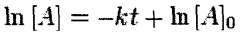The Role of Hypochlorous Acid in Wound Care Innovation
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl in Wound Care: Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a revolutionary agent in wound care, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of medical treatments. This naturally occurring molecule, produced by the human immune system, has been harnessed for its potent antimicrobial properties and ability to promote healing. The journey of HOCl in wound care began with the recognition of its role in the body's defense mechanisms, leading to extensive research and development efforts to replicate and enhance its effects in clinical settings.
The primary objective of incorporating HOCl in wound care is to address the critical challenges faced in managing complex wounds, particularly those prone to infection or slow healing. By leveraging the innate properties of HOCl, researchers and clinicians aim to develop more effective, safer, and faster-acting wound care solutions. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing healthcare costs, minimizing antibiotic resistance, and improving patient outcomes.
The technological evolution of HOCl in wound care has been marked by significant advancements in production methods, stability, and delivery systems. Early attempts to utilize HOCl were hampered by its instability and short shelf life. However, recent innovations have overcome these limitations, enabling the development of stable, long-lasting HOCl formulations suitable for clinical use. This progress has opened new avenues for research and application, positioning HOCl as a key player in the future of wound management.
As the field progresses, the objectives for HOCl in wound care continue to expand. Current research focuses on optimizing HOCl concentrations for different wound types, exploring synergistic effects with other wound care agents, and developing novel delivery methods to enhance efficacy. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the molecular mechanisms by which HOCl promotes wound healing, beyond its known antimicrobial effects.
The potential of HOCl extends beyond traditional wound care, with emerging applications in surgical site infection prevention, biofilm disruption, and even chronic wound management. These expanding horizons reflect the versatility of HOCl and its potential to revolutionize multiple aspects of patient care. As such, the ongoing research and development in this field aim not only to refine existing applications but also to uncover new therapeutic possibilities that could significantly impact healthcare practices globally.
The primary objective of incorporating HOCl in wound care is to address the critical challenges faced in managing complex wounds, particularly those prone to infection or slow healing. By leveraging the innate properties of HOCl, researchers and clinicians aim to develop more effective, safer, and faster-acting wound care solutions. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing healthcare costs, minimizing antibiotic resistance, and improving patient outcomes.
The technological evolution of HOCl in wound care has been marked by significant advancements in production methods, stability, and delivery systems. Early attempts to utilize HOCl were hampered by its instability and short shelf life. However, recent innovations have overcome these limitations, enabling the development of stable, long-lasting HOCl formulations suitable for clinical use. This progress has opened new avenues for research and application, positioning HOCl as a key player in the future of wound management.
As the field progresses, the objectives for HOCl in wound care continue to expand. Current research focuses on optimizing HOCl concentrations for different wound types, exploring synergistic effects with other wound care agents, and developing novel delivery methods to enhance efficacy. Additionally, there is growing interest in understanding the molecular mechanisms by which HOCl promotes wound healing, beyond its known antimicrobial effects.
The potential of HOCl extends beyond traditional wound care, with emerging applications in surgical site infection prevention, biofilm disruption, and even chronic wound management. These expanding horizons reflect the versatility of HOCl and its potential to revolutionize multiple aspects of patient care. As such, the ongoing research and development in this field aim not only to refine existing applications but also to uncover new therapeutic possibilities that could significantly impact healthcare practices globally.
Market Analysis: Wound Care Solutions
The global wound care market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, and advancements in wound care technologies. As of 2021, the market was valued at approximately $20 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% through 2026. This growth is particularly evident in advanced wound care solutions, which are gaining traction due to their effectiveness in managing complex wounds.
Within this expanding market, hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising innovation in wound care solutions. HOCl is a naturally occurring molecule produced by the human immune system to fight infection and promote healing. Its synthetic counterpart is now being harnessed for wound care applications, offering a unique combination of antimicrobial efficacy and biocompatibility.
The demand for HOCl-based wound care products is on the rise, driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing awareness among healthcare professionals about the benefits of HOCl in wound management, including its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and lack of bacterial resistance development. Secondly, the increasing incidence of antibiotic-resistant infections has created a need for alternative antimicrobial solutions, positioning HOCl as a viable option.
Market segmentation reveals that HOCl products are gaining traction across various wound types, including chronic wounds (such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers), surgical wounds, and burns. The home healthcare segment is also showing significant potential for HOCl-based solutions, as they are generally safe for patient self-application and can reduce the frequency of clinical visits.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the HOCl wound care market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher adoption rates of innovative wound care technologies. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present substantial growth opportunities due to improving healthcare access and rising awareness about advanced wound care solutions.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the HOCl wound care market. These include the need for more extensive clinical evidence to support long-term efficacy, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and competition from established wound care products. Additionally, educating healthcare providers and patients about the benefits and proper use of HOCl-based products remains crucial for market expansion.
In conclusion, the wound care market is ripe for innovation, with HOCl-based solutions poised to play a significant role in addressing unmet needs in wound management. As research continues and more products enter the market, HOCl is expected to carve out a substantial niche within the broader wound care landscape, offering new possibilities for improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Within this expanding market, hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising innovation in wound care solutions. HOCl is a naturally occurring molecule produced by the human immune system to fight infection and promote healing. Its synthetic counterpart is now being harnessed for wound care applications, offering a unique combination of antimicrobial efficacy and biocompatibility.
The demand for HOCl-based wound care products is on the rise, driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing awareness among healthcare professionals about the benefits of HOCl in wound management, including its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and lack of bacterial resistance development. Secondly, the increasing incidence of antibiotic-resistant infections has created a need for alternative antimicrobial solutions, positioning HOCl as a viable option.
Market segmentation reveals that HOCl products are gaining traction across various wound types, including chronic wounds (such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers), surgical wounds, and burns. The home healthcare segment is also showing significant potential for HOCl-based solutions, as they are generally safe for patient self-application and can reduce the frequency of clinical visits.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the HOCl wound care market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher adoption rates of innovative wound care technologies. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to present substantial growth opportunities due to improving healthcare access and rising awareness about advanced wound care solutions.
Despite the promising outlook, challenges remain in the HOCl wound care market. These include the need for more extensive clinical evidence to support long-term efficacy, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and competition from established wound care products. Additionally, educating healthcare providers and patients about the benefits and proper use of HOCl-based products remains crucial for market expansion.
In conclusion, the wound care market is ripe for innovation, with HOCl-based solutions poised to play a significant role in addressing unmet needs in wound management. As research continues and more products enter the market, HOCl is expected to carve out a substantial niche within the broader wound care landscape, offering new possibilities for improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Current HOCl Technology and Challenges
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising agent in wound care, offering potent antimicrobial properties while being gentle on human tissues. Current HOCl technology primarily focuses on stabilization and delivery methods to maintain its efficacy in clinical settings. One of the main challenges is the inherent instability of HOCl solutions, which can rapidly degrade when exposed to light, heat, or organic matter.
To address this, manufacturers have developed various stabilization techniques. Some employ proprietary formulations that include specific buffers and additives to extend shelf life. Others utilize advanced packaging systems, such as opaque, airtight containers with specialized dispensing mechanisms to minimize exposure to environmental factors. These innovations have significantly improved the practicality of HOCl-based wound care products.
Another technological focus is on the production of HOCl solutions with consistent concentration and pH levels. This is crucial for ensuring reproducible clinical outcomes and safety. Current methods include electrochemical activation of saline solutions and chemical synthesis processes. However, maintaining precise control over these parameters during large-scale production remains a challenge.
The delivery of HOCl to wound sites presents another area of ongoing development. Spray formulations have gained popularity due to their ease of application and ability to cover large surface areas. Gel-based HOCl products are also being explored to provide longer contact time with the wound bed. Additionally, researchers are investigating the incorporation of HOCl into advanced wound dressings and biocompatible materials for sustained release.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in HOCl technology for wound care. The relatively short shelf life of HOCl products, even with current stabilization methods, limits their widespread adoption in certain healthcare settings. There is a need for further improvements in long-term stability without compromising antimicrobial efficacy.
Another significant challenge is the standardization of HOCl solutions across different manufacturers. The lack of a universally accepted method for measuring HOCl concentration and activity makes it difficult to compare products and establish optimal treatment protocols. This variability can lead to inconsistent clinical outcomes and hinder the broader acceptance of HOCl-based therapies in wound care.
Furthermore, the integration of HOCl technology with other wound healing modalities, such as negative pressure wound therapy or bioengineered tissue substitutes, remains an area requiring further research and development. Optimizing these combinations could potentially enhance overall wound healing outcomes and expand the application of HOCl in complex wound management scenarios.
To address this, manufacturers have developed various stabilization techniques. Some employ proprietary formulations that include specific buffers and additives to extend shelf life. Others utilize advanced packaging systems, such as opaque, airtight containers with specialized dispensing mechanisms to minimize exposure to environmental factors. These innovations have significantly improved the practicality of HOCl-based wound care products.
Another technological focus is on the production of HOCl solutions with consistent concentration and pH levels. This is crucial for ensuring reproducible clinical outcomes and safety. Current methods include electrochemical activation of saline solutions and chemical synthesis processes. However, maintaining precise control over these parameters during large-scale production remains a challenge.
The delivery of HOCl to wound sites presents another area of ongoing development. Spray formulations have gained popularity due to their ease of application and ability to cover large surface areas. Gel-based HOCl products are also being explored to provide longer contact time with the wound bed. Additionally, researchers are investigating the incorporation of HOCl into advanced wound dressings and biocompatible materials for sustained release.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in HOCl technology for wound care. The relatively short shelf life of HOCl products, even with current stabilization methods, limits their widespread adoption in certain healthcare settings. There is a need for further improvements in long-term stability without compromising antimicrobial efficacy.
Another significant challenge is the standardization of HOCl solutions across different manufacturers. The lack of a universally accepted method for measuring HOCl concentration and activity makes it difficult to compare products and establish optimal treatment protocols. This variability can lead to inconsistent clinical outcomes and hinder the broader acceptance of HOCl-based therapies in wound care.
Furthermore, the integration of HOCl technology with other wound healing modalities, such as negative pressure wound therapy or bioengineered tissue substitutes, remains an area requiring further research and development. Optimizing these combinations could potentially enhance overall wound healing outcomes and expand the application of HOCl in complex wound management scenarios.
Existing HOCl Wound Care Applications
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and the use of specialized equipment for on-site generation. These methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: Stabilization of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining their efficacy over time. Various techniques are employed, such as pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging methods, to prevent degradation and extend the shelf life of hypochlorous acid products.
- Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its natural occurrence in the human immune system and its ability to promote healing while combating infections make it a valuable compound in medical formulations.
- Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in various environmental and industrial applications, such as water treatment, agriculture, and surface disinfection. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness in removing contaminants make it a preferred choice for sustainable cleaning and disinfection processes.
02 Applications in disinfection and sanitization
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as a powerful disinfectant and sanitizing agent. It is effective against a broad spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Applications range from water treatment and surface disinfection to medical sterilization and food safety.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulation and stability enhancement
Research focuses on improving the stability and shelf life of hypochlorous acid solutions. This includes developing specialized formulations, adjusting pH levels, and incorporating stabilizing agents to maintain the efficacy of the acid over extended periods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations
Studies address the environmental impact and safety aspects of hypochlorous acid use. This includes research on biodegradability, toxicity assessments, and the development of eco-friendly production methods to ensure sustainable and safe application across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications and delivery systems
Innovative uses of hypochlorous acid are being explored, including applications in agriculture, wound healing, and air purification. Additionally, new delivery systems and devices are being developed to optimize the application and effectiveness of hypochlorous acid in various settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCl Wound Care Industry
The wound care innovation landscape centered on hypochlorous acid is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global wound care market is projected to reach significant value, driven by factors such as an aging population and rising chronic diseases. Technologically, hypochlorous acid solutions are gaining traction due to their effectiveness and safety profile. Companies like Integrated Healing Technologies, Aquaox, and Realm Therapeutics are at the forefront, developing innovative products and applications. Research institutions such as the Technical University of Denmark and hospitals like Bispebjerg Hospital are contributing to the scientific understanding and clinical validation of hypochlorous acid in wound care, indicating a collaborative ecosystem driving innovation in this field.
Aquaox, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aquaox has developed a proprietary electrochemical activation (ECA) technology to produce Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) solutions for wound care. Their process creates a stable, pH-neutral HOCl solution with a concentration of 200-500 ppm, which has been shown to be effective against a wide range of pathogens[1]. The company's ECA technology allows for on-site generation of HOCl, ensuring freshness and potency. Aquaox's HOCl solutions have demonstrated rapid killing of bacteria, viruses, and fungi within seconds of contact, while being gentle on human tissue[2]. The company has also developed specialized delivery systems, including foggers and sprayers, to optimize the application of HOCl in various wound care settings[3].
Strengths: On-site generation ensures product freshness; Broad-spectrum antimicrobial efficacy; Non-toxic to human cells. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for generation; Shelf life can be limited compared to traditional antiseptics.
Realm Therapeutics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Realm Therapeutics has pioneered the development of stabilized HOCl formulations for wound care under the brand name ReLyve. Their proprietary technology focuses on maintaining the stability and efficacy of HOCl at physiological pH levels, which is crucial for its antimicrobial activity[4]. The company's formulations have been engineered to have an extended shelf life of up to 18 months, addressing one of the key challenges in HOCl-based products[5]. Realm's HOCl solutions have shown effectiveness in reducing biofilm formation and promoting wound healing in both in vitro and clinical studies[6]. They have also developed a range of delivery formats, including gels and sprays, to cater to different types of wounds and clinical settings.
Strengths: Extended shelf life; Variety of application formats; Proven efficacy against biofilms. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than traditional antiseptics; Limited long-term clinical data compared to established wound care products.
Innovations in HOCl Formulation and Delivery
Wound treatment therapy
PatentInactiveUS20180098935A1
Innovation
- Combining stabilized hypochlorous acid with hydrophobic wound dressings to deactivate pathogens without disrupting cell walls and physically remove them, using hypochlorous acid to disrupt biofilms and the hydrophobic dressing to bind and remove microorganisms and toxins.
METHOD FOR STABILIZING AN ELECTROCHEMICALLY GENERATED SANITIZING SOLUTION HAVING A PREDETERMINED LEVEL OF FREE AVAILABLE CHLORINE AND pH
PatentWO2014179692A1
Innovation
- A stabilized Hypochlorous Acid solution is developed with a stabilizing amount of dissolved ionic compounds (DIC) such as sodium phosphate or polyphosphate, maintaining a pH of 4.0 to 7.5 and FAC content of 10 to 1000 ppm, which is electrochemically generated and formulated as a hydrogel to ensure stability and non-irritating properties.
Regulatory Framework for HOCl in Healthcare
The regulatory framework for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in healthcare is a complex and evolving landscape. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the use of HOCl in medical applications. The FDA classifies HOCl-based products under different categories depending on their intended use and formulation.
For wound care applications, HOCl solutions are typically regulated as medical devices. They fall under the category of wound cleansers or irrigation solutions. The FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of these products through premarket notification (510(k)) submissions. This process involves providing substantial evidence that the new HOCl product is at least as safe and effective as a legally marketed predicate device.
In Europe, the regulatory framework for HOCl in healthcare is governed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and national regulatory bodies. The classification of HOCl products can vary depending on their specific use and claims. Some may be regulated as medical devices under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), while others might be considered biocidal products under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR).
The regulatory landscape also extends to manufacturing practices. Producers of HOCl solutions for healthcare applications must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines. These guidelines ensure consistent quality and safety in the production process. Additionally, facilities producing HOCl for medical use are subject to regular inspections by regulatory authorities to maintain compliance.
Labeling and marketing claims for HOCl products are strictly regulated. Manufacturers must ensure that all claims are supported by scientific evidence and comply with regulatory guidelines. This includes clear instructions for use, storage conditions, and any potential contraindications or side effects.
As the use of HOCl in wound care continues to expand, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging applications. This includes considerations for combination products that incorporate HOCl with other wound care technologies. The regulatory approach for such innovations may require a case-by-case evaluation to determine the most appropriate pathway for approval.
Internationally, the regulatory status of HOCl can vary significantly. Some countries may have specific regulations for HOCl in healthcare, while others may rely on broader frameworks for antiseptics or medical devices. This diversity in regulatory approaches can present challenges for global market access and necessitates a thorough understanding of regional requirements.
For wound care applications, HOCl solutions are typically regulated as medical devices. They fall under the category of wound cleansers or irrigation solutions. The FDA requires manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of these products through premarket notification (510(k)) submissions. This process involves providing substantial evidence that the new HOCl product is at least as safe and effective as a legally marketed predicate device.
In Europe, the regulatory framework for HOCl in healthcare is governed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and national regulatory bodies. The classification of HOCl products can vary depending on their specific use and claims. Some may be regulated as medical devices under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), while others might be considered biocidal products under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR).
The regulatory landscape also extends to manufacturing practices. Producers of HOCl solutions for healthcare applications must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines. These guidelines ensure consistent quality and safety in the production process. Additionally, facilities producing HOCl for medical use are subject to regular inspections by regulatory authorities to maintain compliance.
Labeling and marketing claims for HOCl products are strictly regulated. Manufacturers must ensure that all claims are supported by scientific evidence and comply with regulatory guidelines. This includes clear instructions for use, storage conditions, and any potential contraindications or side effects.
As the use of HOCl in wound care continues to expand, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging applications. This includes considerations for combination products that incorporate HOCl with other wound care technologies. The regulatory approach for such innovations may require a case-by-case evaluation to determine the most appropriate pathway for approval.
Internationally, the regulatory status of HOCl can vary significantly. Some countries may have specific regulations for HOCl in healthcare, while others may rely on broader frameworks for antiseptics or medical devices. This diversity in regulatory approaches can present challenges for global market access and necessitates a thorough understanding of regional requirements.
Safety and Efficacy Studies of HOCl in Wound Care
The safety and efficacy of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in wound care have been extensively studied, demonstrating its potential as a revolutionary treatment option. Numerous clinical trials and laboratory studies have consistently shown that HOCl exhibits potent antimicrobial properties while maintaining a favorable safety profile for human tissues.
In vitro studies have demonstrated that HOCl effectively eliminates a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, within seconds of exposure. This broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity is particularly valuable in wound care, where infections can significantly impede healing processes. Importantly, these studies have also shown that HOCl does not induce bacterial resistance, a critical advantage over traditional antibiotics.
Clinical trials focusing on wound healing have provided compelling evidence for HOCl's efficacy. Patients treated with HOCl-based solutions have shown accelerated wound closure rates compared to standard care protocols. These studies have encompassed various wound types, including chronic ulcers, surgical incisions, and burn injuries, demonstrating the versatility of HOCl in wound management.
Safety assessments have consistently reported minimal adverse effects associated with HOCl use. Unlike some antiseptic agents, HOCl does not cause tissue irritation or delay wound healing. In fact, several studies have observed improved tissue regeneration and reduced inflammation in HOCl-treated wounds. This favorable safety profile extends to long-term use, with no reported systemic toxicity or accumulation in tissues.
Comparative studies have positioned HOCl favorably against other wound care solutions. When compared to povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine, HOCl has shown equal or superior antimicrobial efficacy with significantly less cytotoxicity to human cells. This balance of effectiveness and safety makes HOCl an attractive option for wound care practitioners.
Recent research has also explored the potential of HOCl in biofilm management, a critical aspect of chronic wound care. Preliminary findings suggest that HOCl can effectively disrupt established biofilms and prevent their formation, addressing a major challenge in wound healing.
While the body of evidence supporting HOCl's use in wound care is substantial, ongoing research continues to refine its applications and explore new potential benefits. Current studies are investigating optimal concentrations, application methods, and combination therapies to maximize HOCl's therapeutic potential in diverse clinical scenarios.
In vitro studies have demonstrated that HOCl effectively eliminates a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, within seconds of exposure. This broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity is particularly valuable in wound care, where infections can significantly impede healing processes. Importantly, these studies have also shown that HOCl does not induce bacterial resistance, a critical advantage over traditional antibiotics.
Clinical trials focusing on wound healing have provided compelling evidence for HOCl's efficacy. Patients treated with HOCl-based solutions have shown accelerated wound closure rates compared to standard care protocols. These studies have encompassed various wound types, including chronic ulcers, surgical incisions, and burn injuries, demonstrating the versatility of HOCl in wound management.
Safety assessments have consistently reported minimal adverse effects associated with HOCl use. Unlike some antiseptic agents, HOCl does not cause tissue irritation or delay wound healing. In fact, several studies have observed improved tissue regeneration and reduced inflammation in HOCl-treated wounds. This favorable safety profile extends to long-term use, with no reported systemic toxicity or accumulation in tissues.
Comparative studies have positioned HOCl favorably against other wound care solutions. When compared to povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine, HOCl has shown equal or superior antimicrobial efficacy with significantly less cytotoxicity to human cells. This balance of effectiveness and safety makes HOCl an attractive option for wound care practitioners.
Recent research has also explored the potential of HOCl in biofilm management, a critical aspect of chronic wound care. Preliminary findings suggest that HOCl can effectively disrupt established biofilms and prevent their formation, addressing a major challenge in wound healing.
While the body of evidence supporting HOCl's use in wound care is substantial, ongoing research continues to refine its applications and explore new potential benefits. Current studies are investigating optimal concentrations, application methods, and combination therapies to maximize HOCl's therapeutic potential in diverse clinical scenarios.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!