Realizing the Potential of Hypochlorous Acid in Pandemic Preparedness
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising agent in the fight against infectious diseases, particularly in the context of pandemic preparedness. This naturally occurring molecule, produced by the human immune system, has been known for its antimicrobial properties for over a century. However, recent advancements in production techniques and a growing understanding of its mechanisms have reignited interest in its potential applications.
The evolution of HOCl technology can be traced back to its discovery in the early 20th century. Initially, its unstable nature and short shelf life limited its practical use. Over the decades, researchers have made significant strides in stabilizing HOCl solutions, extending their efficacy, and developing more efficient production methods. These advancements have paved the way for HOCl's current resurgence in various fields, including healthcare, water treatment, and agriculture.
In the context of pandemic preparedness, HOCl presents a unique set of advantages. Its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, coupled with its non-toxic nature to human cells, positions it as a potentially game-changing solution for disinfection and sanitization. Unlike many conventional disinfectants, HOCl is effective against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, while being gentle on human skin and mucous membranes.
The primary objective of exploring HOCl's potential in pandemic preparedness is to develop robust, safe, and efficient disinfection strategies that can be rapidly deployed in various settings. This includes healthcare facilities, public spaces, transportation systems, and even personal use. The goal is to create a multi-faceted approach that can effectively reduce the spread of infectious agents while minimizing the environmental and health impacts associated with traditional chemical disinfectants.
Another critical objective is to investigate HOCl's potential as a preventive measure. This includes exploring its use in air and water purification systems, as well as in personal protective equipment (PPE). The aim is to create proactive barriers against pathogen transmission, potentially reducing the initial spread of infectious agents during a pandemic outbreak.
Furthermore, research is focused on optimizing HOCl production and delivery systems to ensure widespread availability and ease of use. This involves developing stable formulations, innovative application methods, and scalable production processes that can meet the demands of a global health crisis.
As we delve deeper into the potential of HOCl in pandemic preparedness, it is crucial to consider its integration with existing protocols and technologies. The ultimate aim is to create a comprehensive, multi-layered approach to pandemic management that leverages the unique properties of HOCl alongside other proven strategies, enhancing our overall resilience against future health crises.
The evolution of HOCl technology can be traced back to its discovery in the early 20th century. Initially, its unstable nature and short shelf life limited its practical use. Over the decades, researchers have made significant strides in stabilizing HOCl solutions, extending their efficacy, and developing more efficient production methods. These advancements have paved the way for HOCl's current resurgence in various fields, including healthcare, water treatment, and agriculture.
In the context of pandemic preparedness, HOCl presents a unique set of advantages. Its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, coupled with its non-toxic nature to human cells, positions it as a potentially game-changing solution for disinfection and sanitization. Unlike many conventional disinfectants, HOCl is effective against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, while being gentle on human skin and mucous membranes.
The primary objective of exploring HOCl's potential in pandemic preparedness is to develop robust, safe, and efficient disinfection strategies that can be rapidly deployed in various settings. This includes healthcare facilities, public spaces, transportation systems, and even personal use. The goal is to create a multi-faceted approach that can effectively reduce the spread of infectious agents while minimizing the environmental and health impacts associated with traditional chemical disinfectants.
Another critical objective is to investigate HOCl's potential as a preventive measure. This includes exploring its use in air and water purification systems, as well as in personal protective equipment (PPE). The aim is to create proactive barriers against pathogen transmission, potentially reducing the initial spread of infectious agents during a pandemic outbreak.
Furthermore, research is focused on optimizing HOCl production and delivery systems to ensure widespread availability and ease of use. This involves developing stable formulations, innovative application methods, and scalable production processes that can meet the demands of a global health crisis.
As we delve deeper into the potential of HOCl in pandemic preparedness, it is crucial to consider its integration with existing protocols and technologies. The ultimate aim is to create a comprehensive, multi-layered approach to pandemic management that leverages the unique properties of HOCl alongside other proven strategies, enhancing our overall resilience against future health crises.
Pandemic Market Analysis
The global pandemic market has experienced unprecedented growth and transformation since the outbreak of COVID-19. This surge in demand for pandemic-related products and services has created a fertile ground for innovative solutions, including those leveraging hypochlorous acid (HOCl) for pandemic preparedness. The market size for pandemic-related products reached significant levels during the peak of the COVID-19 crisis, with projections indicating sustained growth in the coming years.
Hypochlorous acid, known for its potent antimicrobial properties, has emerged as a promising contender in the fight against infectious diseases. The pandemic market for HOCl-based products spans various sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, education, and public transportation. In the healthcare segment, HOCl solutions have gained traction for surface disinfection, hand sanitization, and even potential therapeutic applications.
The demand for effective, safe, and environmentally friendly disinfectants has driven the adoption of HOCl in institutional and consumer markets. Schools, offices, and public spaces have increasingly turned to HOCl-based products for their cleaning and sanitization protocols. This shift has been further accelerated by growing awareness of the limitations and potential risks associated with traditional chemical disinfectants.
Consumer behavior has also played a crucial role in shaping the pandemic market. The heightened focus on personal hygiene and home sanitation has led to a surge in demand for household disinfectants, with HOCl-based products gaining market share due to their efficacy and safety profile. This trend is expected to persist beyond the immediate pandemic response, as consumers maintain higher hygiene standards in their daily lives.
The global supply chain for pandemic-related products, including HOCl solutions, has undergone significant restructuring to meet the explosive demand. Manufacturers have ramped up production capacities, while new players have entered the market to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the pandemic. This has led to increased competition and innovation in product formulations and delivery systems for HOCl-based solutions.
Looking ahead, the pandemic market is expected to evolve as the world transitions from crisis response to long-term preparedness. The potential of HOCl in this context is significant, with opportunities for expansion into new application areas and markets. As governments and organizations worldwide invest in pandemic readiness, the demand for versatile, effective, and sustainable solutions like HOCl is likely to grow, driving further innovation and market development in this space.
Hypochlorous acid, known for its potent antimicrobial properties, has emerged as a promising contender in the fight against infectious diseases. The pandemic market for HOCl-based products spans various sectors, including healthcare, hospitality, education, and public transportation. In the healthcare segment, HOCl solutions have gained traction for surface disinfection, hand sanitization, and even potential therapeutic applications.
The demand for effective, safe, and environmentally friendly disinfectants has driven the adoption of HOCl in institutional and consumer markets. Schools, offices, and public spaces have increasingly turned to HOCl-based products for their cleaning and sanitization protocols. This shift has been further accelerated by growing awareness of the limitations and potential risks associated with traditional chemical disinfectants.
Consumer behavior has also played a crucial role in shaping the pandemic market. The heightened focus on personal hygiene and home sanitation has led to a surge in demand for household disinfectants, with HOCl-based products gaining market share due to their efficacy and safety profile. This trend is expected to persist beyond the immediate pandemic response, as consumers maintain higher hygiene standards in their daily lives.
The global supply chain for pandemic-related products, including HOCl solutions, has undergone significant restructuring to meet the explosive demand. Manufacturers have ramped up production capacities, while new players have entered the market to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the pandemic. This has led to increased competition and innovation in product formulations and delivery systems for HOCl-based solutions.
Looking ahead, the pandemic market is expected to evolve as the world transitions from crisis response to long-term preparedness. The potential of HOCl in this context is significant, with opportunities for expansion into new application areas and markets. As governments and organizations worldwide invest in pandemic readiness, the demand for versatile, effective, and sustainable solutions like HOCl is likely to grow, driving further innovation and market development in this space.
HOCl Technology Status
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising technology in pandemic preparedness, with significant advancements in recent years. The current status of HOCl technology reflects a growing recognition of its potential as a powerful disinfectant and sanitizing agent.
In terms of production, there have been notable improvements in the generation of stable and effective HOCl solutions. Advanced electrolysis techniques now allow for the production of HOCl with consistent concentration and pH levels, addressing previous challenges related to stability and shelf life. These advancements have made HOCl more viable for large-scale applications in various settings.
The efficacy of HOCl against a wide range of pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi, has been well-established through numerous scientific studies. Recent research has further validated its effectiveness against emerging pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. This has positioned HOCl as a valuable tool in the arsenal against current and future pandemics.
Application methods for HOCl have also seen significant progress. Innovative delivery systems, such as electrostatic sprayers and fogging devices, have enhanced the coverage and efficiency of HOCl application in large spaces. These advancements have made HOCl more practical for use in healthcare facilities, public transportation, and other high-traffic areas where rapid and thorough disinfection is crucial.
Safety profiles of HOCl have been extensively studied, confirming its non-toxic nature to humans and animals when used as directed. This has led to increased adoption in sensitive environments such as food processing facilities and medical settings. The eco-friendly characteristics of HOCl, breaking down into simple salt and water, align well with growing environmental concerns.
Regulatory acceptance of HOCl has expanded globally, with many countries approving its use for various applications. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has included HOCl-based products on its list of disinfectants effective against SARS-CoV-2, further legitimizing its role in pandemic response.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of HOCl technology. These include the need for standardized production methods to ensure consistent quality across different manufacturers, as well as the development of more robust storage solutions to extend shelf life. Additionally, public awareness and education about the benefits and proper use of HOCl are still limited, presenting opportunities for further market penetration.
In conclusion, the current status of HOCl technology in pandemic preparedness is characterized by significant advancements in production, application, and regulatory acceptance. While challenges persist, the potential of HOCl as a safe, effective, and environmentally friendly disinfectant positions it as a key player in current and future pandemic response strategies.
In terms of production, there have been notable improvements in the generation of stable and effective HOCl solutions. Advanced electrolysis techniques now allow for the production of HOCl with consistent concentration and pH levels, addressing previous challenges related to stability and shelf life. These advancements have made HOCl more viable for large-scale applications in various settings.
The efficacy of HOCl against a wide range of pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi, has been well-established through numerous scientific studies. Recent research has further validated its effectiveness against emerging pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. This has positioned HOCl as a valuable tool in the arsenal against current and future pandemics.
Application methods for HOCl have also seen significant progress. Innovative delivery systems, such as electrostatic sprayers and fogging devices, have enhanced the coverage and efficiency of HOCl application in large spaces. These advancements have made HOCl more practical for use in healthcare facilities, public transportation, and other high-traffic areas where rapid and thorough disinfection is crucial.
Safety profiles of HOCl have been extensively studied, confirming its non-toxic nature to humans and animals when used as directed. This has led to increased adoption in sensitive environments such as food processing facilities and medical settings. The eco-friendly characteristics of HOCl, breaking down into simple salt and water, align well with growing environmental concerns.
Regulatory acceptance of HOCl has expanded globally, with many countries approving its use for various applications. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has included HOCl-based products on its list of disinfectants effective against SARS-CoV-2, further legitimizing its role in pandemic response.
However, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of HOCl technology. These include the need for standardized production methods to ensure consistent quality across different manufacturers, as well as the development of more robust storage solutions to extend shelf life. Additionally, public awareness and education about the benefits and proper use of HOCl are still limited, presenting opportunities for further market penetration.
In conclusion, the current status of HOCl technology in pandemic preparedness is characterized by significant advancements in production, application, and regulatory acceptance. While challenges persist, the potential of HOCl as a safe, effective, and environmentally friendly disinfectant positions it as a key player in current and future pandemic response strategies.
Current HOCl Solutions
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
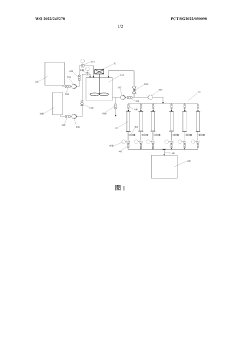
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: Stabilization of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining their efficacy over time. Various techniques are employed, such as pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging methods, to prevent degradation and extend the shelf life of hypochlorous acid products.
- Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its natural occurrence in the human immune system and its ability to promote healing while combating infections make it a valuable component in various medical formulations.
- Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation and industrial processes due to its oxidizing properties and eco-friendly nature. Applications include water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination in various industrial settings, offering an effective and environmentally conscious alternative to harsher chemicals.
02 Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions
Stabilization of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining their efficacy over time. Various techniques are employed, such as pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging methods, to prevent degradation and ensure a longer shelf life of the product.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid finds applications in medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its ability to promote healing while providing antimicrobial protection makes it valuable in various medical formulations and devices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation and industrial processes. It serves as an effective oxidizing agent for water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination in various industrial settings, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to harsher chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HOCl Industry Players
The market for hypochlorous acid in pandemic preparedness is in a growth phase, driven by increasing awareness of its effectiveness as a disinfectant. The global market size is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Annihilare Medical Systems and Industrie De Nora SpA leading innovation in on-site generation and electrochemical production. Other key players such as Hypo-Stream Ltd. and MannKind Corp. are focusing on therapeutic applications, particularly for respiratory conditions. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with disinfection solutions being more established than medical treatments. Overall, the competitive landscape is diverse, with both specialized firms and larger conglomerates investing in research and development to capitalize on the growing demand for effective, safe disinfection solutions.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS has developed an innovative hypochlorous acid (HOCl) generation system for pandemic preparedness. Their technology produces a stable, highly effective HOCl solution on-site, eliminating the need for storage and transportation of hazardous chemicals. The system utilizes electrochemical activation to generate HOCl from salt, water, and electricity, ensuring a consistent supply of this powerful disinfectant[1]. The company's HOCl solution has demonstrated broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi, including enveloped viruses like SARS-CoV-2[2]. ANNIHILARE's system can be scaled to meet the needs of various facilities, from small clinics to large hospitals, providing a sustainable and cost-effective solution for infection control and pandemic response[3].
Strengths: On-site generation eliminates storage and transportation issues; Scalable solution for various facility sizes; Broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Weaknesses: Requires initial investment in equipment; Dependent on stable electricity supply.
Industrie De Nora SpA
Technical Solution: Industrie De Nora SpA has developed advanced electrochemical technologies for the production of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in pandemic preparedness applications. Their system utilizes membrane electrolysis to generate high-purity HOCl solutions with precise control over concentration and pH[4]. De Nora's technology allows for the production of HOCl with concentrations ranging from 50 to 8000 mg/L, catering to various disinfection needs[5]. The company's electrochemical cells are designed for long-term operation, with some models capable of producing up to 2000 kg/day of chlorine equivalent[6]. De Nora's HOCl generation systems have been implemented in water treatment plants, hospitals, and industrial facilities worldwide, demonstrating their effectiveness in large-scale disinfection applications[7].
Strengths: High-purity HOCl production with precise control; Scalable for large-scale applications; Proven track record in various industries. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to traditional disinfection methods; Requires technical expertise for operation and maintenance.
HOCl Core Innovations
System for preparing weakly acidic hypochlorous acid solution
PatentWO2022245278A1
Innovation
- Using a system including a first storage device, a reaction system and a second storage device, the dilute hypochlorite solution flows into the weakly acidic ion exchange column to control the reaction process and ensure the pH stability of the generated weakly acidic hypochlorous acid solution. The system also contains storage devices for water and concentrated hypochlorite solution, accurately controls the reaction process through the settings of valves and pumps, and utilizes multiple weakly acidic ion exchange columns and floating elements to achieve pH stability.
Mixing device
PatentActiveUS20210346854A1
Innovation
- A mixing device that produces a stable form of HOCl by creating fluidic vortices within a chamber with apertures, allowing controlled protonation and hypochlorite ion reaction in an air-free environment, using compounds like acetic acid and NaOCl, and maintaining pH stability through buffering, enabling longer storage and reduced need for onsite generation.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in the context of pandemic preparedness is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental agencies and international bodies. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating HOCl as a disinfectant. The EPA has included HOCl on its List N, which catalogs disinfectants effective against SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. This listing has significantly bolstered the legitimacy of HOCl as a pandemic preparedness tool.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also exercises regulatory oversight on HOCl, particularly when it is used in medical settings or as a component in medical devices. The FDA has granted clearance for certain HOCl-based products for wound care and other medical applications, further validating its potential in healthcare scenarios during pandemics.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized the efficacy of chlorine-based disinfectants, including HOCl, in its guidelines for infection prevention and control. This global endorsement has encouraged many countries to incorporate HOCl into their pandemic response strategies.
However, regulatory challenges persist. The classification of HOCl can vary between countries, affecting its availability and approved uses. In some jurisdictions, it may be regulated as a biocide, while in others, it could be considered a medical product or a general-purpose disinfectant. This lack of uniformity in classification can complicate international trade and deployment during global health crises.
Moreover, the concentration and production methods of HOCl are subject to regulatory scrutiny. Agencies typically specify acceptable concentration ranges and production standards to ensure safety and efficacy. Manufacturers must adhere to these guidelines, which can vary across different regulatory bodies, potentially creating barriers to rapid scaling of production during emergencies.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses labeling requirements, which are critical for ensuring proper use and safety. Accurate labeling of HOCl products, including concentration, intended use, and safety precautions, is mandated by most regulatory agencies. This is particularly important given the potential for confusion with other chlorine-based products that may have different applications or safety profiles.
As the potential of HOCl in pandemic preparedness becomes increasingly recognized, there is a growing need for harmonization of regulatory approaches across different countries and regions. This would facilitate faster approval processes, easier distribution, and more effective global deployment of HOCl-based solutions during public health emergencies.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also exercises regulatory oversight on HOCl, particularly when it is used in medical settings or as a component in medical devices. The FDA has granted clearance for certain HOCl-based products for wound care and other medical applications, further validating its potential in healthcare scenarios during pandemics.
Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized the efficacy of chlorine-based disinfectants, including HOCl, in its guidelines for infection prevention and control. This global endorsement has encouraged many countries to incorporate HOCl into their pandemic response strategies.
However, regulatory challenges persist. The classification of HOCl can vary between countries, affecting its availability and approved uses. In some jurisdictions, it may be regulated as a biocide, while in others, it could be considered a medical product or a general-purpose disinfectant. This lack of uniformity in classification can complicate international trade and deployment during global health crises.
Moreover, the concentration and production methods of HOCl are subject to regulatory scrutiny. Agencies typically specify acceptable concentration ranges and production standards to ensure safety and efficacy. Manufacturers must adhere to these guidelines, which can vary across different regulatory bodies, potentially creating barriers to rapid scaling of production during emergencies.
The regulatory landscape also encompasses labeling requirements, which are critical for ensuring proper use and safety. Accurate labeling of HOCl products, including concentration, intended use, and safety precautions, is mandated by most regulatory agencies. This is particularly important given the potential for confusion with other chlorine-based products that may have different applications or safety profiles.
As the potential of HOCl in pandemic preparedness becomes increasingly recognized, there is a growing need for harmonization of regulatory approaches across different countries and regions. This would facilitate faster approval processes, easier distribution, and more effective global deployment of HOCl-based solutions during public health emergencies.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in pandemic preparedness is a critical consideration that warrants thorough examination. HOCl, known for its potent disinfectant properties, offers a promising solution for large-scale sanitization efforts during public health crises. However, its widespread use necessitates a comprehensive assessment of its ecological footprint.
One of the primary advantages of HOCl is its eco-friendly nature. Unlike many conventional disinfectants, HOCl breaks down into harmless components - primarily salt and water - after use. This characteristic significantly reduces the risk of harmful chemical accumulation in the environment, making it a sustainable option for long-term pandemic management strategies.
The production process of HOCl also contributes to its environmental appeal. It can be generated on-site through the electrolysis of salt water, eliminating the need for transportation and storage of hazardous chemicals. This not only reduces the carbon footprint associated with distribution but also minimizes the risk of accidental spills during transport.
However, the large-scale production and use of HOCl are not without environmental concerns. The electrolysis process requires electricity, and depending on the energy source, this could contribute to increased carbon emissions. To mitigate this impact, integrating renewable energy sources into HOCl production facilities would be crucial for maintaining its environmental benefits.
Water usage is another factor to consider. While HOCl production does not require excessive amounts of water, its widespread application for disinfection purposes could lead to increased water consumption. Implementing efficient application methods and recycling systems could help address this concern.
The impact of HOCl on aquatic ecosystems also merits attention. Although it breaks down rapidly, high concentrations in water bodies could potentially affect sensitive aquatic organisms. Proper dilution and controlled release mechanisms are essential to prevent any adverse effects on local ecosystems.
In terms of air quality, HOCl presents a significant advantage over many traditional disinfectants. It does not release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other harmful gases, contributing to improved indoor air quality - a crucial factor in enclosed spaces during a pandemic.
Lastly, the potential for HOCl to reduce reliance on single-use plastic packaging commonly associated with liquid disinfectants should not be overlooked. On-site generation capabilities could significantly decrease plastic waste, aligning with global efforts to reduce plastic pollution.
One of the primary advantages of HOCl is its eco-friendly nature. Unlike many conventional disinfectants, HOCl breaks down into harmless components - primarily salt and water - after use. This characteristic significantly reduces the risk of harmful chemical accumulation in the environment, making it a sustainable option for long-term pandemic management strategies.
The production process of HOCl also contributes to its environmental appeal. It can be generated on-site through the electrolysis of salt water, eliminating the need for transportation and storage of hazardous chemicals. This not only reduces the carbon footprint associated with distribution but also minimizes the risk of accidental spills during transport.
However, the large-scale production and use of HOCl are not without environmental concerns. The electrolysis process requires electricity, and depending on the energy source, this could contribute to increased carbon emissions. To mitigate this impact, integrating renewable energy sources into HOCl production facilities would be crucial for maintaining its environmental benefits.
Water usage is another factor to consider. While HOCl production does not require excessive amounts of water, its widespread application for disinfection purposes could lead to increased water consumption. Implementing efficient application methods and recycling systems could help address this concern.
The impact of HOCl on aquatic ecosystems also merits attention. Although it breaks down rapidly, high concentrations in water bodies could potentially affect sensitive aquatic organisms. Proper dilution and controlled release mechanisms are essential to prevent any adverse effects on local ecosystems.
In terms of air quality, HOCl presents a significant advantage over many traditional disinfectants. It does not release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other harmful gases, contributing to improved indoor air quality - a crucial factor in enclosed spaces during a pandemic.
Lastly, the potential for HOCl to reduce reliance on single-use plastic packaging commonly associated with liquid disinfectants should not be overlooked. On-site generation capabilities could significantly decrease plastic waste, aligning with global efforts to reduce plastic pollution.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!