A Visionary Approach to Hypochlorous Acid in Waste Recycling
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCL in Waste Recycling: Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising agent in waste recycling, offering a novel approach to addressing environmental challenges. The evolution of waste management technologies has led to the exploration of innovative solutions, with HOCl standing out for its potential to revolutionize recycling processes. This visionary approach aims to harness the unique properties of HOCl to enhance waste treatment efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and promote sustainable resource management.
The primary objective of incorporating HOCl in waste recycling is to develop more effective and environmentally friendly methods for processing various types of waste materials. By leveraging the powerful oxidizing and disinfecting properties of HOCl, researchers and industry professionals seek to overcome existing limitations in waste treatment technologies. This includes improving the breakdown of complex organic compounds, neutralizing harmful pathogens, and facilitating the separation of recyclable materials from mixed waste streams.
HOCl's role in waste recycling is rooted in its chemical versatility and eco-friendly nature. As a naturally occurring compound produced by the human immune system, HOCl presents a non-toxic alternative to harsh chemical treatments commonly used in waste management. Its ability to effectively neutralize a wide range of contaminants without leaving harmful residues aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and safe environmental practices.
The technological trajectory of HOCl in waste recycling encompasses several key areas of development. These include optimizing HOCl production methods for large-scale applications, designing specialized equipment for HOCl-based waste treatment, and integrating HOCl processes into existing recycling infrastructures. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of HOCl in addressing specific waste management challenges, such as the treatment of electronic waste, medical waste, and difficult-to-recycle plastics.
As global waste production continues to rise, the need for innovative recycling solutions becomes increasingly critical. The exploration of HOCl in this context represents a forward-thinking approach to tackling one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. By focusing on HOCl's potential, the waste management industry aims to develop more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible recycling processes that can adapt to the evolving nature of waste streams and regulatory requirements.
The integration of HOCl into waste recycling systems also aligns with broader sustainability goals, including the reduction of landfill usage, minimization of greenhouse gas emissions from waste treatment processes, and the promotion of circular economy principles. As such, the development of HOCl-based recycling technologies is not only a technical endeavor but also a strategic initiative with far-reaching implications for environmental conservation and resource management.
The primary objective of incorporating HOCl in waste recycling is to develop more effective and environmentally friendly methods for processing various types of waste materials. By leveraging the powerful oxidizing and disinfecting properties of HOCl, researchers and industry professionals seek to overcome existing limitations in waste treatment technologies. This includes improving the breakdown of complex organic compounds, neutralizing harmful pathogens, and facilitating the separation of recyclable materials from mixed waste streams.
HOCl's role in waste recycling is rooted in its chemical versatility and eco-friendly nature. As a naturally occurring compound produced by the human immune system, HOCl presents a non-toxic alternative to harsh chemical treatments commonly used in waste management. Its ability to effectively neutralize a wide range of contaminants without leaving harmful residues aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and safe environmental practices.
The technological trajectory of HOCl in waste recycling encompasses several key areas of development. These include optimizing HOCl production methods for large-scale applications, designing specialized equipment for HOCl-based waste treatment, and integrating HOCl processes into existing recycling infrastructures. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of HOCl in addressing specific waste management challenges, such as the treatment of electronic waste, medical waste, and difficult-to-recycle plastics.
As global waste production continues to rise, the need for innovative recycling solutions becomes increasingly critical. The exploration of HOCl in this context represents a forward-thinking approach to tackling one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time. By focusing on HOCl's potential, the waste management industry aims to develop more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible recycling processes that can adapt to the evolving nature of waste streams and regulatory requirements.
The integration of HOCl into waste recycling systems also aligns with broader sustainability goals, including the reduction of landfill usage, minimization of greenhouse gas emissions from waste treatment processes, and the promotion of circular economy principles. As such, the development of HOCl-based recycling technologies is not only a technical endeavor but also a strategic initiative with far-reaching implications for environmental conservation and resource management.
Market Analysis for HOCL-based Recycling Solutions
The market for HOCL-based recycling solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent waste management regulations. The global waste recycling market is projected to reach $80 billion by 2025, with HOCL-based technologies poised to capture a substantial share due to their effectiveness and eco-friendly nature.
Hypochlorous acid (HOCL) has emerged as a promising agent in waste recycling, particularly in the treatment of organic waste and contaminated water. Its strong oxidizing properties make it highly effective in breaking down complex organic compounds, while its low toxicity and biodegradability address environmental concerns associated with traditional chemical treatments.
The demand for HOCL-based recycling solutions is particularly strong in the municipal waste management sector, where there is a growing need for efficient and sustainable waste treatment methods. Local governments and waste management companies are increasingly adopting HOCL technologies to improve recycling rates and reduce landfill usage.
In the industrial sector, HOCL-based solutions are gaining traction in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and textiles. These industries generate large volumes of organic waste and contaminated water, creating a significant market opportunity for HOCL-based recycling technologies.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market for HOCL-based recycling solutions, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental awareness. Countries like China and India are implementing stricter waste management policies, creating a favorable environment for the adoption of advanced recycling technologies.
North America and Europe remain significant markets, with established waste management infrastructure and a strong focus on sustainability. These regions are likely to drive innovation in HOCL-based recycling technologies, particularly in areas such as process optimization and integration with existing waste management systems.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Large waste management companies are investing in HOCL-based technologies to enhance their service offerings, while specialized technology providers are developing novel applications and solutions.
Key growth factors for the HOCL-based recycling market include increasing awareness of environmental issues, government regulations promoting sustainable waste management practices, and the cost-effectiveness of HOCL solutions compared to traditional chemical treatments. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized handling and storage of HOCL may impact market growth in some sectors.
Hypochlorous acid (HOCL) has emerged as a promising agent in waste recycling, particularly in the treatment of organic waste and contaminated water. Its strong oxidizing properties make it highly effective in breaking down complex organic compounds, while its low toxicity and biodegradability address environmental concerns associated with traditional chemical treatments.
The demand for HOCL-based recycling solutions is particularly strong in the municipal waste management sector, where there is a growing need for efficient and sustainable waste treatment methods. Local governments and waste management companies are increasingly adopting HOCL technologies to improve recycling rates and reduce landfill usage.
In the industrial sector, HOCL-based solutions are gaining traction in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and textiles. These industries generate large volumes of organic waste and contaminated water, creating a significant market opportunity for HOCL-based recycling technologies.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market for HOCL-based recycling solutions, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental awareness. Countries like China and India are implementing stricter waste management policies, creating a favorable environment for the adoption of advanced recycling technologies.
North America and Europe remain significant markets, with established waste management infrastructure and a strong focus on sustainability. These regions are likely to drive innovation in HOCL-based recycling technologies, particularly in areas such as process optimization and integration with existing waste management systems.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Large waste management companies are investing in HOCL-based technologies to enhance their service offerings, while specialized technology providers are developing novel applications and solutions.
Key growth factors for the HOCL-based recycling market include increasing awareness of environmental issues, government regulations promoting sustainable waste management practices, and the cost-effectiveness of HOCL solutions compared to traditional chemical treatments. However, challenges such as high initial investment costs and the need for specialized handling and storage of HOCL may impact market growth in some sectors.
Current Challenges in HOCL Waste Treatment
The treatment of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) waste presents several significant challenges in the realm of waste recycling. One of the primary issues is the inherent instability of HOCl, which tends to decompose rapidly into chlorine gas and water. This instability makes it difficult to store and transport HOCl waste over extended periods, necessitating immediate treatment or utilization.
Another major challenge lies in the corrosive nature of HOCl. Its high oxidizing potential can lead to the degradation of storage containers, pipelines, and treatment equipment, requiring the use of specialized materials that can withstand its corrosive effects. This not only increases the cost of waste management but also poses potential safety risks if not properly addressed.
The concentration of HOCl in waste streams presents an additional hurdle. Waste streams with high concentrations of HOCl can be particularly hazardous and challenging to handle, while dilute solutions may require large volumes of water for treatment, leading to increased processing costs and environmental concerns related to water usage.
Environmental regulations pose yet another challenge in HOCl waste treatment. Stringent guidelines regarding the discharge of chlorine-containing compounds into water bodies necessitate advanced treatment processes to ensure compliance. This often involves complex neutralization or dechlorination steps, adding to the overall complexity and cost of waste management.
The potential for by-product formation during HOCl waste treatment is a significant concern. Reactions between HOCl and organic matter in waste streams can lead to the formation of disinfection by-products (DBPs), such as trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids, which are known to have adverse health effects. Mitigating the formation of these by-products while effectively treating HOCl waste requires careful process control and monitoring.
Furthermore, the variability in waste composition presents challenges in developing standardized treatment protocols. Different industrial processes generate HOCl waste with varying concentrations and contaminants, necessitating flexible and adaptable treatment solutions. This variability complicates the design of universal treatment systems and often requires site-specific solutions.
Lastly, the energy intensity of some HOCl waste treatment methods poses both economic and environmental challenges. Advanced oxidation processes or electrochemical treatments, while effective, can be energy-intensive, contributing to higher operational costs and increased carbon footprints. Balancing treatment efficacy with energy efficiency remains a key challenge in developing sustainable HOCl waste management strategies.
Another major challenge lies in the corrosive nature of HOCl. Its high oxidizing potential can lead to the degradation of storage containers, pipelines, and treatment equipment, requiring the use of specialized materials that can withstand its corrosive effects. This not only increases the cost of waste management but also poses potential safety risks if not properly addressed.
The concentration of HOCl in waste streams presents an additional hurdle. Waste streams with high concentrations of HOCl can be particularly hazardous and challenging to handle, while dilute solutions may require large volumes of water for treatment, leading to increased processing costs and environmental concerns related to water usage.
Environmental regulations pose yet another challenge in HOCl waste treatment. Stringent guidelines regarding the discharge of chlorine-containing compounds into water bodies necessitate advanced treatment processes to ensure compliance. This often involves complex neutralization or dechlorination steps, adding to the overall complexity and cost of waste management.
The potential for by-product formation during HOCl waste treatment is a significant concern. Reactions between HOCl and organic matter in waste streams can lead to the formation of disinfection by-products (DBPs), such as trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids, which are known to have adverse health effects. Mitigating the formation of these by-products while effectively treating HOCl waste requires careful process control and monitoring.
Furthermore, the variability in waste composition presents challenges in developing standardized treatment protocols. Different industrial processes generate HOCl waste with varying concentrations and contaminants, necessitating flexible and adaptable treatment solutions. This variability complicates the design of universal treatment systems and often requires site-specific solutions.
Lastly, the energy intensity of some HOCl waste treatment methods poses both economic and environmental challenges. Advanced oxidation processes or electrochemical treatments, while effective, can be energy-intensive, contributing to higher operational costs and increased carbon footprints. Balancing treatment efficacy with energy efficiency remains a key challenge in developing sustainable HOCl waste management strategies.
Existing HOCL Waste Recycling Methods
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions and chemical reactions involving chlorine and water. These processes are optimized for efficiency and purity, with considerations for pH control and stabilization of the resulting solution.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods for producing hypochlorous acid are described, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and novel techniques for generating stable hypochlorous acid solutions. These methods aim to improve the efficiency and purity of hypochlorous acid production for various applications.
- Applications in disinfection and sterilization: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as a powerful disinfectant and sterilizing agent. It is effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Applications include water treatment, surface disinfection, and medical sterilization, with emphasis on its safety and eco-friendly nature compared to traditional chlorine-based disinfectants.
- Formulations and stability enhancement: Research focuses on developing stable formulations of hypochlorous acid to extend its shelf life and maintain its efficacy. This includes the use of specific additives, pH adjustments, and packaging innovations to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability for various commercial and industrial applications.
- Medical and therapeutic applications: Hypochlorous acid is explored for various medical and therapeutic uses due to its antimicrobial properties and low toxicity to human cells. Applications include wound care, eye care, respiratory treatments, and dermatological therapies. Research focuses on optimizing concentrations and delivery methods for these medical applications.
- Environmental and industrial uses: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in environmental remediation and industrial processes. It is used in wastewater treatment, air purification systems, and as a green alternative in various industrial cleaning and sanitization processes. Research also explores its potential in agriculture for crop protection and soil treatment.
02 Applications in disinfection and sterilization
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as a powerful disinfectant and sterilizing agent. It is effective against a broad spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Applications range from water treatment to surface disinfection in healthcare settings and food processing industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulation and stabilization techniques
Developing stable formulations of hypochlorous acid is crucial for its effectiveness and shelf life. Techniques include pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and packaging innovations to prevent degradation and maintain potency over time.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic applications
Hypochlorous acid has found applications in various medical and therapeutic contexts. It is used in wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments due to its antimicrobial properties and low toxicity to human cells when properly formulated.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial uses
Beyond medical applications, hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation, industrial cleaning, and agriculture. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness make it suitable for large-scale disinfection processes and as an alternative to harsher chemicals in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCL Waste Management
The hypochlorous acid waste recycling technology is in an early development stage, with a growing market driven by increasing environmental concerns and waste management regulations. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with significant growth potential. Technologically, it is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like LG Chem, Wacker Chemie, and FUJIFILM are leveraging their chemical expertise to develop advanced solutions, while specialized firms such as WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB and Symbiosis Technology are focusing on niche applications. Academic institutions like Nanjing University and Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology are contributing to fundamental research, potentially accelerating technological advancements in this field.
WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB
Technical Solution: WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB has developed an innovative approach to utilizing hypochlorous acid in waste recycling. Their technology focuses on the production of stable, high-quality hypochlorous acid through electrolysis of salt water. This process generates a powerful yet environmentally friendly disinfectant that can be used in various waste management applications. The company's system is designed to produce hypochlorous acid on-site, reducing transportation costs and ensuring a fresh supply for waste treatment facilities. Their method allows for precise control of the acid concentration, making it suitable for different types of waste streams[1][3].
Strengths: On-site production reduces costs and ensures freshness. Environmentally friendly disinfectant. Precise concentration control. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and training for operation.
LG Chem Ltd.
Technical Solution: LG Chem Ltd. has integrated hypochlorous acid technology into their waste recycling processes, particularly focusing on industrial and electronic waste. Their approach involves using hypochlorous acid as a key component in the treatment of contaminated water from recycling operations. The company has developed a proprietary system that generates hypochlorous acid at varying concentrations to tackle different types of pollutants. This system is integrated into their larger waste management infrastructure, allowing for efficient treatment of wastewater while recovering valuable materials from electronic waste. LG Chem's method also incorporates advanced sensors and control systems to optimize the use of hypochlorous acid, minimizing chemical consumption while maximizing treatment efficacy[2][5].
Strengths: Integrated system for electronic waste recycling. Advanced control systems for optimization. Weaknesses: May be limited to specific types of industrial waste.
Innovative HOCL Applications in Recycling
Reduction treatment method of waste water
PatentActiveJP2018167238A
Innovation
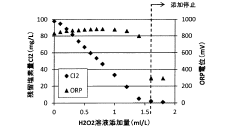
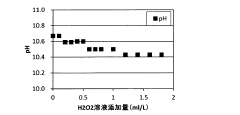
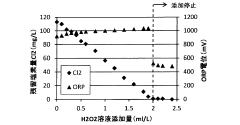
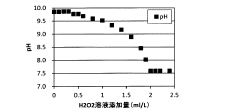
- A wastewater treatment method using hydrogen peroxide solution is applied, with the optimal amount determined by measuring oxidation-reduction potential, to remove hypochlorous acid without increasing sulfate ion concentration.
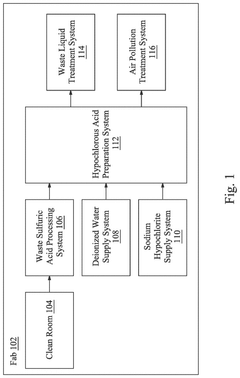
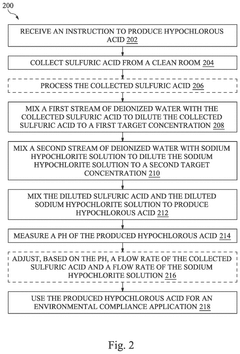
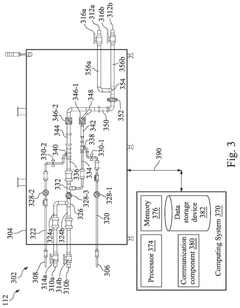
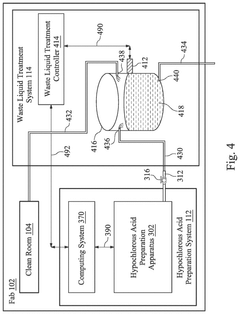
Waste-based hypochlorous acid preparation in a semiconductor fabrication plant
PatentPendingUS20250033965A1
Innovation
- A hypochlorous acid preparation system that recycles waste sulfuric acid by mixing it with sodium hypochlorite solution and deionized water, producing hypochlorous acid in situ and adjusting flow rates based on pH measurements to ensure optimal concentration and stability.
Environmental Impact of HOCL Recycling
The implementation of hypochlorous acid (HOCL) in waste recycling processes presents a significant opportunity for environmental improvement. HOCL, known for its powerful disinfectant properties, offers a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical treatments in waste management. Its use in recycling systems can lead to reduced environmental pollution and enhanced sustainability practices.
One of the primary environmental benefits of HOCL recycling is the reduction of harmful chemical residues. Unlike conventional disinfectants, HOCL breaks down into harmless components, primarily water and salt. This characteristic minimizes the risk of toxic substances leaching into soil and water systems, thereby protecting ecosystems and biodiversity. The natural decomposition of HOCL also means less chemical accumulation in landfills and water treatment facilities.
Furthermore, the production and use of HOCL in waste recycling contribute to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional chemical treatments. The process of generating HOCL on-site through electrolysis of saltwater requires minimal energy input, reducing the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing and transporting conventional disinfectants. This aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and transition towards more sustainable industrial practices.
HOCL recycling also promotes water conservation, a critical environmental concern. The efficiency of HOCL in disinfection allows for reduced water usage in cleaning processes. Additionally, the treated water can often be reused in subsequent recycling cycles, further minimizing water consumption. This aspect is particularly valuable in regions facing water scarcity issues, where sustainable water management is crucial.
The implementation of HOCL in waste recycling systems can lead to improved air quality in and around recycling facilities. Traditional chemical treatments often release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. In contrast, HOCL produces minimal off-gassing, resulting in cleaner air for workers and surrounding communities. This reduction in air pollution contributes to overall environmental health and reduces the risk of respiratory issues associated with poor air quality.
Moreover, the use of HOCL in recycling processes can enhance the quality and safety of recycled materials. By effectively eliminating pathogens and contaminants, HOCL treatment ensures that recycled products meet stringent health and safety standards. This not only protects consumers but also increases confidence in recycled materials, potentially boosting recycling rates and reducing the demand for virgin resources.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of HOCL recycling is predominantly positive, offering a more sustainable approach to waste management. Its implementation aligns with circular economy principles, promoting resource efficiency and minimizing environmental harm. As industries continue to seek greener solutions, the adoption of HOCL in waste recycling represents a significant step towards more environmentally responsible practices.
One of the primary environmental benefits of HOCL recycling is the reduction of harmful chemical residues. Unlike conventional disinfectants, HOCL breaks down into harmless components, primarily water and salt. This characteristic minimizes the risk of toxic substances leaching into soil and water systems, thereby protecting ecosystems and biodiversity. The natural decomposition of HOCL also means less chemical accumulation in landfills and water treatment facilities.
Furthermore, the production and use of HOCL in waste recycling contribute to lower carbon emissions compared to traditional chemical treatments. The process of generating HOCL on-site through electrolysis of saltwater requires minimal energy input, reducing the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing and transporting conventional disinfectants. This aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and transition towards more sustainable industrial practices.
HOCL recycling also promotes water conservation, a critical environmental concern. The efficiency of HOCL in disinfection allows for reduced water usage in cleaning processes. Additionally, the treated water can often be reused in subsequent recycling cycles, further minimizing water consumption. This aspect is particularly valuable in regions facing water scarcity issues, where sustainable water management is crucial.
The implementation of HOCL in waste recycling systems can lead to improved air quality in and around recycling facilities. Traditional chemical treatments often release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants. In contrast, HOCL produces minimal off-gassing, resulting in cleaner air for workers and surrounding communities. This reduction in air pollution contributes to overall environmental health and reduces the risk of respiratory issues associated with poor air quality.
Moreover, the use of HOCL in recycling processes can enhance the quality and safety of recycled materials. By effectively eliminating pathogens and contaminants, HOCL treatment ensures that recycled products meet stringent health and safety standards. This not only protects consumers but also increases confidence in recycled materials, potentially boosting recycling rates and reducing the demand for virgin resources.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of HOCL recycling is predominantly positive, offering a more sustainable approach to waste management. Its implementation aligns with circular economy principles, promoting resource efficiency and minimizing environmental harm. As industries continue to seek greener solutions, the adoption of HOCL in waste recycling represents a significant step towards more environmentally responsible practices.
Regulatory Framework for HOCL in Waste Treatment
The regulatory framework for hypochlorous acid (HOCL) in waste treatment is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in shaping the adoption and implementation of this innovative technology. At the federal level, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established guidelines for the use of HOCL in various applications, including waste treatment. These regulations primarily focus on ensuring the safety and efficacy of HOCL-based solutions while minimizing potential environmental impacts.
One of the key aspects of the regulatory framework is the registration and approval process for HOCL-based products. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with EPA standards, including providing data on product composition, efficacy, and safety. The EPA's Pesticide Registration Program oversees this process, ensuring that HOCL products meet stringent criteria before being approved for use in waste treatment applications.
State-level regulations also play a significant role in governing the use of HOCL in waste treatment. Many states have adopted their own guidelines and requirements, which may be more stringent than federal regulations. These state-specific regulations often address issues such as storage, handling, and disposal of HOCL solutions, as well as worker safety protocols and environmental monitoring requirements.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established workplace safety standards for the handling and use of HOCL in waste treatment facilities. These regulations cover aspects such as personal protective equipment, exposure limits, and emergency response procedures. Compliance with OSHA standards is essential for waste treatment facilities implementing HOCL-based technologies.
International regulations also influence the adoption of HOCL in waste treatment, particularly for multinational corporations or facilities operating in multiple countries. Organizations such as the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have established guidelines and standards for the use of HOCL in various applications, including waste treatment.
As the technology continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are actively reviewing and updating their frameworks to address emerging concerns and opportunities. This includes ongoing research into the long-term environmental impacts of HOCL use in waste treatment, as well as the development of new standards for monitoring and reporting.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses waste classification and disposal regulations, which may impact the implementation of HOCL-based treatment solutions. Facilities must ensure that their HOCL-treated waste meets applicable standards for disposal or reuse, depending on the specific waste stream and local regulations.
One of the key aspects of the regulatory framework is the registration and approval process for HOCL-based products. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with EPA standards, including providing data on product composition, efficacy, and safety. The EPA's Pesticide Registration Program oversees this process, ensuring that HOCL products meet stringent criteria before being approved for use in waste treatment applications.
State-level regulations also play a significant role in governing the use of HOCL in waste treatment. Many states have adopted their own guidelines and requirements, which may be more stringent than federal regulations. These state-specific regulations often address issues such as storage, handling, and disposal of HOCL solutions, as well as worker safety protocols and environmental monitoring requirements.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established workplace safety standards for the handling and use of HOCL in waste treatment facilities. These regulations cover aspects such as personal protective equipment, exposure limits, and emergency response procedures. Compliance with OSHA standards is essential for waste treatment facilities implementing HOCL-based technologies.
International regulations also influence the adoption of HOCL in waste treatment, particularly for multinational corporations or facilities operating in multiple countries. Organizations such as the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have established guidelines and standards for the use of HOCL in various applications, including waste treatment.
As the technology continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are actively reviewing and updating their frameworks to address emerging concerns and opportunities. This includes ongoing research into the long-term environmental impacts of HOCL use in waste treatment, as well as the development of new standards for monitoring and reporting.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses waste classification and disposal regulations, which may impact the implementation of HOCL-based treatment solutions. Facilities must ensure that their HOCL-treated waste meets applicable standards for disposal or reuse, depending on the specific waste stream and local regulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!