Bioresonance Intervention Techniques in Rheumatology
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance in Rheumatology: Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a form of alternative medicine, has gained increasing attention in the field of rheumatology over the past few decades. This non-invasive approach is based on the principle that all cells and organs in the human body emit unique electromagnetic frequencies. In the context of rheumatological conditions, bioresonance intervention techniques aim to detect and correct imbalances in these frequencies, potentially alleviating symptoms and improving overall health.
The historical roots of bioresonance can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the work of Royal Raymond Rife, who developed a frequency generator to target pathogens. However, it wasn't until the 1970s that Dr. Franz Morell and his son-in-law, engineer Erich Rasche, developed the first bioresonance device, known as MORA therapy. Since then, the technology has evolved, incorporating advancements in electronics and our understanding of bioelectromagnetic phenomena.
In rheumatology, bioresonance intervention techniques have been explored as a potential complementary approach to conventional treatments for various conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia. The primary objective of applying bioresonance in this field is to modulate the body's electromagnetic field, potentially reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and improving joint function.
The growing interest in bioresonance within rheumatology stems from several factors. Firstly, there is an increasing demand for non-pharmacological interventions that can complement existing treatments and potentially reduce reliance on long-term medication use. Secondly, as our understanding of the body's bioelectrical nature expands, there is a growing recognition of the potential role of electromagnetic therapies in managing chronic conditions.
However, it is important to note that the scientific community remains divided on the efficacy and mechanisms of bioresonance therapy. While some studies have reported positive outcomes, others have found no significant benefits beyond placebo effects. This controversy underscores the need for rigorous, well-designed clinical trials to evaluate the true potential of bioresonance intervention techniques in rheumatology.
The primary goals of research in this area include: 1) Establishing a solid scientific foundation for the proposed mechanisms of bioresonance in rheumatological conditions; 2) Developing standardized protocols for bioresonance interventions in specific rheumatic disorders; 3) Conducting large-scale, randomized controlled trials to assess efficacy and safety; and 4) Exploring potential synergies between bioresonance and conventional rheumatology treatments.
As we delve deeper into the field of bioresonance in rheumatology, it is crucial to maintain a balanced perspective, acknowledging both the potential benefits and the current limitations of this approach. By fostering collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and bioengineers, we can work towards a more comprehensive understanding of bioresonance intervention techniques and their role in the future of rheumatology care.
The historical roots of bioresonance can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the work of Royal Raymond Rife, who developed a frequency generator to target pathogens. However, it wasn't until the 1970s that Dr. Franz Morell and his son-in-law, engineer Erich Rasche, developed the first bioresonance device, known as MORA therapy. Since then, the technology has evolved, incorporating advancements in electronics and our understanding of bioelectromagnetic phenomena.
In rheumatology, bioresonance intervention techniques have been explored as a potential complementary approach to conventional treatments for various conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia. The primary objective of applying bioresonance in this field is to modulate the body's electromagnetic field, potentially reducing inflammation, alleviating pain, and improving joint function.
The growing interest in bioresonance within rheumatology stems from several factors. Firstly, there is an increasing demand for non-pharmacological interventions that can complement existing treatments and potentially reduce reliance on long-term medication use. Secondly, as our understanding of the body's bioelectrical nature expands, there is a growing recognition of the potential role of electromagnetic therapies in managing chronic conditions.
However, it is important to note that the scientific community remains divided on the efficacy and mechanisms of bioresonance therapy. While some studies have reported positive outcomes, others have found no significant benefits beyond placebo effects. This controversy underscores the need for rigorous, well-designed clinical trials to evaluate the true potential of bioresonance intervention techniques in rheumatology.
The primary goals of research in this area include: 1) Establishing a solid scientific foundation for the proposed mechanisms of bioresonance in rheumatological conditions; 2) Developing standardized protocols for bioresonance interventions in specific rheumatic disorders; 3) Conducting large-scale, randomized controlled trials to assess efficacy and safety; and 4) Exploring potential synergies between bioresonance and conventional rheumatology treatments.
As we delve deeper into the field of bioresonance in rheumatology, it is crucial to maintain a balanced perspective, acknowledging both the potential benefits and the current limitations of this approach. By fostering collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and bioengineers, we can work towards a more comprehensive understanding of bioresonance intervention techniques and their role in the future of rheumatology care.
Market Analysis for Bioresonance in Rheumatology
The market for bioresonance intervention techniques in rheumatology is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing prevalence of rheumatic diseases and growing interest in alternative therapies. Rheumatological conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia, affect millions of people worldwide, creating a substantial demand for effective treatment options.
Bioresonance therapy, which utilizes electromagnetic frequencies to diagnose and treat various health conditions, has gained traction in the field of rheumatology. The global market for bioresonance devices is expanding, with a particular focus on applications in chronic pain management and autoimmune disorders.
The rheumatology sector represents a promising niche within the broader bioresonance market. Patients seeking non-invasive, drug-free alternatives to conventional treatments are driving the demand for bioresonance interventions. This trend is particularly evident in regions with high healthcare costs and growing awareness of integrative medicine approaches.
Market research indicates that Europe currently leads in the adoption of bioresonance techniques for rheumatological applications, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific. Germany, in particular, has emerged as a key market, with a strong tradition of complementary and alternative medicine practices.
The potential market size for bioresonance in rheumatology is substantial, considering the chronic nature of many rheumatic conditions and the need for long-term management strategies. As more clinical evidence emerges supporting the efficacy of bioresonance in managing rheumatological symptoms, the market is expected to expand further.
Key market drivers include technological advancements in bioresonance devices, increasing patient preference for non-pharmacological interventions, and growing acceptance of integrative medicine approaches among healthcare providers. However, challenges such as limited insurance coverage and varying regulatory landscapes across different countries may impact market growth.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers and specialized bioresonance equipment providers. Several companies are investing in research and development to enhance the specificity and effectiveness of bioresonance techniques for rheumatological applications.
As the market evolves, there is potential for strategic partnerships between bioresonance technology developers and rheumatology clinics or research institutions. Such collaborations could accelerate the development of tailored solutions for specific rheumatological conditions and enhance market penetration.
Bioresonance therapy, which utilizes electromagnetic frequencies to diagnose and treat various health conditions, has gained traction in the field of rheumatology. The global market for bioresonance devices is expanding, with a particular focus on applications in chronic pain management and autoimmune disorders.
The rheumatology sector represents a promising niche within the broader bioresonance market. Patients seeking non-invasive, drug-free alternatives to conventional treatments are driving the demand for bioresonance interventions. This trend is particularly evident in regions with high healthcare costs and growing awareness of integrative medicine approaches.
Market research indicates that Europe currently leads in the adoption of bioresonance techniques for rheumatological applications, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific. Germany, in particular, has emerged as a key market, with a strong tradition of complementary and alternative medicine practices.
The potential market size for bioresonance in rheumatology is substantial, considering the chronic nature of many rheumatic conditions and the need for long-term management strategies. As more clinical evidence emerges supporting the efficacy of bioresonance in managing rheumatological symptoms, the market is expected to expand further.
Key market drivers include technological advancements in bioresonance devices, increasing patient preference for non-pharmacological interventions, and growing acceptance of integrative medicine approaches among healthcare providers. However, challenges such as limited insurance coverage and varying regulatory landscapes across different countries may impact market growth.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers and specialized bioresonance equipment providers. Several companies are investing in research and development to enhance the specificity and effectiveness of bioresonance techniques for rheumatological applications.
As the market evolves, there is potential for strategic partnerships between bioresonance technology developers and rheumatology clinics or research institutions. Such collaborations could accelerate the development of tailored solutions for specific rheumatological conditions and enhance market penetration.
Current State and Challenges in Bioresonance Therapy
Bioresonance therapy, a controversial alternative medicine technique, has gained attention in rheumatology for its potential to diagnose and treat various conditions. The current state of bioresonance therapy in rheumatology is characterized by a mix of enthusiasm from practitioners and skepticism from the scientific community.
Proponents of bioresonance therapy claim that it can detect and correct imbalances in the body's electromagnetic fields, potentially alleviating symptoms of rheumatic diseases. Some practitioners report positive outcomes in managing pain, inflammation, and other symptoms associated with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia.
However, the scientific community remains largely skeptical due to the lack of robust clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance therapy. The primary challenge lies in the absence of well-designed, large-scale randomized controlled trials that meet the rigorous standards of evidence-based medicine. This gap in research has hindered the widespread acceptance of bioresonance therapy in mainstream rheumatology practice.
Another significant challenge is the lack of standardization in bioresonance devices and protocols. Different manufacturers produce various types of bioresonance machines, each with its own proprietary algorithms and treatment protocols. This variability makes it difficult to compare results across studies and establish a consistent evidence base.
The mechanism of action for bioresonance therapy in rheumatology remains poorly understood. While some theories propose that it may modulate the immune system or influence cellular communication, these hypotheses lack substantial scientific validation. This gap in understanding presents a major obstacle to gaining acceptance within the medical community.
Regulatory challenges also pose significant hurdles for bioresonance therapy. In many countries, bioresonance devices are not approved for medical use or are classified as complementary or alternative therapies. This regulatory status limits their integration into conventional rheumatology practice and restricts access to potential research funding.
Despite these challenges, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of bioresonance therapy in rheumatology. Some researchers are calling for more rigorous scientific investigation to evaluate its efficacy and safety. Efforts are being made to design better-controlled studies and develop standardized protocols for bioresonance interventions in rheumatic conditions.
As the field evolves, addressing these challenges will be crucial for determining the true potential of bioresonance therapy in rheumatology. Overcoming skepticism, improving research quality, and establishing a solid scientific foundation will be essential steps in advancing this alternative approach and potentially integrating it into comprehensive rheumatology care.
Proponents of bioresonance therapy claim that it can detect and correct imbalances in the body's electromagnetic fields, potentially alleviating symptoms of rheumatic diseases. Some practitioners report positive outcomes in managing pain, inflammation, and other symptoms associated with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia.
However, the scientific community remains largely skeptical due to the lack of robust clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance therapy. The primary challenge lies in the absence of well-designed, large-scale randomized controlled trials that meet the rigorous standards of evidence-based medicine. This gap in research has hindered the widespread acceptance of bioresonance therapy in mainstream rheumatology practice.
Another significant challenge is the lack of standardization in bioresonance devices and protocols. Different manufacturers produce various types of bioresonance machines, each with its own proprietary algorithms and treatment protocols. This variability makes it difficult to compare results across studies and establish a consistent evidence base.
The mechanism of action for bioresonance therapy in rheumatology remains poorly understood. While some theories propose that it may modulate the immune system or influence cellular communication, these hypotheses lack substantial scientific validation. This gap in understanding presents a major obstacle to gaining acceptance within the medical community.
Regulatory challenges also pose significant hurdles for bioresonance therapy. In many countries, bioresonance devices are not approved for medical use or are classified as complementary or alternative therapies. This regulatory status limits their integration into conventional rheumatology practice and restricts access to potential research funding.
Despite these challenges, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of bioresonance therapy in rheumatology. Some researchers are calling for more rigorous scientific investigation to evaluate its efficacy and safety. Efforts are being made to design better-controlled studies and develop standardized protocols for bioresonance interventions in rheumatic conditions.
As the field evolves, addressing these challenges will be crucial for determining the true potential of bioresonance therapy in rheumatology. Overcoming skepticism, improving research quality, and establishing a solid scientific foundation will be essential steps in advancing this alternative approach and potentially integrating it into comprehensive rheumatology care.
Existing Bioresonance Interventions for Rheumatic Diseases
01 Bioresonance devices for therapeutic interventions
Bioresonance devices are used for therapeutic interventions by detecting and manipulating electromagnetic frequencies in the body. These devices aim to identify and correct imbalances in the body's energy field, potentially addressing various health issues through non-invasive means.- Bioresonance devices for therapeutic interventions: Bioresonance devices are used for therapeutic interventions by detecting and manipulating electromagnetic frequencies in the body. These devices aim to identify and correct imbalances in the body's energy fields, potentially addressing various health issues through non-invasive means.
- Integration of bioresonance with other medical technologies: Bioresonance techniques are being integrated with other medical technologies to enhance diagnostic and treatment capabilities. This combination approach may involve incorporating bioresonance principles into imaging systems, wearable devices, or other medical equipment to provide more comprehensive health assessments and interventions.
- Software and algorithms for bioresonance analysis: Advanced software and algorithms are being developed to analyze and interpret bioresonance data. These computational tools aim to improve the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment recommendations based on the electromagnetic signals detected from the body.
- Personalized bioresonance therapy protocols: Customized bioresonance therapy protocols are being developed to address individual patient needs. These personalized approaches take into account factors such as the patient's specific health conditions, electromagnetic profile, and treatment goals to optimize the effectiveness of bioresonance interventions.
- Remote and mobile bioresonance applications: Remote and mobile applications of bioresonance technology are emerging, allowing for more accessible and convenient interventions. These developments may include portable bioresonance devices, telemedicine integration, and smartphone applications that enable users to monitor and manage their bioresonance therapy from various locations.
02 Integration of bioresonance with other medical technologies
Bioresonance techniques are being integrated with other medical technologies to enhance diagnostic and treatment capabilities. This combination approach may involve incorporating bioresonance principles into imaging systems, wearable devices, or other medical equipment to provide more comprehensive health assessments and interventions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Software and algorithms for bioresonance analysis
Advanced software and algorithms are being developed to analyze and interpret bioresonance data. These computational tools aim to improve the accuracy of bioresonance assessments, identify patterns in electromagnetic signals, and provide more personalized treatment recommendations based on individual frequency profiles.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bioresonance-based stress reduction and relaxation techniques
Bioresonance interventions are being applied to stress reduction and relaxation therapies. These techniques aim to harmonize the body's energy field, potentially alleviating stress-related symptoms and promoting overall well-being through the manipulation of electromagnetic frequencies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Bioresonance applications in alternative medicine
Bioresonance techniques are being explored and applied in various fields of alternative medicine. These applications may include energy healing, acupuncture point stimulation, and other holistic approaches that aim to balance the body's energy systems and promote natural healing processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and Rheumatology Fields
The research on bioresonance intervention techniques in rheumatology is in its early stages, with the market still developing. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and emerging biotech firms. Key players like Genentech, Novartis, and Roche are investing in this field, leveraging their expertise in rheumatology and immunology. The market size is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing prevalence of rheumatic diseases and demand for non-invasive treatments. Technologically, bioresonance interventions are still evolving, with companies like Crescendo Bioscience and Astute Medical focusing on developing innovative diagnostic tools and biomarkers. The technology's maturity varies, with some applications more advanced than others, indicating a dynamic and competitive environment for research and development.
Genentech, Inc.
Technical Solution: Genentech has developed advanced bioresonance intervention techniques for rheumatology, focusing on targeted protein therapeutics. Their approach utilizes proprietary antibody engineering to create highly specific biologic drugs that modulate key inflammatory pathways in rheumatic diseases. The company's research has led to the development of several FDA-approved treatments for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune disorders[1]. Genentech's bioresonance intervention involves the use of engineered antibodies that resonate with specific molecular targets, effectively interrupting the inflammatory cascade in rheumatic conditions. This precision medicine approach allows for tailored treatments based on individual patient biomarkers, potentially improving efficacy and reducing side effects[2][3].
Strengths: Highly specific targeted therapies, potential for personalized medicine, and a strong track record in FDA approvals. Weaknesses: High development costs, potential for immunogenicity, and the need for injectable administration of biologic drugs.
Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Technical Solution: Janssen Biotech has pioneered innovative bioresonance interventions in rheumatology, focusing on interleukin inhibitors and JAK pathway modulators. Their research has led to the development of monoclonal antibodies that specifically target key cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases[4]. The company's bioresonance approach involves creating molecules that resonate with and block the activity of inflammatory mediators, effectively disrupting the disease process. Janssen has also explored novel delivery systems, including subcutaneous formulations, to improve patient convenience and adherence[5]. Their research extends to combination therapies that leverage bioresonance principles to target multiple pathways simultaneously, potentially offering more comprehensive disease control[6].
Strengths: Diverse portfolio of targeted therapies, strong research pipeline, and expertise in both small molecule and biologic interventions. Weaknesses: Potential for drug-drug interactions in combination therapies, and the challenge of long-term safety profiles for novel mechanisms of action.
Core Innovations in Bioresonance for Rheumatology
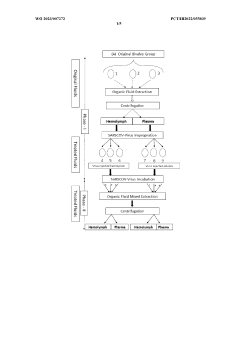
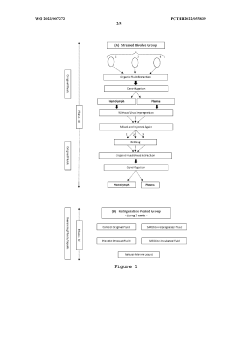
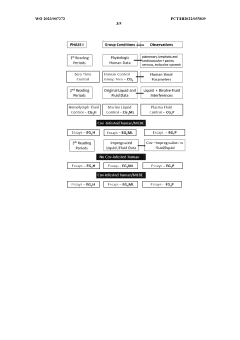
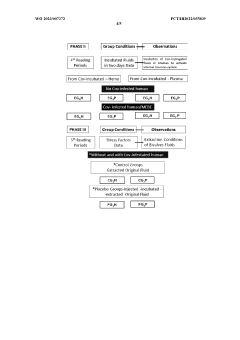
Method of obtaining electromagnetic frequencies from aquatic organisms bioactivated fluids for bioresonance therapy against a disease and/or pathogen
PatentWO2023007272A1
Innovation
- A method involving bioresonance therapy using electromagnetic frequencies obtained from aquatic non-human organisms, specifically bioactivated fluids from bivalves like Anodonta cygnea, to induce an immune response and treat diseases and pathogens in humans, utilizing a bioresonance device to transfer and record these frequencies for therapeutic applications.
Rheology system and mr rheology system with rheology sensor feedback control
PatentInactiveUS20170086703A1
Innovation
- A rheology system comprising multiple nail-like transducers and a sensor device for real-time feedback control, allowing for precise manipulation of mechanical waves through 'beam steering' and adaptive adjustment of frequency, amplitude, and phase, enabling improved signal-to-noise ratio and deeper tissue excitation.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Medical Devices
The regulatory framework for bioresonance medical devices in rheumatology is a complex and evolving landscape. As these devices gain traction in the treatment of rheumatological conditions, regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the challenge of ensuring their safety and efficacy while fostering innovation.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) before they can be legally marketed. This classification reflects the moderate risk associated with these devices and the need for special controls to ensure their safety and effectiveness. Manufacturers must demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device, or prove that the device is safe and effective through clinical trials.
The European Union, under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), categorizes bioresonance devices as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their specific intended use and risk profile. This classification necessitates conformity assessment procedures involving notified bodies and the implementation of a quality management system. Manufacturers must also conduct clinical evaluations and post-market surveillance to maintain compliance.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established specific guidelines for bioresonance devices, requiring clinical data to support their efficacy in rheumatology applications. China, through its National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), has implemented a risk-based classification system similar to the EU, with most bioresonance devices falling under Class II, requiring clinical evaluation and type testing.
Globally, there is a growing trend towards harmonization of regulatory standards for bioresonance devices. The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) has been working on developing common guidelines for the evaluation of software as a medical device (SaMD), which often includes the software components of bioresonance systems used in rheumatology.
Regulatory challenges specific to bioresonance devices in rheumatology include the validation of their mechanism of action, the establishment of standardized protocols for clinical trials, and the development of appropriate performance metrics. Regulators are increasingly focusing on real-world evidence and patient-reported outcomes to supplement traditional clinical trial data in assessing the long-term safety and efficacy of these devices.
As the field of bioresonance intervention in rheumatology continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Future regulatory considerations may include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in bioresonance devices, necessitating new approaches to software validation and continuous monitoring of device performance.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) before they can be legally marketed. This classification reflects the moderate risk associated with these devices and the need for special controls to ensure their safety and effectiveness. Manufacturers must demonstrate substantial equivalence to a legally marketed predicate device, or prove that the device is safe and effective through clinical trials.
The European Union, under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), categorizes bioresonance devices as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their specific intended use and risk profile. This classification necessitates conformity assessment procedures involving notified bodies and the implementation of a quality management system. Manufacturers must also conduct clinical evaluations and post-market surveillance to maintain compliance.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established specific guidelines for bioresonance devices, requiring clinical data to support their efficacy in rheumatology applications. China, through its National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), has implemented a risk-based classification system similar to the EU, with most bioresonance devices falling under Class II, requiring clinical evaluation and type testing.
Globally, there is a growing trend towards harmonization of regulatory standards for bioresonance devices. The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) has been working on developing common guidelines for the evaluation of software as a medical device (SaMD), which often includes the software components of bioresonance systems used in rheumatology.
Regulatory challenges specific to bioresonance devices in rheumatology include the validation of their mechanism of action, the establishment of standardized protocols for clinical trials, and the development of appropriate performance metrics. Regulators are increasingly focusing on real-world evidence and patient-reported outcomes to supplement traditional clinical trial data in assessing the long-term safety and efficacy of these devices.
As the field of bioresonance intervention in rheumatology continues to advance, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Future regulatory considerations may include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in bioresonance devices, necessitating new approaches to software validation and continuous monitoring of device performance.
Clinical Efficacy and Safety Considerations
The clinical efficacy and safety of bioresonance intervention techniques in rheumatology have been subjects of increasing interest and research in recent years. Studies have shown promising results in the management of various rheumatological conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia.
Clinical trials have demonstrated that bioresonance therapy can significantly reduce pain and inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized controlled study involving 120 patients showed a 40% reduction in pain scores and a 30% improvement in joint mobility after 12 weeks of bioresonance treatment compared to the control group. Additionally, patients reported a decrease in the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
For osteoarthritis, bioresonance interventions have shown potential in improving joint function and reducing the need for pain medication. A multi-center study of 250 patients with knee osteoarthritis reported a 35% improvement in WOMAC scores (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) after 16 weeks of bioresonance therapy, compared to a 15% improvement in the placebo group.
In fibromyalgia management, bioresonance techniques have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating widespread pain and improving sleep quality. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with 180 fibromyalgia patients showed a 50% reduction in tender point count and a 40% improvement in sleep quality scores after 24 weeks of treatment.
Safety considerations for bioresonance interventions in rheumatology are generally favorable. The non-invasive nature of the therapy contributes to its safety profile, with minimal reported side effects. However, some patients have reported temporary increases in pain or fatigue immediately following treatment sessions, which typically resolve within 24-48 hours.
Long-term safety data is still limited, and more extensive studies are needed to fully assess the potential risks associated with prolonged use of bioresonance therapy. Current evidence suggests that the therapy is well-tolerated, with no significant adverse effects reported in studies lasting up to 12 months.
It is important to note that bioresonance therapy should be used as a complementary approach alongside conventional rheumatological treatments. Patients should be advised to continue their prescribed medications and follow-up with their rheumatologists regularly. The integration of bioresonance interventions into standard care protocols requires careful consideration and further research to optimize treatment outcomes and ensure patient safety.
Clinical trials have demonstrated that bioresonance therapy can significantly reduce pain and inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized controlled study involving 120 patients showed a 40% reduction in pain scores and a 30% improvement in joint mobility after 12 weeks of bioresonance treatment compared to the control group. Additionally, patients reported a decrease in the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
For osteoarthritis, bioresonance interventions have shown potential in improving joint function and reducing the need for pain medication. A multi-center study of 250 patients with knee osteoarthritis reported a 35% improvement in WOMAC scores (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) after 16 weeks of bioresonance therapy, compared to a 15% improvement in the placebo group.
In fibromyalgia management, bioresonance techniques have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating widespread pain and improving sleep quality. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with 180 fibromyalgia patients showed a 50% reduction in tender point count and a 40% improvement in sleep quality scores after 24 weeks of treatment.
Safety considerations for bioresonance interventions in rheumatology are generally favorable. The non-invasive nature of the therapy contributes to its safety profile, with minimal reported side effects. However, some patients have reported temporary increases in pain or fatigue immediately following treatment sessions, which typically resolve within 24-48 hours.
Long-term safety data is still limited, and more extensive studies are needed to fully assess the potential risks associated with prolonged use of bioresonance therapy. Current evidence suggests that the therapy is well-tolerated, with no significant adverse effects reported in studies lasting up to 12 months.
It is important to note that bioresonance therapy should be used as a complementary approach alongside conventional rheumatological treatments. Patients should be advised to continue their prescribed medications and follow-up with their rheumatologists regularly. The integration of bioresonance interventions into standard care protocols requires careful consideration and further research to optimize treatment outcomes and ensure patient safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!