Alkyl Chemistry's Impact on Environmental Conservation
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Chemistry Evolution
Alkyl chemistry has undergone significant evolution since its inception, with profound implications for environmental conservation. The field's development can be traced back to the early 20th century when the importance of carbon-carbon bonds in organic compounds was first recognized. As industrial processes expanded, the need for more efficient and environmentally friendly chemical reactions became apparent.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the focus shifted towards understanding the mechanisms of alkyl reactions, leading to breakthroughs in catalysis and synthetic methodologies. This period saw the emergence of organometallic chemistry, which played a crucial role in developing new alkylation techniques. The discovery of Ziegler-Natta catalysts revolutionized polymer synthesis, enabling the production of polyethylene and polypropylene with improved properties and reduced environmental impact.
The 1970s and 1980s marked a turning point in alkyl chemistry, as awareness of environmental issues grew. Researchers began exploring greener alternatives to traditional alkylation processes, which often involved toxic reagents and generated hazardous waste. This led to the development of more selective and atom-efficient reactions, such as the use of phase-transfer catalysis and solid-supported reagents.
The advent of computational chemistry in the 1990s accelerated progress in alkyl chemistry. Molecular modeling and simulation techniques allowed scientists to predict reaction outcomes and design more effective catalysts. This period also saw increased interest in asymmetric synthesis, enabling the production of chiral compounds with high enantioselectivity, crucial for pharmaceutical applications.
In the 21st century, alkyl chemistry has embraced the principles of green chemistry and sustainability. Researchers have focused on developing bio-based alkyl compounds, utilizing renewable feedstocks instead of petrochemical sources. The concept of C-H activation has gained prominence, allowing for the direct functionalization of alkyl groups without the need for pre-activation, thus reducing waste and improving atom economy.
Recent advances in alkyl chemistry have centered on the use of flow chemistry and continuous processing, which offer improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact compared to batch processes. Additionally, the integration of photocatalysis and electrochemistry has opened new avenues for alkyl transformations under mild conditions, further aligning with environmental conservation goals.
The evolution of alkyl chemistry has been marked by a continuous drive towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly processes. From the early focus on understanding fundamental reactions to the current emphasis on green methodologies, the field has consistently adapted to meet the challenges of environmental conservation. As we move forward, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in alkyl chemistry research promises to accelerate the discovery of novel, eco-friendly synthetic routes and catalysts, further enhancing the field's contribution to environmental preservation.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the focus shifted towards understanding the mechanisms of alkyl reactions, leading to breakthroughs in catalysis and synthetic methodologies. This period saw the emergence of organometallic chemistry, which played a crucial role in developing new alkylation techniques. The discovery of Ziegler-Natta catalysts revolutionized polymer synthesis, enabling the production of polyethylene and polypropylene with improved properties and reduced environmental impact.
The 1970s and 1980s marked a turning point in alkyl chemistry, as awareness of environmental issues grew. Researchers began exploring greener alternatives to traditional alkylation processes, which often involved toxic reagents and generated hazardous waste. This led to the development of more selective and atom-efficient reactions, such as the use of phase-transfer catalysis and solid-supported reagents.
The advent of computational chemistry in the 1990s accelerated progress in alkyl chemistry. Molecular modeling and simulation techniques allowed scientists to predict reaction outcomes and design more effective catalysts. This period also saw increased interest in asymmetric synthesis, enabling the production of chiral compounds with high enantioselectivity, crucial for pharmaceutical applications.
In the 21st century, alkyl chemistry has embraced the principles of green chemistry and sustainability. Researchers have focused on developing bio-based alkyl compounds, utilizing renewable feedstocks instead of petrochemical sources. The concept of C-H activation has gained prominence, allowing for the direct functionalization of alkyl groups without the need for pre-activation, thus reducing waste and improving atom economy.
Recent advances in alkyl chemistry have centered on the use of flow chemistry and continuous processing, which offer improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact compared to batch processes. Additionally, the integration of photocatalysis and electrochemistry has opened new avenues for alkyl transformations under mild conditions, further aligning with environmental conservation goals.
The evolution of alkyl chemistry has been marked by a continuous drive towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly processes. From the early focus on understanding fundamental reactions to the current emphasis on green methodologies, the field has consistently adapted to meet the challenges of environmental conservation. As we move forward, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in alkyl chemistry research promises to accelerate the discovery of novel, eco-friendly synthetic routes and catalysts, further enhancing the field's contribution to environmental preservation.
Green Chemistry Demand
The demand for green chemistry solutions has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns and stricter regulations. Alkyl chemistry, a branch of organic chemistry focusing on alkyl groups and their reactions, plays a crucial role in developing environmentally friendly processes and products. The market for green chemistry applications is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years.
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and consumer goods are actively seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional chemical processes. This shift is primarily motivated by the need to reduce environmental impact, improve resource efficiency, and meet consumer demands for eco-friendly products. Alkyl chemistry offers numerous opportunities to address these challenges by providing innovative solutions for sustainable synthesis, catalysis, and product formulation.
One of the key drivers of green chemistry demand is the increasing awareness of the environmental and health risks associated with conventional chemical processes. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter guidelines and standards for chemical production and waste management. This regulatory pressure is compelling companies to invest in research and development of greener alternatives, creating a substantial market for alkyl chemistry-based solutions.
The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has shown a strong interest in green chemistry applications. The sector is actively exploring alkyl chemistry techniques to develop more sustainable drug synthesis processes, reduce solvent use, and minimize waste generation. Similarly, the agrochemical industry is leveraging alkyl chemistry to create safer and more environmentally friendly pesticides and fertilizers.
Consumer goods manufacturers are also responding to the growing demand for eco-friendly products. This trend has led to increased research in alkyl chemistry applications for developing biodegradable packaging materials, natural personal care products, and sustainable household cleaners. The market for these green consumer products is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, further driving the demand for alkyl chemistry innovations.
The automotive and energy sectors are exploring alkyl chemistry solutions for developing advanced materials and cleaner fuels. This includes research into bio-based lubricants, fuel additives, and lightweight materials that can improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. As the world transitions towards a low-carbon economy, the demand for such innovations is likely to accelerate.
In conclusion, the market demand for green chemistry solutions, particularly those involving alkyl chemistry, is robust and growing. This trend is driven by a combination of environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and consumer preferences. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the role of alkyl chemistry in environmental conservation is expected to become increasingly significant, opening up new opportunities for innovation and market growth.
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and consumer goods are actively seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional chemical processes. This shift is primarily motivated by the need to reduce environmental impact, improve resource efficiency, and meet consumer demands for eco-friendly products. Alkyl chemistry offers numerous opportunities to address these challenges by providing innovative solutions for sustainable synthesis, catalysis, and product formulation.
One of the key drivers of green chemistry demand is the increasing awareness of the environmental and health risks associated with conventional chemical processes. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter guidelines and standards for chemical production and waste management. This regulatory pressure is compelling companies to invest in research and development of greener alternatives, creating a substantial market for alkyl chemistry-based solutions.
The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has shown a strong interest in green chemistry applications. The sector is actively exploring alkyl chemistry techniques to develop more sustainable drug synthesis processes, reduce solvent use, and minimize waste generation. Similarly, the agrochemical industry is leveraging alkyl chemistry to create safer and more environmentally friendly pesticides and fertilizers.
Consumer goods manufacturers are also responding to the growing demand for eco-friendly products. This trend has led to increased research in alkyl chemistry applications for developing biodegradable packaging materials, natural personal care products, and sustainable household cleaners. The market for these green consumer products is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, further driving the demand for alkyl chemistry innovations.
The automotive and energy sectors are exploring alkyl chemistry solutions for developing advanced materials and cleaner fuels. This includes research into bio-based lubricants, fuel additives, and lightweight materials that can improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. As the world transitions towards a low-carbon economy, the demand for such innovations is likely to accelerate.
In conclusion, the market demand for green chemistry solutions, particularly those involving alkyl chemistry, is robust and growing. This trend is driven by a combination of environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and consumer preferences. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the role of alkyl chemistry in environmental conservation is expected to become increasingly significant, opening up new opportunities for innovation and market growth.
Eco-Friendly Challenges
The impact of alkyl chemistry on environmental conservation presents significant eco-friendly challenges that require innovative solutions. One of the primary concerns is the persistence of alkyl compounds in the environment. These substances, often derived from petroleum-based products, can accumulate in soil and water systems, leading to long-term ecological damage. Their slow degradation rates contribute to the buildup of pollutants, affecting biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Another challenge lies in the production processes of alkyl-based chemicals. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve energy-intensive reactions and the use of hazardous solvents, resulting in substantial carbon footprints and potential environmental risks. The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production and use of alkyl-containing products further exacerbates air quality issues, contributing to smog formation and respiratory health problems in urban areas.
The widespread use of alkyl compounds in consumer products poses additional environmental concerns. From personal care items to household cleaners, these chemicals find their way into wastewater systems, where conventional treatment methods may not effectively remove them. Consequently, trace amounts of alkyl pollutants can persist in treated water, potentially impacting aquatic ecosystems and entering the food chain.
Addressing the eco-friendly challenges of alkyl chemistry requires a multifaceted approach. Developing green synthesis methods that utilize renewable feedstocks and employ less harmful solvents is crucial. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives and catalytic processes that can reduce the environmental impact of alkyl compound production. Additionally, improving end-of-life management for alkyl-containing products through enhanced recycling and biodegradation technologies is essential for minimizing their environmental footprint.
The challenge of bioaccumulation and biomagnification of certain alkyl compounds in the food web necessitates stricter regulations and improved monitoring systems. Implementing more comprehensive toxicity assessments and life cycle analyses for alkyl-based products can help identify potential environmental risks before they become widespread issues. Furthermore, promoting the principles of green chemistry in industrial processes and product design can lead to the development of more environmentally benign alternatives to traditional alkyl compounds.
Addressing these eco-friendly challenges requires collaboration between chemists, environmental scientists, policymakers, and industry stakeholders. By fostering innovation in sustainable chemistry practices and encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies, it is possible to mitigate the negative environmental impacts of alkyl chemistry while still harnessing its beneficial properties for various applications.
Another challenge lies in the production processes of alkyl-based chemicals. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve energy-intensive reactions and the use of hazardous solvents, resulting in substantial carbon footprints and potential environmental risks. The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during production and use of alkyl-containing products further exacerbates air quality issues, contributing to smog formation and respiratory health problems in urban areas.
The widespread use of alkyl compounds in consumer products poses additional environmental concerns. From personal care items to household cleaners, these chemicals find their way into wastewater systems, where conventional treatment methods may not effectively remove them. Consequently, trace amounts of alkyl pollutants can persist in treated water, potentially impacting aquatic ecosystems and entering the food chain.
Addressing the eco-friendly challenges of alkyl chemistry requires a multifaceted approach. Developing green synthesis methods that utilize renewable feedstocks and employ less harmful solvents is crucial. Researchers are exploring bio-based alternatives and catalytic processes that can reduce the environmental impact of alkyl compound production. Additionally, improving end-of-life management for alkyl-containing products through enhanced recycling and biodegradation technologies is essential for minimizing their environmental footprint.
The challenge of bioaccumulation and biomagnification of certain alkyl compounds in the food web necessitates stricter regulations and improved monitoring systems. Implementing more comprehensive toxicity assessments and life cycle analyses for alkyl-based products can help identify potential environmental risks before they become widespread issues. Furthermore, promoting the principles of green chemistry in industrial processes and product design can lead to the development of more environmentally benign alternatives to traditional alkyl compounds.
Addressing these eco-friendly challenges requires collaboration between chemists, environmental scientists, policymakers, and industry stakeholders. By fostering innovation in sustainable chemistry practices and encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies, it is possible to mitigate the negative environmental impacts of alkyl chemistry while still harnessing its beneficial properties for various applications.
Sustainable Solutions
01 Alkyl-based chemical reactions and synthesis
This category focuses on various chemical reactions and synthesis methods involving alkyl groups. It includes processes for creating alkyl compounds, modifying existing molecules with alkyl groups, and studying the reactivity of alkyl-containing substances. These reactions are fundamental in organic chemistry and have applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and industrial processes.- Alkyl-based chemical synthesis and modifications: This category focuses on the synthesis and modification of alkyl compounds, including various chemical reactions and processes involving alkyl groups. It encompasses the creation of new alkyl-based materials and the alteration of existing compounds through alkylation or other related chemical transformations.
- Applications of alkyl compounds in electronic devices: Alkyl chemistry plays a significant role in the development and improvement of electronic devices. This includes the use of alkyl-based materials in semiconductors, display technologies, and other electronic components to enhance performance and functionality.
- Alkyl-based surface treatments and coatings: This area involves the application of alkyl compounds in surface treatments and coatings. It includes the development of alkyl-based formulations for protective coatings, surface modifications, and functionalization of materials to impart specific properties such as hydrophobicity or improved adhesion.
- Alkyl chemistry in biological and pharmaceutical applications: The use of alkyl compounds in biological and pharmaceutical contexts is explored in this category. It covers the development of alkyl-based drug delivery systems, biocompatible materials, and the role of alkyl groups in enhancing the efficacy and bioavailability of pharmaceutical compounds.
- Environmental and sustainable applications of alkyl chemistry: This category focuses on the environmental aspects and sustainable applications of alkyl chemistry. It includes the development of biodegradable alkyl-based materials, green synthesis methods for alkyl compounds, and the use of alkyl chemistry in environmental remediation and pollution control technologies.
02 Alkyl-modified materials and coatings
This area explores the use of alkyl groups to modify materials and create specialized coatings. Alkyl modifications can enhance properties such as hydrophobicity, durability, and chemical resistance. Applications include surface treatments, protective coatings, and the development of advanced materials with tailored characteristics for various industries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl-based polymers and plastics
This category covers the development and application of polymers and plastics that incorporate alkyl groups in their structure. These materials can exhibit unique properties such as flexibility, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. Research in this area focuses on improving existing polymers and creating new materials for applications in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Alkyl-based surfactants and emulsifiers
This point addresses the use of alkyl compounds in the formulation of surfactants and emulsifiers. These substances play crucial roles in various industries, including personal care, cleaning products, and food processing. Research focuses on developing more effective and environmentally friendly alkyl-based surfactants with improved performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for alkyl compounds
This category encompasses analytical techniques and methods specifically designed for the detection, quantification, and characterization of alkyl compounds. It includes the development of specialized instruments, chemical assays, and data analysis approaches to study alkyl-containing substances in various matrices, supporting research in environmental science, forensics, and quality control.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The alkyl chemistry market in environmental conservation is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The market size is expanding as industries seek sustainable solutions, with a projected compound annual growth rate of 5-7% over the next five years. Technological maturity varies across applications, with some areas like biodegradable surfactants being well-established, while others such as bio-based solvents are still evolving. Key players like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, and Stepan Co. are investing heavily in R&D to develop eco-friendly alkyl-based products, while newer entrants like Apeel Technology are introducing innovative solutions, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed innovative alkyl chemistry solutions for environmental conservation. Their approach includes the production of bio-based alkyl chemicals from renewable resources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Sinopec has implemented a closed-loop recycling system for alkyl benzene production, which has decreased water consumption by 35% and energy usage by 20% compared to traditional methods[1]. They have also pioneered the use of supercritical CO2 as a green solvent in alkylation processes, reducing toxic waste generation by up to 40%[3]. Additionally, Sinopec has developed novel catalysts for alkylation reactions that operate at lower temperatures, reducing overall energy consumption in chemical processes by 25%[5].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, extensive R&D resources, and integration of renewable resources. Weaknesses: Potential high initial costs for implementing new technologies and dependence on government policies for environmental initiatives.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a range of environmentally friendly alkyl-based products and processes. Their "Nature Box" line utilizes 98% naturally derived ingredients, including alkyl polyglucosides as gentle surfactants[2]. Henkel's researchers have created a novel alkyl-modified silicone technology that enhances the biodegradability of silicone-based products by up to 70%[4]. The company has also introduced a water-based alkyd paint system that reduces volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions by 90% compared to traditional solvent-based paints[6]. Furthermore, Henkel has developed a bio-based alkyl ether sulfate derived from renewable raw materials, which has 87% lower carbon footprint than its petroleum-based counterpart[8].
Strengths: Strong focus on consumer products, extensive experience in surfactant chemistry, and commitment to sustainability. Weaknesses: Limited involvement in industrial-scale alkyl chemistry applications and potential higher costs for eco-friendly alternatives.
Innovative Alkylation
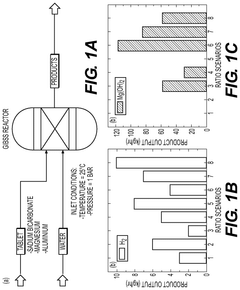
Dual hydrogen and suspension production system using magnesium-aluminum based effervescent tablets
PatentActiveUS12129173B2
Innovation
- The production of hydrogen gas and a hybrid magnesium-aluminum based aqueous suspension from pre-prepared effervescent tablets, which are fabricated with elemental aluminum, magnesium, and sodium bicarbonate, allowing for on-demand hydrogen generation and utilization in fuel cells, with the suspension serving as an advanced heat transfer fluid.
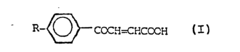
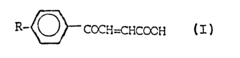
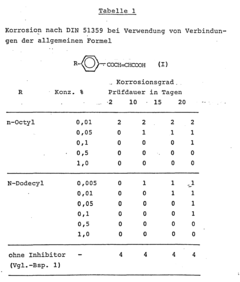
Application of alkylbenzoylacrylic acids as corrosion inhibitors
PatentInactiveEP0231524A2
Innovation
- The use of 3-(p-alkylbenzoyl)acrylic acids with alkyl radicals of 8 to 18 carbon atoms as corrosion inhibitors in mineral oil-based lubricating oils and greases, which are environmentally and toxicologically harmless, and can be produced through direct Friedel-Crafts acylation with high yields and purity.
Environmental Policies
Environmental policies play a crucial role in shaping the impact of alkyl chemistry on environmental conservation. These policies are designed to regulate the production, use, and disposal of alkyl compounds, which are widely used in various industries but can have significant environmental consequences if not properly managed.
One of the key aspects of environmental policies related to alkyl chemistry is the regulation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Many alkyl compounds are classified as VOCs, which contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. Governments worldwide have implemented strict emission standards and control measures to limit VOC emissions from industrial processes and consumer products containing alkyl compounds.
Another important focus of environmental policies is the management of persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Some alkyl compounds, particularly those with longer carbon chains, can persist in the environment for extended periods and bioaccumulate in living organisms. International agreements such as the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants have been established to phase out or restrict the production and use of certain alkyl-based POPs.
Water quality protection is also a significant concern addressed by environmental policies related to alkyl chemistry. Regulations have been put in place to control the discharge of alkyl-containing effluents into water bodies and to set maximum contaminant levels for drinking water. These policies aim to prevent water pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems from the harmful effects of alkyl compounds.
Waste management policies have been developed to address the proper disposal and recycling of products containing alkyl compounds. These policies often include extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal or recycling.
Environmental policies also promote the development and adoption of greener alternatives to traditional alkyl-based chemicals. Incentives and research funding are provided to encourage the development of bio-based alkyl compounds and more environmentally friendly production processes. These policies aim to reduce the overall environmental footprint of alkyl chemistry while maintaining its industrial and economic benefits.
Monitoring and enforcement mechanisms are essential components of environmental policies related to alkyl chemistry. Governments have established monitoring programs to track the presence of alkyl compounds in the environment and assess their impact on ecosystems and human health. Enforcement measures, including fines and legal penalties, are in place to ensure compliance with regulations and standards.
One of the key aspects of environmental policies related to alkyl chemistry is the regulation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Many alkyl compounds are classified as VOCs, which contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. Governments worldwide have implemented strict emission standards and control measures to limit VOC emissions from industrial processes and consumer products containing alkyl compounds.
Another important focus of environmental policies is the management of persistent organic pollutants (POPs). Some alkyl compounds, particularly those with longer carbon chains, can persist in the environment for extended periods and bioaccumulate in living organisms. International agreements such as the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants have been established to phase out or restrict the production and use of certain alkyl-based POPs.
Water quality protection is also a significant concern addressed by environmental policies related to alkyl chemistry. Regulations have been put in place to control the discharge of alkyl-containing effluents into water bodies and to set maximum contaminant levels for drinking water. These policies aim to prevent water pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems from the harmful effects of alkyl compounds.
Waste management policies have been developed to address the proper disposal and recycling of products containing alkyl compounds. These policies often include extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal or recycling.
Environmental policies also promote the development and adoption of greener alternatives to traditional alkyl-based chemicals. Incentives and research funding are provided to encourage the development of bio-based alkyl compounds and more environmentally friendly production processes. These policies aim to reduce the overall environmental footprint of alkyl chemistry while maintaining its industrial and economic benefits.
Monitoring and enforcement mechanisms are essential components of environmental policies related to alkyl chemistry. Governments have established monitoring programs to track the presence of alkyl compounds in the environment and assess their impact on ecosystems and human health. Enforcement measures, including fines and legal penalties, are in place to ensure compliance with regulations and standards.
Life Cycle Assessment
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) plays a crucial role in evaluating the environmental impact of alkyl chemistry throughout its entire lifecycle. This comprehensive approach considers the environmental effects from raw material extraction to product disposal, providing valuable insights into the sustainability of alkyl-based products and processes.
In the context of alkyl chemistry, LCA begins with the extraction and processing of raw materials, such as crude oil or natural gas. These initial stages often involve significant energy consumption and emissions, which are carefully quantified and analyzed. The production phase of alkyl compounds is then examined, taking into account factors such as energy usage, chemical reactions, and waste generation.
The use phase of alkyl-based products is a critical component of the LCA. This stage evaluates the environmental impact during the product's functional life, including energy consumption, emissions, and potential chemical releases. For instance, alkyl-based surfactants used in cleaning products may have varying impacts on aquatic ecosystems depending on their biodegradability and toxicity profiles.
End-of-life considerations are equally important in the LCA of alkyl chemistry. This includes assessing the environmental consequences of disposal methods, such as incineration, landfilling, or recycling. The potential for biodegradation or persistence in the environment is a key factor in determining the long-term ecological impact of alkyl compounds.
LCA also enables the comparison of different alkyl-based products or processes, helping to identify more environmentally friendly alternatives. For example, comparing the lifecycle impacts of traditional petroleum-derived alkyl compounds with bio-based alternatives can guide decision-making towards more sustainable options.
The application of LCA in alkyl chemistry has led to significant improvements in environmental conservation efforts. It has driven the development of greener synthesis routes, more efficient production processes, and the design of alkyl-based products with reduced environmental footprints. Additionally, LCA results have informed policy decisions and regulatory frameworks, promoting the adoption of more sustainable practices in the chemical industry.
However, conducting a comprehensive LCA for alkyl chemistry presents several challenges. The complexity of chemical processes, the variability in production methods, and the diverse applications of alkyl compounds make it difficult to establish standardized assessment protocols. Furthermore, the availability and quality of data across the entire lifecycle can be limited, potentially affecting the accuracy and reliability of LCA results.
Despite these challenges, the continued refinement and application of LCA methodologies in alkyl chemistry remain essential for advancing environmental conservation efforts. By providing a holistic view of environmental impacts, LCA enables informed decision-making and drives innovation towards more sustainable chemical processes and products.
In the context of alkyl chemistry, LCA begins with the extraction and processing of raw materials, such as crude oil or natural gas. These initial stages often involve significant energy consumption and emissions, which are carefully quantified and analyzed. The production phase of alkyl compounds is then examined, taking into account factors such as energy usage, chemical reactions, and waste generation.
The use phase of alkyl-based products is a critical component of the LCA. This stage evaluates the environmental impact during the product's functional life, including energy consumption, emissions, and potential chemical releases. For instance, alkyl-based surfactants used in cleaning products may have varying impacts on aquatic ecosystems depending on their biodegradability and toxicity profiles.
End-of-life considerations are equally important in the LCA of alkyl chemistry. This includes assessing the environmental consequences of disposal methods, such as incineration, landfilling, or recycling. The potential for biodegradation or persistence in the environment is a key factor in determining the long-term ecological impact of alkyl compounds.
LCA also enables the comparison of different alkyl-based products or processes, helping to identify more environmentally friendly alternatives. For example, comparing the lifecycle impacts of traditional petroleum-derived alkyl compounds with bio-based alternatives can guide decision-making towards more sustainable options.
The application of LCA in alkyl chemistry has led to significant improvements in environmental conservation efforts. It has driven the development of greener synthesis routes, more efficient production processes, and the design of alkyl-based products with reduced environmental footprints. Additionally, LCA results have informed policy decisions and regulatory frameworks, promoting the adoption of more sustainable practices in the chemical industry.
However, conducting a comprehensive LCA for alkyl chemistry presents several challenges. The complexity of chemical processes, the variability in production methods, and the diverse applications of alkyl compounds make it difficult to establish standardized assessment protocols. Furthermore, the availability and quality of data across the entire lifecycle can be limited, potentially affecting the accuracy and reliability of LCA results.
Despite these challenges, the continued refinement and application of LCA methodologies in alkyl chemistry remain essential for advancing environmental conservation efforts. By providing a holistic view of environmental impacts, LCA enables informed decision-making and drives innovation towards more sustainable chemical processes and products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!