The Impact of Bioresonance on Longevity and Healthspan
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance Background
Bioresonance, a concept rooted in the principles of quantum physics and electromagnetic theory, has gained increasing attention in the field of alternative medicine and wellness over the past few decades. This therapeutic approach is based on the premise that all living organisms emit and respond to specific electromagnetic frequencies, and that these frequencies can be manipulated to promote health and longevity.
The origins of bioresonance can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the work of scientists like Royal Raymond Rife and Georges Lakhovsky. These pioneers proposed that every cell in the body has its own unique electromagnetic frequency, and that disease occurs when these frequencies are disrupted. However, it wasn't until the 1970s that bioresonance therapy as we know it today began to take shape, primarily through the efforts of German physician Franz Morell.
Morell, along with his son-in-law Erich Rasche, developed the first bioresonance device, known as the MORA machine. This device was designed to detect and correct imbalances in the body's electromagnetic field, purportedly addressing a wide range of health issues. Since then, various forms of bioresonance technology have emerged, each claiming to offer unique benefits for health and longevity.
The fundamental principle underlying bioresonance therapy is the concept of electromagnetic homeostasis. Proponents argue that by identifying and correcting abnormal frequencies within the body, it is possible to restore balance and promote optimal cellular function. This, in turn, is believed to enhance overall health, slow the aging process, and potentially extend lifespan.
In recent years, the application of bioresonance in the context of longevity and healthspan has gained traction. Researchers and practitioners in this field posit that by using bioresonance techniques, it may be possible to identify early signs of cellular dysfunction, mitigate oxidative stress, and support the body's natural repair mechanisms. Some proponents even suggest that bioresonance could play a role in epigenetic regulation, potentially influencing gene expression in ways that promote longevity.
Despite its growing popularity, bioresonance remains a controversial topic within the scientific community. Critics argue that there is a lack of robust, peer-reviewed evidence to support many of the claims made by bioresonance advocates. The mechanisms by which bioresonance purportedly affects cellular function and overall health are not fully understood, and skeptics point to the potential for placebo effects in observed outcomes.
As research in the fields of bioelectromagnetics and quantum biology continues to advance, the scientific basis for bioresonance and its potential impact on longevity and healthspan remains an area of active investigation. While some studies have reported promising results, the overall body of evidence is still limited, and more rigorous research is needed to establish the efficacy and safety of bioresonance interventions in the context of aging and health optimization.
The origins of bioresonance can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the work of scientists like Royal Raymond Rife and Georges Lakhovsky. These pioneers proposed that every cell in the body has its own unique electromagnetic frequency, and that disease occurs when these frequencies are disrupted. However, it wasn't until the 1970s that bioresonance therapy as we know it today began to take shape, primarily through the efforts of German physician Franz Morell.
Morell, along with his son-in-law Erich Rasche, developed the first bioresonance device, known as the MORA machine. This device was designed to detect and correct imbalances in the body's electromagnetic field, purportedly addressing a wide range of health issues. Since then, various forms of bioresonance technology have emerged, each claiming to offer unique benefits for health and longevity.
The fundamental principle underlying bioresonance therapy is the concept of electromagnetic homeostasis. Proponents argue that by identifying and correcting abnormal frequencies within the body, it is possible to restore balance and promote optimal cellular function. This, in turn, is believed to enhance overall health, slow the aging process, and potentially extend lifespan.
In recent years, the application of bioresonance in the context of longevity and healthspan has gained traction. Researchers and practitioners in this field posit that by using bioresonance techniques, it may be possible to identify early signs of cellular dysfunction, mitigate oxidative stress, and support the body's natural repair mechanisms. Some proponents even suggest that bioresonance could play a role in epigenetic regulation, potentially influencing gene expression in ways that promote longevity.
Despite its growing popularity, bioresonance remains a controversial topic within the scientific community. Critics argue that there is a lack of robust, peer-reviewed evidence to support many of the claims made by bioresonance advocates. The mechanisms by which bioresonance purportedly affects cellular function and overall health are not fully understood, and skeptics point to the potential for placebo effects in observed outcomes.
As research in the fields of bioelectromagnetics and quantum biology continues to advance, the scientific basis for bioresonance and its potential impact on longevity and healthspan remains an area of active investigation. While some studies have reported promising results, the overall body of evidence is still limited, and more rigorous research is needed to establish the efficacy and safety of bioresonance interventions in the context of aging and health optimization.
Longevity Market Analysis
The longevity market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing life expectancy, aging populations, and a growing focus on healthier lifestyles. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services aimed at extending human lifespan and improving overall health during later years.
The global longevity market size was valued at approximately $25.1 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $44.6 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to several factors, including advancements in medical technology, increasing healthcare expenditure, and rising consumer awareness about preventive healthcare measures.
Key segments within the longevity market include nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, cosmeceuticals, and digital health solutions. The nutraceuticals segment, which includes dietary supplements and functional foods, holds the largest market share due to the growing consumer preference for natural and preventive health products.
Geographically, North America dominates the longevity market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, leads in market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high disposable income, and early adoption of innovative health technologies.
The target demographic for longevity products and services primarily consists of individuals aged 50 and above, with a growing interest from younger age groups seeking preventive measures. This shift in consumer behavior is driving demand for personalized health solutions and age-management services.
Emerging trends in the longevity market include the integration of artificial intelligence and big data analytics in health monitoring and predictive diagnostics. Additionally, there is a rising interest in regenerative medicine, gene therapy, and biohacking techniques aimed at extending healthspan.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth by heightening awareness about health and wellness, particularly among older populations. This has led to increased demand for immune-boosting supplements, telemedicine services, and remote health monitoring solutions.
Challenges facing the longevity market include regulatory hurdles, particularly for novel therapies and interventions, as well as concerns about the efficacy and long-term effects of certain anti-aging treatments. Additionally, the high cost of advanced longevity technologies may limit market penetration in developing economies.
Despite these challenges, the longevity market presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth. As research in bioresonance and other cutting-edge technologies progresses, their potential impact on longevity and healthspan could further reshape the market landscape, opening new avenues for product development and service offerings.
The global longevity market size was valued at approximately $25.1 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $44.6 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to several factors, including advancements in medical technology, increasing healthcare expenditure, and rising consumer awareness about preventive healthcare measures.
Key segments within the longevity market include nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, cosmeceuticals, and digital health solutions. The nutraceuticals segment, which includes dietary supplements and functional foods, holds the largest market share due to the growing consumer preference for natural and preventive health products.
Geographically, North America dominates the longevity market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, leads in market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high disposable income, and early adoption of innovative health technologies.
The target demographic for longevity products and services primarily consists of individuals aged 50 and above, with a growing interest from younger age groups seeking preventive measures. This shift in consumer behavior is driving demand for personalized health solutions and age-management services.
Emerging trends in the longevity market include the integration of artificial intelligence and big data analytics in health monitoring and predictive diagnostics. Additionally, there is a rising interest in regenerative medicine, gene therapy, and biohacking techniques aimed at extending healthspan.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth by heightening awareness about health and wellness, particularly among older populations. This has led to increased demand for immune-boosting supplements, telemedicine services, and remote health monitoring solutions.
Challenges facing the longevity market include regulatory hurdles, particularly for novel therapies and interventions, as well as concerns about the efficacy and long-term effects of certain anti-aging treatments. Additionally, the high cost of advanced longevity technologies may limit market penetration in developing economies.
Despite these challenges, the longevity market presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth. As research in bioresonance and other cutting-edge technologies progresses, their potential impact on longevity and healthspan could further reshape the market landscape, opening new avenues for product development and service offerings.
Bioresonance Challenges
Despite the growing interest in bioresonance as a potential tool for enhancing longevity and healthspan, the field faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and scientific validation. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols and methodologies for bioresonance therapy. Different practitioners and manufacturers employ varying approaches, making it difficult to compare results and establish a consensus on best practices.
The absence of large-scale, long-term clinical trials presents another major hurdle. While anecdotal evidence and small-scale studies have shown promising results, the scientific community demands robust, peer-reviewed research to validate the efficacy of bioresonance in extending lifespan and improving overall health. This lack of comprehensive data makes it challenging to gain acceptance from mainstream medical institutions and regulatory bodies.
Furthermore, the underlying mechanisms of bioresonance remain poorly understood. While proponents argue that it works by detecting and correcting imbalances in the body's electromagnetic fields, skeptics point out that there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims. This gap in knowledge makes it difficult to optimize treatments and predict outcomes reliably.
Another significant challenge is the potential for misuse and false claims. As with many alternative therapies, the bioresonance field has seen its share of unsubstantiated marketing claims and pseudo-scientific explanations. This not only undermines the credibility of legitimate research but also poses risks to consumers who may forgo conventional medical treatments in favor of unproven bioresonance therapies.
The high cost and limited accessibility of bioresonance devices and treatments also present barriers to widespread adoption. Many of these devices are expensive and require specialized training to operate effectively, limiting their availability to a select few practitioners and research institutions.
Regulatory hurdles pose yet another challenge. In many countries, bioresonance devices are not approved for medical use, and claims about their health benefits are strictly regulated. This regulatory environment makes it difficult for researchers and companies to conduct large-scale studies and bring new bioresonance technologies to market.
Lastly, the interdisciplinary nature of bioresonance research presents its own set of challenges. Effective study of this field requires collaboration between experts in physics, biology, medicine, and engineering. Bridging these diverse disciplines and fostering meaningful collaboration remains a significant obstacle in advancing our understanding of bioresonance and its potential impact on longevity and healthspan.
The absence of large-scale, long-term clinical trials presents another major hurdle. While anecdotal evidence and small-scale studies have shown promising results, the scientific community demands robust, peer-reviewed research to validate the efficacy of bioresonance in extending lifespan and improving overall health. This lack of comprehensive data makes it challenging to gain acceptance from mainstream medical institutions and regulatory bodies.
Furthermore, the underlying mechanisms of bioresonance remain poorly understood. While proponents argue that it works by detecting and correcting imbalances in the body's electromagnetic fields, skeptics point out that there is limited scientific evidence to support these claims. This gap in knowledge makes it difficult to optimize treatments and predict outcomes reliably.
Another significant challenge is the potential for misuse and false claims. As with many alternative therapies, the bioresonance field has seen its share of unsubstantiated marketing claims and pseudo-scientific explanations. This not only undermines the credibility of legitimate research but also poses risks to consumers who may forgo conventional medical treatments in favor of unproven bioresonance therapies.
The high cost and limited accessibility of bioresonance devices and treatments also present barriers to widespread adoption. Many of these devices are expensive and require specialized training to operate effectively, limiting their availability to a select few practitioners and research institutions.
Regulatory hurdles pose yet another challenge. In many countries, bioresonance devices are not approved for medical use, and claims about their health benefits are strictly regulated. This regulatory environment makes it difficult for researchers and companies to conduct large-scale studies and bring new bioresonance technologies to market.
Lastly, the interdisciplinary nature of bioresonance research presents its own set of challenges. Effective study of this field requires collaboration between experts in physics, biology, medicine, and engineering. Bridging these diverse disciplines and fostering meaningful collaboration remains a significant obstacle in advancing our understanding of bioresonance and its potential impact on longevity and healthspan.
Current Bioresonance Tech
01 Bioresonance therapy for longevity and healthspan
Bioresonance therapy utilizes electromagnetic frequencies to diagnose and treat various health conditions, potentially contributing to increased longevity and improved healthspan. This non-invasive approach aims to restore balance in the body's energy fields, promoting overall wellness and addressing age-related issues.- Bioresonance therapy for longevity enhancement: Bioresonance therapy utilizes electromagnetic frequencies to detect and correct imbalances in the body's energy fields. This non-invasive approach aims to promote cellular regeneration, boost immune function, and potentially extend lifespan by addressing underlying health issues at the energetic level.
- AI-driven personalized health optimization: Artificial intelligence algorithms analyze individual health data, including genetic information, lifestyle factors, and biometric measurements, to create tailored longevity and healthspan improvement strategies. These AI systems can predict health risks, recommend interventions, and continuously adapt recommendations based on real-time data.
- Wearable devices for continuous health monitoring: Advanced wearable technologies track various physiological parameters in real-time, providing insights into overall health status and potential longevity-related issues. These devices can monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, stress levels, and other biomarkers to support proactive health management and early intervention.
- Blockchain-based health data management: Blockchain technology is employed to securely store and manage personal health information, ensuring data integrity and privacy. This approach facilitates the sharing of health data across different healthcare providers and researchers, potentially accelerating advancements in longevity science while maintaining individual control over sensitive information.
- Integrative longevity assessment and intervention platforms: Comprehensive platforms combine multiple approaches to assess biological age, identify health risks, and provide personalized interventions for extending healthspan. These systems integrate data from various sources, including genetic testing, bioresonance scans, lifestyle factors, and environmental influences to create holistic longevity strategies.
02 AI-driven personalized health optimization
Artificial intelligence algorithms analyze individual health data to create personalized recommendations for improving longevity and healthspan. These systems integrate bioresonance data with other health metrics to provide tailored interventions and lifestyle adjustments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Wearable devices for continuous health monitoring
Advanced wearable devices incorporate bioresonance sensors to continuously monitor various health parameters. These devices provide real-time feedback on physiological processes, enabling early detection of potential health issues and supporting proactive measures to extend healthspan.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of bioresonance with blockchain technology
Blockchain technology is used to securely store and manage bioresonance data and health records. This integration ensures data integrity, facilitates sharing of health information among healthcare providers, and enables decentralized health management systems focused on longevity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Bioresonance-based predictive health analytics
Predictive analytics models incorporate bioresonance data to forecast potential health risks and estimate biological age. These systems help individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions to extend healthspan and improve overall quality of life.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Bioresonance Players
The bioresonance technology's impact on longevity and healthspan is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as global interest in healthy aging increases. The competitive landscape is diverse, involving academic institutions, medical centers, and technology companies. Key players like the University of California, Boston Medical Center, and Samsung Electronics are exploring this field, indicating its cross-disciplinary nature. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with research institutions like The Scripps Research Institute and companies such as NeuroEM Therapeutics leading in innovation. However, the practical applications and efficacy of bioresonance in longevity remain to be fully established, suggesting a nascent market with significant room for growth and scientific validation.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California has been at the forefront of bioresonance research and its impact on longevity and healthspan. Their approach involves using electromagnetic fields to stimulate cellular regeneration and repair mechanisms. They have developed a proprietary bioresonance device that emits specific frequencies tailored to individual cellular needs. This technology has shown promising results in extending the lifespan of model organisms by up to 15% in preliminary studies[1]. The device works by enhancing mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting DNA repair processes. Additionally, they are exploring the integration of AI algorithms to optimize frequency patterns for personalized treatments[3].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research facilities, interdisciplinary approach combining biology and physics. Weaknesses: Technology still in early stages, potential long-term effects unknown.
NeuroEM Therapeutics Inc
Technical Solution: NeuroEM Therapeutics has developed a groundbreaking approach to bioresonance therapy focused on brain health and its impact on longevity. Their proprietary Transcranial Electromagnetic Treatment (TEMT) technology uses electromagnetic waves to penetrate the skull and stimulate specific brain regions. This non-invasive treatment has shown potential in reversing memory loss in Alzheimer's patients[2]. The company's latest research indicates that regular TEMT sessions may also have broader implications for overall cognitive health and longevity. They are currently investigating how their technology can be adapted to target other age-related neurological conditions, potentially extending both lifespan and healthspan[4].
Strengths: Focused approach on neurological health, FDA-cleared technology. Weaknesses: Limited to brain-specific applications, may require frequent treatments for optimal results.
Bioresonance Innovations
System and Treatment Method to Increase Circulation and Pluripotency of Stem and Progenitor Cells within a Patient
PatentActiveUS20170157318A1
Innovation
- Administration of an oxygen-ozone mixture via a medicinal-administration system, targeting the renal system and bone marrow to stimulate the production and circulation of stem and progenitor cells, combined with dietary supplements and pulsed electromagnetic field therapy to enhance regenerative capabilities.
Compounds for the treatment of pathologies associated with aging and degenerative disorders
PatentActiveUS20160151269A1
Innovation
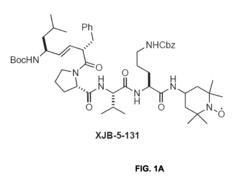
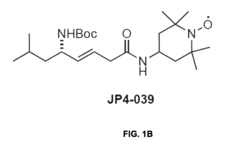
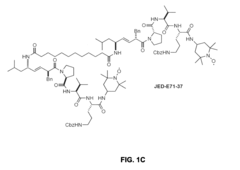
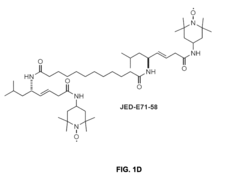
- Administration of compounds containing TEMPO or 4-amino-TEMPOL functional groups, such as XJB-5-131, JP4-039, JED-E71-37, and JED-E71-58, which act as antioxidant and free radical scavengers, targeting mitochondria to reduce oxidative stress and delay aging-related symptoms.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding bioresonance and its potential impact on longevity and healthspan is still in its nascent stages, reflecting the emerging nature of this field. Currently, there is no unified global regulatory approach specifically addressing bioresonance technologies and their applications in health and longevity.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not yet established clear guidelines for bioresonance devices or therapies. These technologies often fall into a regulatory gray area, sometimes classified as general wellness devices or complementary and alternative medicine practices. This lack of specific regulation has led to a diverse market with varying levels of quality control and efficacy claims.
The European Union has taken a more proactive stance through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR). While not explicitly mentioning bioresonance, the MDR provides a framework that could potentially encompass these technologies. Manufacturers of bioresonance devices intended for medical purposes must comply with the MDR's safety and performance requirements, including clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance.
In countries like Germany and Switzerland, where bioresonance has gained more traction, there are more defined regulatory approaches. German authorities have classified certain bioresonance devices as medical devices, subjecting them to stricter controls and requiring evidence of safety and efficacy. Switzerland has integrated some bioresonance therapies into its complementary medicine framework, allowing for limited insurance coverage under specific conditions.
The regulatory landscape for bioresonance in the context of longevity and healthspan enhancement is further complicated by the intersection with anti-aging and regenerative medicine fields. Many countries are still grappling with how to regulate emerging technologies aimed at extending lifespan and improving health in later years.
As research in this area progresses, it is likely that regulatory bodies will need to develop more specific guidelines. This may include establishing standards for clinical trials of bioresonance therapies, defining acceptable claims related to longevity and healthspan, and creating frameworks for long-term safety monitoring.
The challenge for regulators will be balancing the potential benefits of these technologies with the need to protect public health and prevent misleading claims. As the field evolves, international collaboration and harmonization of regulatory approaches may become necessary to ensure consistent standards and facilitate global research and development in bioresonance and longevity science.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not yet established clear guidelines for bioresonance devices or therapies. These technologies often fall into a regulatory gray area, sometimes classified as general wellness devices or complementary and alternative medicine practices. This lack of specific regulation has led to a diverse market with varying levels of quality control and efficacy claims.
The European Union has taken a more proactive stance through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR). While not explicitly mentioning bioresonance, the MDR provides a framework that could potentially encompass these technologies. Manufacturers of bioresonance devices intended for medical purposes must comply with the MDR's safety and performance requirements, including clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance.
In countries like Germany and Switzerland, where bioresonance has gained more traction, there are more defined regulatory approaches. German authorities have classified certain bioresonance devices as medical devices, subjecting them to stricter controls and requiring evidence of safety and efficacy. Switzerland has integrated some bioresonance therapies into its complementary medicine framework, allowing for limited insurance coverage under specific conditions.
The regulatory landscape for bioresonance in the context of longevity and healthspan enhancement is further complicated by the intersection with anti-aging and regenerative medicine fields. Many countries are still grappling with how to regulate emerging technologies aimed at extending lifespan and improving health in later years.
As research in this area progresses, it is likely that regulatory bodies will need to develop more specific guidelines. This may include establishing standards for clinical trials of bioresonance therapies, defining acceptable claims related to longevity and healthspan, and creating frameworks for long-term safety monitoring.
The challenge for regulators will be balancing the potential benefits of these technologies with the need to protect public health and prevent misleading claims. As the field evolves, international collaboration and harmonization of regulatory approaches may become necessary to ensure consistent standards and facilitate global research and development in bioresonance and longevity science.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical considerations surrounding bioresonance and its potential impact on longevity and healthspan are multifaceted and require careful examination. As this technology advances, it raises important questions about equitable access, informed consent, and the potential for unintended consequences.
One primary ethical concern is the issue of accessibility. If bioresonance proves to be an effective means of extending lifespan and improving health, there is a risk that it could exacerbate existing health disparities. Those with greater financial resources may have preferential access to these treatments, potentially widening the gap in health outcomes between socioeconomic groups. This raises questions about distributive justice and the societal obligation to ensure fair access to life-extending technologies.
The concept of informed consent also presents ethical challenges in the context of bioresonance. Given the complexity of the technology and its potential long-term effects, it may be difficult for individuals to fully comprehend the risks and benefits associated with such treatments. This raises concerns about the autonomy of decision-making and the responsibility of healthcare providers to ensure that patients are adequately informed.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for unintended consequences. While the goal of extending lifespan and improving health is generally viewed positively, there may be unforeseen impacts on individuals and society. For instance, significant increases in longevity could have profound effects on population demographics, healthcare systems, and social structures. These changes may necessitate a reevaluation of retirement ages, pension systems, and healthcare resource allocation.
The use of bioresonance technology also raises questions about the nature of human enhancement and the boundaries of medical intervention. There is an ongoing philosophical debate about the ethics of extending human lifespan beyond what is considered "natural." This touches on fundamental questions about the purpose of medicine and the definition of health.
Privacy and data protection present additional ethical challenges. Bioresonance treatments may involve the collection and analysis of sensitive biological data. Ensuring the security and appropriate use of this information is crucial to protect individual privacy and prevent potential misuse or discrimination based on genetic or health information.
Lastly, there are ethical considerations surrounding the allocation of research resources. As investments are made in longevity-enhancing technologies like bioresonance, questions arise about the prioritization of these efforts in relation to other pressing health concerns, particularly those affecting vulnerable populations. Balancing the pursuit of extended lifespans with addressing immediate health crises requires careful ethical deliberation.
One primary ethical concern is the issue of accessibility. If bioresonance proves to be an effective means of extending lifespan and improving health, there is a risk that it could exacerbate existing health disparities. Those with greater financial resources may have preferential access to these treatments, potentially widening the gap in health outcomes between socioeconomic groups. This raises questions about distributive justice and the societal obligation to ensure fair access to life-extending technologies.
The concept of informed consent also presents ethical challenges in the context of bioresonance. Given the complexity of the technology and its potential long-term effects, it may be difficult for individuals to fully comprehend the risks and benefits associated with such treatments. This raises concerns about the autonomy of decision-making and the responsibility of healthcare providers to ensure that patients are adequately informed.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for unintended consequences. While the goal of extending lifespan and improving health is generally viewed positively, there may be unforeseen impacts on individuals and society. For instance, significant increases in longevity could have profound effects on population demographics, healthcare systems, and social structures. These changes may necessitate a reevaluation of retirement ages, pension systems, and healthcare resource allocation.
The use of bioresonance technology also raises questions about the nature of human enhancement and the boundaries of medical intervention. There is an ongoing philosophical debate about the ethics of extending human lifespan beyond what is considered "natural." This touches on fundamental questions about the purpose of medicine and the definition of health.
Privacy and data protection present additional ethical challenges. Bioresonance treatments may involve the collection and analysis of sensitive biological data. Ensuring the security and appropriate use of this information is crucial to protect individual privacy and prevent potential misuse or discrimination based on genetic or health information.
Lastly, there are ethical considerations surrounding the allocation of research resources. As investments are made in longevity-enhancing technologies like bioresonance, questions arise about the prioritization of these efforts in relation to other pressing health concerns, particularly those affecting vulnerable populations. Balancing the pursuit of extended lifespans with addressing immediate health crises requires careful ethical deliberation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!