Alkyl Compounds in the Evolution of Modern Chemistry
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Compound History
Alkyl compounds have played a pivotal role in the evolution of modern chemistry, with their history dating back to the early 19th century. The discovery and understanding of these organic molecules marked a significant turning point in chemical research and industrial applications.
The journey of alkyl compounds began in 1825 when Michael Faraday isolated and identified benzene, a cyclic hydrocarbon. This breakthrough laid the foundation for the exploration of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons. In 1849, Edward Frankland synthesized the first organometallic compound, diethylzinc, which opened up new avenues for alkyl chemistry.
The late 19th century saw rapid advancements in the field, with August Kekulé proposing the structural theory of organic compounds in 1858. This theory provided a framework for understanding the bonding and arrangement of carbon atoms in alkyl compounds, revolutionizing organic chemistry.
The early 20th century brought about significant developments in alkyl compound synthesis and characterization. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel Prize for his work on organomagnesium compounds, known as Grignard reagents. These reagents became powerful tools for creating carbon-carbon bonds and synthesizing complex organic molecules.
The mid-20th century witnessed the emergence of petrochemistry, driven by the increasing demand for fossil fuels. This led to the development of catalytic cracking and reforming processes, which produced a wide range of alkyl compounds as byproducts. These compounds became essential raw materials for the burgeoning plastics and synthetic materials industries.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the advent of spectroscopic techniques such as NMR and mass spectrometry revolutionized the analysis and characterization of alkyl compounds. These tools allowed chemists to elucidate complex molecular structures and study reaction mechanisms with unprecedented precision.
The latter half of the 20th century saw a shift towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable chemistry. This led to the development of new synthetic methods for alkyl compounds, including green chemistry approaches and the use of renewable feedstocks.
In recent decades, the focus has expanded to include the synthesis of complex alkyl-containing natural products and pharmaceuticals. Advanced catalytic methods, such as cross-coupling reactions and asymmetric synthesis, have enabled the creation of intricate molecular architectures with precise control over stereochemistry.
Today, alkyl compounds continue to be at the forefront of chemical research and innovation. From materials science to drug discovery, these versatile molecules play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of modern chemistry and driving technological advancements across various industries.
The journey of alkyl compounds began in 1825 when Michael Faraday isolated and identified benzene, a cyclic hydrocarbon. This breakthrough laid the foundation for the exploration of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons. In 1849, Edward Frankland synthesized the first organometallic compound, diethylzinc, which opened up new avenues for alkyl chemistry.
The late 19th century saw rapid advancements in the field, with August Kekulé proposing the structural theory of organic compounds in 1858. This theory provided a framework for understanding the bonding and arrangement of carbon atoms in alkyl compounds, revolutionizing organic chemistry.
The early 20th century brought about significant developments in alkyl compound synthesis and characterization. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel Prize for his work on organomagnesium compounds, known as Grignard reagents. These reagents became powerful tools for creating carbon-carbon bonds and synthesizing complex organic molecules.
The mid-20th century witnessed the emergence of petrochemistry, driven by the increasing demand for fossil fuels. This led to the development of catalytic cracking and reforming processes, which produced a wide range of alkyl compounds as byproducts. These compounds became essential raw materials for the burgeoning plastics and synthetic materials industries.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the advent of spectroscopic techniques such as NMR and mass spectrometry revolutionized the analysis and characterization of alkyl compounds. These tools allowed chemists to elucidate complex molecular structures and study reaction mechanisms with unprecedented precision.
The latter half of the 20th century saw a shift towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable chemistry. This led to the development of new synthetic methods for alkyl compounds, including green chemistry approaches and the use of renewable feedstocks.
In recent decades, the focus has expanded to include the synthesis of complex alkyl-containing natural products and pharmaceuticals. Advanced catalytic methods, such as cross-coupling reactions and asymmetric synthesis, have enabled the creation of intricate molecular architectures with precise control over stereochemistry.
Today, alkyl compounds continue to be at the forefront of chemical research and innovation. From materials science to drug discovery, these versatile molecules play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of modern chemistry and driving technological advancements across various industries.
Market Applications
Alkyl compounds have become integral to numerous market applications across various industries, driving innovation and technological advancements. In the pharmaceutical sector, these compounds play a crucial role in drug development and synthesis. They serve as building blocks for complex organic molecules, enabling the creation of novel therapeutic agents. Alkyl groups are often incorporated into drug molecules to enhance their pharmacokinetic properties, such as improved solubility, bioavailability, and metabolic stability. This has led to the development of more effective and targeted medications, revolutionizing treatment options for various diseases.
The petrochemical industry heavily relies on alkyl compounds for the production of fuels, lubricants, and plastics. Alkylation processes are employed to create high-octane gasoline components, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. In the polymer industry, alkyl-based monomers are essential for manufacturing a wide range of plastics, elastomers, and synthetic fibers. These materials find applications in packaging, automotive parts, textiles, and construction materials, contributing significantly to the global economy.
Alkyl compounds have also found extensive use in the agrochemical sector. They are utilized in the synthesis of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, enhancing crop protection and agricultural productivity. The ability to tailor alkyl groups allows for the development of more environmentally friendly and targeted agrochemicals, addressing concerns about sustainability and ecological impact.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, alkyl compounds are employed as emollients, surfactants, and preservatives. They contribute to the formulation of skincare products, hair care solutions, and fragrances, meeting consumer demands for effective and safe personal care items. The versatility of alkyl compounds enables the creation of multifunctional ingredients that can improve product performance and stability.
The electronics industry benefits from alkyl compounds in the production of semiconductors and electronic materials. Organosilicon compounds, which often contain alkyl groups, are used in the manufacture of silicon wafers and as precursors for chemical vapor deposition processes. These applications are critical for the continued advancement of microelectronics and the development of more powerful and efficient electronic devices.
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, alkyl compounds are finding new applications in green chemistry and renewable energy technologies. They are being explored for use in biodegradable plastics, environmentally friendly solvents, and as components in next-generation solar cells and energy storage systems. The adaptability of alkyl chemistry positions these compounds at the forefront of efforts to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly industrial processes and products.
The petrochemical industry heavily relies on alkyl compounds for the production of fuels, lubricants, and plastics. Alkylation processes are employed to create high-octane gasoline components, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. In the polymer industry, alkyl-based monomers are essential for manufacturing a wide range of plastics, elastomers, and synthetic fibers. These materials find applications in packaging, automotive parts, textiles, and construction materials, contributing significantly to the global economy.
Alkyl compounds have also found extensive use in the agrochemical sector. They are utilized in the synthesis of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, enhancing crop protection and agricultural productivity. The ability to tailor alkyl groups allows for the development of more environmentally friendly and targeted agrochemicals, addressing concerns about sustainability and ecological impact.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, alkyl compounds are employed as emollients, surfactants, and preservatives. They contribute to the formulation of skincare products, hair care solutions, and fragrances, meeting consumer demands for effective and safe personal care items. The versatility of alkyl compounds enables the creation of multifunctional ingredients that can improve product performance and stability.
The electronics industry benefits from alkyl compounds in the production of semiconductors and electronic materials. Organosilicon compounds, which often contain alkyl groups, are used in the manufacture of silicon wafers and as precursors for chemical vapor deposition processes. These applications are critical for the continued advancement of microelectronics and the development of more powerful and efficient electronic devices.
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, alkyl compounds are finding new applications in green chemistry and renewable energy technologies. They are being explored for use in biodegradable plastics, environmentally friendly solvents, and as components in next-generation solar cells and energy storage systems. The adaptability of alkyl chemistry positions these compounds at the forefront of efforts to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly industrial processes and products.
Current Challenges
Despite the significant advancements in alkyl compound chemistry, several challenges persist in this field, hindering further progress and limiting potential applications. One of the primary obstacles is the development of more efficient and selective catalysts for alkyl compound synthesis. Current catalytic systems often lack the precision required for complex transformations, leading to unwanted side products and reduced yields.
Environmental concerns pose another significant challenge. Many traditional methods for synthesizing and manipulating alkyl compounds involve the use of toxic reagents or generate hazardous waste. The push towards greener chemistry necessitates the development of more sustainable processes that minimize environmental impact while maintaining or improving efficiency.
The control of stereochemistry in alkyl compound reactions remains a persistent challenge. Achieving high levels of stereoselectivity, particularly in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds, is crucial for many applications, including pharmaceutical synthesis. Current methods often struggle to provide the desired level of control, limiting the potential for creating complex, stereochemically pure molecules.
Scalability is another hurdle faced by researchers and industry professionals. Many reactions that work well on a laboratory scale encounter difficulties when scaled up for industrial production. Issues such as heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and reagent compatibility can become problematic at larger scales, necessitating the development of new methodologies and equipment.
The exploration of novel alkyl compound functionalities and properties represents both a challenge and an opportunity. As the field evolves, there is a growing need to discover and exploit new types of alkyl compounds with unique characteristics that could lead to innovative applications in materials science, energy storage, and other emerging fields.
Computational modeling and prediction of alkyl compound behavior and reactivity remain areas of ongoing challenge. While significant progress has been made in computational chemistry, accurately predicting the outcomes of complex reactions involving alkyl compounds, especially in diverse solvent environments or under varying conditions, continues to be difficult.
Lastly, the integration of alkyl compound chemistry with other cutting-edge fields, such as nanotechnology and biotechnology, presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. Developing methods to precisely manipulate and functionalize alkyl compounds at the nanoscale or within biological systems could open up new avenues for research and application but requires overcoming numerous technical hurdles.
Environmental concerns pose another significant challenge. Many traditional methods for synthesizing and manipulating alkyl compounds involve the use of toxic reagents or generate hazardous waste. The push towards greener chemistry necessitates the development of more sustainable processes that minimize environmental impact while maintaining or improving efficiency.
The control of stereochemistry in alkyl compound reactions remains a persistent challenge. Achieving high levels of stereoselectivity, particularly in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds, is crucial for many applications, including pharmaceutical synthesis. Current methods often struggle to provide the desired level of control, limiting the potential for creating complex, stereochemically pure molecules.
Scalability is another hurdle faced by researchers and industry professionals. Many reactions that work well on a laboratory scale encounter difficulties when scaled up for industrial production. Issues such as heat transfer, mixing efficiency, and reagent compatibility can become problematic at larger scales, necessitating the development of new methodologies and equipment.
The exploration of novel alkyl compound functionalities and properties represents both a challenge and an opportunity. As the field evolves, there is a growing need to discover and exploit new types of alkyl compounds with unique characteristics that could lead to innovative applications in materials science, energy storage, and other emerging fields.
Computational modeling and prediction of alkyl compound behavior and reactivity remain areas of ongoing challenge. While significant progress has been made in computational chemistry, accurately predicting the outcomes of complex reactions involving alkyl compounds, especially in diverse solvent environments or under varying conditions, continues to be difficult.
Lastly, the integration of alkyl compound chemistry with other cutting-edge fields, such as nanotechnology and biotechnology, presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. Developing methods to precisely manipulate and functionalize alkyl compounds at the nanoscale or within biological systems could open up new avenues for research and application but requires overcoming numerous technical hurdles.
Modern Synthesis Methods
01 Synthesis of alkyl compounds
Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl derivatives.- Synthesis of alkyl compounds: Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl compounds efficiently.
- Applications of alkyl compounds in industrial processes: Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of polymers, lubricants, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds and play a role in petroleum refining.
- Alkyl compounds in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations: Alkyl compounds are utilized in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations due to their properties as solvents, emollients, and active ingredients. They contribute to the stability, efficacy, and sensory characteristics of various products.
- Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds: The use and handling of alkyl compounds often require consideration of environmental impact and safety measures. This includes proper disposal methods, toxicity assessments, and the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives or processes.
- Modification and functionalization of alkyl compounds: Techniques for modifying and functionalizing alkyl compounds are explored to enhance their properties or create new derivatives. This includes processes such as alkylation, oxidation, and the introduction of various functional groups to tailor the compounds for specific applications.
02 Applications of alkyl compounds in industry
Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of plastics, lubricants, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl compounds in pharmaceutical formulations
Certain alkyl compounds are utilized in pharmaceutical formulations as active ingredients, excipients, or as part of drug delivery systems. These compounds can enhance the solubility, stability, or bioavailability of drugs.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental impact and biodegradation of alkyl compounds
Research on the environmental fate and biodegradation of alkyl compounds is conducted to assess their impact on ecosystems. Studies focus on developing eco-friendly alternatives and improving the biodegradability of alkyl-based products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl compounds in polymer chemistry
Alkyl groups play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, influencing the properties of various polymeric materials. They are used in the synthesis of polymers and copolymers, affecting characteristics such as solubility, thermal stability, and mechanical properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The field of alkyl compounds in modern chemistry is in a mature stage of development, with a well-established market and significant ongoing research. The global market for alkyl compounds is substantial, driven by their widespread applications in pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and materials science. Major players like Janssen Pharmaceutica, Novartis, and Pfizer are heavily invested in this area, particularly for drug development. Academic institutions such as Columbia University and the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry contribute significantly to fundamental research. The technology is mature, with continuous innovations in synthesis methods and applications. Companies like Syngenta and Chevron Oronite focus on specialized applications in agrochemicals and lubricants, respectively, indicating the diverse and evolving nature of the field.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has made significant contributions to the evolution of modern chemistry through its work with alkyl compounds. The company has developed novel synthetic methodologies for creating complex alkyl structures, particularly in the realm of pharmaceutical development. Their approach involves using transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions to form carbon-carbon bonds, allowing for the efficient synthesis of alkyl-containing drug candidates[1]. Novartis has also pioneered the use of flow chemistry techniques for continuous production of alkylated intermediates, improving both yield and safety in large-scale manufacturing processes[2]. Additionally, the company has invested in developing sustainable alkylation methods, utilizing bio-based feedstocks and green solvents to reduce environmental impact[3].
Strengths: Strong R&D capabilities, innovative synthetic methodologies, and a focus on sustainable chemistry. Weaknesses: High costs associated with drug development and potential regulatory challenges in implementing new chemical processes.
Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry
Technical Solution: The Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry (SIOC) has been at the forefront of research into alkyl compounds and their role in modern chemistry. SIOC has developed groundbreaking methodologies for alkyl C-H functionalization, enabling the direct transformation of previously unreactive C-H bonds into valuable functional groups[1]. Their work on transition metal-catalyzed alkyl cross-coupling reactions has expanded the toolkit for organic synthesis, allowing for the creation of complex molecules with improved efficiency[2]. SIOC researchers have also made significant advances in asymmetric catalysis involving alkyl substrates, contributing to the development of enantioselective reactions crucial for pharmaceutical and materials science applications[3]. Furthermore, the institute has pioneered the use of photoredox catalysis for alkyl radical generation, opening new avenues for sustainable and mild alkylation processes[4].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research in C-H functionalization and catalysis, strong international collaborations. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up academic discoveries for industrial applications.
Innovative Alkylation
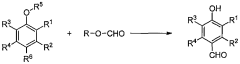
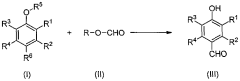
Process for production of vanillin and vanillin derivatives
PatentWO2013166642A1
Innovation
- A one-step regio- and chemoselective formylation process using a superacid to produce vanillin or vanillin derivatives from guaiacol or its derivatives, achieving high yields with minimal isomer formation by reacting guaiacol or its derivatives with a superacid, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, in the presence of a formyl source like methyl formate, without the need for specific solvents or harsh conditions.
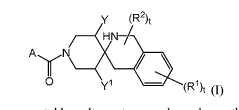
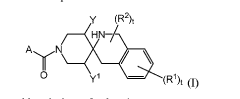
PRMT5 inhibitors
PatentWO2021126729A1
Innovation
- Development of compounds that inhibit PRMT5 activity, specifically described by the formula I compounds and their pharmaceutical compositions, which can be used to treat cancer, β-thalassemia, and hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH) mutations by targeting PRMT5 inhibition.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of alkyl compounds in modern chemistry is a critical consideration that has gained increasing attention in recent years. These organic molecules, characterized by their carbon-hydrogen bonds, have become ubiquitous in various industrial processes and consumer products. However, their widespread use has raised significant concerns regarding their effects on ecosystems and human health.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with alkyl compounds is their persistence in the environment. Many of these substances are resistant to natural degradation processes, leading to long-term accumulation in soil, water, and air. This persistence can result in bioaccumulation within food chains, potentially affecting a wide range of organisms across different trophic levels.
The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), many of which are alkyl-based, contributes to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. This not only impacts air quality but also plays a role in climate change, as some alkyl compounds have high global warming potentials. Additionally, the production and disposal of alkyl-containing products often involve energy-intensive processes, further contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Water pollution is another significant concern. Alkyl compounds can contaminate both surface and groundwater sources through industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, and improper disposal of consumer products. This contamination can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, disrupting the balance of marine and freshwater environments and potentially affecting the health of aquatic organisms.
The impact on soil quality is equally important. Alkyl compounds can alter soil chemistry, affecting microbial communities and plant growth. In some cases, this can lead to reduced agricultural productivity and changes in local ecosystems. Furthermore, the remediation of contaminated soils often requires extensive and costly interventions.
Human health risks associated with exposure to certain alkyl compounds have also been identified. These range from short-term effects like respiratory irritation to long-term concerns such as carcinogenicity and endocrine disruption. The ubiquity of these compounds in everyday products means that human exposure can occur through multiple pathways, including inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact.
In response to these environmental and health concerns, there has been a growing push for the development of greener alternatives and more sustainable chemical processes. This includes research into bio-based alkyl compounds, improved waste management strategies, and the implementation of stricter regulations on the production and use of potentially harmful alkyl substances.
One of the primary environmental issues associated with alkyl compounds is their persistence in the environment. Many of these substances are resistant to natural degradation processes, leading to long-term accumulation in soil, water, and air. This persistence can result in bioaccumulation within food chains, potentially affecting a wide range of organisms across different trophic levels.
The release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), many of which are alkyl-based, contributes to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone. This not only impacts air quality but also plays a role in climate change, as some alkyl compounds have high global warming potentials. Additionally, the production and disposal of alkyl-containing products often involve energy-intensive processes, further contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Water pollution is another significant concern. Alkyl compounds can contaminate both surface and groundwater sources through industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, and improper disposal of consumer products. This contamination can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, disrupting the balance of marine and freshwater environments and potentially affecting the health of aquatic organisms.
The impact on soil quality is equally important. Alkyl compounds can alter soil chemistry, affecting microbial communities and plant growth. In some cases, this can lead to reduced agricultural productivity and changes in local ecosystems. Furthermore, the remediation of contaminated soils often requires extensive and costly interventions.
Human health risks associated with exposure to certain alkyl compounds have also been identified. These range from short-term effects like respiratory irritation to long-term concerns such as carcinogenicity and endocrine disruption. The ubiquity of these compounds in everyday products means that human exposure can occur through multiple pathways, including inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact.
In response to these environmental and health concerns, there has been a growing push for the development of greener alternatives and more sustainable chemical processes. This includes research into bio-based alkyl compounds, improved waste management strategies, and the implementation of stricter regulations on the production and use of potentially harmful alkyl substances.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding alkyl compounds has evolved significantly in response to their widespread use and potential environmental and health impacts. Governments and international organizations have implemented various regulations to control the production, use, and disposal of these chemicals.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating alkyl compounds under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers to submit premanufacture notices for new chemical substances, including alkyl compounds, and allows the EPA to restrict or ban chemicals that pose unreasonable risks to human health or the environment.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to a wide range of chemicals, including alkyl compounds. REACH requires companies to register chemical substances and provide safety data, with the aim of improving the protection of human health and the environment.
Internationally, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) addresses certain alkyl compounds that are considered persistent and bioaccumulative. This treaty aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of specific POPs, some of which are alkyl compounds or their derivatives.
Many countries have also established occupational safety and health regulations to protect workers from exposure to hazardous alkyl compounds. These regulations often include exposure limits, personal protective equipment requirements, and safe handling procedures.
The transportation of alkyl compounds is regulated under various international agreements, such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines provide a framework for the safe transport of hazardous materials, including many alkyl compounds.
As scientific understanding of the potential risks associated with alkyl compounds has grown, regulatory frameworks have become more comprehensive and stringent. Many regulations now focus on the entire lifecycle of these chemicals, from production to disposal, to minimize environmental and health risks.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly adopting a precautionary approach, requiring more extensive safety data and risk assessments before approving new alkyl compounds or novel uses of existing ones. This shift has led to greater emphasis on developing safer alternatives and promoting green chemistry principles in the synthesis and application of alkyl compounds.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating alkyl compounds under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers to submit premanufacture notices for new chemical substances, including alkyl compounds, and allows the EPA to restrict or ban chemicals that pose unreasonable risks to human health or the environment.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which applies to a wide range of chemicals, including alkyl compounds. REACH requires companies to register chemical substances and provide safety data, with the aim of improving the protection of human health and the environment.
Internationally, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) addresses certain alkyl compounds that are considered persistent and bioaccumulative. This treaty aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of specific POPs, some of which are alkyl compounds or their derivatives.
Many countries have also established occupational safety and health regulations to protect workers from exposure to hazardous alkyl compounds. These regulations often include exposure limits, personal protective equipment requirements, and safe handling procedures.
The transportation of alkyl compounds is regulated under various international agreements, such as the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines provide a framework for the safe transport of hazardous materials, including many alkyl compounds.
As scientific understanding of the potential risks associated with alkyl compounds has grown, regulatory frameworks have become more comprehensive and stringent. Many regulations now focus on the entire lifecycle of these chemicals, from production to disposal, to minimize environmental and health risks.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly adopting a precautionary approach, requiring more extensive safety data and risk assessments before approving new alkyl compounds or novel uses of existing ones. This shift has led to greater emphasis on developing safer alternatives and promoting green chemistry principles in the synthesis and application of alkyl compounds.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!