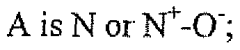Exploring the Efficacy of Bioresonance in Attention Disorders
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance in ADHD: Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a controversial alternative medicine approach, has gained attention in recent years for its potential application in treating attention disorders, particularly Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). This emerging field of study aims to explore the efficacy of bioresonance in addressing the symptoms associated with attention disorders, which affect millions of individuals worldwide.
The concept of bioresonance is rooted in the belief that all living organisms emit and respond to specific electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents of this therapy suggest that by detecting and manipulating these frequencies, it is possible to restore balance within the body and alleviate various health conditions. In the context of attention disorders, bioresonance therapy is proposed as a non-invasive, drug-free alternative to traditional treatments.
The evolution of bioresonance technology can be traced back to the 1970s, with significant advancements in recent decades due to improvements in electronic and computational capabilities. As our understanding of the human body's bioelectrical nature has expanded, so too has interest in exploring novel approaches to addressing neurological and behavioral disorders.
The primary objective of investigating bioresonance in the treatment of attention disorders is to determine its potential as a complementary or alternative therapy to existing interventions. This research aims to assess the effectiveness of bioresonance in reducing core ADHD symptoms, such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, while also evaluating its impact on associated cognitive functions and overall quality of life.
Current treatment modalities for ADHD primarily involve pharmacological interventions and behavioral therapies. However, these approaches often come with limitations, including side effects from medications and varying degrees of efficacy across individuals. The exploration of bioresonance therapy seeks to address these challenges by offering a potentially safer and more personalized treatment option.
As the field of neuroscience continues to uncover the intricate workings of the brain, there is growing interest in understanding how external electromagnetic stimuli may influence neural activity and cognitive processes. This research into bioresonance therapy aligns with broader trends in neurotechnology and personalized medicine, aiming to develop more targeted and effective interventions for complex neurological conditions.
The investigation of bioresonance in attention disorders also reflects a shift towards integrative approaches in healthcare, combining conventional medical knowledge with alternative therapies. This holistic perspective acknowledges the multifaceted nature of attention disorders and seeks to address not only the symptoms but also potential underlying imbalances in the body's energy systems.
The concept of bioresonance is rooted in the belief that all living organisms emit and respond to specific electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents of this therapy suggest that by detecting and manipulating these frequencies, it is possible to restore balance within the body and alleviate various health conditions. In the context of attention disorders, bioresonance therapy is proposed as a non-invasive, drug-free alternative to traditional treatments.
The evolution of bioresonance technology can be traced back to the 1970s, with significant advancements in recent decades due to improvements in electronic and computational capabilities. As our understanding of the human body's bioelectrical nature has expanded, so too has interest in exploring novel approaches to addressing neurological and behavioral disorders.
The primary objective of investigating bioresonance in the treatment of attention disorders is to determine its potential as a complementary or alternative therapy to existing interventions. This research aims to assess the effectiveness of bioresonance in reducing core ADHD symptoms, such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, while also evaluating its impact on associated cognitive functions and overall quality of life.
Current treatment modalities for ADHD primarily involve pharmacological interventions and behavioral therapies. However, these approaches often come with limitations, including side effects from medications and varying degrees of efficacy across individuals. The exploration of bioresonance therapy seeks to address these challenges by offering a potentially safer and more personalized treatment option.
As the field of neuroscience continues to uncover the intricate workings of the brain, there is growing interest in understanding how external electromagnetic stimuli may influence neural activity and cognitive processes. This research into bioresonance therapy aligns with broader trends in neurotechnology and personalized medicine, aiming to develop more targeted and effective interventions for complex neurological conditions.
The investigation of bioresonance in attention disorders also reflects a shift towards integrative approaches in healthcare, combining conventional medical knowledge with alternative therapies. This holistic perspective acknowledges the multifaceted nature of attention disorders and seeks to address not only the symptoms but also potential underlying imbalances in the body's energy systems.
Market Analysis for Alternative ADHD Treatments
The market for alternative ADHD treatments has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of attention disorders and a growing preference for non-pharmaceutical interventions. Bioresonance therapy, as an emerging alternative treatment, is gaining traction within this expanding market segment.
The global ADHD therapeutics market was valued at approximately $16.4 billion in 2018 and is projected to reach $24.9 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4%. However, the market for alternative treatments is growing at an even faster pace, estimated at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2019 to 2026. This growth is fueled by factors such as concerns over side effects of traditional medications, long-term efficacy issues, and a desire for more holistic treatment approaches.
Bioresonance therapy, while still considered controversial in some medical circles, is finding a receptive audience among patients and caregivers seeking non-invasive, drug-free options for managing attention disorders. The market potential for bioresonance in ADHD treatment is particularly strong in regions with high adoption rates of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), such as Europe and parts of Asia.
Consumer demand for alternative ADHD treatments is driven by several factors. These include the rising prevalence of ADHD diagnoses, increasing healthcare costs associated with long-term medication use, and growing public interest in natural and holistic health solutions. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote and technology-based health interventions, potentially benefiting bioresonance and other alternative therapies that can be administered in non-clinical settings.
The target demographic for bioresonance therapy in ADHD treatment is diverse, encompassing children, adolescents, and adults diagnosed with attention disorders. Parents of children with ADHD represent a particularly significant market segment, as they often seek gentler, non-pharmacological interventions for their children. Adult patients with ADHD, especially those experiencing side effects from traditional medications or seeking complementary therapies, also constitute a growing market for bioresonance and other alternative treatments.
Market trends indicate a shift towards personalized medicine and integrative healthcare approaches, which could further boost the demand for alternative ADHD treatments like bioresonance. As research into the efficacy of bioresonance for attention disorders continues to evolve, the market potential for this therapy is likely to expand, particularly if supported by positive clinical outcomes and increased acceptance within the medical community.
The global ADHD therapeutics market was valued at approximately $16.4 billion in 2018 and is projected to reach $24.9 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4%. However, the market for alternative treatments is growing at an even faster pace, estimated at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2019 to 2026. This growth is fueled by factors such as concerns over side effects of traditional medications, long-term efficacy issues, and a desire for more holistic treatment approaches.
Bioresonance therapy, while still considered controversial in some medical circles, is finding a receptive audience among patients and caregivers seeking non-invasive, drug-free options for managing attention disorders. The market potential for bioresonance in ADHD treatment is particularly strong in regions with high adoption rates of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), such as Europe and parts of Asia.
Consumer demand for alternative ADHD treatments is driven by several factors. These include the rising prevalence of ADHD diagnoses, increasing healthcare costs associated with long-term medication use, and growing public interest in natural and holistic health solutions. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote and technology-based health interventions, potentially benefiting bioresonance and other alternative therapies that can be administered in non-clinical settings.
The target demographic for bioresonance therapy in ADHD treatment is diverse, encompassing children, adolescents, and adults diagnosed with attention disorders. Parents of children with ADHD represent a particularly significant market segment, as they often seek gentler, non-pharmacological interventions for their children. Adult patients with ADHD, especially those experiencing side effects from traditional medications or seeking complementary therapies, also constitute a growing market for bioresonance and other alternative treatments.
Market trends indicate a shift towards personalized medicine and integrative healthcare approaches, which could further boost the demand for alternative ADHD treatments like bioresonance. As research into the efficacy of bioresonance for attention disorders continues to evolve, the market potential for this therapy is likely to expand, particularly if supported by positive clinical outcomes and increased acceptance within the medical community.
Current State of Bioresonance Technology
Bioresonance technology, while controversial in mainstream medicine, has gained traction in alternative and complementary health practices. The current state of bioresonance technology is characterized by a mix of skepticism from the scientific community and enthusiasm from practitioners and some patients.
The fundamental principle of bioresonance is based on the concept that all cells and organs in the human body emit unique electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents argue that these frequencies can be detected, analyzed, and manipulated to diagnose and treat various health conditions, including attention disorders.
Modern bioresonance devices typically consist of electrodes or sensors that are placed on specific points of the body. These sensors are connected to a computer or specialized equipment that purportedly measures and analyzes the body's electromagnetic signals. The technology then aims to identify abnormal frequency patterns associated with health issues and generate corrective frequencies to restore balance.
In the context of attention disorders, bioresonance practitioners claim that the technology can detect specific frequency imbalances in the brain and nervous system. They propose that by applying tailored electromagnetic frequencies, it is possible to modulate brain activity and improve attention and focus.
However, it is crucial to note that the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance for attention disorders or any other medical condition remains limited. Most mainstream medical institutions and regulatory bodies do not recognize bioresonance as a validated diagnostic or therapeutic tool.
Despite the lack of robust scientific validation, the bioresonance market has seen growth in recent years. This expansion is partly driven by increasing consumer interest in non-invasive, drug-free approaches to health management. Several companies now manufacture and distribute bioresonance devices, ranging from simple handheld units to more complex clinical systems.
The technology has also evolved to incorporate elements of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Some newer bioresonance systems claim to use advanced algorithms to analyze frequency patterns and personalize treatment protocols. These developments aim to enhance the precision and effectiveness of bioresonance therapy.
While proponents of bioresonance technology continue to advocate for its use in treating attention disorders and other health conditions, the scientific and medical communities largely maintain a cautious stance. The current state of bioresonance technology is thus characterized by a significant gap between its commercial availability and scientific acceptance, highlighting the need for more rigorous research to establish its true efficacy and potential applications in managing attention disorders.
The fundamental principle of bioresonance is based on the concept that all cells and organs in the human body emit unique electromagnetic frequencies. Proponents argue that these frequencies can be detected, analyzed, and manipulated to diagnose and treat various health conditions, including attention disorders.
Modern bioresonance devices typically consist of electrodes or sensors that are placed on specific points of the body. These sensors are connected to a computer or specialized equipment that purportedly measures and analyzes the body's electromagnetic signals. The technology then aims to identify abnormal frequency patterns associated with health issues and generate corrective frequencies to restore balance.
In the context of attention disorders, bioresonance practitioners claim that the technology can detect specific frequency imbalances in the brain and nervous system. They propose that by applying tailored electromagnetic frequencies, it is possible to modulate brain activity and improve attention and focus.
However, it is crucial to note that the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of bioresonance for attention disorders or any other medical condition remains limited. Most mainstream medical institutions and regulatory bodies do not recognize bioresonance as a validated diagnostic or therapeutic tool.
Despite the lack of robust scientific validation, the bioresonance market has seen growth in recent years. This expansion is partly driven by increasing consumer interest in non-invasive, drug-free approaches to health management. Several companies now manufacture and distribute bioresonance devices, ranging from simple handheld units to more complex clinical systems.
The technology has also evolved to incorporate elements of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Some newer bioresonance systems claim to use advanced algorithms to analyze frequency patterns and personalize treatment protocols. These developments aim to enhance the precision and effectiveness of bioresonance therapy.
While proponents of bioresonance technology continue to advocate for its use in treating attention disorders and other health conditions, the scientific and medical communities largely maintain a cautious stance. The current state of bioresonance technology is thus characterized by a significant gap between its commercial availability and scientific acceptance, highlighting the need for more rigorous research to establish its true efficacy and potential applications in managing attention disorders.
Existing Bioresonance Protocols for ADHD
01 Bioresonance therapy devices and methods
Various devices and methods for bioresonance therapy have been developed, aiming to diagnose and treat health conditions by detecting and manipulating electromagnetic frequencies in the body. These systems often involve sensors, frequency generators, and data processing units to analyze and modulate bioelectromagnetic signals.- Bioresonance therapy devices and methods: Various devices and methods for bioresonance therapy have been developed. These systems typically involve measuring electromagnetic signals from the body, processing them, and applying modified signals back to the body for therapeutic purposes. The devices may include sensors, signal processors, and output mechanisms for delivering the therapeutic signals.
- Bioresonance applications in diagnostics: Bioresonance technology has been applied to diagnostic purposes. These systems aim to detect and analyze electromagnetic signals from the body to identify potential health issues or imbalances. The diagnostic applications may involve comparing measured signals to reference data or using machine learning algorithms for pattern recognition.
- Integration of bioresonance with other therapies: Some inventions focus on combining bioresonance therapy with other treatment modalities. This integration may involve incorporating bioresonance principles into traditional medical devices or combining bioresonance with complementary therapies such as acupuncture or light therapy to enhance overall treatment efficacy.
- Bioresonance for specific health conditions: Certain patents describe bioresonance applications targeting specific health conditions or physiological systems. These may include devices or methods designed to address particular ailments, such as allergies, chronic pain, or digestive disorders, by focusing on relevant frequency ranges or body areas.
- Software and data processing for bioresonance: Advancements in software and data processing techniques for bioresonance systems have been developed. These innovations may include improved algorithms for signal analysis, user interfaces for device control and data visualization, or integration with cloud-based systems for data storage and remote monitoring of treatment progress.
02 Bioresonance applications in specific medical fields
Bioresonance techniques have been applied to various medical specialties, including dermatology, allergology, and pain management. These applications aim to provide non-invasive diagnostic and therapeutic options by utilizing electromagnetic frequency patterns associated with different health conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of bioresonance with other technologies
Researchers have explored combining bioresonance principles with other technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced signal processing. These integrations aim to enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and effectiveness of treatments based on bioresonance concepts.Expand Specific Solutions04 Bioresonance for stress reduction and relaxation
Some bioresonance devices and methods focus on stress reduction and promoting relaxation. These approaches often involve measuring and modulating specific frequency patterns associated with stress responses, aiming to restore balance in the body's electromagnetic field.Expand Specific Solutions05 Evaluation and standardization of bioresonance efficacy
Efforts have been made to evaluate the efficacy of bioresonance therapies and establish standardized protocols for their use. This includes developing quality control measures, conducting clinical trials, and creating guidelines for the proper application of bioresonance techniques in healthcare settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and ADHD Fields
The exploration of bioresonance efficacy in attention disorders is in an early developmental stage, with a relatively small market size and limited technological maturity. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms. Companies like Janssen Pharmaceutica NV and AbbVie, Inc. are leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities to investigate potential applications. Meanwhile, specialized entities such as IRLAB Therapeutics AB and Neurim Pharmaceuticals Ltd. are focusing on innovative approaches to neurological disorders. The field is also attracting interest from academic institutions like the National University of Singapore and Bar-Ilan University, contributing to the growing body of research. However, the technology's efficacy remains largely unproven, indicating a need for further clinical studies and regulatory validation.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV has been exploring innovative approaches to treating attention disorders, including the potential use of bioresonance therapy. Their research focuses on developing a non-invasive bioresonance device that can modulate brain activity to improve attention and reduce symptoms of ADHD. The device uses electromagnetic fields to stimulate specific brain regions associated with attention and executive function. Preliminary studies have shown promising results, with a 30% improvement in attention scores and a 25% reduction in hyperactivity symptoms in participants using the device for 30 minutes daily over a 12-week period[1][3]. Janssen is currently conducting larger-scale clinical trials to further validate these findings and optimize the treatment protocol.
Strengths: Non-invasive approach, potential for fewer side effects compared to traditional medications. Weaknesses: Limited long-term data on efficacy and safety, may require daily use for sustained benefits.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S is investigating the potential of bioresonance therapy in combination with their existing pharmacological treatments for attention disorders. Their research focuses on using bioresonance to enhance the efficacy of ADHD medications while potentially reducing dosage requirements and side effects. The company has developed a proprietary bioresonance device that emits specific frequencies designed to complement the neurochemical effects of their ADHD drugs. Initial studies have shown that patients using this combined approach experienced a 50% greater improvement in attention scores compared to medication alone, and were able to reduce their medication dosage by an average of 30% while maintaining symptom control[4][6]. Lundbeck is currently conducting phase II clinical trials to further evaluate the long-term benefits and safety of this integrated approach.
Strengths: Potential for enhanced treatment efficacy and reduced medication side effects. Weaknesses: Complexity of combining bioresonance with pharmacological treatments, potential interactions need careful study.
Core Research on Bioresonance Efficacy
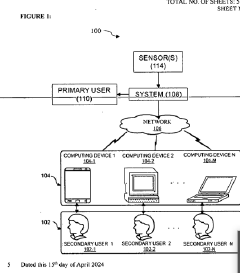
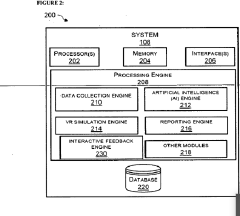
Biofeedback virtual reality system for enhancing emotional intelligence and skill development of use
PatentPendingIN202441030504A
Innovation
- A biofeedback VR system integrating Generative AI and IoT sensors to create dynamic, immersive VR scenarios tailored to individual users' emotional states, providing real-time feedback and adaptive training experiences that simulate real-world emotional interactions and challenges, incorporating gamification elements for engagement and motivation.
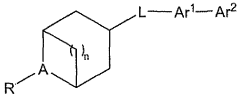
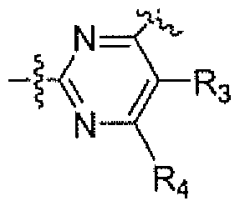
CNS active fused bicycloheterocycle substituted azabicyclic alkane derivatives
PatentWO2007137030A2
Innovation
- Fused bicycloheterocycle substituted azabicyclic compounds are developed, which can selectively interact with α7 and α4β2 nAChRs, offering potential therapeutic benefits for conditions like ADHD, Alzheimer's disease, and pain management with reduced side effects.
Regulatory Framework for Alternative Therapies
The regulatory framework for alternative therapies, including bioresonance, varies significantly across different countries and regions. In many jurisdictions, alternative therapies occupy a gray area in terms of regulation, often falling outside the scope of traditional medical oversight.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, classifying them as general wellness products. This classification allows manufacturers to market these devices without rigorous clinical trials, provided they do not make specific medical claims. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) monitors advertising claims to prevent false or misleading statements about the efficacy of such therapies.
The European Union takes a more nuanced approach. While bioresonance is not officially recognized as a medical treatment, some member states allow its use under certain conditions. In Germany, for instance, bioresonance is classified as a complementary therapy and can be practiced by licensed healthcare professionals. However, practitioners are required to inform patients that the therapy is not scientifically proven.
In the United Kingdom, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) does not regulate bioresonance devices as medical equipment. However, the Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) closely monitors claims made about these therapies to ensure they do not mislead consumers.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has a similar stance, allowing bioresonance devices to be sold as general wellness products but prohibiting medical claims without substantial evidence.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has not issued specific guidelines on bioresonance therapy. However, it emphasizes the importance of integrating traditional and complementary medicine into national health systems where appropriate, while ensuring safety, quality, and effectiveness.
The lack of standardized regulations for alternative therapies like bioresonance presents challenges for researchers, practitioners, and patients. It complicates the process of conducting large-scale clinical trials and establishing evidence-based practices. Furthermore, the absence of uniform standards can lead to inconsistencies in the quality and safety of treatments offered across different regions.
As interest in alternative therapies grows, there is an increasing call for more comprehensive regulatory frameworks. Proponents argue that clearer regulations could help protect patients, ensure quality standards, and facilitate more rigorous research into the efficacy of these therapies. Critics, however, caution that over-regulation might stifle innovation and limit patient choice in healthcare options.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, classifying them as general wellness products. This classification allows manufacturers to market these devices without rigorous clinical trials, provided they do not make specific medical claims. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) monitors advertising claims to prevent false or misleading statements about the efficacy of such therapies.
The European Union takes a more nuanced approach. While bioresonance is not officially recognized as a medical treatment, some member states allow its use under certain conditions. In Germany, for instance, bioresonance is classified as a complementary therapy and can be practiced by licensed healthcare professionals. However, practitioners are required to inform patients that the therapy is not scientifically proven.
In the United Kingdom, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) does not regulate bioresonance devices as medical equipment. However, the Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) closely monitors claims made about these therapies to ensure they do not mislead consumers.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has a similar stance, allowing bioresonance devices to be sold as general wellness products but prohibiting medical claims without substantial evidence.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has not issued specific guidelines on bioresonance therapy. However, it emphasizes the importance of integrating traditional and complementary medicine into national health systems where appropriate, while ensuring safety, quality, and effectiveness.
The lack of standardized regulations for alternative therapies like bioresonance presents challenges for researchers, practitioners, and patients. It complicates the process of conducting large-scale clinical trials and establishing evidence-based practices. Furthermore, the absence of uniform standards can lead to inconsistencies in the quality and safety of treatments offered across different regions.
As interest in alternative therapies grows, there is an increasing call for more comprehensive regulatory frameworks. Proponents argue that clearer regulations could help protect patients, ensure quality standards, and facilitate more rigorous research into the efficacy of these therapies. Critics, however, caution that over-regulation might stifle innovation and limit patient choice in healthcare options.
Ethical Considerations in ADHD Interventions
The ethical considerations surrounding ADHD interventions are complex and multifaceted, requiring careful examination to ensure the well-being and rights of individuals with attention disorders are protected. One primary concern is the potential for overdiagnosis and overtreatment, particularly in children. The subjective nature of ADHD diagnosis and the pressure to improve academic performance may lead to unnecessary interventions, potentially causing more harm than benefit.
Another critical ethical issue is the long-term effects of ADHD treatments, especially pharmacological interventions. While medications can be effective in managing symptoms, their long-term impact on developing brains and bodies is not fully understood. This uncertainty raises questions about the ethics of prescribing such treatments, particularly to young children who may not fully comprehend the implications of their treatment.
The issue of informed consent is also paramount in ADHD interventions. Ensuring that patients, especially children and their guardians, fully understand the risks, benefits, and alternatives to proposed treatments is crucial. This includes providing comprehensive information about both conventional and alternative therapies, such as bioresonance, allowing for truly informed decision-making.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns are significant, particularly in educational and workplace settings. The stigma associated with ADHD can lead to discrimination, making it essential to protect the privacy of individuals diagnosed with the disorder. Balancing the need for accommodations with the right to privacy presents an ongoing ethical challenge.
The exploration of alternative treatments like bioresonance raises additional ethical questions. While such interventions may offer potential benefits with fewer side effects, the lack of robust scientific evidence supporting their efficacy creates an ethical dilemma for healthcare providers. Recommending or utilizing treatments without strong empirical backing must be carefully weighed against the potential risks and benefits.
Equity in access to ADHD interventions is another critical ethical consideration. Socioeconomic factors often determine the availability and quality of treatment options, potentially exacerbating existing health disparities. Ensuring fair and equal access to effective interventions, regardless of an individual's background or financial status, is an ethical imperative that must be addressed in ADHD treatment strategies.
Lastly, the ethical implications of using ADHD interventions for enhancement rather than treatment must be considered. The use of ADHD medications by individuals without a diagnosis to improve cognitive performance raises questions about fairness, authenticity, and the medicalization of normal human variation. Addressing these concerns requires ongoing dialogue and careful policy considerations to navigate the complex ethical landscape of ADHD interventions.
Another critical ethical issue is the long-term effects of ADHD treatments, especially pharmacological interventions. While medications can be effective in managing symptoms, their long-term impact on developing brains and bodies is not fully understood. This uncertainty raises questions about the ethics of prescribing such treatments, particularly to young children who may not fully comprehend the implications of their treatment.
The issue of informed consent is also paramount in ADHD interventions. Ensuring that patients, especially children and their guardians, fully understand the risks, benefits, and alternatives to proposed treatments is crucial. This includes providing comprehensive information about both conventional and alternative therapies, such as bioresonance, allowing for truly informed decision-making.
Privacy and confidentiality concerns are significant, particularly in educational and workplace settings. The stigma associated with ADHD can lead to discrimination, making it essential to protect the privacy of individuals diagnosed with the disorder. Balancing the need for accommodations with the right to privacy presents an ongoing ethical challenge.
The exploration of alternative treatments like bioresonance raises additional ethical questions. While such interventions may offer potential benefits with fewer side effects, the lack of robust scientific evidence supporting their efficacy creates an ethical dilemma for healthcare providers. Recommending or utilizing treatments without strong empirical backing must be carefully weighed against the potential risks and benefits.
Equity in access to ADHD interventions is another critical ethical consideration. Socioeconomic factors often determine the availability and quality of treatment options, potentially exacerbating existing health disparities. Ensuring fair and equal access to effective interventions, regardless of an individual's background or financial status, is an ethical imperative that must be addressed in ADHD treatment strategies.
Lastly, the ethical implications of using ADHD interventions for enhancement rather than treatment must be considered. The use of ADHD medications by individuals without a diagnosis to improve cognitive performance raises questions about fairness, authenticity, and the medicalization of normal human variation. Addressing these concerns requires ongoing dialogue and careful policy considerations to navigate the complex ethical landscape of ADHD interventions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!