Alkyl Research: Bridging Gaps in Innovative Chemistry
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Research Background and Objectives
Alkyl research has emerged as a critical field in innovative chemistry, bridging gaps between fundamental organic synthesis and practical applications across various industries. The evolution of alkyl chemistry can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements in carbon-carbon bond formation and functionalization techniques. Over the decades, this field has expanded to encompass a wide range of reactions, from simple alkylation processes to complex multi-step syntheses involving alkyl intermediates.
The primary objective of contemporary alkyl research is to develop more efficient, sustainable, and selective methods for the manipulation of alkyl groups. This includes the exploration of novel catalytic systems, the utilization of renewable feedstocks, and the implementation of green chemistry principles. Researchers aim to overcome longstanding challenges such as regioselectivity in alkylation reactions, stereocontrol in carbon-carbon bond formation, and the activation of traditionally unreactive C-H bonds.
Recent trends in alkyl chemistry have focused on the development of transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, which have revolutionized the synthesis of complex organic molecules. These methodologies have found extensive applications in pharmaceutical development, materials science, and agrochemistry. Additionally, there is a growing interest in photoredox catalysis and electrochemical methods for alkyl transformations, offering new avenues for sustainable synthesis under mild conditions.
The technological landscape of alkyl research is rapidly evolving, with advancements in analytical techniques and computational methods playing a crucial role. High-throughput experimentation and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to accelerate the discovery of new reactions and optimize existing processes. These tools enable researchers to explore vast chemical spaces and predict reaction outcomes with unprecedented accuracy.
Looking ahead, the field of alkyl research is poised to address several key challenges. These include the development of more atom-economical processes, the utilization of abundant and inexpensive alkyl sources, and the design of catalysts capable of activating traditionally inert alkyl substrates. There is also a growing emphasis on the integration of alkyl chemistry with other emerging fields, such as flow chemistry and biocatalysis, to create hybrid systems that combine the best of synthetic and biological approaches.
In conclusion, alkyl research stands at the forefront of innovative chemistry, continuously pushing the boundaries of what is possible in organic synthesis. By bridging gaps between fundamental research and practical applications, this field holds immense potential for addressing global challenges in energy, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. The ongoing efforts in this area are expected to yield transformative technologies and methodologies that will shape the future of chemical manufacturing and beyond.
The primary objective of contemporary alkyl research is to develop more efficient, sustainable, and selective methods for the manipulation of alkyl groups. This includes the exploration of novel catalytic systems, the utilization of renewable feedstocks, and the implementation of green chemistry principles. Researchers aim to overcome longstanding challenges such as regioselectivity in alkylation reactions, stereocontrol in carbon-carbon bond formation, and the activation of traditionally unreactive C-H bonds.
Recent trends in alkyl chemistry have focused on the development of transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, which have revolutionized the synthesis of complex organic molecules. These methodologies have found extensive applications in pharmaceutical development, materials science, and agrochemistry. Additionally, there is a growing interest in photoredox catalysis and electrochemical methods for alkyl transformations, offering new avenues for sustainable synthesis under mild conditions.
The technological landscape of alkyl research is rapidly evolving, with advancements in analytical techniques and computational methods playing a crucial role. High-throughput experimentation and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to accelerate the discovery of new reactions and optimize existing processes. These tools enable researchers to explore vast chemical spaces and predict reaction outcomes with unprecedented accuracy.
Looking ahead, the field of alkyl research is poised to address several key challenges. These include the development of more atom-economical processes, the utilization of abundant and inexpensive alkyl sources, and the design of catalysts capable of activating traditionally inert alkyl substrates. There is also a growing emphasis on the integration of alkyl chemistry with other emerging fields, such as flow chemistry and biocatalysis, to create hybrid systems that combine the best of synthetic and biological approaches.
In conclusion, alkyl research stands at the forefront of innovative chemistry, continuously pushing the boundaries of what is possible in organic synthesis. By bridging gaps between fundamental research and practical applications, this field holds immense potential for addressing global challenges in energy, healthcare, and environmental sustainability. The ongoing efforts in this area are expected to yield transformative technologies and methodologies that will shape the future of chemical manufacturing and beyond.
Market Analysis for Alkyl Compounds
The alkyl compounds market has shown significant growth and diversification in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. These versatile organic molecules, characterized by their carbon-hydrogen chains, play crucial roles in numerous applications, from pharmaceuticals to petrochemicals.
In the pharmaceutical sector, alkyl compounds serve as essential building blocks for drug synthesis, contributing to the development of novel therapeutic agents. The growing emphasis on personalized medicine and targeted drug delivery systems has further amplified the demand for specialized alkyl derivatives. This trend is expected to continue, with the pharmaceutical industry projected to be a major consumer of alkyl compounds in the coming years.
The petrochemical industry remains a dominant force in the alkyl compounds market, utilizing these substances in the production of lubricants, fuel additives, and various polymers. As the automotive and manufacturing sectors evolve, there is an increasing need for high-performance materials, driving innovation in alkyl-based products. The shift towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable practices has also spurred research into bio-based alkyl compounds, opening new avenues for market growth.
In the realm of personal care and cosmetics, alkyl compounds find extensive use as emollients, surfactants, and preservatives. The rising consumer awareness regarding product ingredients and the demand for natural and organic formulations have led to the development of milder, plant-derived alkyl alternatives. This segment of the market is experiencing rapid expansion, particularly in emerging economies with growing middle-class populations.
The agricultural sector represents another significant market for alkyl compounds, particularly in the formulation of pesticides and herbicides. As global food demand increases and agricultural practices intensify, the need for effective crop protection solutions continues to drive market growth. However, this area also faces challenges due to increasing regulatory scrutiny and the push for more sustainable farming methods.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key region for alkyl compound production and consumption, fueled by rapid industrialization and urbanization. North America and Europe maintain strong market positions, particularly in high-value, specialized applications. The Middle East, with its robust petrochemical industry, is also a significant player in the global alkyl compounds market.
Looking ahead, the market for alkyl compounds is poised for continued growth, with innovations in green chemistry and sustainable production methods likely to shape future developments. The increasing focus on circular economy principles and the need for more efficient resource utilization are expected to drive research into novel alkyl compounds with enhanced performance and reduced environmental impact.
In the pharmaceutical sector, alkyl compounds serve as essential building blocks for drug synthesis, contributing to the development of novel therapeutic agents. The growing emphasis on personalized medicine and targeted drug delivery systems has further amplified the demand for specialized alkyl derivatives. This trend is expected to continue, with the pharmaceutical industry projected to be a major consumer of alkyl compounds in the coming years.
The petrochemical industry remains a dominant force in the alkyl compounds market, utilizing these substances in the production of lubricants, fuel additives, and various polymers. As the automotive and manufacturing sectors evolve, there is an increasing need for high-performance materials, driving innovation in alkyl-based products. The shift towards more environmentally friendly and sustainable practices has also spurred research into bio-based alkyl compounds, opening new avenues for market growth.
In the realm of personal care and cosmetics, alkyl compounds find extensive use as emollients, surfactants, and preservatives. The rising consumer awareness regarding product ingredients and the demand for natural and organic formulations have led to the development of milder, plant-derived alkyl alternatives. This segment of the market is experiencing rapid expansion, particularly in emerging economies with growing middle-class populations.
The agricultural sector represents another significant market for alkyl compounds, particularly in the formulation of pesticides and herbicides. As global food demand increases and agricultural practices intensify, the need for effective crop protection solutions continues to drive market growth. However, this area also faces challenges due to increasing regulatory scrutiny and the push for more sustainable farming methods.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key region for alkyl compound production and consumption, fueled by rapid industrialization and urbanization. North America and Europe maintain strong market positions, particularly in high-value, specialized applications. The Middle East, with its robust petrochemical industry, is also a significant player in the global alkyl compounds market.
Looking ahead, the market for alkyl compounds is poised for continued growth, with innovations in green chemistry and sustainable production methods likely to shape future developments. The increasing focus on circular economy principles and the need for more efficient resource utilization are expected to drive research into novel alkyl compounds with enhanced performance and reduced environmental impact.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Chemistry
Alkyl chemistry, a cornerstone of organic synthesis, faces several significant challenges that hinder its full potential in innovative applications. One of the primary obstacles is the control of selectivity in alkyl reactions. Achieving precise regioselectivity and stereoselectivity remains difficult, particularly in complex molecular systems. This challenge is exacerbated when dealing with multiple reactive sites or when attempting to functionalize specific positions in alkyl chains.
Another pressing issue is the activation of unreactive C-H bonds in alkyl compounds. While progress has been made in C-H activation chemistry, many alkyl C-H bonds remain stubbornly inert under conventional conditions. This limitation restricts the scope of late-stage functionalization and impedes the development of more efficient synthetic routes.
The stability and handling of alkyl intermediates pose additional challenges. Many alkyl radicals and organometallic species are highly reactive and short-lived, making their controlled manipulation and incorporation into synthetic sequences problematic. This instability often leads to unwanted side reactions or decomposition, reducing overall reaction efficiency and yield.
Environmental concerns also present a significant hurdle in alkyl chemistry. Traditional alkylation methods often rely on toxic or environmentally harmful reagents and solvents. The development of greener alternatives that maintain or improve reaction efficiency is crucial for the sustainable advancement of the field.
Furthermore, the scalability of alkyl reactions remains a challenge, particularly for industrial applications. Many laboratory-scale processes do not translate well to larger production scales due to heat transfer issues, mixing problems, or the accumulation of byproducts. Addressing these scale-up challenges is essential for bridging the gap between academic research and industrial implementation.
Lastly, the limited substrate scope of many alkyl transformations restricts their broader applicability. Many reactions work well with simple, unfunctionalized alkyl groups but fail when applied to more complex, functionalized substrates. Expanding the tolerance of alkyl chemistry to a wider range of functional groups and molecular architectures is crucial for its application in the synthesis of complex natural products and pharmaceuticals.
Another pressing issue is the activation of unreactive C-H bonds in alkyl compounds. While progress has been made in C-H activation chemistry, many alkyl C-H bonds remain stubbornly inert under conventional conditions. This limitation restricts the scope of late-stage functionalization and impedes the development of more efficient synthetic routes.
The stability and handling of alkyl intermediates pose additional challenges. Many alkyl radicals and organometallic species are highly reactive and short-lived, making their controlled manipulation and incorporation into synthetic sequences problematic. This instability often leads to unwanted side reactions or decomposition, reducing overall reaction efficiency and yield.
Environmental concerns also present a significant hurdle in alkyl chemistry. Traditional alkylation methods often rely on toxic or environmentally harmful reagents and solvents. The development of greener alternatives that maintain or improve reaction efficiency is crucial for the sustainable advancement of the field.
Furthermore, the scalability of alkyl reactions remains a challenge, particularly for industrial applications. Many laboratory-scale processes do not translate well to larger production scales due to heat transfer issues, mixing problems, or the accumulation of byproducts. Addressing these scale-up challenges is essential for bridging the gap between academic research and industrial implementation.
Lastly, the limited substrate scope of many alkyl transformations restricts their broader applicability. Many reactions work well with simple, unfunctionalized alkyl groups but fail when applied to more complex, functionalized substrates. Expanding the tolerance of alkyl chemistry to a wider range of functional groups and molecular architectures is crucial for its application in the synthesis of complex natural products and pharmaceuticals.
Current Alkyl Synthesis Methodologies
01 Synthesis of alkyl compounds
Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl compounds efficiently.- Synthesis of alkyl compounds: Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl compounds efficiently.
- Applications of alkyl compounds in industry: Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of plastics, lubricants, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules and pharmaceuticals.
- Alkyl compounds in polymer chemistry: Alkyl compounds play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, serving as monomers or modifiers in the production of various polymeric materials. They can influence the properties of the resulting polymers, such as flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance.
- Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds: The use and handling of alkyl compounds often require careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. This includes proper storage, disposal methods, and measures to prevent environmental contamination or workplace hazards associated with these chemicals.
- Alkyl compounds in organic synthesis: Alkyl compounds serve as important building blocks in organic synthesis. They are used in various reactions such as alkylation, elimination, and substitution to create more complex organic molecules. The reactivity and selectivity of these compounds are crucial in designing synthetic routes.
02 Applications of alkyl compounds in industrial processes
Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of polymers, lubricants, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds and play a role in petroleum refining.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl compounds in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations
Alkyl compounds are utilized in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations due to their properties such as emolliency, solubility enhancement, and preservative effects. They are incorporated into various products including creams, lotions, and drug delivery systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds
The environmental impact and safety aspects of alkyl compounds are addressed, including their biodegradability, toxicity, and potential for bioaccumulation. Research focuses on developing more environmentally friendly alkyl compounds and improving handling and disposal methods.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for alkyl compounds
Various analytical techniques are employed for the identification, quantification, and characterization of alkyl compounds. These methods include chromatography, spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry, which are crucial for quality control and research purposes in industries using alkyl compounds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alkyl Chemistry Industry
The alkyl research field is currently in a dynamic phase, with significant potential for innovation and market growth. The industry is characterized by a mix of established players and emerging companies, indicating a maturing but still evolving sector. Key players like Novartis AG, Bayer Intellectual Property GmbH, and Gilead Sciences, Inc. are driving technological advancements, while smaller firms such as AiCuris GmbH & Co. KG and Kainos Medicine, Inc. are contributing to niche areas. The market size is expanding, fueled by increasing demand for novel chemical compounds in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and industrial applications. Technological maturity varies across sub-sectors, with some areas reaching advanced stages while others remain ripe for breakthrough discoveries.
Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co., Inc. has made significant contributions to alkyl research, particularly in the field of specialty chemicals. They have developed innovative processes for the production of high-purity alkyl compounds used in electronic materials and semiconductor manufacturing[13]. Their research also extends to the development of alkyl-based epoxy resins with improved thermal and mechanical properties for advanced composite materials[14]. Additionally, Mitsubishi Gas Chemical has invested in the development of bio-based alkyl compounds, exploring renewable feedstocks for their chemical processes[15].
Strengths: Strong presence in high-tech industries, focus on high-purity materials, and investment in bio-based technologies. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up specialty chemical production and competition in niche markets.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has developed innovative alkyl research techniques focusing on sustainable chemistry. Their approach includes the development of novel catalysts for alkylation processes, which significantly reduce energy consumption and waste production[1]. They have also pioneered the use of bio-based feedstocks for alkyl compound synthesis, aligning with green chemistry principles[2]. Additionally, Dow has implemented advanced computational modeling to predict and optimize alkylation reactions, leading to more efficient and selective processes[3].
Strengths: Strong focus on sustainability, advanced catalysis technology, and computational modeling capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential higher initial costs for implementing new technologies and possible limitations in scaling up bio-based processes.
Innovative Alkyl Research Breakthroughs
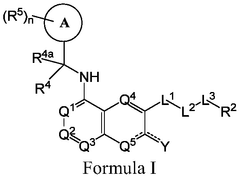
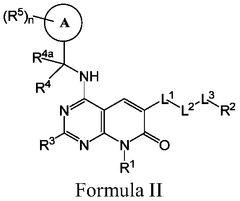
Heterocyclic compounds as SOS1 inhibitors
PatentWO2022156792A1
Innovation
- The invention introduces a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and a novel compound, expanding the potential therapeutic applications.
- The invention provides a comprehensive definition of "alkyl" groups, including straight, branched, and cyclic hydrocarbons, which can be fully saturated or unsaturated.
- The invention allows for halogen substitution on alkyl groups, potentially modifying the compound's physicochemical properties.
Novel naphthyl and isoquinoline sulfonamide derivatives
PatentWO2024017858A1
Innovation
- Development of novel naphthyl and isoquinoline sulfonamide derivatives that modulate GPR17 activity, facilitating the differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells into mature myelinating oligodendrocytes, thereby enhancing myelination and remyelination processes.
Environmental Impact of Alkyl Compounds
Alkyl compounds, ubiquitous in both natural and synthetic environments, have a significant impact on ecosystems and human health. Their environmental footprint spans air, water, and soil, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of their behavior and consequences.
In the atmosphere, volatile alkyl compounds contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and ozone depletion. Short-chain alkanes, such as methane and ethane, are potent greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change. Longer-chain alkyl compounds can form aerosols, affecting air quality and visibility.
Aquatic ecosystems face challenges from alkyl pollutants through various pathways. Oil spills release large quantities of alkanes into marine environments, causing immediate and long-term damage to flora and fauna. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) containing alkyl groups bioaccumulate in aquatic food chains, leading to biomagnification in higher trophic levels.
Soil contamination by alkyl compounds, often resulting from industrial activities or improper waste disposal, can persist for decades. These contaminants alter soil microbial communities, affecting nutrient cycling and plant growth. Leaching of alkyl compounds from soil can contaminate groundwater, posing risks to drinking water sources.
The biodegradability of alkyl compounds varies widely, influencing their environmental persistence. Short-chain alkanes are generally more biodegradable, while branched and longer-chain alkyl compounds tend to be more recalcitrant. This variability necessitates tailored remediation strategies for different alkyl pollutants.
Human exposure to alkyl compounds occurs through multiple routes, including inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact. Some alkyl compounds are known carcinogens or endocrine disruptors, raising concerns about long-term health effects. Occupational exposure in industries utilizing alkyl compounds requires stringent safety measures and monitoring.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of alkyl compounds include developing green chemistry alternatives, improving industrial processes to reduce emissions, and enhancing remediation technologies. Bioremediation techniques, utilizing microorganisms capable of degrading alkyl compounds, show promise for cleaning contaminated sites.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address the environmental challenges posed by alkyl compounds. Stricter emission controls, improved waste management practices, and the promotion of circular economy principles aim to reduce the release of these compounds into the environment.
As research in alkyl chemistry advances, there is a growing focus on designing environmentally benign alkyl compounds and developing more sustainable production methods. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives and implementing life cycle assessments to minimize environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle.
In the atmosphere, volatile alkyl compounds contribute to the formation of photochemical smog and ozone depletion. Short-chain alkanes, such as methane and ethane, are potent greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change. Longer-chain alkyl compounds can form aerosols, affecting air quality and visibility.
Aquatic ecosystems face challenges from alkyl pollutants through various pathways. Oil spills release large quantities of alkanes into marine environments, causing immediate and long-term damage to flora and fauna. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) containing alkyl groups bioaccumulate in aquatic food chains, leading to biomagnification in higher trophic levels.
Soil contamination by alkyl compounds, often resulting from industrial activities or improper waste disposal, can persist for decades. These contaminants alter soil microbial communities, affecting nutrient cycling and plant growth. Leaching of alkyl compounds from soil can contaminate groundwater, posing risks to drinking water sources.
The biodegradability of alkyl compounds varies widely, influencing their environmental persistence. Short-chain alkanes are generally more biodegradable, while branched and longer-chain alkyl compounds tend to be more recalcitrant. This variability necessitates tailored remediation strategies for different alkyl pollutants.
Human exposure to alkyl compounds occurs through multiple routes, including inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact. Some alkyl compounds are known carcinogens or endocrine disruptors, raising concerns about long-term health effects. Occupational exposure in industries utilizing alkyl compounds requires stringent safety measures and monitoring.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of alkyl compounds include developing green chemistry alternatives, improving industrial processes to reduce emissions, and enhancing remediation technologies. Bioremediation techniques, utilizing microorganisms capable of degrading alkyl compounds, show promise for cleaning contaminated sites.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address the environmental challenges posed by alkyl compounds. Stricter emission controls, improved waste management practices, and the promotion of circular economy principles aim to reduce the release of these compounds into the environment.
As research in alkyl chemistry advances, there is a growing focus on designing environmentally benign alkyl compounds and developing more sustainable production methods. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives and implementing life cycle assessments to minimize environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle.
Regulatory Framework for Alkyl Research
The regulatory framework for alkyl research is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in shaping the development and application of innovative chemistry. As alkyl compounds are widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science, regulatory bodies worldwide have established comprehensive guidelines to ensure safety, environmental protection, and ethical practices.
At the forefront of alkyl research regulation is the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework in the European Union. REACH requires companies to register chemical substances, including alkyl compounds, and provide detailed information on their properties, hazards, and potential risks. This approach has set a global standard for chemical regulation, influencing similar initiatives in other regions.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees alkyl research through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA mandates that new chemical substances, including novel alkyl compounds, undergo rigorous safety assessments before entering the market. Recent amendments to the TSCA have strengthened the EPA's authority to evaluate existing chemicals and implement risk management measures.
International collaboration has led to the development of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. This system has been widely adopted, facilitating the exchange of safety information across borders and enhancing the global management of alkyl compounds.
Specific to research activities, many countries have implemented regulations governing laboratory practices and waste management. For instance, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US sets standards for handling hazardous chemicals, including many alkyl compounds, in research settings. These regulations aim to protect researchers and minimize environmental impact.
As the field of alkyl chemistry advances, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging challenges. Nanotechnology applications involving alkyl compounds, for example, have prompted the development of new guidelines to assess potential risks associated with nanomaterials. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable chemistry has led to regulations promoting green chemistry principles in alkyl research, encouraging the development of environmentally friendly processes and products.
The regulatory landscape also extends to intellectual property protection, with patent laws playing a significant role in fostering innovation while ensuring fair competition. Many countries have established specialized patent examination procedures for chemical inventions, including those related to alkyl research, to balance innovation incentives with public interest considerations.
At the forefront of alkyl research regulation is the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) framework in the European Union. REACH requires companies to register chemical substances, including alkyl compounds, and provide detailed information on their properties, hazards, and potential risks. This approach has set a global standard for chemical regulation, influencing similar initiatives in other regions.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees alkyl research through the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA mandates that new chemical substances, including novel alkyl compounds, undergo rigorous safety assessments before entering the market. Recent amendments to the TSCA have strengthened the EPA's authority to evaluate existing chemicals and implement risk management measures.
International collaboration has led to the development of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards. This system has been widely adopted, facilitating the exchange of safety information across borders and enhancing the global management of alkyl compounds.
Specific to research activities, many countries have implemented regulations governing laboratory practices and waste management. For instance, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US sets standards for handling hazardous chemicals, including many alkyl compounds, in research settings. These regulations aim to protect researchers and minimize environmental impact.
As the field of alkyl chemistry advances, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging challenges. Nanotechnology applications involving alkyl compounds, for example, have prompted the development of new guidelines to assess potential risks associated with nanomaterials. Additionally, the increasing focus on sustainable chemistry has led to regulations promoting green chemistry principles in alkyl research, encouraging the development of environmentally friendly processes and products.
The regulatory landscape also extends to intellectual property protection, with patent laws playing a significant role in fostering innovation while ensuring fair competition. Many countries have established specialized patent examination procedures for chemical inventions, including those related to alkyl research, to balance innovation incentives with public interest considerations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!