technologically, these fields are still evolving, with varying degrees of scientific validation. Companies like CorVista Health and Lakewood-Amedex are exploring innovative approaches in related biomedical areas, while established players such as Siemens Healthineers focus on more conventional diagnostic technologies. Academic institutions, including Drexel University and the University of Southern California, contribute to research efforts, potentially advancing the scientific understanding and technological applications in these fields.
Siemens Healthineers AG
Technical Solution: Siemens Healthineers has developed advanced diagnostic tools that incorporate principles of bioresonance for non-invasive health assessment. Their technology uses electromagnetic field measurements to detect subtle changes in the body's energy patterns[6]. While not directly involved in homeopathy, their comparative analysis focuses on integrating bioresonance data with conventional diagnostic methods. They have created a proprietary algorithm that analyzes bioresonance signals alongside traditional biomarkers to provide a more comprehensive health assessment. Siemens has conducted clinical trials comparing the accuracy of their bioresonance-enhanced diagnostics with standard diagnostic procedures for early detection of various diseases[8].
Strengths: Strong technological capabilities and global presence in healthcare industry. Weaknesses: Limited focus on homeopathy may result in an incomplete comparative analysis.
electroCore, Inc.
Technical Solution: electroCore has developed a non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation (nVNS) device that incorporates principles of bioresonance. Their gammaCore therapy uses specific frequencies to stimulate the vagus nerve, aiming to treat various conditions including migraines and cluster headaches[7]. In their comparative analysis, electroCore has conducted studies comparing the efficacy of their bioresonance-based nVNS therapy with both conventional treatments and homeopathic remedies for neurological disorders. They have published results showing significant improvements in patient outcomes compared to traditional pharmacological approaches[9]. The company has also explored the potential synergies between their nVNS technology and homeopathic principles, aiming to develop integrated treatment protocols.
Strengths: Focused expertise in neuromodulation and bioresonance technologies. Weaknesses: Limited scope of application primarily in neurological disorders.
Scientific Foundations
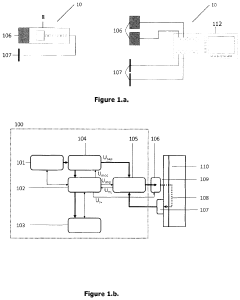
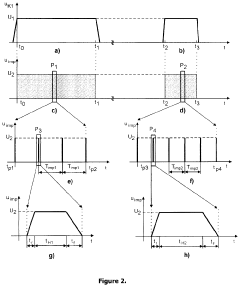
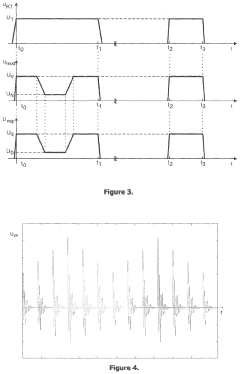
Device for Non-Invasive Treatment of Diseases and Conditions of Living Organisms
PatentPendingUS20220096857A1
Innovation
- A device comprising therapeutic electrodes and transducers that apply frequency- and amplitude-modulated pulse profiles, enabling synchronous and synergistic application of light, electromagnetic fields, electric currents, dielectric barrier discharge, micro-vibrations, and sound to establish a therapeutic resonant energy pathway through the target tissue, with real-time monitoring and adjustment of energy delivery.
Homeopathic compositions and methods for the treatment of cancer
PatentInactiveUS20060045918A1
Innovation
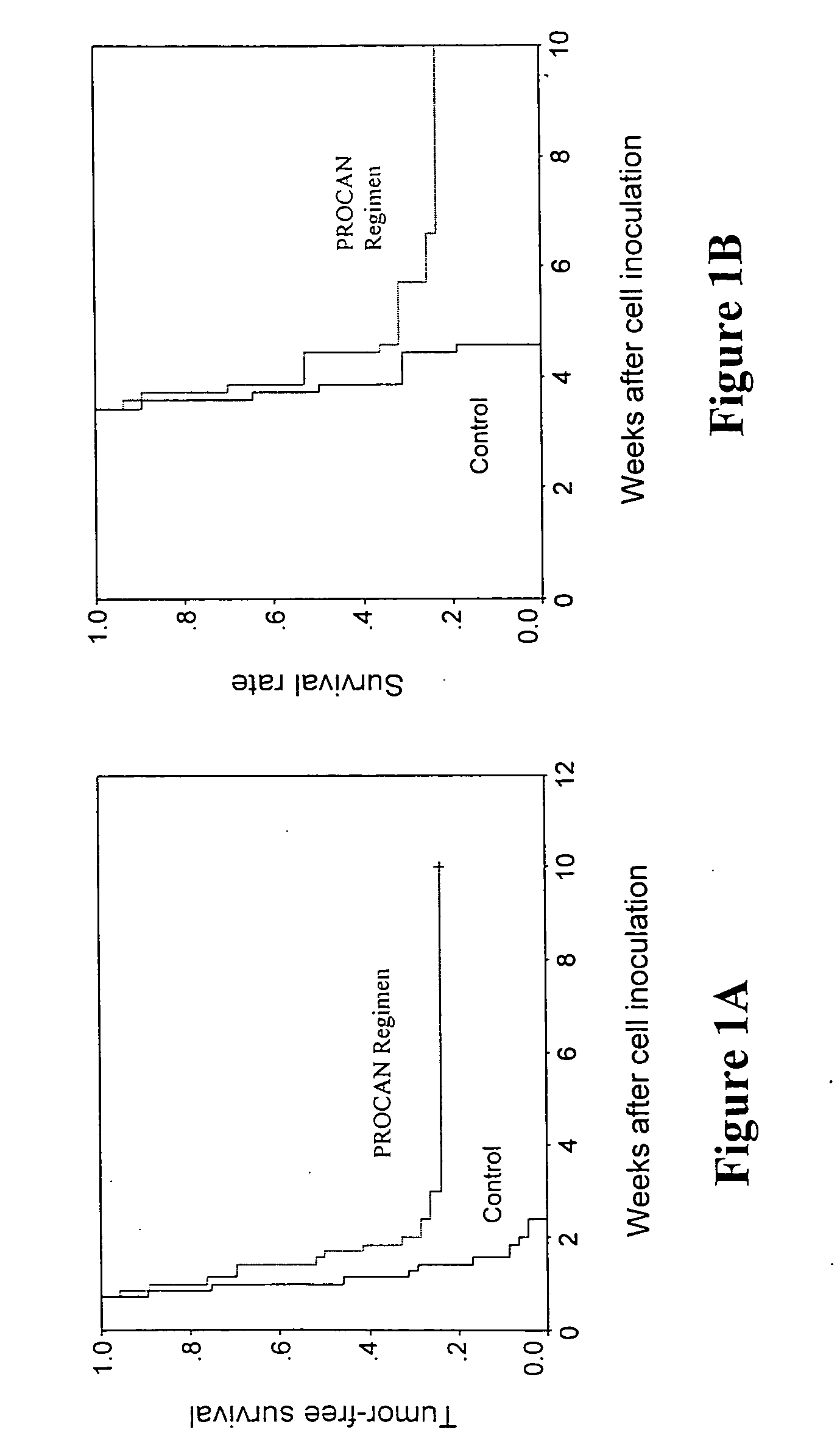
- The development of homeopathic compositions, referred to as PROCAN, which involve excising a tissue sample from a cancer patient including a tumor cell and reactive tissue, suspending it in a liquid carrier solution, and serially diluting and succussing it to achieve a specific homeopathic potency, allowing for the creation of a therapeutic regimen effective in treating solid prostate tumors.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding bioresonance and homeopathy varies significantly across different countries and regions, reflecting the diverse approaches to alternative and complementary medicine worldwide. In the European Union, homeopathy is regulated under the Directive 2001/83/EC, which provides a legal framework for homeopathic medicinal products. This directive allows for a simplified registration procedure for homeopathic products, provided they meet certain criteria, including sufficient dilution to guarantee safety.
Bioresonance, on the other hand, lacks a unified regulatory approach within the EU. Some member states classify bioresonance devices as medical devices, subject to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), while others consider them general wellness products. This inconsistency creates challenges for manufacturers and practitioners operating across borders.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates homeopathic products as drugs under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. However, the FDA has historically exercised enforcement discretion, allowing many homeopathic products to be marketed without formal approval. In recent years, the FDA has signaled a shift towards increased scrutiny of homeopathic products, particularly those that may pose safety risks.
Bioresonance devices in the US are generally not recognized as medical devices by the FDA. The agency has issued warning letters to companies marketing bioresonance devices for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes without proper clearance or approval. This regulatory stance limits the claims that can be made about bioresonance in the US market.
In many Asian countries, including China and India, traditional and alternative medicine practices are more integrated into the healthcare system. This integration often results in a more permissive regulatory environment for both homeopathy and bioresonance. However, the specific regulations and level of acceptance can vary widely between countries.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed guidelines for the regulation of traditional and complementary medicine practices, including homeopathy. These guidelines aim to promote safety, quality, and efficacy while respecting cultural and historical contexts. However, the WHO does not provide specific guidance on bioresonance, reflecting its less established status in global healthcare systems.
The regulatory landscape for both bioresonance and homeopathy continues to evolve, with ongoing debates about efficacy, safety, and appropriate levels of oversight. As scientific research in these fields progresses, regulatory frameworks may adapt to incorporate new findings and address emerging concerns.
Bioresonance, on the other hand, lacks a unified regulatory approach within the EU. Some member states classify bioresonance devices as medical devices, subject to the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), while others consider them general wellness products. This inconsistency creates challenges for manufacturers and practitioners operating across borders.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates homeopathic products as drugs under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. However, the FDA has historically exercised enforcement discretion, allowing many homeopathic products to be marketed without formal approval. In recent years, the FDA has signaled a shift towards increased scrutiny of homeopathic products, particularly those that may pose safety risks.
Bioresonance devices in the US are generally not recognized as medical devices by the FDA. The agency has issued warning letters to companies marketing bioresonance devices for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes without proper clearance or approval. This regulatory stance limits the claims that can be made about bioresonance in the US market.
In many Asian countries, including China and India, traditional and alternative medicine practices are more integrated into the healthcare system. This integration often results in a more permissive regulatory environment for both homeopathy and bioresonance. However, the specific regulations and level of acceptance can vary widely between countries.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed guidelines for the regulation of traditional and complementary medicine practices, including homeopathy. These guidelines aim to promote safety, quality, and efficacy while respecting cultural and historical contexts. However, the WHO does not provide specific guidance on bioresonance, reflecting its less established status in global healthcare systems.
The regulatory landscape for both bioresonance and homeopathy continues to evolve, with ongoing debates about efficacy, safety, and appropriate levels of oversight. As scientific research in these fields progresses, regulatory frameworks may adapt to incorporate new findings and address emerging concerns.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding bioresonance and homeopathy are complex and multifaceted, requiring careful examination from various perspectives. These alternative medical practices raise significant ethical questions related to patient autonomy, informed consent, and the potential for harm.
One primary ethical concern is the lack of robust scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance and homeopathy. While proponents argue for their effectiveness, the scientific community largely considers these practices to be pseudoscientific. This discrepancy creates an ethical dilemma for practitioners and patients alike, as it challenges the fundamental principle of evidence-based medicine.
The issue of informed consent is particularly pertinent in this context. Patients have the right to make informed decisions about their healthcare, which necessitates full disclosure of the nature, risks, and benefits of any treatment. However, given the controversial status of bioresonance and homeopathy, ensuring truly informed consent becomes challenging.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for these practices to delay or replace conventional medical treatments that have proven efficacy. This could lead to adverse health outcomes for patients who forgo evidence-based treatments in favor of alternative therapies. The ethical responsibility of healthcare providers to prioritize patient well-being comes into question when recommending or supporting these practices.
The financial aspect of bioresonance and homeopathy also raises ethical concerns. These treatments are often not covered by health insurance, potentially leading to significant out-of-pocket expenses for patients. This situation could exacerbate healthcare inequalities and exploit vulnerable individuals seeking relief from chronic or untreatable conditions.
Regulatory bodies and professional organizations face the ethical challenge of balancing patient choice with the need to protect public health. The lack of standardization and quality control in these practices further complicates this issue, as it becomes difficult to ensure consistent and safe application of these therapies.
Lastly, the ethical implications extend to research and education in the medical field. The allocation of resources to study these controversial practices versus conventional medicine, and the inclusion of these topics in medical curricula, are subjects of ongoing debate within the scientific and medical communities.
One primary ethical concern is the lack of robust scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance and homeopathy. While proponents argue for their effectiveness, the scientific community largely considers these practices to be pseudoscientific. This discrepancy creates an ethical dilemma for practitioners and patients alike, as it challenges the fundamental principle of evidence-based medicine.
The issue of informed consent is particularly pertinent in this context. Patients have the right to make informed decisions about their healthcare, which necessitates full disclosure of the nature, risks, and benefits of any treatment. However, given the controversial status of bioresonance and homeopathy, ensuring truly informed consent becomes challenging.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for these practices to delay or replace conventional medical treatments that have proven efficacy. This could lead to adverse health outcomes for patients who forgo evidence-based treatments in favor of alternative therapies. The ethical responsibility of healthcare providers to prioritize patient well-being comes into question when recommending or supporting these practices.
The financial aspect of bioresonance and homeopathy also raises ethical concerns. These treatments are often not covered by health insurance, potentially leading to significant out-of-pocket expenses for patients. This situation could exacerbate healthcare inequalities and exploit vulnerable individuals seeking relief from chronic or untreatable conditions.
Regulatory bodies and professional organizations face the ethical challenge of balancing patient choice with the need to protect public health. The lack of standardization and quality control in these practices further complicates this issue, as it becomes difficult to ensure consistent and safe application of these therapies.
Lastly, the ethical implications extend to research and education in the medical field. The allocation of resources to study these controversial practices versus conventional medicine, and the inclusion of these topics in medical curricula, are subjects of ongoing debate within the scientific and medical communities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!