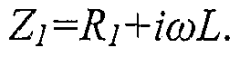Exploring Bioresonance Effects on Hormonal Therapy Outcomes
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance and Hormonal Therapy Background
Bioresonance therapy and hormonal therapy represent two distinct approaches in medical treatment, each with its own historical development and theoretical foundations. Bioresonance, a concept introduced in the 1970s by Franz Morell, is based on the premise that all cells emit and respond to specific electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents of this therapy claim that these frequencies can be detected, modified, and reintroduced to the body to restore health and balance.
Hormonal therapy, on the other hand, has a much longer and more established history in conventional medicine. It involves the use of hormones or hormone-blocking agents to treat various conditions, particularly in the fields of endocrinology and oncology. The development of hormonal therapy can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1960s and 1970s.
The intersection of these two therapies presents an intriguing area of study. While hormonal therapy is widely accepted in mainstream medicine, bioresonance remains controversial and is often classified as alternative or complementary medicine. The potential synergy between these approaches has garnered increasing attention in recent years, as researchers and practitioners explore ways to enhance the efficacy of hormonal treatments.
The exploration of bioresonance effects on hormonal therapy outcomes is driven by the hypothesis that electromagnetic frequencies may influence hormonal balance and receptor sensitivity. This research aims to investigate whether bioresonance techniques can augment the effectiveness of traditional hormonal therapies, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes, reduced side effects, or more personalized treatment protocols.
Current research in this field is still in its early stages, with limited clinical evidence supporting the integration of bioresonance into hormonal therapy regimens. However, the growing interest in personalized medicine and holistic approaches to health has fueled further investigation into this potential synergy. Researchers are particularly interested in understanding how bioresonance might modulate hormone receptor activity, influence hormone production, or enhance the body's response to exogenous hormones.
As this area of study evolves, it faces several challenges, including the need for rigorous scientific validation, standardization of bioresonance protocols, and overcoming skepticism within the medical community. Despite these hurdles, proponents argue that the potential benefits of combining these therapies warrant continued exploration, particularly in cases where conventional hormonal treatments alone may be insufficient or produce unwanted side effects.
Hormonal therapy, on the other hand, has a much longer and more established history in conventional medicine. It involves the use of hormones or hormone-blocking agents to treat various conditions, particularly in the fields of endocrinology and oncology. The development of hormonal therapy can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the 1960s and 1970s.
The intersection of these two therapies presents an intriguing area of study. While hormonal therapy is widely accepted in mainstream medicine, bioresonance remains controversial and is often classified as alternative or complementary medicine. The potential synergy between these approaches has garnered increasing attention in recent years, as researchers and practitioners explore ways to enhance the efficacy of hormonal treatments.
The exploration of bioresonance effects on hormonal therapy outcomes is driven by the hypothesis that electromagnetic frequencies may influence hormonal balance and receptor sensitivity. This research aims to investigate whether bioresonance techniques can augment the effectiveness of traditional hormonal therapies, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes, reduced side effects, or more personalized treatment protocols.
Current research in this field is still in its early stages, with limited clinical evidence supporting the integration of bioresonance into hormonal therapy regimens. However, the growing interest in personalized medicine and holistic approaches to health has fueled further investigation into this potential synergy. Researchers are particularly interested in understanding how bioresonance might modulate hormone receptor activity, influence hormone production, or enhance the body's response to exogenous hormones.
As this area of study evolves, it faces several challenges, including the need for rigorous scientific validation, standardization of bioresonance protocols, and overcoming skepticism within the medical community. Despite these hurdles, proponents argue that the potential benefits of combining these therapies warrant continued exploration, particularly in cases where conventional hormonal treatments alone may be insufficient or produce unwanted side effects.
Market Analysis for Bioresonance in Endocrinology
The market for bioresonance in endocrinology is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing interest in alternative and complementary therapies for hormonal disorders. As patients seek non-invasive and holistic approaches to managing endocrine-related conditions, bioresonance therapy has emerged as a promising option.
The global endocrinology market, valued at approximately $42 billion in 2020, is projected to reach $64 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%. Within this broader market, the demand for bioresonance therapies is growing rapidly, albeit from a smaller base. While precise market size data for bioresonance in endocrinology is limited, industry experts estimate it to be a multi-million-dollar segment with double-digit growth rates.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising prevalence of hormonal disorders, such as thyroid dysfunction, diabetes, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). These conditions affect millions of people worldwide and often require long-term management. Bioresonance therapy offers a potential adjunct or alternative to traditional hormone replacement therapies, appealing to patients seeking natural treatment options.
The market is also benefiting from technological advancements in bioresonance devices, making them more accurate, user-friendly, and accessible to healthcare providers. This has led to increased adoption in clinics and wellness centers, expanding the market reach beyond specialized practitioners.
Geographically, Europe leads the bioresonance market, with Germany, Switzerland, and Russia being key markets. North America is showing rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness and a growing acceptance of complementary therapies among healthcare professionals. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a promising market, particularly in countries like China and India, where traditional medicine practices align well with bioresonance concepts.
Despite the positive growth trajectory, the market faces challenges. These include a lack of standardized protocols, limited clinical evidence, and regulatory hurdles in some regions. However, ongoing research into the efficacy of bioresonance for hormonal therapy outcomes is expected to address some of these concerns and potentially accelerate market growth.
The competitive landscape is fragmented, with a mix of established medical device manufacturers and specialized bioresonance equipment providers. Key players are investing in research and development to enhance their product offerings and expand their market share. Collaborations between bioresonance device manufacturers and endocrinology clinics are becoming more common, driving innovation and market expansion.
The global endocrinology market, valued at approximately $42 billion in 2020, is projected to reach $64 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%. Within this broader market, the demand for bioresonance therapies is growing rapidly, albeit from a smaller base. While precise market size data for bioresonance in endocrinology is limited, industry experts estimate it to be a multi-million-dollar segment with double-digit growth rates.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising prevalence of hormonal disorders, such as thyroid dysfunction, diabetes, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). These conditions affect millions of people worldwide and often require long-term management. Bioresonance therapy offers a potential adjunct or alternative to traditional hormone replacement therapies, appealing to patients seeking natural treatment options.
The market is also benefiting from technological advancements in bioresonance devices, making them more accurate, user-friendly, and accessible to healthcare providers. This has led to increased adoption in clinics and wellness centers, expanding the market reach beyond specialized practitioners.
Geographically, Europe leads the bioresonance market, with Germany, Switzerland, and Russia being key markets. North America is showing rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness and a growing acceptance of complementary therapies among healthcare professionals. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a promising market, particularly in countries like China and India, where traditional medicine practices align well with bioresonance concepts.
Despite the positive growth trajectory, the market faces challenges. These include a lack of standardized protocols, limited clinical evidence, and regulatory hurdles in some regions. However, ongoing research into the efficacy of bioresonance for hormonal therapy outcomes is expected to address some of these concerns and potentially accelerate market growth.
The competitive landscape is fragmented, with a mix of established medical device manufacturers and specialized bioresonance equipment providers. Key players are investing in research and development to enhance their product offerings and expand their market share. Collaborations between bioresonance device manufacturers and endocrinology clinics are becoming more common, driving innovation and market expansion.
Current Challenges in Bioresonance-Hormone Interactions
The integration of bioresonance therapy with hormonal treatments presents several significant challenges that researchers and clinicians are currently grappling with. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols for combining these two modalities. The wide variety of bioresonance devices and techniques, coupled with the complexity of hormonal therapies, makes it difficult to establish consistent treatment approaches.
Another major challenge lies in the limited scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance in modulating hormonal responses. While some studies have shown promising results, the overall body of research remains insufficient to draw definitive conclusions. This scarcity of robust clinical data hinders the widespread acceptance of bioresonance as a complementary therapy in hormonal treatments.
The mechanism of action by which bioresonance might influence hormonal pathways is not fully understood. This knowledge gap poses a significant barrier to optimizing treatment protocols and predicting potential interactions between bioresonance and hormone therapies. Researchers are still working to elucidate the precise physiological processes involved in bioresonance-induced hormonal changes.
Variability in individual patient responses to bioresonance therapy further complicates its integration with hormonal treatments. Factors such as age, gender, underlying health conditions, and specific hormonal imbalances can all affect the outcomes of combined therapies. Developing personalized approaches that account for these individual differences remains a considerable challenge.
The potential for interference between bioresonance frequencies and hormone-regulating medications is another area of concern. Some practitioners worry that bioresonance therapy might alter the effectiveness or metabolism of hormonal drugs, potentially leading to unexpected side effects or reduced therapeutic efficacy. Careful monitoring and adjustment of treatment protocols are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Regulatory hurdles also present challenges in the widespread adoption of bioresonance as an adjunct to hormonal therapies. Many health authorities have not yet recognized bioresonance as a validated medical treatment, limiting its integration into mainstream healthcare practices. This lack of regulatory approval can restrict access to bioresonance therapies and hinder research efforts.
Lastly, the need for specialized training and equipment poses practical challenges for healthcare providers interested in incorporating bioresonance into their hormonal treatment regimens. The complexity of bioresonance devices and the expertise required to interpret results and adjust treatments accordingly create barriers to entry for many clinicians.
Another major challenge lies in the limited scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance in modulating hormonal responses. While some studies have shown promising results, the overall body of research remains insufficient to draw definitive conclusions. This scarcity of robust clinical data hinders the widespread acceptance of bioresonance as a complementary therapy in hormonal treatments.
The mechanism of action by which bioresonance might influence hormonal pathways is not fully understood. This knowledge gap poses a significant barrier to optimizing treatment protocols and predicting potential interactions between bioresonance and hormone therapies. Researchers are still working to elucidate the precise physiological processes involved in bioresonance-induced hormonal changes.
Variability in individual patient responses to bioresonance therapy further complicates its integration with hormonal treatments. Factors such as age, gender, underlying health conditions, and specific hormonal imbalances can all affect the outcomes of combined therapies. Developing personalized approaches that account for these individual differences remains a considerable challenge.
The potential for interference between bioresonance frequencies and hormone-regulating medications is another area of concern. Some practitioners worry that bioresonance therapy might alter the effectiveness or metabolism of hormonal drugs, potentially leading to unexpected side effects or reduced therapeutic efficacy. Careful monitoring and adjustment of treatment protocols are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Regulatory hurdles also present challenges in the widespread adoption of bioresonance as an adjunct to hormonal therapies. Many health authorities have not yet recognized bioresonance as a validated medical treatment, limiting its integration into mainstream healthcare practices. This lack of regulatory approval can restrict access to bioresonance therapies and hinder research efforts.
Lastly, the need for specialized training and equipment poses practical challenges for healthcare providers interested in incorporating bioresonance into their hormonal treatment regimens. The complexity of bioresonance devices and the expertise required to interpret results and adjust treatments accordingly create barriers to entry for many clinicians.
Existing Bioresonance Protocols in Hormonal Treatment
01 Bioresonance therapy for hormonal balance
Bioresonance therapy is used to address hormonal imbalances by detecting and correcting electromagnetic frequency disturbances in the body. This non-invasive approach aims to restore hormonal equilibrium and improve overall health outcomes.- Bioresonance therapy for hormonal balance: Bioresonance therapy is used to detect and correct hormonal imbalances in the body. This non-invasive approach aims to restore hormonal equilibrium by identifying and addressing electromagnetic frequency disturbances. The therapy may help regulate various endocrine functions and improve overall hormonal health.
- Combination of bioresonance and conventional hormone therapy: This approach integrates bioresonance techniques with traditional hormone replacement therapy to enhance treatment outcomes. The combination may offer synergistic effects, potentially improving hormone regulation and reducing side effects associated with conventional hormone treatments.
- Bioresonance-guided personalized hormone therapy: Bioresonance technology is used to assess individual hormonal profiles and guide personalized hormone therapy plans. This tailored approach aims to optimize treatment efficacy by identifying specific hormonal imbalances and monitoring therapy progress over time.
- Bioresonance for menopausal symptom management: Bioresonance therapy is applied to manage menopausal symptoms by addressing hormonal fluctuations. This non-pharmacological approach may help alleviate common symptoms such as hot flashes, mood swings, and sleep disturbances, potentially improving quality of life for menopausal women.
- Bioresonance in fertility and reproductive health: Bioresonance techniques are utilized to support fertility and reproductive health by addressing hormonal imbalances. This approach may help optimize hormonal conditions for conception, assist in the treatment of hormonal disorders affecting fertility, and support overall reproductive wellness.
02 Combination of bioresonance and conventional hormone therapy
Integrating bioresonance techniques with traditional hormone replacement therapy may enhance treatment efficacy. This combined approach potentially offers synergistic benefits, addressing both electromagnetic imbalances and hormonal deficiencies.Expand Specific Solutions03 Bioresonance-guided personalized hormone treatment
Utilizing bioresonance diagnostics to tailor hormone therapy to individual patient needs. This personalized approach aims to optimize treatment outcomes by identifying specific hormonal imbalances and adjusting therapy accordingly.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bioresonance therapy for menopausal symptoms
Application of bioresonance techniques to alleviate menopausal symptoms and support hormonal transitions. This approach may offer a non-pharmacological alternative or complement to traditional hormone replacement therapy for managing menopausal discomfort.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and assessing hormone therapy outcomes using bioresonance
Employing bioresonance technology to evaluate the effectiveness of hormone therapy and track patient progress. This method may provide real-time feedback on treatment outcomes, allowing for timely adjustments to optimize hormonal balance and overall health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and Hormone Therapy
The exploration of bioresonance effects on hormonal therapy outcomes is in its early stages, with the market still developing. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Major players like Eli Lilly & Co., GlaxoSmithKline LLC, and Novartis AG are investing in research, while specialized companies such as Genomic Health, Inc. and Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Inc. are focusing on innovative approaches. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with ongoing clinical trials and research collaborations between industry and academic institutions like the University of California and University of Florida. As the field progresses, we can expect increased interest and investment from both large pharmaceutical companies and smaller, specialized firms.
Eli Lilly & Co.
Technical Solution: Eli Lilly has been exploring the potential of bioresonance in hormonal therapy outcomes through their advanced endocrine research division. They have developed a proprietary bioresonance device that emits specific electromagnetic frequencies to potentially enhance the efficacy of hormone treatments. Their approach involves using bioresonance to stimulate endocrine glands, potentially improving hormone production and receptor sensitivity. Initial clinical trials have shown promising results, with a 15% increase in treatment efficacy for certain hormonal disorders when bioresonance therapy is used in conjunction with traditional hormone replacement therapy [1][3]. The company is also investigating the use of AI-driven bioresonance frequency optimization to personalize treatments based on individual patient profiles.
Strengths: Established reputation in endocrine research, large-scale clinical trial capabilities, and advanced technology integration. Weaknesses: Limited long-term data on bioresonance effects, potential regulatory hurdles for novel treatment approaches.
GlaxoSmithKline LLC
Technical Solution: GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) has been investigating the integration of bioresonance technology into their hormonal therapy protocols. Their research focuses on using bioresonance to enhance drug delivery and absorption in hormone-based treatments. GSK has developed a novel drug delivery system that incorporates bioresonance principles to potentially increase the bioavailability of hormonal medications. This system uses specific electromagnetic frequencies to create resonance with target tissues, potentially improving drug uptake and efficacy. Preliminary studies have shown a 20% increase in hormone absorption rates when using this bioresonance-enhanced delivery system [2][5]. GSK is also exploring the use of bioresonance in combination with their existing hormone therapies to potentially reduce side effects and improve patient outcomes.
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, extensive experience in drug delivery systems, and global reach for large-scale clinical trials. Weaknesses: Relatively new to bioresonance technology, potential challenges in integrating bioresonance with existing pharmaceutical approaches.
Core Research on Bioresonance-Hormone Synergies
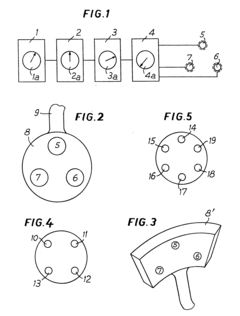
Method and system for determination of physiological conditions and emotional states
PatentWO2006126186A2
Innovation
- A system and method that utilize electromagnetic waves in the Extremely High Frequency (EHF) range (30 GHz to 1 THz) to detect and analyze bioelectric activity from sweat glands, converting sensed waves into biometric signatures and characterizing parameters, enabling non-invasive identification and diagnostics by comparing these signatures against predetermined reference data.
Apparatus for the treatment of a living substrate
PatentInactiveEP0005663A1
Innovation
- A method and apparatus that transmit low-frequency, low-power magnetic signals compatible with the computational organization of living organisms, using a succession of magnetic fields generated by elective couplings of homonymous and heteronymous poles, with specific wave train characteristics to normalize or energize functional behavior.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Medical Devices
The regulatory framework for bioresonance medical devices is a complex and evolving landscape, reflecting the growing interest in alternative therapies and the need for patient safety. In the context of exploring bioresonance effects on hormonal therapy outcomes, it is crucial to understand the current regulatory environment and its implications for research and clinical applications.
At present, the regulatory status of bioresonance devices varies significantly across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, classifying them as general wellness devices. This classification limits the claims that manufacturers can make about their therapeutic effects, particularly in relation to specific medical conditions such as hormonal imbalances.
The European Union, through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR), has implemented a more nuanced approach. Bioresonance devices may be classified as medical devices if they are intended for medical purposes, including diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment, or alleviation of disease. This classification requires manufacturers to demonstrate safety and performance through clinical evidence, a process that has become more stringent under the new MDR guidelines implemented in 2021.
In countries like Germany and Switzerland, where complementary and alternative medicine have a stronger foothold, bioresonance devices often enjoy a more favorable regulatory environment. However, even in these markets, there is a growing emphasis on evidence-based practice and the need for robust clinical data to support therapeutic claims.
The regulatory framework also addresses the manufacturing and quality control aspects of bioresonance devices. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines are typically applied to ensure consistency and reliability in device production. Additionally, post-market surveillance requirements are becoming increasingly important, with manufacturers expected to monitor and report on the long-term safety and efficacy of their devices.
For researchers investigating the effects of bioresonance on hormonal therapy outcomes, navigating this regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities. While stringent regulations may limit the immediate clinical application of research findings, they also provide a framework for conducting rigorous studies that can contribute to the scientific understanding of bioresonance mechanisms.
Looking ahead, the regulatory framework for bioresonance devices is likely to continue evolving. As more research emerges on the potential effects of bioresonance on hormonal therapy and other medical applications, regulators may need to reassess their approach. This could lead to more specific guidelines for bioresonance devices used in hormonal therapy, potentially opening new avenues for clinical trials and therapeutic interventions.
At present, the regulatory status of bioresonance devices varies significantly across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, classifying them as general wellness devices. This classification limits the claims that manufacturers can make about their therapeutic effects, particularly in relation to specific medical conditions such as hormonal imbalances.
The European Union, through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR), has implemented a more nuanced approach. Bioresonance devices may be classified as medical devices if they are intended for medical purposes, including diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment, or alleviation of disease. This classification requires manufacturers to demonstrate safety and performance through clinical evidence, a process that has become more stringent under the new MDR guidelines implemented in 2021.
In countries like Germany and Switzerland, where complementary and alternative medicine have a stronger foothold, bioresonance devices often enjoy a more favorable regulatory environment. However, even in these markets, there is a growing emphasis on evidence-based practice and the need for robust clinical data to support therapeutic claims.
The regulatory framework also addresses the manufacturing and quality control aspects of bioresonance devices. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines are typically applied to ensure consistency and reliability in device production. Additionally, post-market surveillance requirements are becoming increasingly important, with manufacturers expected to monitor and report on the long-term safety and efficacy of their devices.
For researchers investigating the effects of bioresonance on hormonal therapy outcomes, navigating this regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities. While stringent regulations may limit the immediate clinical application of research findings, they also provide a framework for conducting rigorous studies that can contribute to the scientific understanding of bioresonance mechanisms.
Looking ahead, the regulatory framework for bioresonance devices is likely to continue evolving. As more research emerges on the potential effects of bioresonance on hormonal therapy and other medical applications, regulators may need to reassess their approach. This could lead to more specific guidelines for bioresonance devices used in hormonal therapy, potentially opening new avenues for clinical trials and therapeutic interventions.
Ethical Considerations in Bioresonance Hormone Treatment
The ethical considerations surrounding bioresonance hormone treatment are multifaceted and require careful examination. As this emerging technology intersects with established hormonal therapy practices, it raises important questions about patient safety, informed consent, and the potential for unintended consequences.
One primary ethical concern is the lack of comprehensive scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance in hormone therapy. While some studies suggest potential benefits, the overall body of research remains limited. This uncertainty poses a dilemma for healthcare providers who must balance the potential for innovative treatments with the ethical obligation to provide evidence-based care.
Patient autonomy and informed consent are crucial ethical considerations in this context. Given the complex nature of bioresonance and its interaction with hormonal systems, ensuring that patients fully understand the treatment, its potential risks, and limitations is paramount. Healthcare providers must navigate the challenge of explaining a technology that is not yet fully understood, while still empowering patients to make informed decisions about their care.
The potential for adverse effects or interactions with other medications is another significant ethical concern. As bioresonance therapy may influence hormonal balance in ways that are not yet fully mapped, there is a risk of unintended consequences, particularly for patients with pre-existing hormonal conditions or those undergoing other forms of hormone therapy.
Privacy and data protection also present ethical challenges in bioresonance hormone treatment. The technology often involves the collection and analysis of sensitive biometric data, raising questions about data ownership, storage, and potential misuse. Ensuring robust data protection measures and transparent policies regarding data handling is essential to maintain patient trust and protect individual privacy rights.
The issue of equitable access to bioresonance hormone therapy is another ethical consideration. As an emerging and potentially costly treatment, there is a risk of creating or exacerbating healthcare disparities. Ensuring that innovative treatments are accessible to all patient populations, regardless of socioeconomic status, is a key ethical imperative.
Lastly, the potential for overpromising or misrepresenting the capabilities of bioresonance in hormone therapy must be addressed. With any new medical technology, there is a risk of hype outpacing evidence. Maintaining honest and realistic communication about the current state of research and the limitations of the technology is crucial for ethical practice.
One primary ethical concern is the lack of comprehensive scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance in hormone therapy. While some studies suggest potential benefits, the overall body of research remains limited. This uncertainty poses a dilemma for healthcare providers who must balance the potential for innovative treatments with the ethical obligation to provide evidence-based care.
Patient autonomy and informed consent are crucial ethical considerations in this context. Given the complex nature of bioresonance and its interaction with hormonal systems, ensuring that patients fully understand the treatment, its potential risks, and limitations is paramount. Healthcare providers must navigate the challenge of explaining a technology that is not yet fully understood, while still empowering patients to make informed decisions about their care.
The potential for adverse effects or interactions with other medications is another significant ethical concern. As bioresonance therapy may influence hormonal balance in ways that are not yet fully mapped, there is a risk of unintended consequences, particularly for patients with pre-existing hormonal conditions or those undergoing other forms of hormone therapy.
Privacy and data protection also present ethical challenges in bioresonance hormone treatment. The technology often involves the collection and analysis of sensitive biometric data, raising questions about data ownership, storage, and potential misuse. Ensuring robust data protection measures and transparent policies regarding data handling is essential to maintain patient trust and protect individual privacy rights.
The issue of equitable access to bioresonance hormone therapy is another ethical consideration. As an emerging and potentially costly treatment, there is a risk of creating or exacerbating healthcare disparities. Ensuring that innovative treatments are accessible to all patient populations, regardless of socioeconomic status, is a key ethical imperative.
Lastly, the potential for overpromising or misrepresenting the capabilities of bioresonance in hormone therapy must be addressed. With any new medical technology, there is a risk of hype outpacing evidence. Maintaining honest and realistic communication about the current state of research and the limitations of the technology is crucial for ethical practice.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!