Promising Advances in Bioresonance Research for Alzheimer's Disease
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance in AD: Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a form of alternative medicine, has recently gained attention in the field of Alzheimer's disease (AD) research. This emerging approach is based on the principle that all cells and organs in the human body emit unique electromagnetic frequencies. In the context of AD, bioresonance aims to detect and correct abnormal frequencies associated with the disease's pathology.
The historical development of bioresonance can be traced back to the 1970s, with its application in AD research gaining momentum in the past decade. As conventional treatments for AD have shown limited efficacy, researchers and clinicians have been exploring alternative approaches to address this devastating neurodegenerative disorder. Bioresonance represents a potential paradigm shift in AD management, offering a non-invasive and potentially complementary approach to existing therapies.
The primary objective of bioresonance research in AD is to investigate its potential as a diagnostic tool and therapeutic intervention. Researchers aim to identify specific frequency patterns associated with AD pathology, including beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles. By detecting these abnormal frequencies, bioresonance could potentially offer early diagnosis of AD, even before clinical symptoms manifest.
Furthermore, bioresonance therapy seeks to correct these abnormal frequencies, potentially slowing or halting disease progression. The underlying hypothesis is that by restoring normal cellular frequencies, bioresonance might mitigate the accumulation of toxic proteins and support neuronal health. This approach aligns with the growing understanding of AD as a complex, multifactorial disease that may require multifaceted interventions.
Recent technological advancements have significantly enhanced the precision and reliability of bioresonance devices, making them more suitable for clinical research. These improvements include better frequency detection capabilities, more sophisticated data analysis algorithms, and enhanced user interfaces for clinicians. As a result, the field has seen an increase in both preclinical and clinical studies exploring the potential of bioresonance in AD.
The integration of bioresonance with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, presents exciting possibilities for personalized AD treatment. These technologies could potentially analyze vast amounts of bioresonance data to identify patient-specific frequency patterns and tailor treatments accordingly.
As research in this field progresses, the scientific community aims to establish standardized protocols for bioresonance application in AD, validate its efficacy through rigorous clinical trials, and explore its potential synergies with conventional treatments. The ultimate goal is to develop a comprehensive, multimodal approach to AD management that incorporates bioresonance as a valuable component in the diagnostic and therapeutic arsenal against this challenging disease.
The historical development of bioresonance can be traced back to the 1970s, with its application in AD research gaining momentum in the past decade. As conventional treatments for AD have shown limited efficacy, researchers and clinicians have been exploring alternative approaches to address this devastating neurodegenerative disorder. Bioresonance represents a potential paradigm shift in AD management, offering a non-invasive and potentially complementary approach to existing therapies.
The primary objective of bioresonance research in AD is to investigate its potential as a diagnostic tool and therapeutic intervention. Researchers aim to identify specific frequency patterns associated with AD pathology, including beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles. By detecting these abnormal frequencies, bioresonance could potentially offer early diagnosis of AD, even before clinical symptoms manifest.
Furthermore, bioresonance therapy seeks to correct these abnormal frequencies, potentially slowing or halting disease progression. The underlying hypothesis is that by restoring normal cellular frequencies, bioresonance might mitigate the accumulation of toxic proteins and support neuronal health. This approach aligns with the growing understanding of AD as a complex, multifactorial disease that may require multifaceted interventions.
Recent technological advancements have significantly enhanced the precision and reliability of bioresonance devices, making them more suitable for clinical research. These improvements include better frequency detection capabilities, more sophisticated data analysis algorithms, and enhanced user interfaces for clinicians. As a result, the field has seen an increase in both preclinical and clinical studies exploring the potential of bioresonance in AD.
The integration of bioresonance with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, presents exciting possibilities for personalized AD treatment. These technologies could potentially analyze vast amounts of bioresonance data to identify patient-specific frequency patterns and tailor treatments accordingly.
As research in this field progresses, the scientific community aims to establish standardized protocols for bioresonance application in AD, validate its efficacy through rigorous clinical trials, and explore its potential synergies with conventional treatments. The ultimate goal is to develop a comprehensive, multimodal approach to AD management that incorporates bioresonance as a valuable component in the diagnostic and therapeutic arsenal against this challenging disease.
Market Analysis: AD Diagnostics and Therapeutics
The Alzheimer's disease (AD) diagnostics and therapeutics market is experiencing significant growth due to the increasing prevalence of AD globally. The market is driven by the rising aging population, growing awareness about early diagnosis, and the urgent need for effective treatment options. Currently, the AD diagnostics market is dominated by neuroimaging techniques, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarker tests, and cognitive assessments. Among these, PET scans and MRI imaging have gained prominence for their ability to detect brain changes associated with AD.
The therapeutics market for AD is primarily focused on symptomatic treatments, with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists being the mainstay of current pharmacological interventions. However, there is a growing shift towards disease-modifying therapies that aim to slow or halt the progression of AD. This has led to increased investment in research and development of novel drug candidates targeting amyloid-beta plaques and tau protein aggregates.
Bioresonance research represents a promising new frontier in AD diagnostics and therapeutics. This emerging field explores the potential of electromagnetic frequencies to detect and potentially treat AD-related brain abnormalities. While still in its early stages, bioresonance technology has shown potential in identifying subtle changes in brain activity that may precede clinical symptoms of AD.
The market for AD diagnostics and therapeutics is highly competitive, with major pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms investing heavily in research and development. Key players in this space include Biogen, Eli Lilly, Roche, and Eisai, among others. These companies are not only developing new drug candidates but also exploring innovative diagnostic tools, including those based on bioresonance principles.
Despite the promising advances, the AD market faces significant challenges. The high failure rate of clinical trials for AD drugs has led to cautious investment strategies. Additionally, the complexity of AD pathology and the lack of a complete understanding of its underlying mechanisms have hindered the development of effective treatments. However, the potential market for successful AD therapies remains enormous, given the high unmet medical need and the substantial economic burden of the disease on healthcare systems worldwide.
As research in bioresonance and other novel approaches progresses, the AD diagnostics and therapeutics market is expected to witness transformative changes. The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, with bioresonance research may lead to more accurate diagnostic tools and personalized treatment strategies. This evolving landscape presents significant opportunities for companies that can successfully navigate the complex regulatory environment and bring innovative solutions to market.
The therapeutics market for AD is primarily focused on symptomatic treatments, with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists being the mainstay of current pharmacological interventions. However, there is a growing shift towards disease-modifying therapies that aim to slow or halt the progression of AD. This has led to increased investment in research and development of novel drug candidates targeting amyloid-beta plaques and tau protein aggregates.
Bioresonance research represents a promising new frontier in AD diagnostics and therapeutics. This emerging field explores the potential of electromagnetic frequencies to detect and potentially treat AD-related brain abnormalities. While still in its early stages, bioresonance technology has shown potential in identifying subtle changes in brain activity that may precede clinical symptoms of AD.
The market for AD diagnostics and therapeutics is highly competitive, with major pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms investing heavily in research and development. Key players in this space include Biogen, Eli Lilly, Roche, and Eisai, among others. These companies are not only developing new drug candidates but also exploring innovative diagnostic tools, including those based on bioresonance principles.
Despite the promising advances, the AD market faces significant challenges. The high failure rate of clinical trials for AD drugs has led to cautious investment strategies. Additionally, the complexity of AD pathology and the lack of a complete understanding of its underlying mechanisms have hindered the development of effective treatments. However, the potential market for successful AD therapies remains enormous, given the high unmet medical need and the substantial economic burden of the disease on healthcare systems worldwide.
As research in bioresonance and other novel approaches progresses, the AD diagnostics and therapeutics market is expected to witness transformative changes. The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, with bioresonance research may lead to more accurate diagnostic tools and personalized treatment strategies. This evolving landscape presents significant opportunities for companies that can successfully navigate the complex regulatory environment and bring innovative solutions to market.
Current Challenges in Bioresonance for AD
Despite the promising potential of bioresonance in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) research, several significant challenges currently hinder its widespread application and acceptance in the scientific community. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardization in bioresonance protocols and equipment. This inconsistency makes it difficult to replicate studies and compare results across different research groups, limiting the ability to draw conclusive evidence about the efficacy of bioresonance in AD treatment.
Another major challenge is the limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms by which bioresonance affects biological systems, particularly in the context of AD pathology. While some theories propose that bioresonance may influence cellular communication or energy transfer, the exact pathways and molecular targets remain largely unknown. This gap in knowledge makes it challenging to optimize bioresonance parameters for maximum therapeutic effect and to predict potential side effects or contraindications.
The complexity of AD itself poses additional challenges for bioresonance research. The disease involves multiple pathological processes, including amyloid-beta accumulation, tau protein aggregation, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress. Determining how bioresonance interacts with these various aspects of AD pathology and which specific components it may influence most effectively requires extensive investigation and sophisticated experimental designs.
Furthermore, the field faces skepticism from the mainstream medical community due to the historical association of bioresonance with alternative medicine practices. This perception has led to difficulties in securing funding for large-scale clinical trials and attracting established researchers to the field. Overcoming this bias and demonstrating the scientific validity of bioresonance through rigorous, well-designed studies remains a significant hurdle.
Technical limitations in current bioresonance devices also present challenges. Many existing devices lack the sensitivity and specificity needed to detect and modulate the subtle electromagnetic signals associated with AD pathology. Improving the resolution, accuracy, and reliability of bioresonance equipment is crucial for advancing research in this area and developing potential diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices and treatments remains uncertain. The lack of clear guidelines for the development, testing, and approval of bioresonance-based interventions creates obstacles for researchers and companies seeking to bring these technologies to market. Establishing a regulatory framework that ensures safety and efficacy while allowing for innovation is essential for the future of bioresonance in AD research and treatment.
Another major challenge is the limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms by which bioresonance affects biological systems, particularly in the context of AD pathology. While some theories propose that bioresonance may influence cellular communication or energy transfer, the exact pathways and molecular targets remain largely unknown. This gap in knowledge makes it challenging to optimize bioresonance parameters for maximum therapeutic effect and to predict potential side effects or contraindications.
The complexity of AD itself poses additional challenges for bioresonance research. The disease involves multiple pathological processes, including amyloid-beta accumulation, tau protein aggregation, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress. Determining how bioresonance interacts with these various aspects of AD pathology and which specific components it may influence most effectively requires extensive investigation and sophisticated experimental designs.
Furthermore, the field faces skepticism from the mainstream medical community due to the historical association of bioresonance with alternative medicine practices. This perception has led to difficulties in securing funding for large-scale clinical trials and attracting established researchers to the field. Overcoming this bias and demonstrating the scientific validity of bioresonance through rigorous, well-designed studies remains a significant hurdle.
Technical limitations in current bioresonance devices also present challenges. Many existing devices lack the sensitivity and specificity needed to detect and modulate the subtle electromagnetic signals associated with AD pathology. Improving the resolution, accuracy, and reliability of bioresonance equipment is crucial for advancing research in this area and developing potential diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices and treatments remains uncertain. The lack of clear guidelines for the development, testing, and approval of bioresonance-based interventions creates obstacles for researchers and companies seeking to bring these technologies to market. Establishing a regulatory framework that ensures safety and efficacy while allowing for innovation is essential for the future of bioresonance in AD research and treatment.
Existing Bioresonance Approaches for AD
01 Bioresonance diagnostic devices
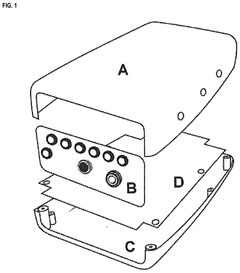
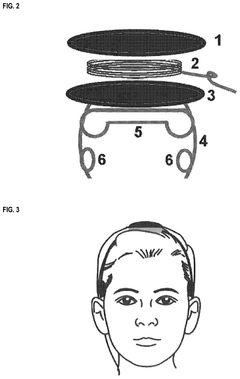
Devices designed for bioresonance diagnosis, which use electromagnetic frequencies to detect and analyze the body's energy patterns. These devices can be used to identify imbalances or health issues in the body by measuring and interpreting the electromagnetic signals emitted by cells and organs.- Bioresonance devices and systems: Various devices and systems have been developed for bioresonance therapy, including portable units, wearable devices, and integrated systems. These devices typically incorporate sensors, electrodes, and signal processing components to detect and analyze electromagnetic signals from the body. Some designs focus on specific applications such as stress reduction or pain management.
- Bioresonance diagnostic methods: Diagnostic methods using bioresonance technology have been developed to assess various health conditions. These methods often involve measuring and analyzing electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the body or its response to external stimuli. Some approaches combine bioresonance with other diagnostic techniques to improve accuracy and provide comprehensive health assessments.
- Bioresonance therapy applications: Bioresonance therapy has been applied to various health conditions and wellness goals. Applications include stress reduction, pain management, allergy treatment, and support for chronic conditions. Some approaches combine bioresonance with other therapeutic modalities to enhance overall effectiveness and address multiple aspects of health simultaneously.
- Bioresonance signal processing and analysis: Advanced signal processing and analysis techniques have been developed to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of bioresonance therapy. These methods may involve filtering, amplification, and interpretation of electromagnetic signals from the body. Some approaches use artificial intelligence or machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and optimize treatment protocols.
- Integration of bioresonance with other technologies: Bioresonance technology has been integrated with other health and wellness technologies to create comprehensive treatment and monitoring systems. This may include combining bioresonance with wearable devices, mobile applications, or telemedicine platforms. Some approaches incorporate biofeedback, virtual reality, or other complementary technologies to enhance the overall therapeutic experience.
02 Bioresonance therapy systems
Systems and methods for applying bioresonance therapy, which involve the use of electromagnetic frequencies to treat various health conditions. These systems typically include devices that can generate and apply specific frequencies to the body, aiming to restore balance and promote healing.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wearable bioresonance devices
Portable or wearable devices that incorporate bioresonance technology for continuous monitoring or treatment. These devices may be designed as wristbands, patches, or other wearable forms, allowing users to receive bioresonance therapy or diagnostics throughout the day.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bioresonance-enhanced products
Various products, such as water, cosmetics, or nutritional supplements, that have been treated or enhanced using bioresonance technology. These products are claimed to have improved properties or health benefits due to the application of specific electromagnetic frequencies during their production or processing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of bioresonance with other therapies
Methods and systems that combine bioresonance technology with other therapeutic approaches, such as acupuncture, homeopathy, or conventional medicine. These integrated approaches aim to provide more comprehensive and effective treatments by leveraging the potential synergies between different healing modalities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and AD Research
The field of bioresonance research for Alzheimer's disease is in its early stages, with a growing market potential due to the increasing prevalence of the condition. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies, emerging biotech firms, and academic institutions. Companies like Novartis AG, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., and Merck Sharp & Dohme are leveraging their extensive resources and expertise in neurodegenerative diseases to explore bioresonance applications. Smaller, specialized firms such as Vivoryon Therapeutics NV and Neuro-Bio Ltd. are focusing on innovative approaches to Alzheimer's treatment. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with ongoing clinical trials and research collaborations between industry players and academic institutions like West Virginia University and McGill University driving advancements in this promising field.
Vivoryon Therapeutics NV
Technical Solution: Vivoryon Therapeutics NV is pioneering a novel approach to Alzheimer's treatment through bioresonance research. Their lead compound, varoglutamstat (PQ912), is a small molecule inhibitor of the enzyme Glutaminyl Cyclase (QC) [1]. This enzyme is involved in the formation of pyroglutamate-modified Abeta peptides, which are highly neurotoxic and contribute to Alzheimer's pathology. By inhibiting QC, varoglutamstat aims to reduce the formation of these toxic peptides, potentially slowing or halting disease progression. The company has completed Phase 2a trials showing promising results in cognitive improvement and is currently conducting larger Phase 2b studies [2].
Strengths: Innovative approach targeting a specific enzyme involved in Alzheimer's pathology; Promising early clinical results. Weaknesses: Still in clinical trial phase; Efficacy and long-term safety need to be fully established.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG is advancing bioresonance research for Alzheimer's through its focus on immunotherapies. Their lead candidate, Remternetug (CAD106), is an active immunotherapy designed to trigger the patient's immune system to produce antibodies against beta-amyloid [3]. This approach aims to clear toxic amyloid plaques from the brain, potentially slowing cognitive decline. Novartis is also exploring combination therapies, pairing Remternetug with BACE inhibitors to target multiple aspects of Alzheimer's pathology simultaneously. The company has initiated the Phase 2/3 Generation Study program to evaluate the efficacy of this approach in preventing or delaying the onset of Alzheimer's symptoms in high-risk individuals [4].
Strengths: Multifaceted approach combining immunotherapy with other mechanisms; Large-scale clinical trials underway. Weaknesses: Complexity of combination therapies may increase side effects; Previous challenges in amyloid-targeting therapies in the field.
Breakthrough Bioresonance Techniques for AD
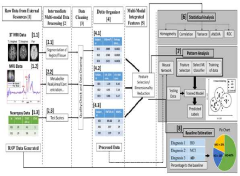
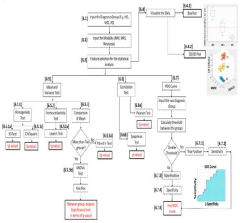
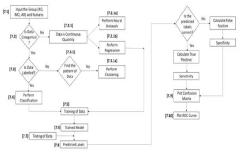
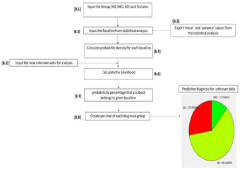
A method and a system using multi-modal neuroimaging for early diagnosis of alzheimer's disease
PatentActiveIN201911019667A
Innovation
- A computer-aided diagnostic system integrating multi-modal imaging data from MRI, MRS, and neuropsychological tests using machine learning techniques for pattern classification and predictive modeling to provide early and accurate diagnosis.
Alzheimer’s disease prevention and treatment with low intensity magnetic stimulation applied at physiologically relevant frequencies
PatentPendingUS20250090854A1
Innovation
- The use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS/gTMS) with specific parameters, including frequencies of less than 50 Hz and intensities of 20,000 to 250,000 milligauss, to stimulate neurons in the brain and potentially slow or prevent the progression of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Medical Devices
The regulatory framework for bioresonance medical devices in the context of Alzheimer's disease research is a complex and evolving landscape. As bioresonance technology gains traction in potential therapeutic applications, regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the need to establish clear guidelines and standards for these devices.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) clearance. However, specific regulations for bioresonance devices in Alzheimer's treatment are still in development. The FDA has expressed interest in adaptive regulatory approaches to accommodate the rapid advancements in this field while ensuring patient safety.
The European Union, through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR), has implemented a more comprehensive framework for bioresonance devices. Under the MDR, these devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with essential requirements, including clinical evaluation and risk management, to obtain CE marking.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established a dedicated pathway for innovative medical technologies, which may benefit bioresonance devices targeting Alzheimer's disease. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has also shown interest in streamlining approval processes for novel neurological treatments, potentially impacting bioresonance device regulations.
International harmonization efforts, such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), are working towards creating consistent global standards for emerging medical technologies. These initiatives aim to address the unique challenges posed by bioresonance devices, including the need for standardized performance metrics and long-term safety monitoring protocols.
As research in bioresonance for Alzheimer's disease progresses, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approaches. Key areas of focus include establishing specific clinical trial designs for bioresonance devices, developing guidelines for electromagnetic exposure limits, and creating frameworks for post-market surveillance of these devices in Alzheimer's patients.
The evolving regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for researchers and manufacturers in the bioresonance field. Proactive engagement with regulatory agencies and participation in standards development processes will be crucial for shaping a balanced regulatory framework that fosters innovation while safeguarding patient interests.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) clearance. However, specific regulations for bioresonance devices in Alzheimer's treatment are still in development. The FDA has expressed interest in adaptive regulatory approaches to accommodate the rapid advancements in this field while ensuring patient safety.
The European Union, through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR), has implemented a more comprehensive framework for bioresonance devices. Under the MDR, these devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with essential requirements, including clinical evaluation and risk management, to obtain CE marking.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established a dedicated pathway for innovative medical technologies, which may benefit bioresonance devices targeting Alzheimer's disease. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has also shown interest in streamlining approval processes for novel neurological treatments, potentially impacting bioresonance device regulations.
International harmonization efforts, such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF), are working towards creating consistent global standards for emerging medical technologies. These initiatives aim to address the unique challenges posed by bioresonance devices, including the need for standardized performance metrics and long-term safety monitoring protocols.
As research in bioresonance for Alzheimer's disease progresses, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approaches. Key areas of focus include establishing specific clinical trial designs for bioresonance devices, developing guidelines for electromagnetic exposure limits, and creating frameworks for post-market surveillance of these devices in Alzheimer's patients.
The evolving regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for researchers and manufacturers in the bioresonance field. Proactive engagement with regulatory agencies and participation in standards development processes will be crucial for shaping a balanced regulatory framework that fosters innovation while safeguarding patient interests.
Ethical Implications of Bioresonance in AD Management
The ethical implications of bioresonance in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) management are multifaceted and require careful consideration. As this emerging technology gains traction in the field of neurodegenerative disorders, it is crucial to address the ethical challenges that arise from its application.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for false hope and exploitation of vulnerable patients and their families. Alzheimer's Disease is a devastating condition, and those affected may be particularly susceptible to unproven treatments. The promise of bioresonance therapy could lead to unrealistic expectations, potentially causing emotional distress and financial burden if the treatment fails to deliver significant improvements.
Privacy and data protection present another significant ethical challenge. Bioresonance technology often involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of personal health data. Ensuring the security and confidentiality of this sensitive information is paramount, as breaches could lead to discrimination or exploitation of patients with AD.
The issue of informed consent is particularly complex in the context of Alzheimer's Disease. As cognitive decline progresses, patients may lose the capacity to make informed decisions about their treatment. This raises questions about who should have the authority to make decisions regarding bioresonance therapy and how to balance patient autonomy with the need for effective care.
Equity and access to bioresonance treatment also pose ethical dilemmas. If proven effective, ensuring fair distribution and affordability of this technology will be crucial to prevent exacerbating existing healthcare disparities. The potential for bioresonance to become a "luxury" treatment accessible only to the wealthy could further marginalize vulnerable populations.
The long-term effects of bioresonance on brain function and overall health are not yet fully understood. This uncertainty raises ethical questions about the responsible implementation of the technology, particularly in the context of a progressive neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer's Disease.
Lastly, the integration of bioresonance into standard AD care protocols may create conflicts with established medical practices and beliefs. Balancing innovation with evidence-based medicine and respecting diverse cultural and religious perspectives on health and treatment will be essential in navigating the ethical landscape of bioresonance in AD management.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for false hope and exploitation of vulnerable patients and their families. Alzheimer's Disease is a devastating condition, and those affected may be particularly susceptible to unproven treatments. The promise of bioresonance therapy could lead to unrealistic expectations, potentially causing emotional distress and financial burden if the treatment fails to deliver significant improvements.
Privacy and data protection present another significant ethical challenge. Bioresonance technology often involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of personal health data. Ensuring the security and confidentiality of this sensitive information is paramount, as breaches could lead to discrimination or exploitation of patients with AD.
The issue of informed consent is particularly complex in the context of Alzheimer's Disease. As cognitive decline progresses, patients may lose the capacity to make informed decisions about their treatment. This raises questions about who should have the authority to make decisions regarding bioresonance therapy and how to balance patient autonomy with the need for effective care.
Equity and access to bioresonance treatment also pose ethical dilemmas. If proven effective, ensuring fair distribution and affordability of this technology will be crucial to prevent exacerbating existing healthcare disparities. The potential for bioresonance to become a "luxury" treatment accessible only to the wealthy could further marginalize vulnerable populations.
The long-term effects of bioresonance on brain function and overall health are not yet fully understood. This uncertainty raises ethical questions about the responsible implementation of the technology, particularly in the context of a progressive neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer's Disease.
Lastly, the integration of bioresonance into standard AD care protocols may create conflicts with established medical practices and beliefs. Balancing innovation with evidence-based medicine and respecting diverse cultural and religious perspectives on health and treatment will be essential in navigating the ethical landscape of bioresonance in AD management.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!