Harnessing Hypochlorous Acid for Veterinary Health Advances
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCL in Veterinary Medicine: Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising agent in veterinary medicine, offering a unique combination of antimicrobial efficacy and safety. This naturally occurring molecule, produced by the immune system of mammals, has been known for over a century but has only recently gained significant attention in the veterinary field. The primary objective of harnessing HOCl for veterinary health advances is to develop innovative, safe, and effective treatments for a wide range of animal health issues.
The evolution of HOCl in veterinary applications can be traced back to its discovery in the early 20th century. Initially recognized for its potent antimicrobial properties, HOCl's potential remained largely untapped due to stability issues and production challenges. However, recent technological advancements have overcome these obstacles, paving the way for its practical application in animal healthcare.
In the veterinary context, HOCl presents a compelling alternative to traditional antiseptics and disinfectants. Its mechanism of action involves the oxidation of microbial cell walls, leading to rapid and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Importantly, HOCl demonstrates effectiveness against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even some parasites, making it a versatile tool in the veterinarian's arsenal.
The growing interest in HOCl aligns with the increasing demand for natural, non-toxic, and environmentally friendly solutions in animal care. As concerns about antibiotic resistance and chemical residues in food-producing animals escalate, HOCl offers a promising avenue for addressing these challenges. Its non-toxic nature and rapid degradation into harmless byproducts make it an attractive option for use in various veterinary settings, from small animal clinics to large-scale livestock operations.
The objectives of harnessing HOCl in veterinary medicine are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers and veterinary professionals aim to develop a range of HOCl-based products tailored for specific veterinary applications. These may include topical treatments for wound care, oral hygiene solutions, and environmental disinfectants for animal housing facilities. Additionally, there is a focus on optimizing HOCl formulations to enhance stability and efficacy, ensuring consistent performance across diverse veterinary scenarios.
Another key objective is to establish comprehensive protocols for HOCl use in veterinary practice. This involves determining optimal concentrations, application methods, and treatment durations for various conditions and animal species. Researchers are also exploring the potential synergistic effects of combining HOCl with other therapeutic agents to enhance overall treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, the veterinary community aims to gather robust clinical evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of HOCl-based interventions. This includes conducting rigorous studies to evaluate its performance in real-world veterinary settings and comparing it with existing standard-of-care treatments. Such evidence is crucial for gaining regulatory approvals and fostering widespread adoption among veterinary practitioners.
The evolution of HOCl in veterinary applications can be traced back to its discovery in the early 20th century. Initially recognized for its potent antimicrobial properties, HOCl's potential remained largely untapped due to stability issues and production challenges. However, recent technological advancements have overcome these obstacles, paving the way for its practical application in animal healthcare.
In the veterinary context, HOCl presents a compelling alternative to traditional antiseptics and disinfectants. Its mechanism of action involves the oxidation of microbial cell walls, leading to rapid and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Importantly, HOCl demonstrates effectiveness against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even some parasites, making it a versatile tool in the veterinarian's arsenal.
The growing interest in HOCl aligns with the increasing demand for natural, non-toxic, and environmentally friendly solutions in animal care. As concerns about antibiotic resistance and chemical residues in food-producing animals escalate, HOCl offers a promising avenue for addressing these challenges. Its non-toxic nature and rapid degradation into harmless byproducts make it an attractive option for use in various veterinary settings, from small animal clinics to large-scale livestock operations.
The objectives of harnessing HOCl in veterinary medicine are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers and veterinary professionals aim to develop a range of HOCl-based products tailored for specific veterinary applications. These may include topical treatments for wound care, oral hygiene solutions, and environmental disinfectants for animal housing facilities. Additionally, there is a focus on optimizing HOCl formulations to enhance stability and efficacy, ensuring consistent performance across diverse veterinary scenarios.
Another key objective is to establish comprehensive protocols for HOCl use in veterinary practice. This involves determining optimal concentrations, application methods, and treatment durations for various conditions and animal species. Researchers are also exploring the potential synergistic effects of combining HOCl with other therapeutic agents to enhance overall treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, the veterinary community aims to gather robust clinical evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of HOCl-based interventions. This includes conducting rigorous studies to evaluate its performance in real-world veterinary settings and comparing it with existing standard-of-care treatments. Such evidence is crucial for gaining regulatory approvals and fostering widespread adoption among veterinary practitioners.
Market Analysis for HOCL-based Veterinary Products
The market for HOCL-based veterinary products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of animal health and the demand for effective, safe, and environmentally friendly solutions. The global veterinary care market, valued at $101.4 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $149.7 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7%. Within this broader market, HOCL-based products are carving out a notable niche.
Hypochlorous acid (HOCL) has gained traction in veterinary applications due to its potent antimicrobial properties and low toxicity profile. The market for HOCL-based veterinary products encompasses a wide range of applications, including wound care, skin conditions, oral hygiene, and disinfection of veterinary facilities. The demand is particularly strong in companion animal care, where pet owners are increasingly seeking natural and non-toxic treatment options.
The livestock sector also presents a substantial market opportunity for HOCL-based products. With the growing concern over antibiotic resistance and the push for reduced antibiotic use in animal husbandry, HOCL offers an attractive alternative for disease prevention and treatment. This segment is expected to show robust growth, especially in regions with large livestock populations such as Asia-Pacific and North America.
Geographically, North America currently leads the market for HOCL-based veterinary products, followed by Europe. These regions benefit from advanced veterinary healthcare infrastructure and high pet ownership rates. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, driven by rising disposable incomes, increasing pet adoption, and modernization of livestock farming practices.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of zoonotic diseases, stringent regulations on antibiotic use in animals, and the shift towards organic and natural products in animal care. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth by heightening awareness of hygiene and infection control in both companion animal and livestock settings.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the need for education on HOCL's benefits and applications among veterinarians and pet owners. Additionally, competition from established antiseptic products and the initial investment required for HOCL generation systems in veterinary practices may slow adoption rates in some segments.
In conclusion, the market for HOCL-based veterinary products shows promising growth potential, driven by its efficacy, safety profile, and alignment with current trends in animal health care. As research continues to validate its applications and regulatory bodies recognize its benefits, HOCL is poised to become a significant player in the veterinary health market.
Hypochlorous acid (HOCL) has gained traction in veterinary applications due to its potent antimicrobial properties and low toxicity profile. The market for HOCL-based veterinary products encompasses a wide range of applications, including wound care, skin conditions, oral hygiene, and disinfection of veterinary facilities. The demand is particularly strong in companion animal care, where pet owners are increasingly seeking natural and non-toxic treatment options.
The livestock sector also presents a substantial market opportunity for HOCL-based products. With the growing concern over antibiotic resistance and the push for reduced antibiotic use in animal husbandry, HOCL offers an attractive alternative for disease prevention and treatment. This segment is expected to show robust growth, especially in regions with large livestock populations such as Asia-Pacific and North America.
Geographically, North America currently leads the market for HOCL-based veterinary products, followed by Europe. These regions benefit from advanced veterinary healthcare infrastructure and high pet ownership rates. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, driven by rising disposable incomes, increasing pet adoption, and modernization of livestock farming practices.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of zoonotic diseases, stringent regulations on antibiotic use in animals, and the shift towards organic and natural products in animal care. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated market growth by heightening awareness of hygiene and infection control in both companion animal and livestock settings.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the need for education on HOCL's benefits and applications among veterinarians and pet owners. Additionally, competition from established antiseptic products and the initial investment required for HOCL generation systems in veterinary practices may slow adoption rates in some segments.
In conclusion, the market for HOCL-based veterinary products shows promising growth potential, driven by its efficacy, safety profile, and alignment with current trends in animal health care. As research continues to validate its applications and regulatory bodies recognize its benefits, HOCL is poised to become a significant player in the veterinary health market.
Current HOCL Applications and Challenges in Animal Health
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising solution in veterinary health, offering a wide range of applications due to its potent antimicrobial properties and safety profile. In animal health, HOCl is currently being utilized for various purposes, including wound care, disinfection, and disease prevention.
One of the primary applications of HOCl in veterinary medicine is in wound management. It has shown remarkable efficacy in cleaning and disinfecting wounds, promoting faster healing, and reducing the risk of infection. Veterinarians are increasingly using HOCl-based solutions for treating cuts, abrasions, and surgical sites in both small and large animals.
In livestock farming, HOCl has gained traction as a safe and effective disinfectant for animal housing and equipment. Its ability to eliminate a broad spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, makes it an invaluable tool in maintaining biosecurity and preventing the spread of diseases within animal populations.
HOCl has also found applications in dental care for animals. It is being used as a mouthwash and for treating oral infections, leveraging its antimicrobial properties without causing irritation or harm to the oral tissues. This is particularly beneficial for pets with dental issues or those recovering from oral surgeries.
In the aquaculture industry, HOCl is being explored as a water treatment solution to maintain optimal water quality and control pathogens in fish farms. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness against waterborne microorganisms make it an attractive alternative to traditional chemical treatments.
Despite these promising applications, several challenges persist in the widespread adoption of HOCl in veterinary health. One significant hurdle is the stability of HOCl solutions. The compound tends to degrade over time, which can affect its efficacy and shelf life. This necessitates careful handling, storage, and timely use of HOCl products.
Another challenge lies in standardizing the concentration and application methods of HOCl across different veterinary uses. The optimal concentration may vary depending on the specific application, animal species, and the nature of the health issue being addressed. Developing standardized protocols and guidelines for various veterinary applications remains an ongoing effort.
The regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl use in animal health also presents challenges. While generally recognized as safe, the regulatory status of HOCl products can vary across different countries and jurisdictions. This can impact the availability and marketing of HOCl-based solutions in the veterinary market.
Educating veterinary professionals and animal owners about the benefits and proper use of HOCl is another hurdle. Many are still unfamiliar with its potential applications and advantages over traditional antimicrobial agents. Overcoming this knowledge gap is crucial for wider acceptance and integration of HOCl in veterinary practice.
One of the primary applications of HOCl in veterinary medicine is in wound management. It has shown remarkable efficacy in cleaning and disinfecting wounds, promoting faster healing, and reducing the risk of infection. Veterinarians are increasingly using HOCl-based solutions for treating cuts, abrasions, and surgical sites in both small and large animals.
In livestock farming, HOCl has gained traction as a safe and effective disinfectant for animal housing and equipment. Its ability to eliminate a broad spectrum of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, makes it an invaluable tool in maintaining biosecurity and preventing the spread of diseases within animal populations.
HOCl has also found applications in dental care for animals. It is being used as a mouthwash and for treating oral infections, leveraging its antimicrobial properties without causing irritation or harm to the oral tissues. This is particularly beneficial for pets with dental issues or those recovering from oral surgeries.
In the aquaculture industry, HOCl is being explored as a water treatment solution to maintain optimal water quality and control pathogens in fish farms. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness against waterborne microorganisms make it an attractive alternative to traditional chemical treatments.
Despite these promising applications, several challenges persist in the widespread adoption of HOCl in veterinary health. One significant hurdle is the stability of HOCl solutions. The compound tends to degrade over time, which can affect its efficacy and shelf life. This necessitates careful handling, storage, and timely use of HOCl products.
Another challenge lies in standardizing the concentration and application methods of HOCl across different veterinary uses. The optimal concentration may vary depending on the specific application, animal species, and the nature of the health issue being addressed. Developing standardized protocols and guidelines for various veterinary applications remains an ongoing effort.
The regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl use in animal health also presents challenges. While generally recognized as safe, the regulatory status of HOCl products can vary across different countries and jurisdictions. This can impact the availability and marketing of HOCl-based solutions in the veterinary market.
Educating veterinary professionals and animal owners about the benefits and proper use of HOCl is another hurdle. Many are still unfamiliar with its potential applications and advantages over traditional antimicrobial agents. Overcoming this knowledge gap is crucial for wider acceptance and integration of HOCl in veterinary practice.
Existing HOCL Formulations for Animal Treatment
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and the use of specialized equipment for on-site generation. These methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
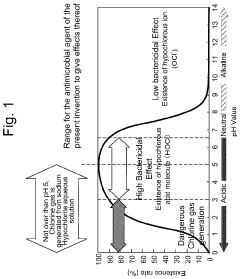
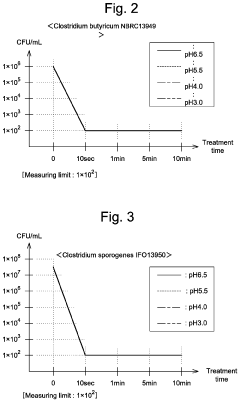
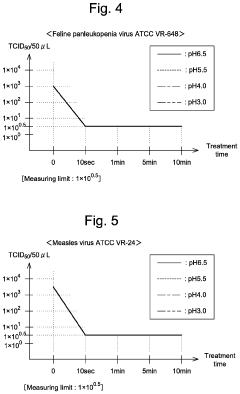
- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.
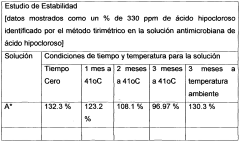
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: To enhance the shelf life and maintain the efficacy of hypochlorous acid solutions, various stabilization techniques are employed. These may include pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging to prevent degradation and maintain the active chlorine content over time.
- Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its gentle yet effective nature makes it suitable for various medical procedures and treatments, particularly where antimicrobial action is required without causing irritation.
- Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation and industrial processes. Its applications include water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination in various industries. The eco-friendly nature of hypochlorous acid makes it an attractive option for sustainable cleaning and disinfection practices.
02 Applications in disinfection and sterilization
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as a powerful disinfectant and sterilizing agent. It is effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Applications include water treatment, surface disinfection, and medical sterilization.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulations and stability enhancement
Research focuses on developing stable formulations of hypochlorous acid to extend its shelf life and maintain its efficacy. This includes the use of stabilizers, pH adjustments, and packaging innovations to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability of the solution.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic applications
Hypochlorous acid is explored for various medical and therapeutic uses, including wound care, eye treatments, and respiratory therapies. Its non-toxic nature and antimicrobial properties make it suitable for these sensitive applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial uses
Hypochlorous acid finds applications in environmental remediation, industrial cleaning, and agriculture. It is used for water treatment, soil decontamination, and as an eco-friendly alternative to harsh chemicals in various industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCL Veterinary Solutions
The market for hypochlorous acid in veterinary health is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for safe and effective disinfectants. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, hypochlorous acid production and application methods are advancing, but there's still room for innovation. Key players like Aquaox, Hypo-Stream, and Annihilare Medical Systems are at the forefront, developing specialized solutions for veterinary use. Established chemical companies such as Albemarle Corp. and Industrie De Nora SpA are also entering this space, leveraging their expertise in chemical manufacturing. Research institutions like Xiamen University and Okayama University are contributing to the scientific understanding and potential applications of hypochlorous acid in animal health.
Aquaox, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aquaox has developed an electrochemical activation (ECA) technology to produce highly effective, stable hypochlorous acid solutions for veterinary use. Their system generates HOCl on-site, ensuring freshness and potency. The company's ECA technology allows for precise control of pH and free available chlorine (FAC) levels, resulting in solutions with optimal antimicrobial efficacy[3]. Aquaox's HOCl products are used in veterinary clinics for wound care, disinfection, and as a general antimicrobial agent. The on-site generation capability addresses the stability issues often associated with HOCl, allowing for consistent quality and reducing transportation and storage costs[4].
Strengths: On-site generation, consistent quality, reduced logistics costs. Weaknesses: Initial equipment investment, requires training for on-site production.
Hypo-Stream Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hypo-Stream has developed a unique continuous flow reactor system for producing high-purity, stable hypochlorous acid solutions. Their technology allows for the production of HOCl with precise control over concentration and pH, tailored for veterinary applications. The company's system utilizes a membrane-free electrolytic cell, which reduces maintenance requirements and improves efficiency[5]. Hypo-Stream's HOCl solutions are used in veterinary settings for wound care, dental hygiene, and as a broad-spectrum disinfectant. The continuous flow system ensures a consistent supply of fresh HOCl, addressing stability concerns and allowing for scalable production to meet varying demand in veterinary facilities[6].
Strengths: Continuous production, high purity, scalable output. Weaknesses: May require specialized technical support, potential for higher initial investment.
Innovative HOCL Delivery Systems for Veterinary Use
Method of producing composition of hypochlorous acid and use thereof
PatentWO2009125297A2
Innovation
- A method involving the dilution of an aged stock solution with specific compositions of sodium hypochlorite, hydrochloric acid, and water, followed by adjustment of pH, to create an antimicrobial hypochlorous acid solution that maintains at least 75% available chlorine for 6 to 12 months when stored away from light at room temperature.
Antimicrobial agent containing hypochlorous acid
PatentActiveUS20200390919A1
Innovation
- A hypochlorous acid aqueous solution with a chlorine concentration between 50 to 260 ppm and a pH range of 3.0 to 6.7, comprising sodium hypochlorite and purified water, which effectively disinfects microorganisms within 1 minute without damaging materials or binding proteins, and is safe for human skin.
Regulatory Framework for HOCL in Animal Healthcare
The regulatory framework for hypochlorous acid (HOCL) in animal healthcare is a complex and evolving landscape that varies across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of veterinary products, including those containing HOCL. The FDA's Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) is responsible for ensuring the safety and efficacy of animal drugs, including antimicrobial agents like HOCL.
Under current regulations, HOCL-based products for veterinary use may be classified as either drugs or medical devices, depending on their intended use and claims. Products marketed as having therapeutic effects or for the treatment of specific conditions are typically regulated as drugs, requiring rigorous safety and efficacy testing before approval. In contrast, products intended for general cleaning or disinfection may be classified as medical devices, subject to less stringent regulatory requirements.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating HOCL-based products used in animal facilities for disinfection purposes. These products must be registered with the EPA and meet specific criteria for efficacy and safety in their intended applications.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework for veterinary products is governed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and national competent authorities. The classification and approval process for HOCL-based products in animal healthcare follows similar principles to those in the US, with distinctions made between medicinal products and biocidal products.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential benefits of HOCL in veterinary applications, leading to ongoing discussions about appropriate regulatory pathways. Some countries have implemented expedited review processes for certain HOCL-based products, acknowledging their low toxicity profile and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity.
As research continues to demonstrate the efficacy of HOCL in various veterinary applications, regulatory agencies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate these innovations. This includes developing specific guidance documents for HOCL-based products and establishing appropriate testing protocols to evaluate their safety and efficacy in animal healthcare settings.
Manufacturers and researchers working with HOCL in veterinary applications must navigate these regulatory requirements carefully, ensuring compliance with relevant standards and guidelines. This often involves extensive documentation, clinical trials, and ongoing safety monitoring to support product approvals and maintain market authorization.
Under current regulations, HOCL-based products for veterinary use may be classified as either drugs or medical devices, depending on their intended use and claims. Products marketed as having therapeutic effects or for the treatment of specific conditions are typically regulated as drugs, requiring rigorous safety and efficacy testing before approval. In contrast, products intended for general cleaning or disinfection may be classified as medical devices, subject to less stringent regulatory requirements.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating HOCL-based products used in animal facilities for disinfection purposes. These products must be registered with the EPA and meet specific criteria for efficacy and safety in their intended applications.
In the European Union, the regulatory framework for veterinary products is governed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and national competent authorities. The classification and approval process for HOCL-based products in animal healthcare follows similar principles to those in the US, with distinctions made between medicinal products and biocidal products.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential benefits of HOCL in veterinary applications, leading to ongoing discussions about appropriate regulatory pathways. Some countries have implemented expedited review processes for certain HOCL-based products, acknowledging their low toxicity profile and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity.
As research continues to demonstrate the efficacy of HOCL in various veterinary applications, regulatory agencies are adapting their frameworks to accommodate these innovations. This includes developing specific guidance documents for HOCL-based products and establishing appropriate testing protocols to evaluate their safety and efficacy in animal healthcare settings.
Manufacturers and researchers working with HOCL in veterinary applications must navigate these regulatory requirements carefully, ensuring compliance with relevant standards and guidelines. This often involves extensive documentation, clinical trials, and ongoing safety monitoring to support product approvals and maintain market authorization.
Environmental Impact of HOCL in Veterinary Practices
The use of hypochlorous acid (HOCL) in veterinary practices has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As a powerful disinfectant, HOCL offers numerous benefits in animal healthcare settings, but its widespread adoption also raises concerns about potential ecological impacts.
One of the primary environmental advantages of HOCL is its rapid degradation into harmless byproducts. Unlike many traditional disinfectants, HOCL breaks down quickly into water and salt, leaving no toxic residues. This characteristic greatly reduces the risk of environmental contamination and minimizes the potential for harmful effects on local ecosystems.
However, the production and storage of HOCL may have indirect environmental consequences. The process of generating HOCL often requires electricity, which, depending on the energy source, could contribute to carbon emissions. Additionally, the packaging and transportation of HOCL solutions may result in plastic waste and increased carbon footprint.
In veterinary clinics and animal hospitals, the use of HOCL as a disinfectant can lead to improved water quality in effluents. Compared to conventional chemical disinfectants, HOCL-treated wastewater contains fewer harmful substances, potentially reducing the burden on water treatment facilities and aquatic ecosystems.
The application of HOCL in livestock farming presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. On one hand, its effectiveness in controlling pathogens can reduce the need for antibiotics, thereby mitigating the risk of antibiotic resistance in the environment. On the other hand, large-scale use in agricultural settings may lead to localized changes in soil and water chemistry, necessitating further research on long-term ecological effects.
Biodiversity conservation efforts may benefit from the adoption of HOCL in veterinary practices. By providing a more environmentally friendly alternative to harsh chemical disinfectants, HOCL can help reduce the impact of veterinary activities on surrounding flora and fauna. This is particularly relevant in wildlife rehabilitation centers and zoos, where maintaining a balance between hygiene and habitat preservation is crucial.
The potential for HOCL to replace more environmentally harmful disinfectants in veterinary settings also presents an opportunity for reducing overall chemical pollution. As veterinary practices transition to HOCL-based disinfection protocols, the cumulative effect could lead to a significant decrease in the release of persistent organic pollutants and other toxic substances into the environment.
In conclusion, while the environmental impact of HOCL in veterinary practices is generally positive, a holistic approach is necessary to fully understand and mitigate any potential negative effects. Ongoing research and monitoring will be essential to ensure that the widespread adoption of HOCL aligns with sustainable environmental practices in the veterinary sector.
One of the primary environmental advantages of HOCL is its rapid degradation into harmless byproducts. Unlike many traditional disinfectants, HOCL breaks down quickly into water and salt, leaving no toxic residues. This characteristic greatly reduces the risk of environmental contamination and minimizes the potential for harmful effects on local ecosystems.
However, the production and storage of HOCL may have indirect environmental consequences. The process of generating HOCL often requires electricity, which, depending on the energy source, could contribute to carbon emissions. Additionally, the packaging and transportation of HOCL solutions may result in plastic waste and increased carbon footprint.
In veterinary clinics and animal hospitals, the use of HOCL as a disinfectant can lead to improved water quality in effluents. Compared to conventional chemical disinfectants, HOCL-treated wastewater contains fewer harmful substances, potentially reducing the burden on water treatment facilities and aquatic ecosystems.
The application of HOCL in livestock farming presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. On one hand, its effectiveness in controlling pathogens can reduce the need for antibiotics, thereby mitigating the risk of antibiotic resistance in the environment. On the other hand, large-scale use in agricultural settings may lead to localized changes in soil and water chemistry, necessitating further research on long-term ecological effects.
Biodiversity conservation efforts may benefit from the adoption of HOCL in veterinary practices. By providing a more environmentally friendly alternative to harsh chemical disinfectants, HOCL can help reduce the impact of veterinary activities on surrounding flora and fauna. This is particularly relevant in wildlife rehabilitation centers and zoos, where maintaining a balance between hygiene and habitat preservation is crucial.
The potential for HOCL to replace more environmentally harmful disinfectants in veterinary settings also presents an opportunity for reducing overall chemical pollution. As veterinary practices transition to HOCL-based disinfection protocols, the cumulative effect could lead to a significant decrease in the release of persistent organic pollutants and other toxic substances into the environment.
In conclusion, while the environmental impact of HOCL in veterinary practices is generally positive, a holistic approach is necessary to fully understand and mitigate any potential negative effects. Ongoing research and monitoring will be essential to ensure that the widespread adoption of HOCL aligns with sustainable environmental practices in the veterinary sector.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!