Bioresonance in Gut Microbiome Balancing: Prospects and Challenges
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance and Gut Microbiome: Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a concept rooted in the principles of quantum physics and energy medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential application in gut microbiome balancing. This emerging field of study explores the intricate relationship between electromagnetic frequencies and the complex ecosystem of microorganisms residing in the human digestive tract.
The gut microbiome, comprising trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a crucial role in human health, influencing everything from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and mental health. As research continues to unveil the profound impact of gut health on overall well-being, there is a growing interest in developing innovative approaches to maintain and restore microbial balance.
Bioresonance therapy posits that every organism and cell in the body emits a unique electromagnetic frequency. By detecting and manipulating these frequencies, practitioners aim to identify and address imbalances within the body, including those within the gut microbiome. The technology behind bioresonance involves sophisticated devices that purportedly measure and modulate these frequencies, potentially influencing the composition and activity of gut microbiota.
The convergence of bioresonance and gut microbiome research represents a novel frontier in personalized medicine and holistic health approaches. This intersection aims to leverage the principles of energy medicine to develop non-invasive, targeted interventions for gut health optimization. The potential applications range from addressing digestive disorders and autoimmune conditions to enhancing overall immune function and mental well-being.
However, the field faces significant challenges and skepticism from the mainstream medical community. The lack of robust scientific evidence and standardized protocols has led to questions about the efficacy and mechanism of action of bioresonance therapy in gut microbiome modulation. Critics argue that the theoretical foundations of bioresonance may not align with established principles of biology and physics.
As research in this area progresses, the primary objectives are to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of bioresonance therapy, establish standardized protocols for gut microbiome assessment and intervention, and conduct rigorous clinical trials to evaluate its efficacy and safety. Additionally, there is a need to develop more sensitive and accurate devices for detecting and modulating electromagnetic frequencies associated with gut microbiota.
The exploration of bioresonance in gut microbiome balancing represents a bold step towards integrating alternative and conventional medicine. It reflects a growing trend towards holistic, personalized health approaches that consider the complex interplay between various bodily systems and environmental factors. As technology advances and our understanding of the gut microbiome deepens, the potential for bioresonance to offer novel solutions in gut health management continues to evolve, promising exciting developments in the field of integrative medicine.
The gut microbiome, comprising trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms, plays a crucial role in human health, influencing everything from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and mental health. As research continues to unveil the profound impact of gut health on overall well-being, there is a growing interest in developing innovative approaches to maintain and restore microbial balance.
Bioresonance therapy posits that every organism and cell in the body emits a unique electromagnetic frequency. By detecting and manipulating these frequencies, practitioners aim to identify and address imbalances within the body, including those within the gut microbiome. The technology behind bioresonance involves sophisticated devices that purportedly measure and modulate these frequencies, potentially influencing the composition and activity of gut microbiota.
The convergence of bioresonance and gut microbiome research represents a novel frontier in personalized medicine and holistic health approaches. This intersection aims to leverage the principles of energy medicine to develop non-invasive, targeted interventions for gut health optimization. The potential applications range from addressing digestive disorders and autoimmune conditions to enhancing overall immune function and mental well-being.
However, the field faces significant challenges and skepticism from the mainstream medical community. The lack of robust scientific evidence and standardized protocols has led to questions about the efficacy and mechanism of action of bioresonance therapy in gut microbiome modulation. Critics argue that the theoretical foundations of bioresonance may not align with established principles of biology and physics.
As research in this area progresses, the primary objectives are to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of bioresonance therapy, establish standardized protocols for gut microbiome assessment and intervention, and conduct rigorous clinical trials to evaluate its efficacy and safety. Additionally, there is a need to develop more sensitive and accurate devices for detecting and modulating electromagnetic frequencies associated with gut microbiota.
The exploration of bioresonance in gut microbiome balancing represents a bold step towards integrating alternative and conventional medicine. It reflects a growing trend towards holistic, personalized health approaches that consider the complex interplay between various bodily systems and environmental factors. As technology advances and our understanding of the gut microbiome deepens, the potential for bioresonance to offer novel solutions in gut health management continues to evolve, promising exciting developments in the field of integrative medicine.
Market Analysis for Microbiome Balancing Solutions
The market for microbiome balancing solutions has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of the gut microbiome's role in overall health and well-being. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services, including probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and diagnostic tools for microbiome analysis.
The global microbiome market size was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.2% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of digestive disorders, increasing research on the human microbiome, and growing consumer interest in preventive healthcare.
Within the microbiome market, probiotics hold the largest share, accounting for over 60% of the total market value. The probiotics segment is expected to maintain its dominance due to the wide availability of probiotic supplements and their incorporation into functional foods and beverages.
Geographically, North America leads the microbiome market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to high consumer awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and substantial investments in microbiome research.
The market is characterized by intense competition, with key players including DuPont, Chr. Hansen, Yakult, Nestle, and Danone. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge.
Emerging trends in the microbiome balancing solutions market include the development of personalized microbiome-based therapies, the integration of artificial intelligence for microbiome analysis, and the exploration of novel delivery mechanisms for probiotics and prebiotics.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers increasingly focus on immune health and overall well-being. This has led to a surge in demand for microbiome-related products, particularly those claiming to boost immunity.
However, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements, limited reimbursement policies for microbiome-based therapies, and the need for more extensive clinical evidence to support product claims. Additionally, consumer skepticism regarding the efficacy of some microbiome products poses a challenge to market growth.
Despite these challenges, the microbiome balancing solutions market is poised for continued expansion, driven by ongoing scientific discoveries, technological advancements, and growing consumer interest in holistic health approaches. The integration of bioresonance technology in microbiome balancing represents a promising avenue for innovation, potentially offering new solutions for gut health management and personalized nutrition.
The global microbiome market size was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.2% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the rising prevalence of digestive disorders, increasing research on the human microbiome, and growing consumer interest in preventive healthcare.
Within the microbiome market, probiotics hold the largest share, accounting for over 60% of the total market value. The probiotics segment is expected to maintain its dominance due to the wide availability of probiotic supplements and their incorporation into functional foods and beverages.
Geographically, North America leads the microbiome market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to high consumer awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and substantial investments in microbiome research.
The market is characterized by intense competition, with key players including DuPont, Chr. Hansen, Yakult, Nestle, and Danone. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to introduce innovative products and gain a competitive edge.
Emerging trends in the microbiome balancing solutions market include the development of personalized microbiome-based therapies, the integration of artificial intelligence for microbiome analysis, and the exploration of novel delivery mechanisms for probiotics and prebiotics.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth, as consumers increasingly focus on immune health and overall well-being. This has led to a surge in demand for microbiome-related products, particularly those claiming to boost immunity.
However, the market faces challenges such as stringent regulatory requirements, limited reimbursement policies for microbiome-based therapies, and the need for more extensive clinical evidence to support product claims. Additionally, consumer skepticism regarding the efficacy of some microbiome products poses a challenge to market growth.
Despite these challenges, the microbiome balancing solutions market is poised for continued expansion, driven by ongoing scientific discoveries, technological advancements, and growing consumer interest in holistic health approaches. The integration of bioresonance technology in microbiome balancing represents a promising avenue for innovation, potentially offering new solutions for gut health management and personalized nutrition.
Current State of Bioresonance in Microbiome Therapy
Bioresonance therapy has gained increasing attention in the field of gut microbiome balancing, with current applications showing promising results. This non-invasive approach utilizes electromagnetic frequencies to detect and address imbalances in the body's energy fields, potentially influencing the gut microbiome composition and function.
Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of bioresonance in modulating gut microbial communities. Researchers have observed shifts in bacterial populations following bioresonance treatments, with increases in beneficial bacteria and decreases in potentially harmful strains. These changes have been associated with improvements in gastrointestinal symptoms and overall gut health.
Clinical applications of bioresonance in microbiome therapy are expanding. Practitioners are using bioresonance devices to assess individual microbial profiles and tailor treatments accordingly. This personalized approach aims to restore balance to the gut ecosystem by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppressing pathogenic organisms.
However, the current state of bioresonance in microbiome therapy faces several challenges. The lack of standardized protocols and limited large-scale clinical trials hinder widespread acceptance in mainstream medicine. Additionally, the mechanisms by which bioresonance influences the microbiome are not fully understood, necessitating further research to elucidate the underlying biological processes.
Despite these challenges, technological advancements are driving progress in the field. New bioresonance devices with improved sensitivity and specificity are being developed, enabling more accurate detection of microbial imbalances. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is enhancing the interpretation of bioresonance data, leading to more precise treatment recommendations.
Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and technology developers is crucial for advancing the field. Ongoing studies are exploring the potential synergies between bioresonance and other microbiome-modulating therapies, such as probiotics and prebiotics. This integrative approach may offer more comprehensive solutions for addressing gut dysbiosis and related health issues.
As the understanding of the gut-brain axis continues to evolve, bioresonance therapy is being investigated for its potential impact on neurological and mental health conditions linked to gut microbiome imbalances. This emerging area of research highlights the broader implications of bioresonance in microbiome therapy beyond gastrointestinal health.
Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of bioresonance in modulating gut microbial communities. Researchers have observed shifts in bacterial populations following bioresonance treatments, with increases in beneficial bacteria and decreases in potentially harmful strains. These changes have been associated with improvements in gastrointestinal symptoms and overall gut health.
Clinical applications of bioresonance in microbiome therapy are expanding. Practitioners are using bioresonance devices to assess individual microbial profiles and tailor treatments accordingly. This personalized approach aims to restore balance to the gut ecosystem by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppressing pathogenic organisms.
However, the current state of bioresonance in microbiome therapy faces several challenges. The lack of standardized protocols and limited large-scale clinical trials hinder widespread acceptance in mainstream medicine. Additionally, the mechanisms by which bioresonance influences the microbiome are not fully understood, necessitating further research to elucidate the underlying biological processes.
Despite these challenges, technological advancements are driving progress in the field. New bioresonance devices with improved sensitivity and specificity are being developed, enabling more accurate detection of microbial imbalances. Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is enhancing the interpretation of bioresonance data, leading to more precise treatment recommendations.
Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and technology developers is crucial for advancing the field. Ongoing studies are exploring the potential synergies between bioresonance and other microbiome-modulating therapies, such as probiotics and prebiotics. This integrative approach may offer more comprehensive solutions for addressing gut dysbiosis and related health issues.
As the understanding of the gut-brain axis continues to evolve, bioresonance therapy is being investigated for its potential impact on neurological and mental health conditions linked to gut microbiome imbalances. This emerging area of research highlights the broader implications of bioresonance in microbiome therapy beyond gastrointestinal health.
Existing Bioresonance Approaches for Gut Health
01 Bioresonance therapy for gut microbiome balancing
Bioresonance therapy is used to balance the gut microbiome by applying specific electromagnetic frequencies to the body. This non-invasive approach aims to restore harmony in the gut ecosystem, potentially improving digestive health and overall well-being. The therapy may involve frequency-based diagnostics and treatments tailored to individual microbiome profiles.- Bioresonance therapy for gut microbiome balance: Bioresonance therapy is used to detect and correct imbalances in the gut microbiome. This non-invasive approach uses electromagnetic frequencies to identify and address dysbiosis, potentially improving overall gut health and function.
- Probiotic and prebiotic interventions: Combining bioresonance therapy with probiotic and prebiotic interventions to support gut microbiome balance. This approach aims to enhance beneficial bacteria populations while reducing harmful microorganisms, promoting a healthier gut environment.
- Personalized microbiome analysis and treatment: Utilizing advanced diagnostic tools and bioresonance technology to perform personalized microbiome analysis. This information is used to develop tailored treatment plans for restoring gut microbiome balance, addressing individual patient needs.
- Integration of dietary and lifestyle modifications: Incorporating dietary and lifestyle modifications alongside bioresonance therapy to support gut microbiome balance. This holistic approach includes recommendations for specific foods, stress reduction techniques, and exercise regimens to complement the bioresonance treatment.
- Monitoring and maintenance of gut microbiome balance: Implementing ongoing monitoring and maintenance protocols using bioresonance technology to ensure long-term gut microbiome balance. This includes regular check-ups, adjustments to treatment plans, and continuous assessment of microbiome health markers.
02 Probiotic and prebiotic interventions for microbiome modulation
Targeted probiotic and prebiotic interventions are employed to modulate the gut microbiome composition. These interventions may include specific strains of beneficial bacteria, as well as dietary fibers and compounds that support their growth. The approach aims to enhance microbial diversity and promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms in the gut.Expand Specific Solutions03 Personalized microbiome analysis and treatment
Advanced diagnostic techniques are used to analyze individual gut microbiome profiles, allowing for personalized treatment strategies. This may involve genomic sequencing, metabolomic analysis, and AI-driven data interpretation to identify imbalances and recommend tailored interventions for restoring microbiome equilibrium.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dietary and lifestyle interventions for microbiome health
Comprehensive approaches combining dietary modifications and lifestyle interventions are used to support gut microbiome balance. This may include specific nutritional plans, stress reduction techniques, exercise regimens, and sleep optimization strategies designed to create an environment conducive to a healthy and diverse gut microbiome.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel compounds and formulations for microbiome modulation
Innovative compounds and formulations are developed to specifically target and modulate the gut microbiome. These may include engineered probiotics, postbiotics, synbiotics, or other bioactive substances designed to interact with the microbiome in precise ways, potentially offering more targeted and effective approaches to balancing gut microbial communities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and Microbiome Research
The bioresonance technology for gut microbiome balancing is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential due to increasing interest in personalized medicine and microbiome health. The global market for microbiome-based therapies is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. However, the technology's efficacy and standardization remain challenges. Key players like Nestlé, DSM, and Novozymes are investing in microbiome research, while emerging companies such as MaaT Pharma and IsoThrive are developing specialized gut health solutions. Academic institutions like Washington University in St. Louis and Duke University are contributing to the fundamental research, indicating a collaborative ecosystem between industry and academia in advancing this field.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Technical Solution: Nestlé's approach to bioresonance in gut microbiome balancing involves the development of specialized probiotic strains and prebiotic compounds. Their research focuses on identifying specific bacterial strains that can resonate with the host's gut frequencies to promote a balanced microbiome. They have developed a proprietary blend of probiotics that, when combined with tailored prebiotics, creates a synbiotic effect that enhances the natural bioresonance of the gut ecosystem[1]. This approach includes the use of advanced microencapsulation techniques to ensure the viability of probiotics through the digestive process, allowing them to reach the intestines intact and maximize their bioresonance potential[3]. Nestlé has also invested in metabolomics research to understand how these synbiotics influence the production of beneficial metabolites that further support gut health and overall well-being[5].
Strengths: Extensive R&D resources, global market reach, and established consumer trust. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory hurdles and the need for long-term studies to prove efficacy in diverse populations.
New York University
Technical Solution: New York University's research on bioresonance in gut microbiome balancing focuses on developing non-invasive diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions. Their approach combines advanced imaging techniques with machine learning algorithms to map the gut's electromagnetic field and its interactions with the microbiome[2]. They have pioneered a method using low-frequency electromagnetic waves to selectively stimulate beneficial bacteria while inhibiting pathogenic strains, effectively rebalancing the gut ecosystem[4]. This technology, termed "Selective Microbiome Resonance Therapy" (SMRT), has shown promising results in preclinical studies for conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease and metabolic disorders[6]. Additionally, NYU researchers are exploring the use of nanoscale sensors that can detect subtle changes in the gut's bioresonance patterns, potentially allowing for early diagnosis of dysbiosis and personalized treatment strategies[8].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research facilities, interdisciplinary collaboration, and potential for novel diagnostic tools. Weaknesses: Technology still in early stages, requiring extensive clinical validation and potential challenges in translating to practical applications.
Core Innovations in Bioresonance-Microbiome Interaction
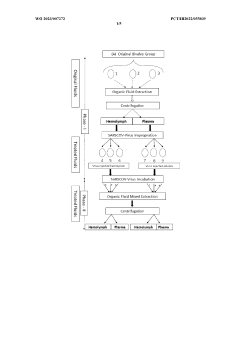
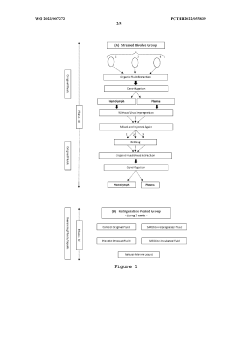
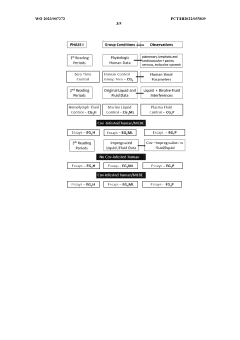
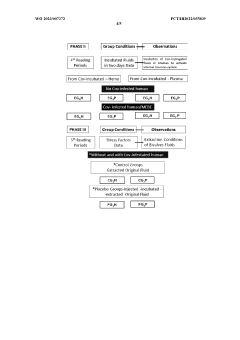
Method of obtaining electromagnetic frequencies from aquatic organisms bioactivated fluids for bioresonance therapy against a disease and/or pathogen
PatentWO2023007272A1
Innovation
- A method involving bioresonance therapy using electromagnetic frequencies obtained from aquatic non-human organisms, specifically bioactivated fluids from bivalves like Anodonta cygnea, to induce an immune response and treat diseases and pathogens in humans, utilizing a bioresonance device to transfer and record these frequencies for therapeutic applications.
Electromagnetic wave applicator
PatentWO2004047875A1
Innovation
- An electromagnetic wave irradiation device that selectively targets microorganisms by emitting frequencies matching their natural frequencies, causing resonant vibrations and destruction without affecting human tissues, using a thin tube with an electromagnetic wave generating means and an irradiation terminal, and an antenna array for precise frequency delivery.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
The safety and efficacy of bioresonance therapy in gut microbiome balancing remain subjects of ongoing research and debate within the scientific community. While proponents claim significant benefits, the lack of extensive clinical trials and standardized protocols raises concerns about its widespread adoption.
Safety considerations primarily revolve around the non-invasive nature of bioresonance therapy. The treatment typically involves placing electrodes on the skin or using handheld devices, which generally pose minimal risk of physical harm. However, potential indirect risks may arise if patients delay or forgo conventional medical treatments in favor of bioresonance therapy, especially for serious gastrointestinal conditions.
Electromagnetic fields used in bioresonance therapy are generally of low intensity and are not known to cause adverse effects in most individuals. Nevertheless, caution is advised for certain populations, such as pregnant women, individuals with pacemakers, or those with electromagnetic hypersensitivity. Long-term effects of repeated exposure to these fields on gut microbiome and overall health have not been thoroughly investigated.
Efficacy considerations are more complex and controversial. While anecdotal evidence and some small-scale studies suggest positive outcomes in balancing gut microbiome and alleviating related symptoms, large-scale, randomized controlled trials are lacking. The mechanism by which bioresonance therapy might influence gut microbiota is not fully understood, making it challenging to establish a clear scientific basis for its efficacy.
Variability in treatment protocols, device specifications, and practitioner expertise further complicates the assessment of efficacy. The highly individualized nature of gut microbiome composition and the complex interplay between microbiota and host health add layers of complexity to evaluating treatment outcomes.
Placebo effects cannot be discounted, as the non-invasive and holistic approach of bioresonance therapy may contribute to positive patient experiences independent of direct physiological effects on the gut microbiome. This underscores the need for well-designed, double-blind studies to differentiate between placebo responses and genuine therapeutic benefits.
Regulatory bodies in many countries have not approved bioresonance devices for medical use in gut microbiome balancing, citing insufficient evidence of efficacy. This lack of regulatory oversight raises concerns about quality control and standardization of treatments across different practitioners and clinics.
In conclusion, while bioresonance therapy for gut microbiome balancing shows promise in terms of safety and potential benefits, significant research gaps exist. Rigorous scientific investigation is necessary to establish its efficacy, optimize treatment protocols, and ensure its safe integration into mainstream healthcare practices for microbiome management.
Safety considerations primarily revolve around the non-invasive nature of bioresonance therapy. The treatment typically involves placing electrodes on the skin or using handheld devices, which generally pose minimal risk of physical harm. However, potential indirect risks may arise if patients delay or forgo conventional medical treatments in favor of bioresonance therapy, especially for serious gastrointestinal conditions.
Electromagnetic fields used in bioresonance therapy are generally of low intensity and are not known to cause adverse effects in most individuals. Nevertheless, caution is advised for certain populations, such as pregnant women, individuals with pacemakers, or those with electromagnetic hypersensitivity. Long-term effects of repeated exposure to these fields on gut microbiome and overall health have not been thoroughly investigated.
Efficacy considerations are more complex and controversial. While anecdotal evidence and some small-scale studies suggest positive outcomes in balancing gut microbiome and alleviating related symptoms, large-scale, randomized controlled trials are lacking. The mechanism by which bioresonance therapy might influence gut microbiota is not fully understood, making it challenging to establish a clear scientific basis for its efficacy.
Variability in treatment protocols, device specifications, and practitioner expertise further complicates the assessment of efficacy. The highly individualized nature of gut microbiome composition and the complex interplay between microbiota and host health add layers of complexity to evaluating treatment outcomes.
Placebo effects cannot be discounted, as the non-invasive and holistic approach of bioresonance therapy may contribute to positive patient experiences independent of direct physiological effects on the gut microbiome. This underscores the need for well-designed, double-blind studies to differentiate between placebo responses and genuine therapeutic benefits.
Regulatory bodies in many countries have not approved bioresonance devices for medical use in gut microbiome balancing, citing insufficient evidence of efficacy. This lack of regulatory oversight raises concerns about quality control and standardization of treatments across different practitioners and clinics.
In conclusion, while bioresonance therapy for gut microbiome balancing shows promise in terms of safety and potential benefits, significant research gaps exist. Rigorous scientific investigation is necessary to establish its efficacy, optimize treatment protocols, and ensure its safe integration into mainstream healthcare practices for microbiome management.
Regulatory Landscape for Bioresonance Devices
The regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices in the context of gut microbiome balancing is complex and evolving. Currently, there is no unified global regulatory framework specifically addressing bioresonance technology for microbiome applications. Different regions and countries have varying approaches to regulating these devices.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices under the broader category of "general wellness devices." These devices are subject to less stringent regulations compared to medical devices, provided they make only general wellness claims and do not pose any safety risks. However, manufacturers must ensure their marketing claims do not venture into the territory of diagnosing or treating specific diseases, which would require more rigorous FDA approval processes.
The European Union has a more structured approach through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Bioresonance devices intended for medical purposes, including gut microbiome balancing, may fall under Class IIa or higher, depending on their intended use and potential risks. This classification necessitates conformity assessment procedures and CE marking before market entry.
In Asia, regulations vary significantly. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has stringent requirements for medical devices, potentially including certain bioresonance applications. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has been increasingly focusing on regulating emerging health technologies, which may impact bioresonance devices in the future.
A key challenge in the regulatory landscape is the lack of standardized protocols for evaluating the efficacy and safety of bioresonance devices, particularly in the context of gut microbiome balancing. This absence of clear guidelines creates uncertainty for manufacturers and may slow down innovation and market entry.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with how to appropriately classify and regulate these devices. The primary concerns revolve around ensuring patient safety, preventing misleading claims, and establishing evidence-based standards for efficacy. As research in gut microbiome science advances, it is likely that regulations will evolve to more specifically address bioresonance applications in this field.
Moving forward, industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies will need to collaborate to develop appropriate frameworks. This may include establishing specific safety and performance standards for bioresonance devices used in gut microbiome applications, creating guidelines for clinical validation studies, and defining acceptable marketing claims based on scientific evidence.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices under the broader category of "general wellness devices." These devices are subject to less stringent regulations compared to medical devices, provided they make only general wellness claims and do not pose any safety risks. However, manufacturers must ensure their marketing claims do not venture into the territory of diagnosing or treating specific diseases, which would require more rigorous FDA approval processes.
The European Union has a more structured approach through its Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Bioresonance devices intended for medical purposes, including gut microbiome balancing, may fall under Class IIa or higher, depending on their intended use and potential risks. This classification necessitates conformity assessment procedures and CE marking before market entry.
In Asia, regulations vary significantly. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has stringent requirements for medical devices, potentially including certain bioresonance applications. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has been increasingly focusing on regulating emerging health technologies, which may impact bioresonance devices in the future.
A key challenge in the regulatory landscape is the lack of standardized protocols for evaluating the efficacy and safety of bioresonance devices, particularly in the context of gut microbiome balancing. This absence of clear guidelines creates uncertainty for manufacturers and may slow down innovation and market entry.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with how to appropriately classify and regulate these devices. The primary concerns revolve around ensuring patient safety, preventing misleading claims, and establishing evidence-based standards for efficacy. As research in gut microbiome science advances, it is likely that regulations will evolve to more specifically address bioresonance applications in this field.
Moving forward, industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies will need to collaborate to develop appropriate frameworks. This may include establishing specific safety and performance standards for bioresonance devices used in gut microbiome applications, creating guidelines for clinical validation studies, and defining acceptable marketing claims based on scientific evidence.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!