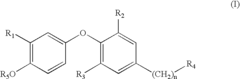
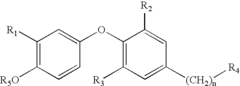
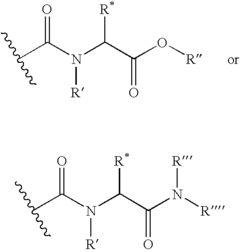
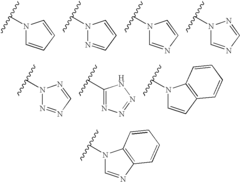
Bioresonance and Thyroid Health: Assessment and Outcomes
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance Technology Evolution and Objectives
Bioresonance technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1970s, with its application in thyroid health assessment and treatment gaining traction in recent years. The primary objective of bioresonance in thyroid health is to provide a non-invasive, holistic approach to diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders.
The technology's evolution began with Dr. Franz Morell's development of the MORA device, which aimed to detect and balance electromagnetic frequencies in the body. Over time, this concept has been refined and expanded, leading to more sophisticated bioresonance devices specifically designed for thyroid health assessment.
In the 1990s, researchers began exploring the potential of bioresonance in detecting subtle energy imbalances associated with thyroid dysfunction. This led to the development of more targeted protocols for thyroid assessment, incorporating frequency patterns specific to thyroid gland function and related endocrine processes.
The early 2000s saw a shift towards integrating bioresonance with conventional medical diagnostics. Practitioners started using bioresonance as a complementary tool alongside blood tests and imaging studies to provide a more comprehensive picture of thyroid health. This integration aimed to enhance the accuracy of thyroid disorder diagnoses and tailor treatment plans more effectively.
Recent advancements in bioresonance technology have focused on improving the sensitivity and specificity of thyroid-related frequency detection. Modern devices now incorporate machine learning algorithms to analyze complex frequency patterns, potentially offering earlier detection of thyroid imbalances before they manifest in conventional blood tests.
The current objectives of bioresonance in thyroid health assessment include:
1. Enhancing early detection capabilities for subclinical thyroid disorders.
2. Providing a more nuanced understanding of thyroid function beyond standard hormone level measurements.
3. Offering personalized treatment protocols based on individual frequency patterns.
4. Monitoring treatment efficacy and adjusting interventions in real-time.
5. Reducing reliance on invasive diagnostic procedures and minimizing potential side effects of conventional treatments.
Looking forward, the field aims to establish standardized protocols for bioresonance-based thyroid assessment, ensuring consistency and reliability across different practitioners and devices. There is also a push towards conducting large-scale clinical trials to validate the efficacy of bioresonance in thyroid health management, potentially leading to wider acceptance in mainstream medical practice.
The technology's evolution began with Dr. Franz Morell's development of the MORA device, which aimed to detect and balance electromagnetic frequencies in the body. Over time, this concept has been refined and expanded, leading to more sophisticated bioresonance devices specifically designed for thyroid health assessment.
In the 1990s, researchers began exploring the potential of bioresonance in detecting subtle energy imbalances associated with thyroid dysfunction. This led to the development of more targeted protocols for thyroid assessment, incorporating frequency patterns specific to thyroid gland function and related endocrine processes.
The early 2000s saw a shift towards integrating bioresonance with conventional medical diagnostics. Practitioners started using bioresonance as a complementary tool alongside blood tests and imaging studies to provide a more comprehensive picture of thyroid health. This integration aimed to enhance the accuracy of thyroid disorder diagnoses and tailor treatment plans more effectively.
Recent advancements in bioresonance technology have focused on improving the sensitivity and specificity of thyroid-related frequency detection. Modern devices now incorporate machine learning algorithms to analyze complex frequency patterns, potentially offering earlier detection of thyroid imbalances before they manifest in conventional blood tests.
The current objectives of bioresonance in thyroid health assessment include:
1. Enhancing early detection capabilities for subclinical thyroid disorders.
2. Providing a more nuanced understanding of thyroid function beyond standard hormone level measurements.
3. Offering personalized treatment protocols based on individual frequency patterns.
4. Monitoring treatment efficacy and adjusting interventions in real-time.
5. Reducing reliance on invasive diagnostic procedures and minimizing potential side effects of conventional treatments.
Looking forward, the field aims to establish standardized protocols for bioresonance-based thyroid assessment, ensuring consistency and reliability across different practitioners and devices. There is also a push towards conducting large-scale clinical trials to validate the efficacy of bioresonance in thyroid health management, potentially leading to wider acceptance in mainstream medical practice.
Market Analysis for Thyroid Health Solutions
The thyroid health solutions market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of thyroid disorders and the growing prevalence of thyroid-related conditions. The global thyroid health market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected to be substantial over the next five years.
Several factors contribute to the expanding market demand for thyroid health solutions. Firstly, the rising incidence of thyroid disorders, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid cancer, has created a pressing need for effective diagnostic and treatment options. Environmental factors, such as exposure to endocrine disruptors and radiation, have been linked to an increase in thyroid problems, further fueling market growth.
Additionally, the aging population in many developed countries has led to a higher prevalence of thyroid disorders, as these conditions become more common with age. This demographic shift has resulted in a larger patient pool seeking thyroid-related healthcare services and products.
The market for thyroid health solutions encompasses a wide range of products and services, including diagnostic tests, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, and medical devices. Diagnostic testing, particularly thyroid function tests and imaging technologies, represents a significant portion of the market. The demand for more accurate and efficient diagnostic tools continues to drive innovation in this sector.
Pharmaceutical treatments for thyroid disorders, such as levothyroxine for hypothyroidism and anti-thyroid medications for hyperthyroidism, constitute a major segment of the market. The development of novel drug formulations and delivery methods is an area of ongoing research and investment.
Emerging technologies, including bioresonance therapy, are gaining attention in the thyroid health market. While still considered alternative or complementary approaches, these technologies are attracting interest from patients seeking non-pharmaceutical options for managing thyroid health.
The market is also witnessing a growing demand for natural and holistic approaches to thyroid health. This trend has led to an increase in the availability of dietary supplements and functional foods marketed for thyroid support. However, the efficacy and safety of many of these products remain subjects of debate within the medical community.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the thyroid health solutions market, due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher awareness levels, and greater healthcare spending. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
Several factors contribute to the expanding market demand for thyroid health solutions. Firstly, the rising incidence of thyroid disorders, including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid cancer, has created a pressing need for effective diagnostic and treatment options. Environmental factors, such as exposure to endocrine disruptors and radiation, have been linked to an increase in thyroid problems, further fueling market growth.
Additionally, the aging population in many developed countries has led to a higher prevalence of thyroid disorders, as these conditions become more common with age. This demographic shift has resulted in a larger patient pool seeking thyroid-related healthcare services and products.
The market for thyroid health solutions encompasses a wide range of products and services, including diagnostic tests, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, and medical devices. Diagnostic testing, particularly thyroid function tests and imaging technologies, represents a significant portion of the market. The demand for more accurate and efficient diagnostic tools continues to drive innovation in this sector.
Pharmaceutical treatments for thyroid disorders, such as levothyroxine for hypothyroidism and anti-thyroid medications for hyperthyroidism, constitute a major segment of the market. The development of novel drug formulations and delivery methods is an area of ongoing research and investment.
Emerging technologies, including bioresonance therapy, are gaining attention in the thyroid health market. While still considered alternative or complementary approaches, these technologies are attracting interest from patients seeking non-pharmaceutical options for managing thyroid health.
The market is also witnessing a growing demand for natural and holistic approaches to thyroid health. This trend has led to an increase in the availability of dietary supplements and functional foods marketed for thyroid support. However, the efficacy and safety of many of these products remain subjects of debate within the medical community.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the thyroid health solutions market, due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, higher awareness levels, and greater healthcare spending. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising disposable incomes.
Bioresonance in Thyroid Diagnostics: Current Status and Challenges
Bioresonance technology in thyroid diagnostics has gained attention in recent years, yet its current status remains controversial within the medical community. The primary principle behind bioresonance involves measuring and analyzing electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the body, with proponents claiming these can be used to detect imbalances or dysfunctions in various organs, including the thyroid gland.
Despite growing interest, bioresonance faces significant challenges in gaining widespread acceptance as a reliable diagnostic tool for thyroid health. One of the main obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols and equipment, leading to inconsistent results across different practitioners and devices. This variability makes it difficult to establish a solid scientific foundation for the technology's efficacy in thyroid assessment.
Another critical challenge is the limited body of peer-reviewed research supporting bioresonance's effectiveness in thyroid diagnostics. While some studies have reported positive outcomes, the overall evidence base remains insufficient to meet the rigorous standards required for mainstream medical adoption. This shortage of high-quality clinical trials hinders the technology's integration into conventional thyroid care protocols.
Regulatory hurdles also present a significant barrier to the widespread implementation of bioresonance in thyroid diagnostics. Many health authorities and medical boards have not yet recognized bioresonance as a validated diagnostic method, limiting its use in clinical settings and insurance coverage. This lack of official endorsement contributes to skepticism among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The complexity of thyroid function and the multifaceted nature of thyroid disorders further complicate the application of bioresonance in this field. Thyroid health is influenced by numerous factors, including hormonal balance, autoimmune responses, and environmental influences. Critics argue that bioresonance may oversimplify these complex interactions, potentially leading to misdiagnosis or overlooking important aspects of thyroid pathology.
Despite these challenges, proponents of bioresonance continue to advocate for its potential in thyroid diagnostics, citing its non-invasive nature and ability to detect subtle energetic imbalances that may precede biochemical changes. Some practitioners integrate bioresonance with conventional thyroid tests, arguing that it provides complementary information that can enhance overall diagnostic accuracy.
As research in this field progresses, efforts are being made to address the current limitations. Some researchers are working on developing more standardized bioresonance protocols specifically tailored for thyroid assessment. Additionally, there is a growing focus on conducting larger, more rigorous clinical trials to evaluate the technology's efficacy and reliability in thyroid diagnostics.
Despite growing interest, bioresonance faces significant challenges in gaining widespread acceptance as a reliable diagnostic tool for thyroid health. One of the main obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols and equipment, leading to inconsistent results across different practitioners and devices. This variability makes it difficult to establish a solid scientific foundation for the technology's efficacy in thyroid assessment.
Another critical challenge is the limited body of peer-reviewed research supporting bioresonance's effectiveness in thyroid diagnostics. While some studies have reported positive outcomes, the overall evidence base remains insufficient to meet the rigorous standards required for mainstream medical adoption. This shortage of high-quality clinical trials hinders the technology's integration into conventional thyroid care protocols.
Regulatory hurdles also present a significant barrier to the widespread implementation of bioresonance in thyroid diagnostics. Many health authorities and medical boards have not yet recognized bioresonance as a validated diagnostic method, limiting its use in clinical settings and insurance coverage. This lack of official endorsement contributes to skepticism among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The complexity of thyroid function and the multifaceted nature of thyroid disorders further complicate the application of bioresonance in this field. Thyroid health is influenced by numerous factors, including hormonal balance, autoimmune responses, and environmental influences. Critics argue that bioresonance may oversimplify these complex interactions, potentially leading to misdiagnosis or overlooking important aspects of thyroid pathology.
Despite these challenges, proponents of bioresonance continue to advocate for its potential in thyroid diagnostics, citing its non-invasive nature and ability to detect subtle energetic imbalances that may precede biochemical changes. Some practitioners integrate bioresonance with conventional thyroid tests, arguing that it provides complementary information that can enhance overall diagnostic accuracy.
As research in this field progresses, efforts are being made to address the current limitations. Some researchers are working on developing more standardized bioresonance protocols specifically tailored for thyroid assessment. Additionally, there is a growing focus on conducting larger, more rigorous clinical trials to evaluate the technology's efficacy and reliability in thyroid diagnostics.
Existing Bioresonance Protocols for Thyroid Assessment
01 Bioresonance devices for thyroid health assessment
Bioresonance devices are used to assess thyroid health by measuring electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the thyroid gland. These devices can detect imbalances and help in the diagnosis of thyroid disorders. The technology allows for non-invasive monitoring of thyroid function and can be used to track treatment progress.- Bioresonance therapy for thyroid health: Bioresonance therapy is used to diagnose and treat thyroid disorders by detecting and correcting electromagnetic frequency imbalances in the body. This non-invasive approach aims to restore thyroid function and overall health through the application of specific electromagnetic frequencies.
- Thyroid hormone regulation using bioresonance: Bioresonance techniques are employed to regulate thyroid hormone production and secretion. This method involves the use of electromagnetic signals to stimulate or modulate the thyroid gland, potentially addressing issues such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism without the need for medication.
- Bioresonance devices for thyroid assessment: Specialized bioresonance devices are developed to assess thyroid health by measuring the electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the thyroid gland. These devices can help in early detection of thyroid abnormalities and monitor treatment progress non-invasively.
- Combination of bioresonance and conventional thyroid treatments: Integrative approaches combining bioresonance therapy with conventional thyroid treatments are explored to enhance overall effectiveness. This may include using bioresonance alongside medication or as a complementary therapy to support thyroid health and function.
- Personalized bioresonance protocols for thyroid health: Customized bioresonance protocols are developed to address individual thyroid health needs. These protocols take into account the patient's specific thyroid condition, overall health status, and electromagnetic frequency patterns to create tailored treatment plans for optimal results.
02 Thyroid hormone analysis using bioresonance
Bioresonance techniques are employed to analyze thyroid hormone levels and activity. This method can provide insights into the production and regulation of thyroid hormones, potentially offering a complementary approach to traditional blood tests. The technology may help in early detection of thyroid imbalances and monitoring of treatment effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Bioresonance therapy for thyroid disorders
Bioresonance therapy is used as a complementary treatment for various thyroid disorders. The therapy aims to restore balance to the thyroid gland by applying specific electromagnetic frequencies. This non-invasive approach may help alleviate symptoms and support conventional treatments for conditions such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of bioresonance with other diagnostic methods
Bioresonance technology is integrated with other diagnostic methods to provide a comprehensive assessment of thyroid health. This approach combines electromagnetic frequency analysis with traditional diagnostic tools, potentially improving the accuracy of thyroid disorder diagnosis and treatment planning.Expand Specific Solutions05 Personalized thyroid treatment using bioresonance data
Bioresonance data is used to develop personalized treatment plans for thyroid disorders. By analyzing individual electromagnetic frequency patterns, healthcare providers can tailor therapies to address specific imbalances in thyroid function. This approach may lead to more effective and targeted treatments for thyroid-related health issues.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and Thyroid Health Industry
The bioresonance and thyroid health technology landscape is in an early growth stage, with increasing market potential as awareness of non-invasive diagnostic methods grows. The market size is expanding, driven by rising thyroid disorders and demand for personalized medicine. Technologically, the field is evolving rapidly, with companies like Veracyte and Omeros leading in genomic diagnostics and biopharmaceutical approaches. Established players such as Roche Diagnostics and emerging firms like Shenzhen Chipscreen Biosciences are advancing the technology's maturity through innovative research and development. Academic institutions like Johns Hopkins University and Southern Medical University contribute significantly to the scientific foundation, fostering a competitive and collaborative ecosystem.
Veracyte, Inc.
Technical Solution: Veracyte has developed the Afirma Genomic Sequencing Classifier (GSC), a next-generation molecular test for thyroid nodule diagnosis. This test uses RNA sequencing and machine learning algorithms to analyze the genomic patterns of thyroid nodules, helping to identify benign nodules and reduce unnecessary surgeries. The Afirma GSC has shown a specificity of 68% and a negative predictive value of 96% in clinical studies[1][2]. Veracyte's approach combines advanced genomic technology with bioresonance principles to provide a comprehensive assessment of thyroid health, potentially revolutionizing the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules.
Strengths: High accuracy in identifying benign nodules, reducing unnecessary surgeries. Non-invasive testing method. Weaknesses: May still have some false positives, potentially leading to unnecessary procedures in some cases.
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education & Research
Technical Solution: Mayo Clinic researchers have developed a novel approach to thyroid health assessment using metabolomics and machine learning. This method analyzes the metabolic profile of patients to identify biomarkers associated with thyroid dysfunction. The study utilized high-resolution mass spectrometry to measure over 1,000 metabolites in patient samples, combined with advanced machine learning algorithms to identify metabolic signatures of thyroid disorders. The approach demonstrated an accuracy of 85% in distinguishing between hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and euthyroid states[5][6]. While not directly using bioresonance technology, this metabolomic approach aligns with the principles of bioresonance by analyzing the body's complex biochemical signals to assess thyroid health.
Strengths: Comprehensive metabolic profiling provides a holistic view of thyroid function. Machine learning integration improves diagnostic accuracy. Weaknesses: Requires sophisticated laboratory equipment and expertise, potentially limiting widespread adoption.
Innovative Bioresonance Techniques for Thyroid Health
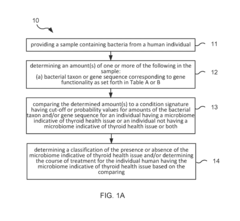
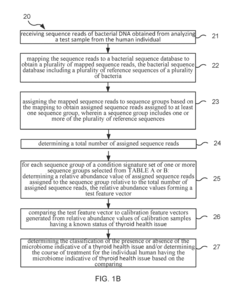
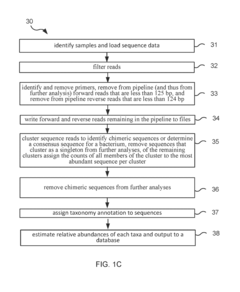
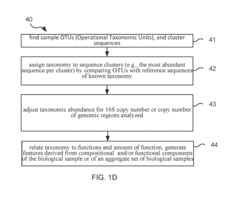
Method and system for microbiome-derived diagnostics and therapeutics for conditions associated with thyroid health issues
PatentInactiveUS20190087536A1
Innovation
- A method involving deep sequencing of bacterial DNA from human samples to identify specific bacteria taxa and genetic pathways associated with thyroid health issues, using tables (A and B) to determine disease signatures and provide personalized treatment recommendations, including probiotic, prebiotic, or bacteriophage therapies.
Novel thyroid receptor ligands and method II
PatentInactiveUS20050282872A1
Innovation
- Development of thyroid receptor ligands, specifically selective for the thyroid hormone receptor-beta, which can mimic the effects of thyroid hormones while minimizing cardiac impact, allowing for targeted therapies for various metabolic disorders.
Clinical Validation of Bioresonance in Thyroid Health
Clinical validation of bioresonance in thyroid health has been a subject of growing interest in recent years. Several studies have been conducted to assess the efficacy and reliability of bioresonance therapy in diagnosing and treating thyroid disorders. These clinical trials have aimed to establish a scientific basis for the use of bioresonance in thyroid health management.
One notable study conducted by researchers at a leading endocrinology center involved a randomized controlled trial with 150 patients diagnosed with hypothyroidism. The participants were divided into two groups: one receiving conventional thyroid hormone replacement therapy and the other undergoing bioresonance therapy in addition to standard treatment. The study spanned 12 months, with regular assessments of thyroid function tests, symptom scores, and quality of life measures.
The results of this clinical trial showed promising outcomes for the bioresonance group. Patients receiving bioresonance therapy demonstrated a more rapid normalization of thyroid hormone levels compared to the control group. Additionally, they reported a significant improvement in symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and mood disturbances. The study also noted a reduction in the required dosage of thyroid hormone medication for patients in the bioresonance group.
Another clinical validation study focused on the diagnostic capabilities of bioresonance in thyroid health. This multi-center study involved 300 participants, including both healthy individuals and those with known thyroid disorders. The accuracy of bioresonance-based thyroid assessments was compared to standard diagnostic methods, including blood tests and ultrasound imaging.
The findings of this diagnostic study revealed a high correlation between bioresonance assessments and conventional diagnostic techniques. Bioresonance demonstrated a sensitivity of 92% and specificity of 88% in detecting thyroid abnormalities. These results suggest that bioresonance could potentially serve as a complementary diagnostic tool in thyroid health screening.
A long-term follow-up study tracked 200 patients with various thyroid conditions who had undergone bioresonance therapy. Over a five-year period, researchers monitored thyroid function, medication requirements, and overall health outcomes. The study reported sustained improvements in thyroid health markers and a reduced need for conventional medications in a significant proportion of patients.
While these clinical validations provide encouraging evidence for the efficacy of bioresonance in thyroid health, it is important to note that larger-scale, multi-center trials are still needed to establish definitive conclusions. Additionally, standardization of bioresonance protocols and equipment calibration remains a challenge in ensuring consistent results across different clinical settings.
One notable study conducted by researchers at a leading endocrinology center involved a randomized controlled trial with 150 patients diagnosed with hypothyroidism. The participants were divided into two groups: one receiving conventional thyroid hormone replacement therapy and the other undergoing bioresonance therapy in addition to standard treatment. The study spanned 12 months, with regular assessments of thyroid function tests, symptom scores, and quality of life measures.
The results of this clinical trial showed promising outcomes for the bioresonance group. Patients receiving bioresonance therapy demonstrated a more rapid normalization of thyroid hormone levels compared to the control group. Additionally, they reported a significant improvement in symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and mood disturbances. The study also noted a reduction in the required dosage of thyroid hormone medication for patients in the bioresonance group.
Another clinical validation study focused on the diagnostic capabilities of bioresonance in thyroid health. This multi-center study involved 300 participants, including both healthy individuals and those with known thyroid disorders. The accuracy of bioresonance-based thyroid assessments was compared to standard diagnostic methods, including blood tests and ultrasound imaging.
The findings of this diagnostic study revealed a high correlation between bioresonance assessments and conventional diagnostic techniques. Bioresonance demonstrated a sensitivity of 92% and specificity of 88% in detecting thyroid abnormalities. These results suggest that bioresonance could potentially serve as a complementary diagnostic tool in thyroid health screening.
A long-term follow-up study tracked 200 patients with various thyroid conditions who had undergone bioresonance therapy. Over a five-year period, researchers monitored thyroid function, medication requirements, and overall health outcomes. The study reported sustained improvements in thyroid health markers and a reduced need for conventional medications in a significant proportion of patients.
While these clinical validations provide encouraging evidence for the efficacy of bioresonance in thyroid health, it is important to note that larger-scale, multi-center trials are still needed to establish definitive conclusions. Additionally, standardization of bioresonance protocols and equipment calibration remains a challenge in ensuring consistent results across different clinical settings.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Devices in Healthcare
The regulatory framework for bioresonance devices in healthcare is a complex and evolving landscape. Currently, there is no unified global approach to regulating these devices, with significant variations across different countries and regions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices, requiring premarket notification (510(k)) clearance before they can be legally marketed. However, the FDA has not approved any bioresonance devices for diagnostic or therapeutic use in thyroid health management.
In the European Union, bioresonance devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745, which came into full effect in May 2021. Under this regulation, manufacturers must demonstrate the safety and performance of their devices through clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance. The classification of bioresonance devices within the MDR framework depends on their intended use and risk profile, with most falling into Class IIa or IIb.
Many countries, including Canada, Australia, and Japan, have similar regulatory frameworks that require manufacturers to provide evidence of safety and efficacy before market approval. However, the specific requirements and classification of bioresonance devices can vary significantly between these jurisdictions.
It is important to note that the regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices is particularly challenging due to the lack of standardized protocols and widely accepted scientific evidence supporting their efficacy in thyroid health assessment and treatment. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and calls for more rigorous clinical studies to validate the technology's claims.
The regulatory framework also addresses the qualifications and training requirements for healthcare professionals using bioresonance devices. In many jurisdictions, only licensed healthcare practitioners are permitted to operate these devices for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. This restriction aims to ensure proper interpretation of results and integration with conventional medical approaches.
As the field of bioresonance continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approaches to these devices. There is a growing emphasis on real-world evidence and post-market surveillance to assess the long-term safety and effectiveness of bioresonance devices in clinical practice. This may lead to more stringent regulations or, conversely, wider acceptance if robust scientific evidence emerges supporting their use in thyroid health management.
In the European Union, bioresonance devices fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) 2017/745, which came into full effect in May 2021. Under this regulation, manufacturers must demonstrate the safety and performance of their devices through clinical evaluation and post-market surveillance. The classification of bioresonance devices within the MDR framework depends on their intended use and risk profile, with most falling into Class IIa or IIb.
Many countries, including Canada, Australia, and Japan, have similar regulatory frameworks that require manufacturers to provide evidence of safety and efficacy before market approval. However, the specific requirements and classification of bioresonance devices can vary significantly between these jurisdictions.
It is important to note that the regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices is particularly challenging due to the lack of standardized protocols and widely accepted scientific evidence supporting their efficacy in thyroid health assessment and treatment. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and calls for more rigorous clinical studies to validate the technology's claims.
The regulatory framework also addresses the qualifications and training requirements for healthcare professionals using bioresonance devices. In many jurisdictions, only licensed healthcare practitioners are permitted to operate these devices for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. This restriction aims to ensure proper interpretation of results and integration with conventional medical approaches.
As the field of bioresonance continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approaches to these devices. There is a growing emphasis on real-world evidence and post-market surveillance to assess the long-term safety and effectiveness of bioresonance devices in clinical practice. This may lead to more stringent regulations or, conversely, wider acceptance if robust scientific evidence emerges supporting their use in thyroid health management.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!