Potential of Bioresonance in Fertility Optimization
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance Fertility Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a concept rooted in the principles of quantum physics and energy medicine, has gained attention in recent years for its potential applications in fertility optimization. This emerging field explores the interaction between electromagnetic frequencies and biological systems, positing that every cell in the human body emits a unique electromagnetic signature. The evolution of bioresonance technology has been driven by advancements in quantum physics, bioelectromagnetics, and cellular biology, converging to create a novel approach to addressing fertility challenges.
The primary objective of bioresonance in fertility optimization is to identify and correct energetic imbalances within the reproductive system, potentially enhancing natural conception rates and supporting assisted reproductive technologies. This non-invasive approach aims to complement traditional fertility treatments by addressing subtle energetic factors that may influence reproductive health. As the global prevalence of infertility continues to rise, with estimates suggesting that up to 15% of couples worldwide experience difficulties conceiving, the exploration of alternative and complementary therapies has become increasingly relevant.
The development of bioresonance technology for fertility applications has been influenced by pioneering work in bioelectromagnetics, particularly studies demonstrating the sensitivity of biological systems to weak electromagnetic fields. Research into the effects of electromagnetic frequencies on cellular function, hormone regulation, and gamete quality has provided a theoretical foundation for the application of bioresonance in reproductive medicine. Additionally, advances in quantum biology have offered new perspectives on the role of quantum coherence in biological processes, potentially explaining some of the observed effects of bioresonance therapy.
As the field progresses, key technological goals include refining the precision and specificity of bioresonance devices for fertility applications, developing standardized protocols for treatment, and integrating bioresonance data with other diagnostic tools in reproductive medicine. There is also a focus on elucidating the mechanisms by which bioresonance may influence reproductive physiology, aiming to bridge the gap between empirical observations and scientific understanding.
The potential of bioresonance in fertility optimization extends beyond its direct application to conception. Researchers are exploring its use in preconception care, addressing hormonal imbalances, improving gamete quality, and potentially enhancing the success rates of in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures. Furthermore, there is growing interest in the role of bioresonance in managing stress and emotional factors that can impact fertility, recognizing the complex interplay between psychological well-being and reproductive health.
The primary objective of bioresonance in fertility optimization is to identify and correct energetic imbalances within the reproductive system, potentially enhancing natural conception rates and supporting assisted reproductive technologies. This non-invasive approach aims to complement traditional fertility treatments by addressing subtle energetic factors that may influence reproductive health. As the global prevalence of infertility continues to rise, with estimates suggesting that up to 15% of couples worldwide experience difficulties conceiving, the exploration of alternative and complementary therapies has become increasingly relevant.
The development of bioresonance technology for fertility applications has been influenced by pioneering work in bioelectromagnetics, particularly studies demonstrating the sensitivity of biological systems to weak electromagnetic fields. Research into the effects of electromagnetic frequencies on cellular function, hormone regulation, and gamete quality has provided a theoretical foundation for the application of bioresonance in reproductive medicine. Additionally, advances in quantum biology have offered new perspectives on the role of quantum coherence in biological processes, potentially explaining some of the observed effects of bioresonance therapy.
As the field progresses, key technological goals include refining the precision and specificity of bioresonance devices for fertility applications, developing standardized protocols for treatment, and integrating bioresonance data with other diagnostic tools in reproductive medicine. There is also a focus on elucidating the mechanisms by which bioresonance may influence reproductive physiology, aiming to bridge the gap between empirical observations and scientific understanding.
The potential of bioresonance in fertility optimization extends beyond its direct application to conception. Researchers are exploring its use in preconception care, addressing hormonal imbalances, improving gamete quality, and potentially enhancing the success rates of in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures. Furthermore, there is growing interest in the role of bioresonance in managing stress and emotional factors that can impact fertility, recognizing the complex interplay between psychological well-being and reproductive health.
Fertility Market Analysis
The fertility market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by various factors such as delayed parenthood, increasing infertility rates, and advancements in reproductive technologies. The global fertility services market was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $41 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period.
Demographic shifts play a crucial role in shaping the fertility market. In developed countries, the trend of delaying childbearing due to career priorities and lifestyle choices has led to increased demand for fertility treatments. Additionally, the rising prevalence of infertility, affecting both men and women, has further fueled market growth. According to the World Health Organization, infertility affects about 15% of couples globally, translating to millions of potential patients seeking fertility solutions.
The market is characterized by a diverse range of services and treatments, including in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), surrogacy, and fertility drugs. IVF remains the most popular and lucrative segment, accounting for a substantial portion of the market revenue. Technological advancements, such as preimplantation genetic testing and time-lapse embryo imaging, have improved success rates and attracted more patients to these procedures.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the fertility market, owing to high awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and favorable reimbursement policies. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing disposable income, changing lifestyles, and growing acceptance of fertility treatments in countries like China and India.
The fertility market is also witnessing a shift towards more personalized and holistic approaches to reproductive health. This trend has opened up opportunities for alternative and complementary therapies, including bioresonance, which aims to optimize fertility through non-invasive methods. While still considered experimental by mainstream medicine, bioresonance is gaining traction among patients seeking natural or integrative approaches to fertility enhancement.
Consumer behavior in the fertility market is evolving, with patients becoming more informed and proactive in their fertility journeys. There is a growing demand for comprehensive fertility wellness programs that address not only medical aspects but also lifestyle factors, nutrition, and stress management. This holistic approach aligns well with the principles of bioresonance therapy, potentially creating a niche market for this technology within the broader fertility industry.
Demographic shifts play a crucial role in shaping the fertility market. In developed countries, the trend of delaying childbearing due to career priorities and lifestyle choices has led to increased demand for fertility treatments. Additionally, the rising prevalence of infertility, affecting both men and women, has further fueled market growth. According to the World Health Organization, infertility affects about 15% of couples globally, translating to millions of potential patients seeking fertility solutions.
The market is characterized by a diverse range of services and treatments, including in vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), surrogacy, and fertility drugs. IVF remains the most popular and lucrative segment, accounting for a substantial portion of the market revenue. Technological advancements, such as preimplantation genetic testing and time-lapse embryo imaging, have improved success rates and attracted more patients to these procedures.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the fertility market, owing to high awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and favorable reimbursement policies. However, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing disposable income, changing lifestyles, and growing acceptance of fertility treatments in countries like China and India.
The fertility market is also witnessing a shift towards more personalized and holistic approaches to reproductive health. This trend has opened up opportunities for alternative and complementary therapies, including bioresonance, which aims to optimize fertility through non-invasive methods. While still considered experimental by mainstream medicine, bioresonance is gaining traction among patients seeking natural or integrative approaches to fertility enhancement.
Consumer behavior in the fertility market is evolving, with patients becoming more informed and proactive in their fertility journeys. There is a growing demand for comprehensive fertility wellness programs that address not only medical aspects but also lifestyle factors, nutrition, and stress management. This holistic approach aligns well with the principles of bioresonance therapy, potentially creating a niche market for this technology within the broader fertility industry.
Bioresonance Technology Status and Challenges
Bioresonance technology, while gaining attention in alternative medicine circles, faces significant challenges in establishing its efficacy and scientific validity in fertility optimization. The current status of bioresonance in this field is characterized by a lack of robust scientific evidence and standardized protocols, which hinders its widespread acceptance in mainstream medical practice.
One of the primary challenges is the absence of a universally accepted mechanism of action for bioresonance therapy. Proponents claim that it works by detecting and correcting imbalances in the body's electromagnetic fields, but this concept remains controversial within the scientific community. The lack of a clear biological basis for its effects on fertility has led to skepticism among many reproductive health specialists.
Another significant hurdle is the scarcity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials specifically focusing on bioresonance's impact on fertility. Most available studies are small in scale, lack proper controls, or suffer from methodological flaws, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the technology's effectiveness. This dearth of high-quality research has resulted in bioresonance being classified as an unproven or experimental treatment by many regulatory bodies and medical associations.
The technology itself also faces challenges in terms of standardization and reproducibility. Different bioresonance devices and practitioners may use varying frequencies, treatment durations, and protocols, making it difficult to compare results across studies or establish best practices. This lack of standardization not only affects the credibility of the technology but also poses potential risks to patients who may receive inconsistent or inappropriate treatments.
Furthermore, the integration of bioresonance into conventional fertility treatments faces resistance from the medical community due to concerns about its scientific basis and potential interference with established protocols. Many fertility specialists are hesitant to recommend or incorporate bioresonance therapy without more substantial evidence of its safety and efficacy.
Despite these challenges, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential of bioresonance in fertility optimization, particularly among patients seeking alternative or complementary approaches. Some practitioners report anecdotal success in using bioresonance to address underlying health issues that may affect fertility, such as hormonal imbalances or stress-related disorders. However, these claims require rigorous scientific validation to move beyond anecdotal evidence.
In conclusion, while bioresonance technology shows potential in the field of fertility optimization, it currently faces significant challenges in terms of scientific validation, standardization, and integration into mainstream medical practice. Overcoming these hurdles will require substantial investment in high-quality research, development of standardized protocols, and collaboration between bioresonance practitioners and reproductive health specialists to establish its place in fertility treatment.
One of the primary challenges is the absence of a universally accepted mechanism of action for bioresonance therapy. Proponents claim that it works by detecting and correcting imbalances in the body's electromagnetic fields, but this concept remains controversial within the scientific community. The lack of a clear biological basis for its effects on fertility has led to skepticism among many reproductive health specialists.
Another significant hurdle is the scarcity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials specifically focusing on bioresonance's impact on fertility. Most available studies are small in scale, lack proper controls, or suffer from methodological flaws, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the technology's effectiveness. This dearth of high-quality research has resulted in bioresonance being classified as an unproven or experimental treatment by many regulatory bodies and medical associations.
The technology itself also faces challenges in terms of standardization and reproducibility. Different bioresonance devices and practitioners may use varying frequencies, treatment durations, and protocols, making it difficult to compare results across studies or establish best practices. This lack of standardization not only affects the credibility of the technology but also poses potential risks to patients who may receive inconsistent or inappropriate treatments.
Furthermore, the integration of bioresonance into conventional fertility treatments faces resistance from the medical community due to concerns about its scientific basis and potential interference with established protocols. Many fertility specialists are hesitant to recommend or incorporate bioresonance therapy without more substantial evidence of its safety and efficacy.
Despite these challenges, there is a growing interest in exploring the potential of bioresonance in fertility optimization, particularly among patients seeking alternative or complementary approaches. Some practitioners report anecdotal success in using bioresonance to address underlying health issues that may affect fertility, such as hormonal imbalances or stress-related disorders. However, these claims require rigorous scientific validation to move beyond anecdotal evidence.
In conclusion, while bioresonance technology shows potential in the field of fertility optimization, it currently faces significant challenges in terms of scientific validation, standardization, and integration into mainstream medical practice. Overcoming these hurdles will require substantial investment in high-quality research, development of standardized protocols, and collaboration between bioresonance practitioners and reproductive health specialists to establish its place in fertility treatment.
Current Bioresonance Fertility Solutions
01 Bioresonance devices for fertility enhancement
Specialized bioresonance devices are designed to improve fertility by balancing the body's electromagnetic fields. These devices emit specific frequencies that may stimulate reproductive organs, regulate hormonal balance, and enhance overall reproductive health. The technology aims to address underlying issues affecting fertility and increase the chances of conception.- Bioresonance devices for fertility enhancement: Specialized bioresonance devices are designed to improve fertility by balancing the body's electromagnetic fields. These devices emit specific frequencies that may stimulate reproductive organs, regulate hormonal balance, and enhance overall reproductive health. The treatment is non-invasive and aims to address underlying causes of infertility.
- Frequency-based diagnosis of fertility issues: Bioresonance technology is used to diagnose fertility problems by detecting imbalances in the body's energy fields. These diagnostic methods involve scanning the body with specific frequencies to identify potential issues affecting reproductive health, such as hormonal imbalances or organ dysfunctions.
- Combination of bioresonance with other fertility treatments: Bioresonance therapy is often combined with other fertility treatments to enhance overall effectiveness. This may include integration with traditional medical approaches, herbal remedies, or lifestyle modifications. The synergistic effect aims to address fertility issues from multiple angles.
- Personalized bioresonance protocols for fertility: Customized bioresonance protocols are developed based on individual patient needs and specific fertility issues. These tailored approaches may involve adjusting frequencies, treatment duration, and targeted areas to optimize reproductive health and increase the chances of conception.
- Bioresonance-enhanced in vitro fertilization (IVF): Bioresonance techniques are applied to improve the success rates of in vitro fertilization procedures. This may involve treating gametes or embryos with specific frequencies to enhance their viability, or using bioresonance to prepare the patient's body for embryo implantation and pregnancy.
02 Frequency-based diagnosis and treatment of infertility
Bioresonance techniques are used to diagnose and treat infertility by analyzing the body's electromagnetic frequencies. This approach involves detecting imbalances or disturbances in the body's energy fields related to reproductive health. Based on the diagnosis, specific frequencies are applied to correct these imbalances and improve fertility outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination of bioresonance with traditional fertility treatments
Integrating bioresonance therapy with conventional fertility treatments may enhance overall effectiveness. This combined approach utilizes bioresonance to complement and potentially boost the results of traditional methods such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), hormone therapy, or other assisted reproductive technologies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bioresonance-based stress reduction for fertility improvement
Bioresonance techniques are employed to reduce stress levels, which can significantly impact fertility. By using specific frequencies to balance the nervous system and promote relaxation, these methods aim to create a more favorable physiological environment for conception and pregnancy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Personalized bioresonance protocols for fertility optimization
Customized bioresonance protocols are developed based on individual electromagnetic profiles to optimize fertility. These tailored approaches consider factors such as age, hormonal status, and specific fertility challenges to create personalized frequency treatments that target the unique needs of each patient.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance Fertility Industry
The bioresonance fertility optimization market is in its early growth stage, with increasing interest but limited widespread adoption. The market size is relatively small but expanding as more couples seek alternative fertility treatments. Technologically, bioresonance for fertility is still emerging, with varying levels of scientific validation. Key players like China Agricultural University and Yokohama City University are conducting research to establish its efficacy. Companies such as Celmatix and The Daily Wellness Co. are developing commercial applications, while established medical institutions like The General Hospital Corp. and McGill University are exploring its potential integration into conventional fertility treatments. The field is characterized by a mix of academic research, startup innovation, and cautious exploration by traditional healthcare providers.
Celmatix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Celmatix is pioneering the application of bioresonance technology in fertility optimization. Their approach integrates advanced genomics with bioresonance principles to create personalized fertility treatment plans. The company has developed a proprietary platform that analyzes an individual's genetic markers and bioenergetic profile to identify potential fertility obstacles. This technology allows for non-invasive assessment of reproductive health, potentially detecting imbalances before they manifest as clinical symptoms[1]. Celmatix's system uses resonance frequencies to stimulate cellular repair and optimize hormonal balance, which may enhance overall reproductive function[3].
Strengths: Personalized approach, non-invasive technology, potential for early intervention. Weaknesses: Limited long-term data on efficacy, potential skepticism from traditional medical community.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California is conducting groundbreaking research on the application of bioresonance in fertility optimization. Their multidisciplinary team is exploring the fundamental mechanisms by which electromagnetic fields interact with biological systems at the cellular and molecular levels. The research focuses on identifying specific frequency ranges that may influence reproductive processes, including gametogenesis, fertilization, and early embryonic development[9]. Using advanced imaging techniques and molecular biology tools, they are mapping the effects of various resonance frequencies on gene expression patterns related to fertility. The university's approach also includes the development of novel, non-invasive devices for delivering targeted bioresonance therapies to reproductive organs[10].
Strengths: Comprehensive scientific approach, potential for fundamental breakthroughs, access to diverse research expertise. Weaknesses: Early-stage research, long path to clinical application, funding dependencies.
Core Bioresonance Fertility Research
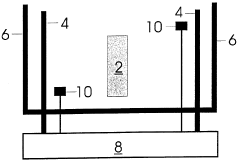
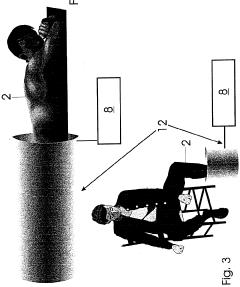
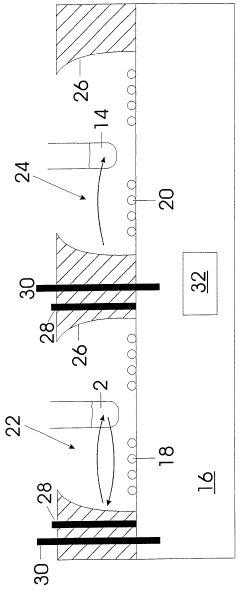
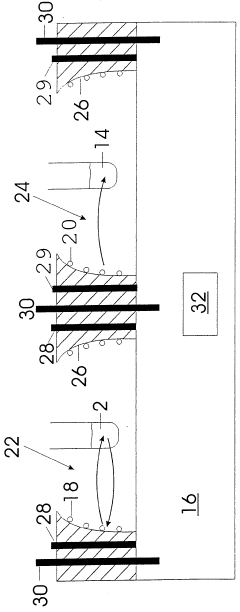
Device and method for activating objects
PatentWO1999021614A1
Innovation
- The device shields the Earth's magnetic field and generates a controlled, variable magnetic field to simulate its natural fluctuations, combined with thermal, electromagnetic, or optical activation methods to enhance resonance effects and stimulate electromagnetic radiation in substances or living organisms.
Device and method for activating objects
PatentWO1999021614A1
Innovation
- The device shields the Earth's magnetic field and generates a controlled, variable magnetic field to simulate its natural fluctuations, combined with thermal, electromagnetic, or optical activation methods to enhance resonance effects and stimulate electromagnetic radiation in substances or living organisms.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Devices
The regulatory framework for bioresonance devices in the context of fertility optimization is complex and varies significantly across different regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class III medical devices, requiring rigorous clinical trials and premarket approval before they can be marketed for fertility-related applications. This stringent approach reflects the FDA's concern over the lack of substantial scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance in fertility treatment.
In contrast, the European Union adopts a more lenient stance. Under the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), bioresonance devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. This classification allows for a less arduous path to market, often requiring only a conformity assessment by a notified body rather than extensive clinical trials. However, manufacturers must still demonstrate compliance with essential safety and performance requirements.
Several countries, including Germany and Switzerland, have embraced bioresonance technology more readily. In these nations, bioresonance devices are often regulated as complementary or alternative medicine tools, subject to less stringent oversight than traditional medical devices. This approach has facilitated wider adoption and integration of bioresonance into fertility clinics and wellness centers.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the challenge of balancing innovation with patient safety. The lack of standardized protocols for bioresonance therapy in fertility treatment has led to calls for more comprehensive regulatory guidelines. Some countries have implemented specific regulations for electromagnetic therapies, which encompass bioresonance devices, to ensure quality control and minimize potential risks to patients.
The global regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices is evolving, with increasing attention paid to their potential applications in fertility optimization. As more research emerges, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt, potentially leading to more harmonized approaches across different regions. This evolution may include the development of specialized guidelines for fertility-focused bioresonance applications, addressing concerns such as electromagnetic exposure limits and treatment protocols.
In contrast, the European Union adopts a more lenient stance. Under the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), bioresonance devices are typically classified as Class IIa or IIb, depending on their intended use and potential risks. This classification allows for a less arduous path to market, often requiring only a conformity assessment by a notified body rather than extensive clinical trials. However, manufacturers must still demonstrate compliance with essential safety and performance requirements.
Several countries, including Germany and Switzerland, have embraced bioresonance technology more readily. In these nations, bioresonance devices are often regulated as complementary or alternative medicine tools, subject to less stringent oversight than traditional medical devices. This approach has facilitated wider adoption and integration of bioresonance into fertility clinics and wellness centers.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the challenge of balancing innovation with patient safety. The lack of standardized protocols for bioresonance therapy in fertility treatment has led to calls for more comprehensive regulatory guidelines. Some countries have implemented specific regulations for electromagnetic therapies, which encompass bioresonance devices, to ensure quality control and minimize potential risks to patients.
The global regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices is evolving, with increasing attention paid to their potential applications in fertility optimization. As more research emerges, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt, potentially leading to more harmonized approaches across different regions. This evolution may include the development of specialized guidelines for fertility-focused bioresonance applications, addressing concerns such as electromagnetic exposure limits and treatment protocols.
Ethical Considerations in Fertility Technologies
The application of bioresonance in fertility optimization raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. As with any emerging technology in reproductive medicine, the potential benefits must be weighed against possible risks and ethical implications.
One primary concern is the safety and efficacy of bioresonance treatments for fertility. While proponents claim positive results, the scientific evidence supporting these claims remains limited. Ethical guidelines in medical practice emphasize the importance of evidence-based treatments, and the use of unproven technologies may expose patients to unnecessary risks or false hopes.
The principle of informed consent is paramount in fertility treatments. Patients must be fully aware of the experimental nature of bioresonance therapy, its potential risks, and the lack of conclusive scientific evidence. Healthcare providers have an ethical obligation to provide accurate information and ensure that patients make informed decisions about their fertility treatment options.
Privacy and data protection are critical ethical considerations in bioresonance fertility treatments. The technology often involves collecting and analyzing sensitive personal and medical information. Ensuring the confidentiality and security of this data is essential to protect patients' rights and prevent potential misuse or unauthorized access.
Equity and access to fertility treatments are also important ethical concerns. If bioresonance proves effective, it may become a sought-after fertility treatment. However, its availability may be limited due to cost or geographical factors, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities in access to reproductive healthcare.
The use of bioresonance in fertility treatments may also raise questions about the boundaries of medical intervention in natural reproductive processes. There are ongoing debates about the extent to which technology should be used to enhance or manipulate human fertility, and where to draw the line between medical necessity and elective enhancement.
Lastly, the potential long-term effects of bioresonance on offspring and future generations are unknown. Ethical considerations must include the welfare of any children born as a result of these treatments, as well as potential impacts on the human gene pool over time.
As research in this field progresses, it is crucial to establish clear ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks to govern the development and application of bioresonance in fertility treatments. These guidelines should prioritize patient safety, scientific validity, informed consent, and equitable access while respecting individual reproductive autonomy.
One primary concern is the safety and efficacy of bioresonance treatments for fertility. While proponents claim positive results, the scientific evidence supporting these claims remains limited. Ethical guidelines in medical practice emphasize the importance of evidence-based treatments, and the use of unproven technologies may expose patients to unnecessary risks or false hopes.
The principle of informed consent is paramount in fertility treatments. Patients must be fully aware of the experimental nature of bioresonance therapy, its potential risks, and the lack of conclusive scientific evidence. Healthcare providers have an ethical obligation to provide accurate information and ensure that patients make informed decisions about their fertility treatment options.
Privacy and data protection are critical ethical considerations in bioresonance fertility treatments. The technology often involves collecting and analyzing sensitive personal and medical information. Ensuring the confidentiality and security of this data is essential to protect patients' rights and prevent potential misuse or unauthorized access.
Equity and access to fertility treatments are also important ethical concerns. If bioresonance proves effective, it may become a sought-after fertility treatment. However, its availability may be limited due to cost or geographical factors, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities in access to reproductive healthcare.
The use of bioresonance in fertility treatments may also raise questions about the boundaries of medical intervention in natural reproductive processes. There are ongoing debates about the extent to which technology should be used to enhance or manipulate human fertility, and where to draw the line between medical necessity and elective enhancement.
Lastly, the potential long-term effects of bioresonance on offspring and future generations are unknown. Ethical considerations must include the welfare of any children born as a result of these treatments, as well as potential impacts on the human gene pool over time.
As research in this field progresses, it is crucial to establish clear ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks to govern the development and application of bioresonance in fertility treatments. These guidelines should prioritize patient safety, scientific validity, informed consent, and equitable access while respecting individual reproductive autonomy.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!