Challenges and Opportunities in the Global Hypochlorous Acid Market
AUG 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Market Overview
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a significant player in the global disinfectant market, with its applications spanning across various industries. The HOCl market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its effectiveness as a powerful yet safe sanitizing agent. This eco-friendly compound, naturally produced by the human immune system, has gained traction in healthcare, water treatment, agriculture, and food processing sectors.
The global HOCl market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including solutions, gels, and sprays, catering to different end-user requirements. The healthcare sector remains a primary consumer, utilizing HOCl for wound care, sterilization, and general disinfection purposes. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for HOCl-based products, as businesses and individuals seek reliable sanitization solutions.
In terms of regional distribution, North America and Europe currently dominate the HOCl market, owing to stringent regulations on hygiene standards and a well-established healthcare infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by rapid industrialization, growing healthcare expenditure, and increasing awareness of infection control measures.
The market landscape is moderately fragmented, with a mix of established players and new entrants vying for market share. Key companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to strengthen their position. The development of stable, long-lasting HOCl formulations and the exploration of new application areas are ongoing trends shaping the market dynamics.
Despite its growth potential, the HOCl market faces challenges such as the short shelf life of some products and the need for specialized production and storage facilities. Additionally, the lack of standardized regulations across different regions poses hurdles for market players in terms of product approval and marketing.
Looking ahead, the HOCl market is poised for continued growth, driven by increasing hygiene consciousness, the rise of antimicrobial resistance, and the growing adoption of sustainable disinfection solutions. The development of advanced production technologies and the expansion of distribution networks are expected to further propel market growth, opening up new opportunities for both established players and innovative startups in this evolving landscape.
The global HOCl market is characterized by a diverse range of products, including solutions, gels, and sprays, catering to different end-user requirements. The healthcare sector remains a primary consumer, utilizing HOCl for wound care, sterilization, and general disinfection purposes. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for HOCl-based products, as businesses and individuals seek reliable sanitization solutions.
In terms of regional distribution, North America and Europe currently dominate the HOCl market, owing to stringent regulations on hygiene standards and a well-established healthcare infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a lucrative market, driven by rapid industrialization, growing healthcare expenditure, and increasing awareness of infection control measures.
The market landscape is moderately fragmented, with a mix of established players and new entrants vying for market share. Key companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographical expansion to strengthen their position. The development of stable, long-lasting HOCl formulations and the exploration of new application areas are ongoing trends shaping the market dynamics.
Despite its growth potential, the HOCl market faces challenges such as the short shelf life of some products and the need for specialized production and storage facilities. Additionally, the lack of standardized regulations across different regions poses hurdles for market players in terms of product approval and marketing.
Looking ahead, the HOCl market is poised for continued growth, driven by increasing hygiene consciousness, the rise of antimicrobial resistance, and the growing adoption of sustainable disinfection solutions. The development of advanced production technologies and the expansion of distribution networks are expected to further propel market growth, opening up new opportunities for both established players and innovative startups in this evolving landscape.
Global Demand Analysis
The global demand for hypochlorous acid has been steadily increasing, driven by its versatile applications across various industries. In the healthcare sector, hypochlorous acid has gained significant traction due to its powerful disinfectant properties and low toxicity. Hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities are increasingly adopting hypochlorous acid-based solutions for surface disinfection and wound care, contributing to market growth.
The food and beverage industry represents another major demand driver for hypochlorous acid. As consumers become more health-conscious and demand safer food processing methods, manufacturers are turning to hypochlorous acid as an effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical sanitizers. Its use in produce washing, equipment sanitization, and food contact surface disinfection has led to a surge in demand from this sector.
Water treatment applications have also fueled the global demand for hypochlorous acid. Municipal water treatment plants and industrial facilities are incorporating hypochlorous acid into their purification processes due to its efficacy in eliminating harmful microorganisms without producing harmful byproducts. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions facing water scarcity and increasing concerns about waterborne diseases.
The agriculture sector has emerged as a promising market for hypochlorous acid, with applications in crop protection, seed treatment, and livestock care. Farmers are increasingly adopting hypochlorous acid-based solutions as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional pesticides and disinfectants, driving demand in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe have been leading the global demand for hypochlorous acid, primarily due to stringent regulations on chemical usage and a growing emphasis on sustainable practices. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and rising awareness about hygiene and sanitation.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly accelerated the demand for hypochlorous acid globally. The heightened focus on disinfection and sanitization across various sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, and public spaces, has led to a surge in the adoption of hypochlorous acid-based products. This trend is expected to continue even post-pandemic, as hygiene practices become more ingrained in society.
Despite the growing demand, challenges such as the short shelf life of hypochlorous acid solutions and the need for specialized equipment for on-site generation have somewhat limited its widespread adoption. However, ongoing research and development efforts are addressing these issues, potentially opening up new avenues for market expansion and increased global demand.
The food and beverage industry represents another major demand driver for hypochlorous acid. As consumers become more health-conscious and demand safer food processing methods, manufacturers are turning to hypochlorous acid as an effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical sanitizers. Its use in produce washing, equipment sanitization, and food contact surface disinfection has led to a surge in demand from this sector.
Water treatment applications have also fueled the global demand for hypochlorous acid. Municipal water treatment plants and industrial facilities are incorporating hypochlorous acid into their purification processes due to its efficacy in eliminating harmful microorganisms without producing harmful byproducts. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions facing water scarcity and increasing concerns about waterborne diseases.
The agriculture sector has emerged as a promising market for hypochlorous acid, with applications in crop protection, seed treatment, and livestock care. Farmers are increasingly adopting hypochlorous acid-based solutions as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional pesticides and disinfectants, driving demand in this segment.
Geographically, North America and Europe have been leading the global demand for hypochlorous acid, primarily due to stringent regulations on chemical usage and a growing emphasis on sustainable practices. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in demand, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing healthcare expenditure, and rising awareness about hygiene and sanitation.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly accelerated the demand for hypochlorous acid globally. The heightened focus on disinfection and sanitization across various sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, and public spaces, has led to a surge in the adoption of hypochlorous acid-based products. This trend is expected to continue even post-pandemic, as hygiene practices become more ingrained in society.
Despite the growing demand, challenges such as the short shelf life of hypochlorous acid solutions and the need for specialized equipment for on-site generation have somewhat limited its widespread adoption. However, ongoing research and development efforts are addressing these issues, potentially opening up new avenues for market expansion and increased global demand.
Technical Challenges
The global hypochlorous acid market faces several technical challenges that impact its growth and widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is the instability of hypochlorous acid solutions. The compound tends to degrade rapidly, especially when exposed to light, heat, or organic matter. This instability necessitates careful handling, storage, and transportation procedures, which can increase operational costs and limit shelf life.
Another significant challenge is the precise control of pH levels during production and application. Hypochlorous acid's effectiveness is highly dependent on maintaining a specific pH range, typically between 5 and 6.5. Deviations from this range can result in reduced efficacy or the formation of undesirable by-products. Achieving and maintaining this optimal pH consistently across various applications and environments poses a considerable technical hurdle.
The production of high-purity hypochlorous acid at scale presents additional challenges. Current manufacturing processes often result in solutions containing other chlorine species or impurities, which can affect the product's performance and safety profile. Developing more efficient and cost-effective purification techniques is crucial for expanding market opportunities and ensuring product quality.
Standardization of production methods and quality control measures across the industry is another area of concern. The lack of universally accepted standards for hypochlorous acid production and testing can lead to inconsistencies in product quality and efficacy, potentially undermining consumer confidence and regulatory compliance.
The development of stable formulations that extend the shelf life of hypochlorous acid products without compromising their effectiveness is an ongoing technical challenge. This includes research into stabilizing additives, packaging innovations, and novel delivery systems that can preserve the acid's potency over extended periods.
Furthermore, the industry faces challenges in optimizing the concentration of hypochlorous acid for different applications. While higher concentrations may be more effective for certain uses, they also increase the risk of material incompatibility and potential safety hazards. Balancing efficacy with safety across diverse applications requires ongoing research and development efforts.
Lastly, the environmental impact of hypochlorous acid production and disposal is a growing concern. Developing greener production methods, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing waste generation are critical challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the long-term sustainability of the hypochlorous acid market.
Another significant challenge is the precise control of pH levels during production and application. Hypochlorous acid's effectiveness is highly dependent on maintaining a specific pH range, typically between 5 and 6.5. Deviations from this range can result in reduced efficacy or the formation of undesirable by-products. Achieving and maintaining this optimal pH consistently across various applications and environments poses a considerable technical hurdle.
The production of high-purity hypochlorous acid at scale presents additional challenges. Current manufacturing processes often result in solutions containing other chlorine species or impurities, which can affect the product's performance and safety profile. Developing more efficient and cost-effective purification techniques is crucial for expanding market opportunities and ensuring product quality.
Standardization of production methods and quality control measures across the industry is another area of concern. The lack of universally accepted standards for hypochlorous acid production and testing can lead to inconsistencies in product quality and efficacy, potentially undermining consumer confidence and regulatory compliance.
The development of stable formulations that extend the shelf life of hypochlorous acid products without compromising their effectiveness is an ongoing technical challenge. This includes research into stabilizing additives, packaging innovations, and novel delivery systems that can preserve the acid's potency over extended periods.
Furthermore, the industry faces challenges in optimizing the concentration of hypochlorous acid for different applications. While higher concentrations may be more effective for certain uses, they also increase the risk of material incompatibility and potential safety hazards. Balancing efficacy with safety across diverse applications requires ongoing research and development efforts.
Lastly, the environmental impact of hypochlorous acid production and disposal is a growing concern. Developing greener production methods, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing waste generation are critical challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the long-term sustainability of the hypochlorous acid market.
Current Production Methods
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: To enhance the shelf life and maintain the efficacy of hypochlorous acid solutions, various stabilization techniques are employed. These may include pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging to protect the solution from degradation factors such as light and air exposure.
- Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in medical treatments and therapies, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its ability to effectively kill pathogens while being gentle on human tissues makes it suitable for various medical applications.
- Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation, industrial cleaning, and agricultural applications. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness in removing contaminants make it a preferred choice for various industrial processes and environmental treatments.
02 Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens makes it valuable for disinfection and sanitization purposes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization and formulation of hypochlorous acid solutions
Techniques for stabilizing hypochlorous acid solutions and formulating them for specific applications are crucial. This includes adjusting pH, adding stabilizers, and developing appropriate packaging to maintain the acid's efficacy over time.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid finds applications in various medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its gentle yet effective nature makes it suitable for use on sensitive tissues.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation, industrial cleaning, and agriculture. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness in removing contaminants make it a preferred choice in these sectors.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The global hypochlorous acid market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly disinfectants and sanitizers. The market size is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB, Annihilare Medical Systems, and Aquaox leading innovation in production methods and applications. Established players such as Robert Bosch GmbH and Dyson Technology Ltd. are also entering the market, leveraging their R&D capabilities. The competitive landscape is diverse, with a mix of specialized biotech firms, medical technology companies, and large conglomerates vying for market share, indicating the technology's broad applicability and potential.
WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB
Technical Solution: WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB has developed an innovative electrolysis-based system for on-site production of hypochlorous acid (HOCl). Their technology utilizes a patented membrane cell design that allows for the efficient generation of stable HOCl solutions with precise control over concentration and pH levels. The system incorporates advanced sensors and automation to ensure consistent quality and optimize resource utilization. WIAB's approach addresses key challenges in the global HOCl market by enabling decentralized production, reducing transportation costs, and minimizing chemical storage requirements[1][3].
Strengths: On-site production reduces logistics costs and improves freshness. Precise control over HOCl properties enhances efficacy and safety. Weaknesses: Initial investment in equipment may be high for some users. Requires reliable access to water and electricity.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS has developed a proprietary electrochemical activation (ECA) technology for producing highly effective hypochlorous acid solutions. Their system utilizes a unique combination of electrode materials and controlled electrolysis parameters to generate HOCl with optimal antimicrobial properties. The company's approach focuses on maximizing the stability and efficacy of the produced HOCl, addressing key challenges in shelf life and potency. Annihilare's technology incorporates real-time monitoring and adjustment of solution characteristics, ensuring consistent quality across various applications in healthcare and industrial settings[2][5].
Strengths: Produces highly stable and effective HOCl solutions. Versatile applications in medical and industrial sectors. Weaknesses: May require specialized training for operation and maintenance. Potential for higher production costs compared to traditional methods.
Innovative HOCl Technologies
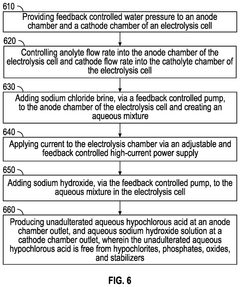
Smart tank predictive production feedback system and method
PatentPendingUS20250101603A1
Innovation
- A system for remote, predictive feedback-controlled production of pure HOCl using electrolysis, which continuously monitors and adjusts parameters like pH, ORP, and chlorine concentration, ensuring the production of HOCl free from hypochlorites and stabilizers, using feedback-controlled water pressure, electric current, and sodium chloride and hydroxide levels.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment surrounding the global hypochlorous acid market plays a crucial role in shaping its challenges and opportunities. As a disinfectant and sanitizing agent, hypochlorous acid is subject to stringent regulations across various jurisdictions, particularly in the areas of public health, food safety, and environmental protection.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates hypochlorous acid under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA has approved hypochlorous acid for use as a sanitizer and disinfectant in various applications, including food contact surfaces and drinking water treatment. However, manufacturers must comply with specific labeling requirements and efficacy testing standards to ensure product safety and effectiveness.
The European Union has implemented the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which governs the use of hypochlorous acid in disinfectants and other biocidal products. Under this regulation, manufacturers must obtain product authorization before placing their hypochlorous acid-based products on the EU market. This process involves extensive safety and efficacy assessments, which can be time-consuming and costly for companies.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own regulatory frameworks for hypochlorous acid. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved hypochlorous acid for use in food processing and as a sanitizer. Similarly, South Korea's Ministry of Food and Drug Safety regulates hypochlorous acid under its biocidal products management system.
The global nature of the hypochlorous acid market presents both challenges and opportunities in terms of regulatory compliance. Companies operating in multiple regions must navigate diverse regulatory landscapes, which can increase operational complexity and costs. However, this also creates opportunities for firms that can successfully meet various international standards, potentially gaining a competitive edge in the global market.
Regulatory trends are shifting towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly disinfection solutions. This presents an opportunity for hypochlorous acid, which is generally considered eco-friendly due to its natural breakdown into salt and water. However, manufacturers must still demonstrate the environmental safety of their production processes and end products to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
As the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of disinfection practices, many regulatory bodies have expedited approval processes for effective sanitizing agents. This has created new opportunities for hypochlorous acid products in various sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, and public transportation. However, companies must remain vigilant in maintaining compliance with rapidly evolving emergency use authorizations and temporary regulatory measures.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates hypochlorous acid under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA has approved hypochlorous acid for use as a sanitizer and disinfectant in various applications, including food contact surfaces and drinking water treatment. However, manufacturers must comply with specific labeling requirements and efficacy testing standards to ensure product safety and effectiveness.
The European Union has implemented the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which governs the use of hypochlorous acid in disinfectants and other biocidal products. Under this regulation, manufacturers must obtain product authorization before placing their hypochlorous acid-based products on the EU market. This process involves extensive safety and efficacy assessments, which can be time-consuming and costly for companies.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have their own regulatory frameworks for hypochlorous acid. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved hypochlorous acid for use in food processing and as a sanitizer. Similarly, South Korea's Ministry of Food and Drug Safety regulates hypochlorous acid under its biocidal products management system.
The global nature of the hypochlorous acid market presents both challenges and opportunities in terms of regulatory compliance. Companies operating in multiple regions must navigate diverse regulatory landscapes, which can increase operational complexity and costs. However, this also creates opportunities for firms that can successfully meet various international standards, potentially gaining a competitive edge in the global market.
Regulatory trends are shifting towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly disinfection solutions. This presents an opportunity for hypochlorous acid, which is generally considered eco-friendly due to its natural breakdown into salt and water. However, manufacturers must still demonstrate the environmental safety of their production processes and end products to meet evolving regulatory requirements.
As the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of disinfection practices, many regulatory bodies have expedited approval processes for effective sanitizing agents. This has created new opportunities for hypochlorous acid products in various sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, and public transportation. However, companies must remain vigilant in maintaining compliance with rapidly evolving emergency use authorizations and temporary regulatory measures.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) production and use is a critical consideration in the global market. HOCl is generally regarded as an environmentally friendly disinfectant due to its low toxicity and rapid breakdown into harmless components. When properly produced and used, it leaves no harmful residues in the environment, making it a preferred choice for various applications.
However, the production process of HOCl can have environmental implications. Traditional methods often involve the electrolysis of salt water, which requires electricity and may contribute to carbon emissions if non-renewable energy sources are used. The energy intensity of production is a key factor in determining the overall environmental footprint of HOCl.
Water consumption is another environmental aspect to consider. The production of HOCl requires water as a primary ingredient, which could be a concern in water-stressed regions. Efficient water management and recycling practices in production facilities can help mitigate this impact.
The raw materials used in HOCl production, primarily salt and water, are abundant and renewable. This contributes to the sustainability of HOCl compared to some synthetic chemical disinfectants that rely on non-renewable petrochemical feedstocks.
In terms of disposal, HOCl breaks down into salt and water, posing minimal environmental risk. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for applications where large volumes of disinfectant may be released into the environment, such as in water treatment or agricultural uses.
The increasing adoption of HOCl as a replacement for more harmful chemical disinfectants is driving positive environmental change. It reduces the release of toxic substances into ecosystems and minimizes the risk of chemical accumulation in soil and water bodies.
However, the environmental benefits of HOCl are contingent on proper handling and application. Overuse or misuse can lead to unnecessary resource consumption and potential ecological imbalances. Education and guidelines for appropriate use are essential to maximize the environmental advantages of HOCl.
As the global market for HOCl expands, there is an opportunity to further improve its environmental profile through innovations in production technology. Research into more energy-efficient electrolysis methods and the integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities could significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with HOCl manufacturing.
However, the production process of HOCl can have environmental implications. Traditional methods often involve the electrolysis of salt water, which requires electricity and may contribute to carbon emissions if non-renewable energy sources are used. The energy intensity of production is a key factor in determining the overall environmental footprint of HOCl.
Water consumption is another environmental aspect to consider. The production of HOCl requires water as a primary ingredient, which could be a concern in water-stressed regions. Efficient water management and recycling practices in production facilities can help mitigate this impact.
The raw materials used in HOCl production, primarily salt and water, are abundant and renewable. This contributes to the sustainability of HOCl compared to some synthetic chemical disinfectants that rely on non-renewable petrochemical feedstocks.
In terms of disposal, HOCl breaks down into salt and water, posing minimal environmental risk. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for applications where large volumes of disinfectant may be released into the environment, such as in water treatment or agricultural uses.
The increasing adoption of HOCl as a replacement for more harmful chemical disinfectants is driving positive environmental change. It reduces the release of toxic substances into ecosystems and minimizes the risk of chemical accumulation in soil and water bodies.
However, the environmental benefits of HOCl are contingent on proper handling and application. Overuse or misuse can lead to unnecessary resource consumption and potential ecological imbalances. Education and guidelines for appropriate use are essential to maximize the environmental advantages of HOCl.
As the global market for HOCl expands, there is an opportunity to further improve its environmental profile through innovations in production technology. Research into more energy-efficient electrolysis methods and the integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities could significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with HOCl manufacturing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!