Best Practices in Isocyanate Supply Chain Management
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Industry Overview and Objectives
Isocyanates are crucial chemical compounds widely used in the production of polyurethanes, a versatile class of materials with applications across various industries. The isocyanate industry has experienced significant growth over the past decades, driven by increasing demand for polyurethane products in construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics sectors. This growth has led to a complex and global supply chain, necessitating effective management practices to ensure efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
The primary objective of isocyanate supply chain management is to optimize the flow of raw materials, intermediates, and finished products while minimizing risks associated with handling these reactive chemicals. This involves coordinating activities from production and storage to transportation and end-use, all while adhering to stringent safety and environmental regulations. Effective supply chain management in the isocyanate industry aims to balance cost-effectiveness with reliability, ensuring a steady supply to meet market demands without compromising on quality or safety standards.
Key challenges in isocyanate supply chain management include the volatile nature of raw materials, stringent storage and transportation requirements, and the need for specialized handling equipment. Additionally, the industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices and reduce its environmental footprint. These challenges underscore the importance of implementing best practices throughout the supply chain to mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency.
The isocyanate market is characterized by a few large-scale producers dominating global production, with regional players catering to specific market segments. Major production hubs are located in North America, Europe, and Asia, with China emerging as a significant player in recent years. The industry's growth trajectory is closely tied to economic cycles and construction activity, making it susceptible to market fluctuations.
Looking ahead, the isocyanate industry is poised for continued growth, driven by expanding applications in emerging markets and innovations in product formulations. However, this growth must be balanced with increasing regulatory scrutiny and environmental concerns. The industry is actively exploring alternatives to traditional isocyanates and investing in technologies to improve production efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
In this context, best practices in isocyanate supply chain management are critical for maintaining competitiveness, ensuring regulatory compliance, and meeting sustainability goals. These practices encompass various aspects, including inventory management, transportation logistics, safety protocols, and supplier relationships. By adopting and refining these best practices, companies can navigate the complexities of the isocyanate supply chain more effectively, positioning themselves for long-term success in a dynamic and challenging market environment.
The primary objective of isocyanate supply chain management is to optimize the flow of raw materials, intermediates, and finished products while minimizing risks associated with handling these reactive chemicals. This involves coordinating activities from production and storage to transportation and end-use, all while adhering to stringent safety and environmental regulations. Effective supply chain management in the isocyanate industry aims to balance cost-effectiveness with reliability, ensuring a steady supply to meet market demands without compromising on quality or safety standards.
Key challenges in isocyanate supply chain management include the volatile nature of raw materials, stringent storage and transportation requirements, and the need for specialized handling equipment. Additionally, the industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices and reduce its environmental footprint. These challenges underscore the importance of implementing best practices throughout the supply chain to mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency.
The isocyanate market is characterized by a few large-scale producers dominating global production, with regional players catering to specific market segments. Major production hubs are located in North America, Europe, and Asia, with China emerging as a significant player in recent years. The industry's growth trajectory is closely tied to economic cycles and construction activity, making it susceptible to market fluctuations.
Looking ahead, the isocyanate industry is poised for continued growth, driven by expanding applications in emerging markets and innovations in product formulations. However, this growth must be balanced with increasing regulatory scrutiny and environmental concerns. The industry is actively exploring alternatives to traditional isocyanates and investing in technologies to improve production efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
In this context, best practices in isocyanate supply chain management are critical for maintaining competitiveness, ensuring regulatory compliance, and meeting sustainability goals. These practices encompass various aspects, including inventory management, transportation logistics, safety protocols, and supplier relationships. By adopting and refining these best practices, companies can navigate the complexities of the isocyanate supply chain more effectively, positioning themselves for long-term success in a dynamic and challenging market environment.
Market Demand Analysis for Isocyanates
The global isocyanate market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from various end-use industries such as construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics. Isocyanates, particularly methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI), are crucial raw materials for polyurethane production, which finds extensive applications in insulation, coatings, adhesives, and flexible foams.
The construction sector remains a primary driver of isocyanate demand, with polyurethane-based insulation materials gaining popularity due to their superior thermal efficiency and energy-saving properties. As governments worldwide implement stricter building energy codes and regulations, the demand for high-performance insulation materials is expected to rise, further boosting isocyanate consumption.
In the automotive industry, isocyanates play a vital role in manufacturing lightweight components, seat cushions, and interior trim. The growing trend towards electric vehicles and the need for improved fuel efficiency have led to increased adoption of polyurethane-based materials, contributing to the expanding isocyanate market.
The furniture and bedding sector also significantly contributes to isocyanate demand, with flexible polyurethane foams being widely used in mattresses, sofas, and other upholstered products. The rising global population, urbanization, and improving living standards in developing countries are driving growth in this segment.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of isocyanates, with China leading the market. The region's rapid industrialization, booming construction activities, and growing automotive production have fueled the demand for isocyanates. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets showing steady growth driven by renovation activities and technological advancements in various industries.
The global isocyanate market is influenced by several factors, including raw material prices, environmental regulations, and technological innovations. Fluctuations in crude oil prices directly impact isocyanate production costs, affecting market dynamics. Additionally, increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are driving the development of eco-friendly alternatives and low-emission isocyanate formulations.
As supply chain management becomes increasingly critical in the isocyanate industry, market players are focusing on optimizing their distribution networks, implementing just-in-time inventory systems, and exploring vertical integration strategies to ensure a stable supply of raw materials and reduce operational costs.
The construction sector remains a primary driver of isocyanate demand, with polyurethane-based insulation materials gaining popularity due to their superior thermal efficiency and energy-saving properties. As governments worldwide implement stricter building energy codes and regulations, the demand for high-performance insulation materials is expected to rise, further boosting isocyanate consumption.
In the automotive industry, isocyanates play a vital role in manufacturing lightweight components, seat cushions, and interior trim. The growing trend towards electric vehicles and the need for improved fuel efficiency have led to increased adoption of polyurethane-based materials, contributing to the expanding isocyanate market.
The furniture and bedding sector also significantly contributes to isocyanate demand, with flexible polyurethane foams being widely used in mattresses, sofas, and other upholstered products. The rising global population, urbanization, and improving living standards in developing countries are driving growth in this segment.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the largest consumer of isocyanates, with China leading the market. The region's rapid industrialization, booming construction activities, and growing automotive production have fueled the demand for isocyanates. North America and Europe follow, with mature markets showing steady growth driven by renovation activities and technological advancements in various industries.
The global isocyanate market is influenced by several factors, including raw material prices, environmental regulations, and technological innovations. Fluctuations in crude oil prices directly impact isocyanate production costs, affecting market dynamics. Additionally, increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are driving the development of eco-friendly alternatives and low-emission isocyanate formulations.
As supply chain management becomes increasingly critical in the isocyanate industry, market players are focusing on optimizing their distribution networks, implementing just-in-time inventory systems, and exploring vertical integration strategies to ensure a stable supply of raw materials and reduce operational costs.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Supply Chain
The isocyanate supply chain faces several significant challenges that impact its efficiency, sustainability, and overall performance. One of the primary concerns is the volatility of raw material prices, particularly for key inputs like propylene and benzene. These fluctuations can lead to unpredictable production costs and affect the entire value chain, from manufacturers to end-users.
Safety and environmental regulations pose another major challenge. Isocyanates are known for their potential health hazards and environmental impact, leading to stringent regulations across different regions. Compliance with these varying standards increases operational complexity and costs, especially for companies operating globally.
Transportation and storage of isocyanates present unique difficulties due to their reactive nature and sensitivity to moisture. Specialized equipment and handling procedures are required, which can lead to increased logistics costs and potential supply chain disruptions if not managed properly.
The isocyanate industry also faces challenges related to supply chain transparency and traceability. With growing consumer and regulatory demands for sustainable and ethically sourced products, companies are under pressure to provide more detailed information about their supply chains, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery.
Capacity management is another critical issue. The cyclical nature of demand in key end-use industries, such as construction and automotive, can lead to periods of overcapacity or shortages. This volatility makes it difficult for producers to optimize their production planning and inventory management.
Technological advancements, while offering potential solutions, also present challenges. The integration of digital technologies for supply chain optimization requires significant investment and expertise. Many companies struggle to implement these technologies effectively, potentially leading to a competitive disadvantage.
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes add another layer of complexity to the isocyanate supply chain. Tariffs, export restrictions, and changing trade agreements can disrupt established supply routes and sourcing strategies, forcing companies to adapt quickly to maintain their competitive edge.
Lastly, the industry faces growing pressure to improve its sustainability profile. This includes reducing carbon emissions, developing bio-based alternatives, and implementing circular economy principles. While necessary for long-term viability, these initiatives often require substantial investments and can be challenging to implement across complex global supply chains.
Safety and environmental regulations pose another major challenge. Isocyanates are known for their potential health hazards and environmental impact, leading to stringent regulations across different regions. Compliance with these varying standards increases operational complexity and costs, especially for companies operating globally.
Transportation and storage of isocyanates present unique difficulties due to their reactive nature and sensitivity to moisture. Specialized equipment and handling procedures are required, which can lead to increased logistics costs and potential supply chain disruptions if not managed properly.
The isocyanate industry also faces challenges related to supply chain transparency and traceability. With growing consumer and regulatory demands for sustainable and ethically sourced products, companies are under pressure to provide more detailed information about their supply chains, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery.
Capacity management is another critical issue. The cyclical nature of demand in key end-use industries, such as construction and automotive, can lead to periods of overcapacity or shortages. This volatility makes it difficult for producers to optimize their production planning and inventory management.
Technological advancements, while offering potential solutions, also present challenges. The integration of digital technologies for supply chain optimization requires significant investment and expertise. Many companies struggle to implement these technologies effectively, potentially leading to a competitive disadvantage.
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes add another layer of complexity to the isocyanate supply chain. Tariffs, export restrictions, and changing trade agreements can disrupt established supply routes and sourcing strategies, forcing companies to adapt quickly to maintain their competitive edge.
Lastly, the industry faces growing pressure to improve its sustainability profile. This includes reducing carbon emissions, developing bio-based alternatives, and implementing circular economy principles. While necessary for long-term viability, these initiatives often require substantial investments and can be challenging to implement across complex global supply chains.
Best Practices in Isocyanate Handling and Storage
01 Synthesis and applications of isocyanates
Isocyanates are versatile compounds used in various industrial applications. They are key ingredients in the production of polyurethanes, coatings, adhesives, and elastomers. The synthesis of isocyanates often involves the reaction of amines with phosgene or other carbonyl compounds. Different types of isocyanates, such as aromatic and aliphatic isocyanates, are used depending on the desired properties of the final product.- Synthesis and properties of isocyanates: Isocyanates are a class of highly reactive compounds characterized by the -N=C=O functional group. They are widely used in the production of polyurethanes and other polymeric materials. The synthesis of isocyanates often involves the reaction of amines with phosgene or other carbonyl-containing compounds. Their reactivity makes them valuable in various industrial applications, but also requires careful handling due to potential health hazards.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. They react with polyols to form urethane linkages, which are the basis for a wide range of materials including foams, elastomers, coatings, and adhesives. The versatility of isocyanates allows for the creation of polymers with tailored properties, such as flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance.
- Isocyanate-based coatings and adhesives: Isocyanates are extensively used in the formulation of high-performance coatings and adhesives. These formulations often involve the reaction of isocyanates with other functional groups to create durable, weather-resistant, and chemically resistant finishes. Isocyanate-based coatings and adhesives find applications in automotive, construction, and industrial sectors, offering excellent bonding strength and protection against environmental factors.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Due to their high reactivity and potential health hazards, proper safety measures and handling procedures are crucial when working with isocyanates. This includes the use of personal protective equipment, adequate ventilation, and proper storage conditions. Exposure to isocyanates can cause respiratory irritation and sensitization, making it important to implement engineering controls and follow strict safety protocols in industrial settings where these compounds are used.
- Environmental considerations and alternatives to isocyanates: With increasing environmental awareness, there is growing interest in developing alternatives to traditional isocyanate-based systems. This includes the exploration of bio-based isocyanates, non-isocyanate polyurethanes, and other environmentally friendly alternatives. Research is ongoing to find sustainable solutions that can match the performance of isocyanate-based products while reducing environmental impact and potential health risks associated with isocyanate use.
02 Isocyanate-based polyurethane formulations
Polyurethanes are formed by the reaction of isocyanates with polyols. These formulations can be tailored to produce materials with a wide range of properties, from flexible foams to rigid plastics. The choice of isocyanate and polyol, along with catalysts and additives, determines the characteristics of the final product. Applications include insulation, automotive parts, furniture, and construction materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-free alternatives and environmental considerations
Due to health and environmental concerns associated with some isocyanates, there is growing interest in developing isocyanate-free alternatives. These include non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) and bio-based materials. Research is focused on creating sustainable alternatives that maintain the desirable properties of traditional isocyanate-based products while reducing potential hazards and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Isocyanate handling and safety measures
Proper handling and safety measures are crucial when working with isocyanates due to their potential health hazards. This includes the use of personal protective equipment, proper ventilation systems, and specialized storage and disposal procedures. Training programs and safety protocols are implemented in industries that use isocyanates to minimize risks and ensure worker safety.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isocyanate modifications and derivatives
Isocyanates can be modified or used to create various derivatives with enhanced properties or specific functionalities. This includes blocked isocyanates, which are less reactive at room temperature and activate under certain conditions, as well as isocyanate-terminated prepolymers. These modifications allow for improved processing, storage stability, or tailored reactivity in different applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Production and Distribution
The isocyanate supply chain management landscape is characterized by a mature market with established players and growing demand across various industries. The market is dominated by global chemical giants such as BASF, Wanhua Chemical, Covestro, and Dow, who have extensive experience in production and distribution. These companies are investing in research and development to improve efficiency and sustainability in isocyanate production. The technology is well-established, but there is ongoing innovation in areas like green chemistry and bio-based alternatives. Emerging players like Novomer are exploring novel catalytic processes to produce more environmentally friendly isocyanates. The market size is substantial, driven by demand from automotive, construction, and furniture industries, with Asia-Pacific region showing the fastest growth.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed an innovative approach to isocyanate supply chain management, focusing on sustainability and efficiency. Their strategy includes the implementation of a closed-loop system for isocyanate production and distribution[1]. This system incorporates advanced tracking technologies and real-time monitoring to optimize inventory levels and reduce waste. BASF has also invested in developing bio-based isocyanates, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of their supply chain[2]. Additionally, they have implemented a rigorous supplier assessment program to ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards throughout the supply chain[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive sustainability approach, advanced tracking technologies, and bio-based product development. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs associated with implementing new technologies and sourcing bio-based materials.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has implemented a vertically integrated supply chain management system for isocyanates. Their approach focuses on controlling the entire production process from raw materials to end products. Wanhua has invested in state-of-the-art production facilities that utilize advanced process control systems to optimize yield and reduce energy consumption[4]. They have also developed a proprietary logistics network that includes specialized transportation and storage solutions for isocyanates, ensuring product integrity and safety throughout the supply chain[5]. Furthermore, Wanhua has implemented a digital twin technology to simulate and optimize their supply chain operations in real-time[6].
Strengths: Vertical integration provides greater control over quality and costs, advanced production facilities, and innovative logistics solutions. Weaknesses: High capital investment required for vertical integration and potential over-reliance on in-house capabilities.
Innovations in Isocyanate Transportation
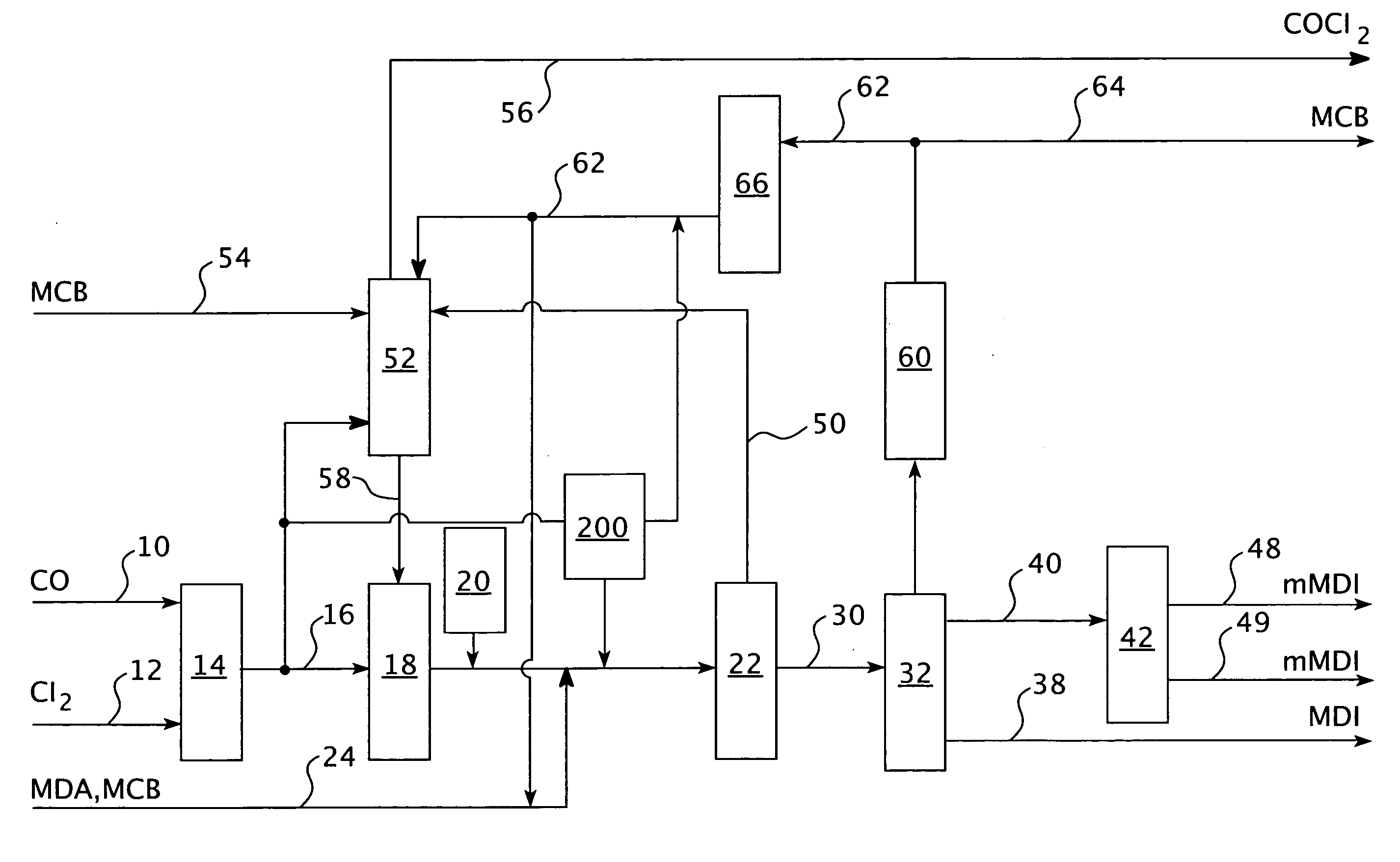
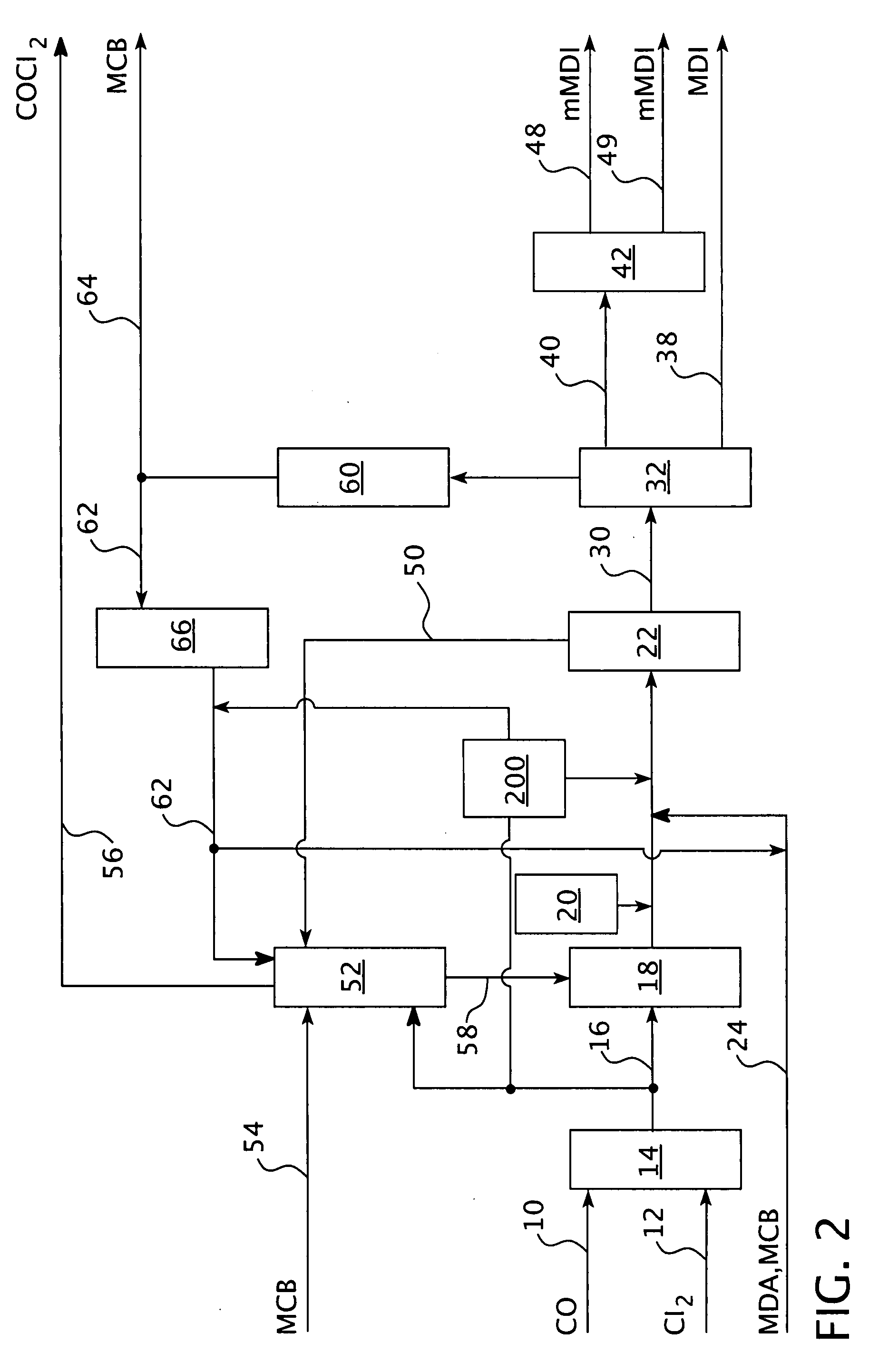
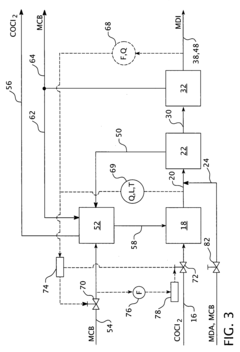
Process for controlling a production process
PatentInactiveEP1932828A2
Innovation
- The process controls the phosgene and solvent feed streams as primary variables, allowing for independent control of subsystems and optimization of the isocyanate production process, enabling the recovery of unused reactants and reducing unwanted substances, thereby stabilizing and automating the process while minimizing production costs.
Process for controlling a production process
PatentInactiveUS20080147208A1
Innovation
- The process controls the phosgene and solvent feed streams as primary variables, allowing for independent control of subsystems and optimization of the isocyanate production process, enabling the recovery of unused reactants and reducing unwanted substances, thereby stabilizing and automating the process.
Regulatory Compliance in Isocyanate Management
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of isocyanate supply chain management, given the hazardous nature of these chemicals. Governments worldwide have implemented strict regulations to ensure the safe handling, storage, and transportation of isocyanates. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established specific standards for isocyanate exposure limits and safety protocols. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
Companies involved in the isocyanate supply chain must adhere to these regulations to maintain compliance and ensure worker safety. This includes implementing robust safety management systems, providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and conducting regular risk assessments. Proper labeling and documentation are essential throughout the supply chain, with Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) required for all isocyanate products.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of isocyanates. Companies must register their isocyanate products with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed information on their properties and potential risks. The Classification, Labelling, and Packaging (CLP) regulation further ensures that hazards are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
Transportation of isocyanates is subject to strict regulations under the United Nations' Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines specify requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation during shipping. Companies must ensure that their logistics partners are certified to handle hazardous materials and follow all applicable transportation regulations.
To maintain regulatory compliance, companies often implement comprehensive training programs for employees involved in isocyanate handling. These programs cover safe handling procedures, emergency response protocols, and proper use of PPE. Regular audits and inspections are conducted to verify compliance with regulatory requirements and identify areas for improvement.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in isocyanate management. Companies must implement proper waste disposal procedures and emissions control measures to minimize environmental impact. This may include installing air filtration systems, implementing closed-loop processes, and developing spill response plans.
As regulations continue to evolve, companies must stay informed of changes and adapt their practices accordingly. This often requires dedicated compliance teams and ongoing collaboration with regulatory agencies. By prioritizing regulatory compliance, companies can mitigate risks, protect workers and the environment, and maintain their license to operate in the isocyanate supply chain.
Companies involved in the isocyanate supply chain must adhere to these regulations to maintain compliance and ensure worker safety. This includes implementing robust safety management systems, providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and conducting regular risk assessments. Proper labeling and documentation are essential throughout the supply chain, with Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) required for all isocyanate products.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of isocyanates. Companies must register their isocyanate products with the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and provide detailed information on their properties and potential risks. The Classification, Labelling, and Packaging (CLP) regulation further ensures that hazards are clearly communicated to workers and consumers.
Transportation of isocyanates is subject to strict regulations under the United Nations' Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. These guidelines specify requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation during shipping. Companies must ensure that their logistics partners are certified to handle hazardous materials and follow all applicable transportation regulations.
To maintain regulatory compliance, companies often implement comprehensive training programs for employees involved in isocyanate handling. These programs cover safe handling procedures, emergency response protocols, and proper use of PPE. Regular audits and inspections are conducted to verify compliance with regulatory requirements and identify areas for improvement.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in isocyanate management. Companies must implement proper waste disposal procedures and emissions control measures to minimize environmental impact. This may include installing air filtration systems, implementing closed-loop processes, and developing spill response plans.
As regulations continue to evolve, companies must stay informed of changes and adapt their practices accordingly. This often requires dedicated compliance teams and ongoing collaboration with regulatory agencies. By prioritizing regulatory compliance, companies can mitigate risks, protect workers and the environment, and maintain their license to operate in the isocyanate supply chain.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Isocyanate Supply Chain
The environmental impact assessment of the isocyanate supply chain is a critical component in evaluating the sustainability and safety of isocyanate production and distribution. Isocyanates, widely used in the manufacture of polyurethanes, pose significant environmental risks if not properly managed throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental concerns in the isocyanate supply chain is air pollution. During production and transportation, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous air pollutants can be released. These emissions contribute to smog formation and can have adverse effects on local air quality. To mitigate this impact, best practices include implementing advanced emission control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and scrubbers, at production facilities. Additionally, the use of sealed transport containers and vapor recovery systems during loading and unloading operations can significantly reduce fugitive emissions.
Water pollution is another significant environmental risk associated with isocyanate production and handling. Accidental spills or improper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste can contaminate water sources, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and human health. To address this issue, comprehensive spill prevention and response plans should be implemented throughout the supply chain. This includes the use of secondary containment systems, regular equipment inspections, and employee training on proper handling procedures.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production also contributes to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process requires substantial amounts of energy, often derived from fossil fuels, leading to greenhouse gas emissions. To reduce this impact, companies are increasingly adopting energy-efficient technologies and exploring renewable energy sources for their production facilities. Some manufacturers are also investing in carbon capture and storage technologies to further mitigate their carbon footprint.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of environmental impact assessment in the isocyanate supply chain. Proper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste, including packaging materials and off-spec products, is essential to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Best practices include implementing closed-loop recycling systems, where possible, and ensuring that any hazardous waste is treated and disposed of in compliance with local and international regulations.
The transportation of isocyanates also presents environmental risks, particularly in the event of accidents or spills during transit. To minimize these risks, companies are adopting safer transportation methods, such as using dedicated rail cars or specially designed trucks with enhanced safety features. Route optimization and real-time tracking systems are also being employed to reduce the overall environmental impact of transportation and improve emergency response capabilities.
One of the primary environmental concerns in the isocyanate supply chain is air pollution. During production and transportation, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous air pollutants can be released. These emissions contribute to smog formation and can have adverse effects on local air quality. To mitigate this impact, best practices include implementing advanced emission control technologies, such as thermal oxidizers and scrubbers, at production facilities. Additionally, the use of sealed transport containers and vapor recovery systems during loading and unloading operations can significantly reduce fugitive emissions.
Water pollution is another significant environmental risk associated with isocyanate production and handling. Accidental spills or improper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste can contaminate water sources, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and human health. To address this issue, comprehensive spill prevention and response plans should be implemented throughout the supply chain. This includes the use of secondary containment systems, regular equipment inspections, and employee training on proper handling procedures.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production also contributes to its environmental footprint. The manufacturing process requires substantial amounts of energy, often derived from fossil fuels, leading to greenhouse gas emissions. To reduce this impact, companies are increasingly adopting energy-efficient technologies and exploring renewable energy sources for their production facilities. Some manufacturers are also investing in carbon capture and storage technologies to further mitigate their carbon footprint.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of environmental impact assessment in the isocyanate supply chain. Proper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste, including packaging materials and off-spec products, is essential to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Best practices include implementing closed-loop recycling systems, where possible, and ensuring that any hazardous waste is treated and disposed of in compliance with local and international regulations.
The transportation of isocyanates also presents environmental risks, particularly in the event of accidents or spills during transit. To minimize these risks, companies are adopting safer transportation methods, such as using dedicated rail cars or specially designed trucks with enhanced safety features. Route optimization and real-time tracking systems are also being employed to reduce the overall environmental impact of transportation and improve emergency response capabilities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!