How Does Bioresonance Aid in Enhancing Fertility Treatment Success?
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance in Fertility: Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a controversial alternative medicine approach, has recently gained attention in the field of fertility treatment. This non-invasive method, based on the principle that all cells emit electromagnetic waves, aims to detect and correct imbalances in the body's energy fields. The technology's application in fertility treatment stems from the belief that these electromagnetic imbalances may contribute to reproductive issues.
The historical context of bioresonance dates back to the 1970s when Dr. Franz Morell developed the MORA device, which purportedly measured and manipulated the body's electromagnetic frequencies. Since then, the technology has evolved, with various manufacturers producing more sophisticated devices claiming to enhance fertility outcomes. However, it is crucial to note that the scientific community remains skeptical about the efficacy of bioresonance, as robust clinical evidence supporting its use in fertility treatment is limited.
The primary objective of exploring bioresonance in fertility treatment is to determine whether this alternative approach can genuinely improve success rates in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and natural conception. Researchers and practitioners aim to investigate if bioresonance can address underlying issues affecting fertility, such as hormonal imbalances, stress, and environmental toxins, which may not be fully addressed by conventional treatments.
Another goal is to assess the potential of bioresonance as a complementary therapy to traditional fertility treatments. Proponents argue that it may enhance the effectiveness of in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), and other established procedures by optimizing the body's overall health and energy balance. This integration could potentially lead to higher pregnancy rates and improved outcomes for couples struggling with infertility.
Furthermore, the exploration of bioresonance in fertility treatment seeks to understand the mechanisms by which this therapy might influence reproductive health. This includes investigating its effects on hormone regulation, egg and sperm quality, uterine receptivity, and overall reproductive system function. By elucidating these potential mechanisms, researchers hope to establish a scientific basis for the use of bioresonance in fertility care.
As the field of reproductive medicine continues to advance, there is a growing interest in holistic and non-invasive approaches to fertility treatment. Bioresonance represents one such avenue of investigation, with the ultimate aim of expanding the range of options available to individuals and couples seeking to conceive. However, it is essential to approach this technology with a critical and evidence-based mindset, ensuring that any claims of efficacy are thoroughly validated through rigorous scientific research and clinical trials.
The historical context of bioresonance dates back to the 1970s when Dr. Franz Morell developed the MORA device, which purportedly measured and manipulated the body's electromagnetic frequencies. Since then, the technology has evolved, with various manufacturers producing more sophisticated devices claiming to enhance fertility outcomes. However, it is crucial to note that the scientific community remains skeptical about the efficacy of bioresonance, as robust clinical evidence supporting its use in fertility treatment is limited.
The primary objective of exploring bioresonance in fertility treatment is to determine whether this alternative approach can genuinely improve success rates in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and natural conception. Researchers and practitioners aim to investigate if bioresonance can address underlying issues affecting fertility, such as hormonal imbalances, stress, and environmental toxins, which may not be fully addressed by conventional treatments.
Another goal is to assess the potential of bioresonance as a complementary therapy to traditional fertility treatments. Proponents argue that it may enhance the effectiveness of in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), and other established procedures by optimizing the body's overall health and energy balance. This integration could potentially lead to higher pregnancy rates and improved outcomes for couples struggling with infertility.
Furthermore, the exploration of bioresonance in fertility treatment seeks to understand the mechanisms by which this therapy might influence reproductive health. This includes investigating its effects on hormone regulation, egg and sperm quality, uterine receptivity, and overall reproductive system function. By elucidating these potential mechanisms, researchers hope to establish a scientific basis for the use of bioresonance in fertility care.
As the field of reproductive medicine continues to advance, there is a growing interest in holistic and non-invasive approaches to fertility treatment. Bioresonance represents one such avenue of investigation, with the ultimate aim of expanding the range of options available to individuals and couples seeking to conceive. However, it is essential to approach this technology with a critical and evidence-based mindset, ensuring that any claims of efficacy are thoroughly validated through rigorous scientific research and clinical trials.
Market Analysis: Fertility Treatment Demand
The global fertility treatment market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by various factors such as delayed parenthood, increasing infertility rates, and advancements in reproductive technologies. The demand for fertility treatments, including bioresonance therapy, has been steadily rising as more couples seek assistance in conceiving.
According to recent market research, the global fertility services market was valued at approximately $21 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $41 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8.5%. This substantial growth indicates a strong and increasing demand for fertility treatments worldwide.
Several key factors contribute to the expanding market for fertility treatments. Firstly, the trend of delayed parenthood, particularly in developed countries, has led to a higher incidence of age-related fertility issues. As women choose to pursue careers and postpone starting families, the need for assisted reproductive technologies has increased.
Secondly, environmental factors, lifestyle changes, and stress have contributed to rising infertility rates globally. The World Health Organization estimates that infertility affects approximately 15% of couples of reproductive age worldwide, translating to millions of potential patients seeking fertility treatments.
Furthermore, societal acceptance of fertility treatments has improved, reducing stigma and encouraging more couples to seek assistance. This shift in perception has expanded the potential market for fertility services, including alternative therapies like bioresonance.
The market for fertility treatments is also being driven by technological advancements and innovative approaches. Bioresonance therapy, as a complementary treatment, has gained attention for its potential to enhance the success rates of conventional fertility treatments. While still considered alternative medicine, the growing interest in holistic and non-invasive approaches has created a niche market within the broader fertility treatment landscape.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the fertility treatment market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher disposable incomes, and greater awareness of fertility issues. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and changing socioeconomic factors.
The increasing demand for fertility treatments has also led to a rise in fertility tourism, with patients traveling across borders to access more affordable or advanced treatments. This trend has further expanded the global market and created opportunities for countries to position themselves as fertility treatment destinations.
According to recent market research, the global fertility services market was valued at approximately $21 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $41 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8.5%. This substantial growth indicates a strong and increasing demand for fertility treatments worldwide.
Several key factors contribute to the expanding market for fertility treatments. Firstly, the trend of delayed parenthood, particularly in developed countries, has led to a higher incidence of age-related fertility issues. As women choose to pursue careers and postpone starting families, the need for assisted reproductive technologies has increased.
Secondly, environmental factors, lifestyle changes, and stress have contributed to rising infertility rates globally. The World Health Organization estimates that infertility affects approximately 15% of couples of reproductive age worldwide, translating to millions of potential patients seeking fertility treatments.
Furthermore, societal acceptance of fertility treatments has improved, reducing stigma and encouraging more couples to seek assistance. This shift in perception has expanded the potential market for fertility services, including alternative therapies like bioresonance.
The market for fertility treatments is also being driven by technological advancements and innovative approaches. Bioresonance therapy, as a complementary treatment, has gained attention for its potential to enhance the success rates of conventional fertility treatments. While still considered alternative medicine, the growing interest in holistic and non-invasive approaches has created a niche market within the broader fertility treatment landscape.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the fertility treatment market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher disposable incomes, and greater awareness of fertility issues. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and changing socioeconomic factors.
The increasing demand for fertility treatments has also led to a rise in fertility tourism, with patients traveling across borders to access more affordable or advanced treatments. This trend has further expanded the global market and created opportunities for countries to position themselves as fertility treatment destinations.
Current Challenges in Fertility Enhancement
Despite significant advancements in fertility treatments, several challenges persist in enhancing fertility success rates. One of the primary obstacles is the limited understanding of individual reproductive health factors. Traditional diagnostic methods often fail to provide a comprehensive picture of a person's fertility status, leading to ineffective or unnecessary treatments.
The high cost and invasiveness of many fertility treatments pose another significant challenge. In vitro fertilization (IVF), while effective for some, remains financially out of reach for many couples. Additionally, the physical and emotional toll of repeated invasive procedures can be substantial, often leading to treatment discontinuation.
Age-related fertility decline continues to be a major hurdle, particularly as more individuals delay parenthood for various reasons. The quality and quantity of eggs decrease with age, making it increasingly difficult to achieve successful pregnancies, even with advanced fertility treatments.
Unexplained infertility remains a frustrating challenge for both patients and healthcare providers. In many cases, despite thorough testing, no clear cause for infertility can be identified, making it difficult to tailor treatments effectively.
Environmental factors and lifestyle choices also present ongoing challenges. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, stress, poor diet, and sedentary lifestyles can all negatively impact fertility. Addressing these factors often requires significant lifestyle changes, which can be difficult for many individuals to implement and maintain.
Male factor infertility is another area that presents unique challenges. While much focus has been placed on female fertility, issues related to sperm quality and quantity are equally important but often overlooked or inadequately addressed in fertility treatment plans.
The psychological impact of infertility and fertility treatments is a challenge that cannot be overlooked. Stress, anxiety, and depression are common among individuals undergoing fertility treatments, potentially impacting treatment outcomes and overall well-being.
Lastly, the lack of personalized treatment approaches remains a significant hurdle. Current fertility treatments often follow a one-size-fits-all model, failing to account for the unique biological and genetic factors of each individual. This approach can lead to suboptimal outcomes and unnecessary treatments.
The high cost and invasiveness of many fertility treatments pose another significant challenge. In vitro fertilization (IVF), while effective for some, remains financially out of reach for many couples. Additionally, the physical and emotional toll of repeated invasive procedures can be substantial, often leading to treatment discontinuation.
Age-related fertility decline continues to be a major hurdle, particularly as more individuals delay parenthood for various reasons. The quality and quantity of eggs decrease with age, making it increasingly difficult to achieve successful pregnancies, even with advanced fertility treatments.
Unexplained infertility remains a frustrating challenge for both patients and healthcare providers. In many cases, despite thorough testing, no clear cause for infertility can be identified, making it difficult to tailor treatments effectively.
Environmental factors and lifestyle choices also present ongoing challenges. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, stress, poor diet, and sedentary lifestyles can all negatively impact fertility. Addressing these factors often requires significant lifestyle changes, which can be difficult for many individuals to implement and maintain.
Male factor infertility is another area that presents unique challenges. While much focus has been placed on female fertility, issues related to sperm quality and quantity are equally important but often overlooked or inadequately addressed in fertility treatment plans.
The psychological impact of infertility and fertility treatments is a challenge that cannot be overlooked. Stress, anxiety, and depression are common among individuals undergoing fertility treatments, potentially impacting treatment outcomes and overall well-being.
Lastly, the lack of personalized treatment approaches remains a significant hurdle. Current fertility treatments often follow a one-size-fits-all model, failing to account for the unique biological and genetic factors of each individual. This approach can lead to suboptimal outcomes and unnecessary treatments.
Bioresonance Fertility Treatment Approaches
01 Bioresonance therapy for fertility enhancement
Bioresonance therapy is used to improve fertility by balancing the body's energy fields and addressing underlying health issues that may affect reproductive function. This non-invasive approach aims to optimize hormonal balance, reduce stress, and enhance overall reproductive health.- Bioresonance therapy for fertility enhancement: Bioresonance therapy is used to improve fertility by balancing the body's electromagnetic fields. This non-invasive treatment aims to identify and correct energetic imbalances that may be affecting reproductive health. The therapy involves using a device to measure and manipulate the body's electromagnetic frequencies, potentially improving overall reproductive function and increasing the chances of successful conception.
- Combination of bioresonance with other fertility treatments: Integrating bioresonance therapy with conventional fertility treatments may enhance overall success rates. This approach combines the energetic balancing effects of bioresonance with established medical interventions, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or hormone therapy. The synergistic effect of these combined treatments may improve reproductive outcomes and increase the likelihood of successful pregnancy.
- Personalized bioresonance protocols for fertility: Customized bioresonance treatment protocols are developed based on individual patient assessments. These personalized approaches take into account specific energetic imbalances, lifestyle factors, and medical history to create tailored treatment plans. By addressing unique patient needs, personalized bioresonance protocols aim to optimize fertility outcomes and increase treatment success rates.
- Bioresonance for male and female fertility issues: Bioresonance therapy is applied to address both male and female fertility challenges. For men, the treatment may focus on improving sperm quality, motility, and count. In women, bioresonance therapy may target hormonal imbalances, ovulation disorders, and uterine health. By addressing fertility issues in both partners, this approach aims to increase the overall success rate of conception.
- Monitoring and assessing bioresonance fertility treatment success: Various methods and devices are used to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of bioresonance fertility treatments. These may include regular electromagnetic frequency measurements, hormonal assessments, and tracking of reproductive health markers. By closely monitoring treatment progress and outcomes, practitioners can adjust protocols as needed and provide evidence-based assessments of bioresonance therapy's success in improving fertility.
02 Combination of bioresonance with conventional fertility treatments
Integrating bioresonance therapy with traditional fertility treatments may enhance overall success rates. This complementary approach can potentially improve the effectiveness of assisted reproductive technologies by addressing energetic imbalances and supporting the body's natural healing processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Bioresonance devices for fertility assessment and treatment
Specialized bioresonance devices are developed to assess and treat fertility issues. These devices may use electromagnetic frequencies to detect imbalances in the reproductive system and provide targeted therapy to improve fertility outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Personalized bioresonance protocols for fertility
Customized bioresonance treatment protocols are designed based on individual patient assessments. These tailored approaches aim to address specific fertility challenges and optimize treatment outcomes by considering each patient's unique energetic profile and health status.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and evaluating bioresonance fertility treatment success
Methods and systems are developed to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of bioresonance fertility treatments. These may include tracking changes in hormonal levels, assessing improvements in reproductive health markers, and analyzing pregnancy rates among treated patients.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance Fertility
The bioresonance fertility treatment market is in its early growth stage, with increasing interest but limited widespread adoption. Market size is expanding as more couples seek alternative fertility solutions, though exact figures are not readily available. Technologically, bioresonance for fertility is still evolving, with varying levels of scientific validation. Companies like JCR Pharmaceuticals, Ferring BV, and The Daily Wellness Co. are exploring complementary approaches to fertility enhancement, while research institutions such as Yokohama City University and the University of Adelaide are contributing to the scientific understanding of fertility treatments. The field is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical players and innovative startups, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape with potential for significant advancements in the coming years.
Ferring BV
Technical Solution: Ferring BV, a global biopharmaceutical company, has been investing in research related to fertility treatments. While not directly involved in bioresonance technology, they have developed innovative approaches to enhance fertility treatment success. Ferring has focused on personalized medicine in reproductive health, using biomarkers and genetic testing to optimize treatment protocols[5]. They have also developed novel drug delivery systems for fertility medications, improving patient compliance and treatment outcomes[6]. Additionally, Ferring is exploring the potential of microbiome modulation to enhance fertility, which could have synergistic effects with other treatment modalities[7].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining pharmaceuticals and diagnostics, global reach for clinical trials and implementation. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on pharmaceutical interventions, may not fully address all aspects of fertility challenges.
Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Technical Solution: Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine has been conducting research on integrating traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with modern fertility treatments. While not specifically focused on bioresonance, their approach includes acupuncture and herbal medicine, which share some conceptual similarities with bioresonance in terms of energy flow and balance. The university has conducted studies on the effects of acupuncture on IVF outcomes, showing potential improvements in pregnancy rates[8]. They are also investigating the use of specific herbal formulations to enhance ovarian function and improve egg quality[9]. Their research extends to the potential synergistic effects of combining TCM practices with conventional fertility treatments.
Strengths: Holistic approach combining traditional and modern medicine, potential for fewer side effects. Weaknesses: Standardization challenges, variability in practitioner expertise, limited large-scale clinical evidence.
Innovative Bioresonance Techniques
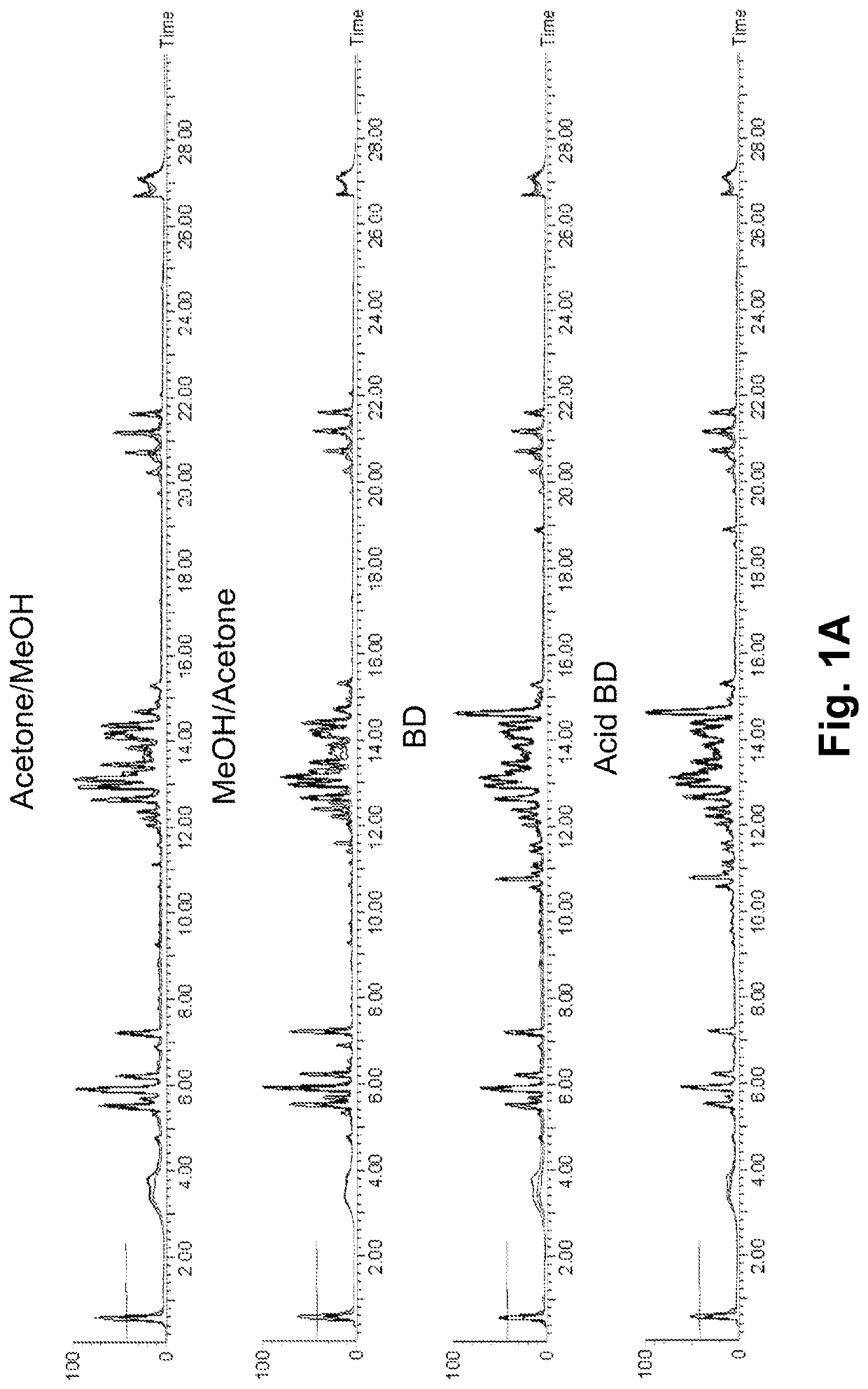
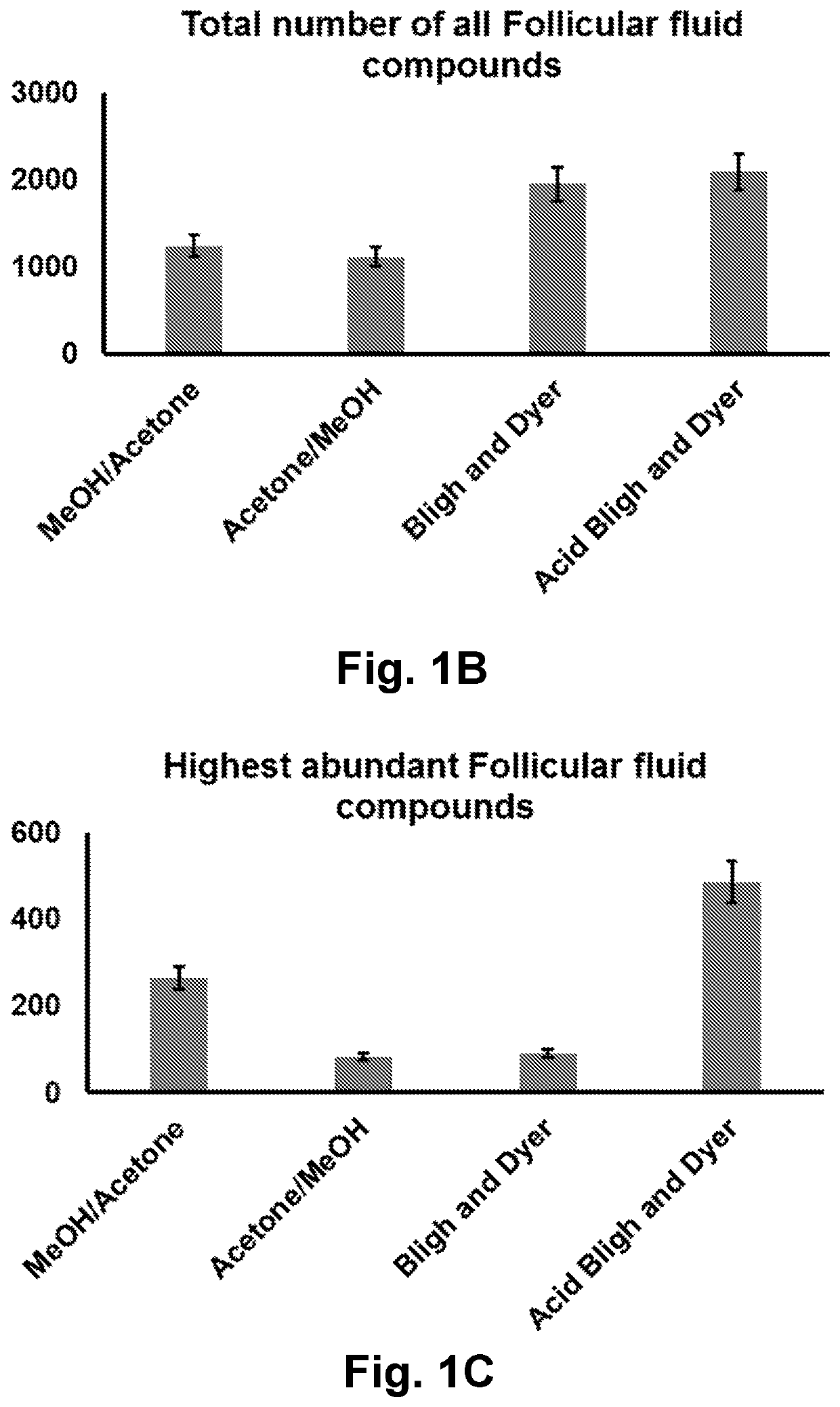
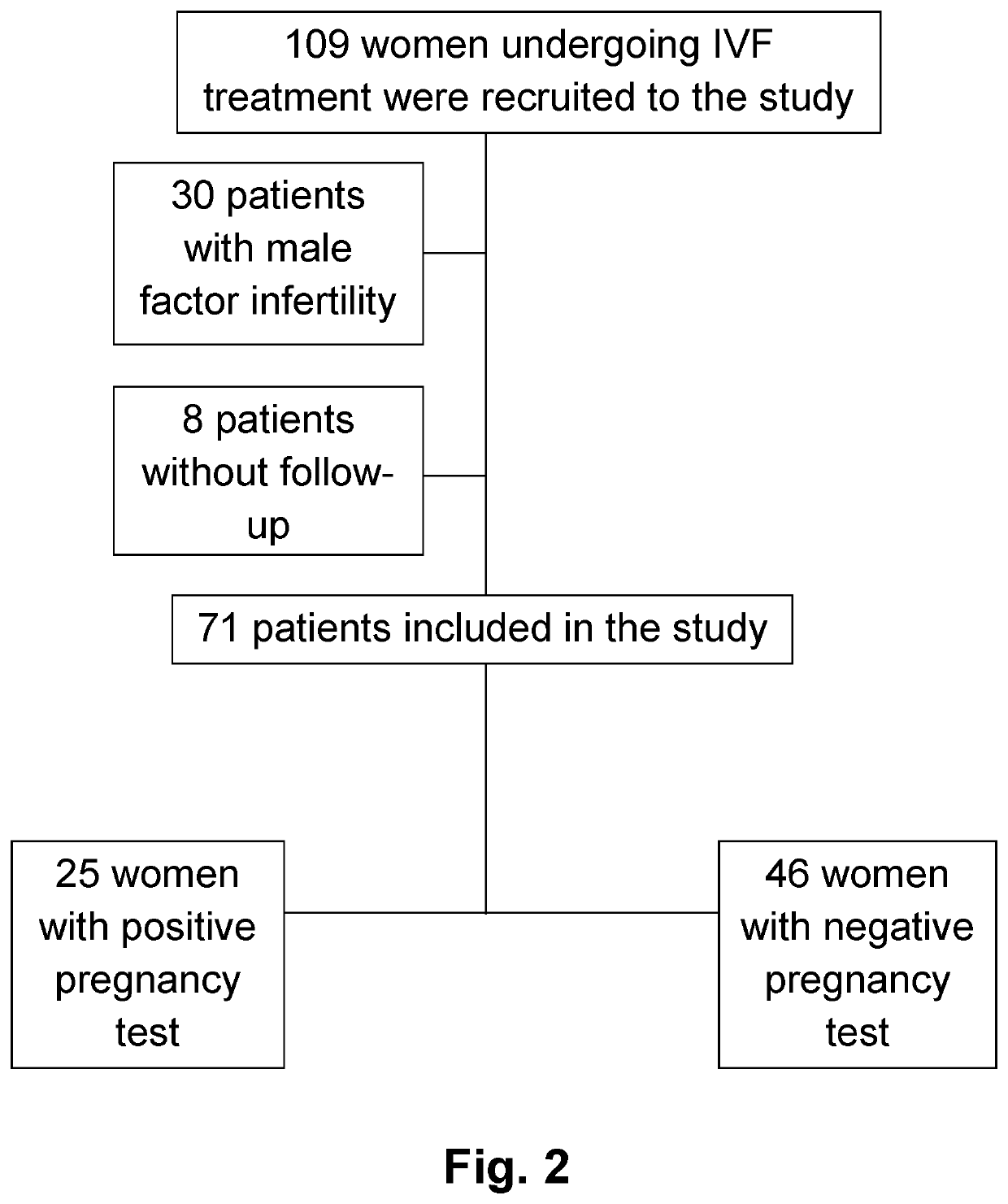
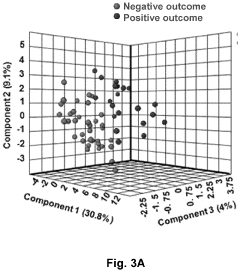
Lipid profiling methods for predicting positive pregnancy outcome
PatentPendingUS20220308075A1
Innovation
- A method involving the analysis of lipid profiles in fluid samples, specifically measuring glycerolipids, phospholipids, lysophospholipids, sphingolipids, and cholesterol derivatives, to determine the likelihood of a positive pregnancy outcome and select suitable oocytes for IVF treatment by comparing lipid levels to predefined standards.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance in Healthcare
The regulatory framework for bioresonance in healthcare varies significantly across different countries and regions, reflecting the diverse approaches to alternative and complementary medicine worldwide. In many jurisdictions, bioresonance therapy falls under the category of complementary or alternative medicine, which often operates in a regulatory gray area.
In the European Union, the regulation of bioresonance devices and treatments is primarily governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device Regulation (IVDR). These regulations set standards for safety, performance, and clinical evidence for medical devices, including those used in bioresonance therapy. However, the specific classification and requirements for bioresonance devices can vary depending on their intended use and claims made by manufacturers.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, including fertility treatment. The FDA classifies most bioresonance devices as general wellness products, which are subject to less stringent regulations than medical devices. However, manufacturers are prohibited from making specific health claims without proper scientific evidence and FDA approval.
In countries like Germany and Switzerland, where complementary medicine has a stronger foothold, bioresonance therapy enjoys a more favorable regulatory environment. These countries have established frameworks for the integration of complementary therapies into their healthcare systems, allowing for greater acceptance and use of bioresonance in clinical settings.
The lack of standardized regulations for bioresonance therapy in many countries has led to concerns about quality control, efficacy, and patient safety. As a result, professional associations and self-regulatory bodies have emerged in some regions to establish guidelines and standards for practitioners. These organizations often provide certification programs and codes of ethics to ensure a level of professionalism and accountability in the field.
As research into bioresonance and its potential applications in fertility treatment continues to evolve, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will adapt to accommodate new findings and evidence. This may include the development of specific guidelines for the use of bioresonance in reproductive medicine, as well as more rigorous requirements for clinical trials and device certification.
The challenge for regulators lies in striking a balance between allowing innovation in complementary therapies and ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy. As the field of bioresonance in fertility treatment advances, it will be crucial for regulatory bodies to work closely with researchers, clinicians, and manufacturers to establish evidence-based standards and protocols that can be consistently applied across different healthcare systems.
In the European Union, the regulation of bioresonance devices and treatments is primarily governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device Regulation (IVDR). These regulations set standards for safety, performance, and clinical evidence for medical devices, including those used in bioresonance therapy. However, the specific classification and requirements for bioresonance devices can vary depending on their intended use and claims made by manufacturers.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, including fertility treatment. The FDA classifies most bioresonance devices as general wellness products, which are subject to less stringent regulations than medical devices. However, manufacturers are prohibited from making specific health claims without proper scientific evidence and FDA approval.
In countries like Germany and Switzerland, where complementary medicine has a stronger foothold, bioresonance therapy enjoys a more favorable regulatory environment. These countries have established frameworks for the integration of complementary therapies into their healthcare systems, allowing for greater acceptance and use of bioresonance in clinical settings.
The lack of standardized regulations for bioresonance therapy in many countries has led to concerns about quality control, efficacy, and patient safety. As a result, professional associations and self-regulatory bodies have emerged in some regions to establish guidelines and standards for practitioners. These organizations often provide certification programs and codes of ethics to ensure a level of professionalism and accountability in the field.
As research into bioresonance and its potential applications in fertility treatment continues to evolve, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will adapt to accommodate new findings and evidence. This may include the development of specific guidelines for the use of bioresonance in reproductive medicine, as well as more rigorous requirements for clinical trials and device certification.
The challenge for regulators lies in striking a balance between allowing innovation in complementary therapies and ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy. As the field of bioresonance in fertility treatment advances, it will be crucial for regulatory bodies to work closely with researchers, clinicians, and manufacturers to establish evidence-based standards and protocols that can be consistently applied across different healthcare systems.
Ethical Considerations in Fertility Treatments
The ethical considerations surrounding fertility treatments, particularly those involving bioresonance, are complex and multifaceted. As bioresonance technology gains traction in enhancing fertility treatment success, it is crucial to address the ethical implications that arise from its use.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for false hope and exploitation. Bioresonance, while promising, is still considered an alternative therapy with limited scientific evidence supporting its efficacy in fertility treatments. There is a risk that vulnerable individuals or couples struggling with infertility may be led to invest time, money, and emotional energy into treatments that may not yield the desired results. This raises questions about informed consent and the responsibility of healthcare providers to ensure patients fully understand the experimental nature of bioresonance in fertility treatments.
Another significant ethical consideration is the long-term safety of bioresonance treatments, particularly for the resulting offspring. As with any emerging medical technology, the potential long-term effects on both the parents and any children conceived through these treatments are not yet fully understood. This uncertainty necessitates careful monitoring and longitudinal studies to ensure that the pursuit of fertility does not come at the cost of future health risks.
The issue of access and equity also presents ethical challenges. As bioresonance treatments for fertility are not widely recognized or covered by most insurance plans, they may only be accessible to those with significant financial resources. This disparity in access could exacerbate existing inequalities in reproductive healthcare, raising questions about fairness and social justice in fertility treatment options.
Furthermore, the use of bioresonance in fertility treatments touches upon broader ethical debates surrounding assisted reproductive technologies. Questions arise about the extent to which technology should be used to intervene in the natural process of conception and the potential societal implications of increasingly sophisticated fertility interventions.
There are also concerns about data privacy and the ethical use of personal health information gathered during bioresonance treatments. As these treatments often involve detailed assessments of an individual's electromagnetic frequencies, there is a need for robust safeguards to protect this sensitive data from misuse or unauthorized access.
Lastly, the integration of bioresonance into fertility treatments raises questions about the medicalization of infertility and the potential pressure on individuals to pursue all available options, regardless of personal beliefs or comfort levels. This could lead to ethical dilemmas for healthcare providers in balancing patient autonomy with professional recommendations and societal expectations surrounding fertility and family planning.
One primary ethical concern is the potential for false hope and exploitation. Bioresonance, while promising, is still considered an alternative therapy with limited scientific evidence supporting its efficacy in fertility treatments. There is a risk that vulnerable individuals or couples struggling with infertility may be led to invest time, money, and emotional energy into treatments that may not yield the desired results. This raises questions about informed consent and the responsibility of healthcare providers to ensure patients fully understand the experimental nature of bioresonance in fertility treatments.
Another significant ethical consideration is the long-term safety of bioresonance treatments, particularly for the resulting offspring. As with any emerging medical technology, the potential long-term effects on both the parents and any children conceived through these treatments are not yet fully understood. This uncertainty necessitates careful monitoring and longitudinal studies to ensure that the pursuit of fertility does not come at the cost of future health risks.
The issue of access and equity also presents ethical challenges. As bioresonance treatments for fertility are not widely recognized or covered by most insurance plans, they may only be accessible to those with significant financial resources. This disparity in access could exacerbate existing inequalities in reproductive healthcare, raising questions about fairness and social justice in fertility treatment options.
Furthermore, the use of bioresonance in fertility treatments touches upon broader ethical debates surrounding assisted reproductive technologies. Questions arise about the extent to which technology should be used to intervene in the natural process of conception and the potential societal implications of increasingly sophisticated fertility interventions.
There are also concerns about data privacy and the ethical use of personal health information gathered during bioresonance treatments. As these treatments often involve detailed assessments of an individual's electromagnetic frequencies, there is a need for robust safeguards to protect this sensitive data from misuse or unauthorized access.
Lastly, the integration of bioresonance into fertility treatments raises questions about the medicalization of infertility and the potential pressure on individuals to pursue all available options, regardless of personal beliefs or comfort levels. This could lead to ethical dilemmas for healthcare providers in balancing patient autonomy with professional recommendations and societal expectations surrounding fertility and family planning.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!