Comparative Analysis of Microcrystalline Cellulose Effect on Binder Erosion
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MCC Binder Erosion Background and Objectives
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) has emerged as a crucial excipient in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly in the development of controlled release dosage forms. The study of MCC's effect on binder erosion is of paramount importance in understanding and optimizing drug delivery systems. This analysis aims to comprehensively examine the impact of MCC on the erosion behavior of binders used in pharmaceutical tablets and capsules.
The evolution of controlled release technologies has been driven by the need for improved therapeutic outcomes and patient compliance. Over the past few decades, researchers have focused on developing formulations that can modulate drug release rates and maintain consistent plasma concentrations over extended periods. In this context, the role of excipients like MCC has become increasingly significant.
MCC, derived from purified wood pulp, possesses unique physicochemical properties that make it an ideal candidate for pharmaceutical applications. Its high compressibility, low moisture content, and excellent flow properties have led to its widespread use as a diluent and binder in tablet formulations. However, its impact on the erosion characteristics of other binders in the formulation matrix has not been fully elucidated.
The primary objective of this comparative analysis is to investigate how MCC influences the erosion kinetics of commonly used pharmaceutical binders. By examining various MCC grades and concentrations, we aim to establish correlations between MCC properties and binder erosion rates. This understanding is crucial for predicting and controlling drug release profiles in solid dosage forms.
Furthermore, this study seeks to explore the mechanisms underlying MCC-binder interactions and their subsequent effects on tablet disintegration and drug dissolution. By elucidating these mechanisms, we can potentially develop more robust and predictable formulation strategies for controlled release systems.
Another key goal is to assess the impact of MCC on different types of binders, including both hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymers. This comparative approach will provide insights into the versatility of MCC as an excipient and its potential for tailoring drug release profiles across a wide range of formulations.
Ultimately, this research aims to contribute to the broader field of pharmaceutical technology by enhancing our understanding of excipient interactions and their implications for drug delivery. The findings from this study may pave the way for innovative formulation approaches and more efficient development of controlled release dosage forms.
The evolution of controlled release technologies has been driven by the need for improved therapeutic outcomes and patient compliance. Over the past few decades, researchers have focused on developing formulations that can modulate drug release rates and maintain consistent plasma concentrations over extended periods. In this context, the role of excipients like MCC has become increasingly significant.
MCC, derived from purified wood pulp, possesses unique physicochemical properties that make it an ideal candidate for pharmaceutical applications. Its high compressibility, low moisture content, and excellent flow properties have led to its widespread use as a diluent and binder in tablet formulations. However, its impact on the erosion characteristics of other binders in the formulation matrix has not been fully elucidated.
The primary objective of this comparative analysis is to investigate how MCC influences the erosion kinetics of commonly used pharmaceutical binders. By examining various MCC grades and concentrations, we aim to establish correlations between MCC properties and binder erosion rates. This understanding is crucial for predicting and controlling drug release profiles in solid dosage forms.
Furthermore, this study seeks to explore the mechanisms underlying MCC-binder interactions and their subsequent effects on tablet disintegration and drug dissolution. By elucidating these mechanisms, we can potentially develop more robust and predictable formulation strategies for controlled release systems.
Another key goal is to assess the impact of MCC on different types of binders, including both hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymers. This comparative approach will provide insights into the versatility of MCC as an excipient and its potential for tailoring drug release profiles across a wide range of formulations.
Ultimately, this research aims to contribute to the broader field of pharmaceutical technology by enhancing our understanding of excipient interactions and their implications for drug delivery. The findings from this study may pave the way for innovative formulation approaches and more efficient development of controlled release dosage forms.
Market Demand for Enhanced Binder Performance
The market demand for enhanced binder performance in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries has been steadily increasing due to the growing emphasis on product quality, stability, and efficacy. Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) has emerged as a key ingredient in addressing these demands, particularly in its role in mitigating binder erosion.
The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has shown a significant interest in improved binder technologies. With the global pharmaceutical market projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, there is a pressing need for excipients that can enhance drug formulation stability and performance. MCC's potential to reduce binder erosion aligns well with this market trend, as it directly impacts the shelf life and effectiveness of various drug formulations.
In the nutraceutical industry, where consumer demand for high-quality supplements continues to rise, the need for superior binder performance is equally critical. The global nutraceutical market's expansion has created opportunities for innovative excipient solutions that can improve product integrity and bioavailability. MCC's role in binder erosion reduction is particularly valuable in this context, as it helps maintain the stability of active ingredients in various supplement formulations.
The food industry also presents a growing market for enhanced binder performance. With increasing consumer awareness of food quality and safety, manufacturers are seeking ways to improve the texture, stability, and shelf life of their products. MCC's potential in reducing binder erosion can contribute to these goals, particularly in processed foods and baked goods.
Market research indicates that companies are willing to invest in advanced excipient technologies that can provide a competitive edge. The demand for MCC and similar excipients that offer improved binder performance is expected to grow as manufacturers seek to differentiate their products and meet stringent quality standards.
Furthermore, the trend towards personalized medicine and precision nutrition is driving the need for more sophisticated formulation technologies. This creates additional opportunities for MCC and other excipients that can enhance binder performance, as they enable the development of more complex and targeted product formulations.
In conclusion, the market demand for enhanced binder performance, particularly through the use of MCC to reduce binder erosion, is robust and multifaceted. It spans across pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food industries, driven by factors such as product quality improvement, regulatory compliance, and consumer expectations. As these industries continue to evolve, the importance of advanced excipient technologies like MCC in addressing binder erosion is likely to increase, presenting significant opportunities for innovation and market growth.
The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has shown a significant interest in improved binder technologies. With the global pharmaceutical market projected to reach substantial growth in the coming years, there is a pressing need for excipients that can enhance drug formulation stability and performance. MCC's potential to reduce binder erosion aligns well with this market trend, as it directly impacts the shelf life and effectiveness of various drug formulations.
In the nutraceutical industry, where consumer demand for high-quality supplements continues to rise, the need for superior binder performance is equally critical. The global nutraceutical market's expansion has created opportunities for innovative excipient solutions that can improve product integrity and bioavailability. MCC's role in binder erosion reduction is particularly valuable in this context, as it helps maintain the stability of active ingredients in various supplement formulations.
The food industry also presents a growing market for enhanced binder performance. With increasing consumer awareness of food quality and safety, manufacturers are seeking ways to improve the texture, stability, and shelf life of their products. MCC's potential in reducing binder erosion can contribute to these goals, particularly in processed foods and baked goods.
Market research indicates that companies are willing to invest in advanced excipient technologies that can provide a competitive edge. The demand for MCC and similar excipients that offer improved binder performance is expected to grow as manufacturers seek to differentiate their products and meet stringent quality standards.
Furthermore, the trend towards personalized medicine and precision nutrition is driving the need for more sophisticated formulation technologies. This creates additional opportunities for MCC and other excipients that can enhance binder performance, as they enable the development of more complex and targeted product formulations.
In conclusion, the market demand for enhanced binder performance, particularly through the use of MCC to reduce binder erosion, is robust and multifaceted. It spans across pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food industries, driven by factors such as product quality improvement, regulatory compliance, and consumer expectations. As these industries continue to evolve, the importance of advanced excipient technologies like MCC in addressing binder erosion is likely to increase, presenting significant opportunities for innovation and market growth.
Current Challenges in MCC-Based Binder Systems
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) has emerged as a crucial component in binder systems, particularly in pharmaceutical and food industries. However, its integration into these systems presents several challenges that researchers and manufacturers are actively addressing.
One of the primary challenges in MCC-based binder systems is achieving consistent particle size distribution. The variability in MCC particle size can significantly impact the erosion behavior of binders, leading to inconsistent product performance. This issue is particularly pronounced in pharmaceutical applications, where precise drug release profiles are essential.
Another significant challenge is the moisture sensitivity of MCC. When exposed to varying humidity levels, MCC can absorb or release moisture, affecting the overall stability and performance of the binder system. This hygroscopic nature can lead to changes in the mechanical properties of the final product, potentially compromising its integrity and functionality.
The interaction between MCC and other binder components also poses a challenge. The complex interplay between MCC and polymeric binders or active ingredients can result in unexpected changes in the erosion behavior of the system. Understanding and controlling these interactions is crucial for developing robust and reliable binder formulations.
Furthermore, the processing conditions for MCC-based binder systems present their own set of challenges. The high shear forces often required during mixing and granulation can lead to MCC particle breakdown, altering the intended properties of the binder system. Balancing the need for thorough mixing with the preservation of MCC's structural integrity remains a key concern for manufacturers.
The scalability of MCC-based binder systems from laboratory to industrial production is another significant challenge. Maintaining consistent quality and performance across different batch sizes and production scales requires careful optimization of process parameters and formulation adjustments.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of MCC production and use in binder systems are becoming increasingly important considerations. Developing eco-friendly sourcing and processing methods for MCC, while maintaining its desirable properties as a binder component, is an ongoing challenge for the industry.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise in materials science, pharmaceutical technology, and process engineering. As research in this field progresses, innovative solutions are emerging to overcome these obstacles and enhance the effectiveness of MCC-based binder systems.
One of the primary challenges in MCC-based binder systems is achieving consistent particle size distribution. The variability in MCC particle size can significantly impact the erosion behavior of binders, leading to inconsistent product performance. This issue is particularly pronounced in pharmaceutical applications, where precise drug release profiles are essential.
Another significant challenge is the moisture sensitivity of MCC. When exposed to varying humidity levels, MCC can absorb or release moisture, affecting the overall stability and performance of the binder system. This hygroscopic nature can lead to changes in the mechanical properties of the final product, potentially compromising its integrity and functionality.
The interaction between MCC and other binder components also poses a challenge. The complex interplay between MCC and polymeric binders or active ingredients can result in unexpected changes in the erosion behavior of the system. Understanding and controlling these interactions is crucial for developing robust and reliable binder formulations.
Furthermore, the processing conditions for MCC-based binder systems present their own set of challenges. The high shear forces often required during mixing and granulation can lead to MCC particle breakdown, altering the intended properties of the binder system. Balancing the need for thorough mixing with the preservation of MCC's structural integrity remains a key concern for manufacturers.
The scalability of MCC-based binder systems from laboratory to industrial production is another significant challenge. Maintaining consistent quality and performance across different batch sizes and production scales requires careful optimization of process parameters and formulation adjustments.
Lastly, the environmental impact and sustainability of MCC production and use in binder systems are becoming increasingly important considerations. Developing eco-friendly sourcing and processing methods for MCC, while maintaining its desirable properties as a binder component, is an ongoing challenge for the industry.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise in materials science, pharmaceutical technology, and process engineering. As research in this field progresses, innovative solutions are emerging to overcome these obstacles and enhance the effectiveness of MCC-based binder systems.
Existing MCC-Based Erosion Mitigation Strategies
01 Microcrystalline cellulose as a binder in pharmaceutical formulations
Microcrystalline cellulose is widely used as a binder in pharmaceutical formulations due to its excellent binding properties and low erosion rate. It provides stability to the formulation and helps control drug release. The use of microcrystalline cellulose as a binder can improve tablet hardness and reduce friability.- Microcrystalline cellulose as a binder in pharmaceutical formulations: Microcrystalline cellulose is widely used as a binder in pharmaceutical formulations due to its excellent binding properties and low erosion rate. It provides stability to the formulation and helps in controlling drug release. The erosion-resistant nature of microcrystalline cellulose makes it suitable for sustained-release formulations.
- Modification of microcrystalline cellulose to improve erosion resistance: Various techniques are employed to modify microcrystalline cellulose to enhance its erosion resistance. These include chemical modifications, surface treatments, and blending with other polymers. Such modifications can improve the binding capacity and reduce the erosion rate of microcrystalline cellulose in different formulations.
- Combination of microcrystalline cellulose with other excipients: Microcrystalline cellulose is often combined with other excipients to optimize its binding properties and erosion characteristics. Combinations with polymers, gums, or other cellulose derivatives can create synergistic effects, leading to improved formulation stability and controlled erosion profiles.
- Particle size and morphology effects on erosion: The particle size and morphology of microcrystalline cellulose significantly influence its erosion behavior. Smaller particle sizes generally lead to faster erosion, while larger particles or specific morphologies can provide enhanced erosion resistance. Controlling these parameters allows for tailored erosion profiles in various applications.
- Application of microcrystalline cellulose in controlled release systems: Microcrystalline cellulose is extensively used in controlled release systems due to its erosion-resistant properties. It can be formulated into matrices, pellets, or tablets to achieve desired drug release profiles. The erosion characteristics of microcrystalline cellulose can be fine-tuned to optimize drug delivery in various therapeutic applications.
02 Erosion control of microcrystalline cellulose binders
Various techniques are employed to control the erosion of microcrystalline cellulose binders in pharmaceutical formulations. These include modifying the particle size, incorporating hydrophobic agents, and using cross-linking agents. Controlling erosion helps maintain the integrity of the dosage form and ensures consistent drug release over time.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination of microcrystalline cellulose with other excipients
Microcrystalline cellulose is often combined with other excipients to enhance its binding properties and control erosion. Common combinations include mixing with other polymers, adding disintegrants, or incorporating lubricants. These combinations can improve tablet properties and modify drug release profiles.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modified microcrystalline cellulose for improved binding and erosion control
Research has focused on developing modified forms of microcrystalline cellulose to enhance its binding properties and reduce erosion. These modifications include chemical treatments, surface modifications, and the creation of co-processed excipients. Modified microcrystalline cellulose can offer improved performance in various pharmaceutical applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Evaluation methods for microcrystalline cellulose binder erosion
Various analytical techniques and methods are used to evaluate the erosion of microcrystalline cellulose binders in pharmaceutical formulations. These include dissolution testing, imaging techniques, and physical characterization methods. Understanding and quantifying binder erosion is crucial for optimizing formulation performance and ensuring product quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in MCC and Binder Industries
The competitive landscape for "Comparative Analysis of Microcrystalline Cellulose Effect on Binder Erosion" is in a growth phase, with increasing market size due to rising demand in pharmaceutical and food industries. The technology is relatively mature, with established players like FMC Corp., Asahi Kasei Corp., and DuPont de Nemours, Inc. leading research and development efforts. Emerging companies such as FiberLean Technologies Ltd. and Yibin Grace Group Co., Ltd. are also contributing to innovation in this field. The market is characterized by ongoing research collaborations between industry and academic institutions, indicating potential for further technological advancements and market expansion.
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shin-Etsu Chemical has developed proprietary MCC-based products for pharmaceutical and food applications, focusing on improving binder performance and erosion control. Their METOLOSE® series of cellulose ethers, including methylcellulose and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, are designed to work synergistically with MCC to enhance binder properties[4]. The company's research has demonstrated that by combining different grades of METOLOSE® with MCC, they can achieve tailored erosion profiles and release kinetics for various formulations[5]. Shin-Etsu has also investigated the impact of MCC particle size and morphology on binder erosion, developing optimized grades for specific applications[6].
Strengths: Diverse portfolio of cellulose-based products; strong focus on synergistic formulations. Weaknesses: May face competition from companies specializing solely in MCC products.
FMC Corp.
Technical Solution: FMC Corp. has developed advanced microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) products specifically designed for controlled release applications in pharmaceutical formulations. Their Avicel® PH series of MCC grades offers tailored particle sizes and moisture contents to optimize binder erosion rates[1]. FMC's research has shown that by carefully controlling the MCC particle size distribution and crystallinity, they can achieve predictable erosion profiles for various drug delivery systems[2]. The company has also explored co-processed MCC formulations, combining MCC with other excipients like silicified microcrystalline cellulose (SMCC), to further enhance binder performance and erosion characteristics[3].
Strengths: Extensive expertise in MCC production and customization; wide range of specialized MCC grades for pharmaceutical applications. Weaknesses: Primarily focused on pharmaceutical sector, potentially limiting applications in other industries.
Core Innovations in MCC-Binder Interactions
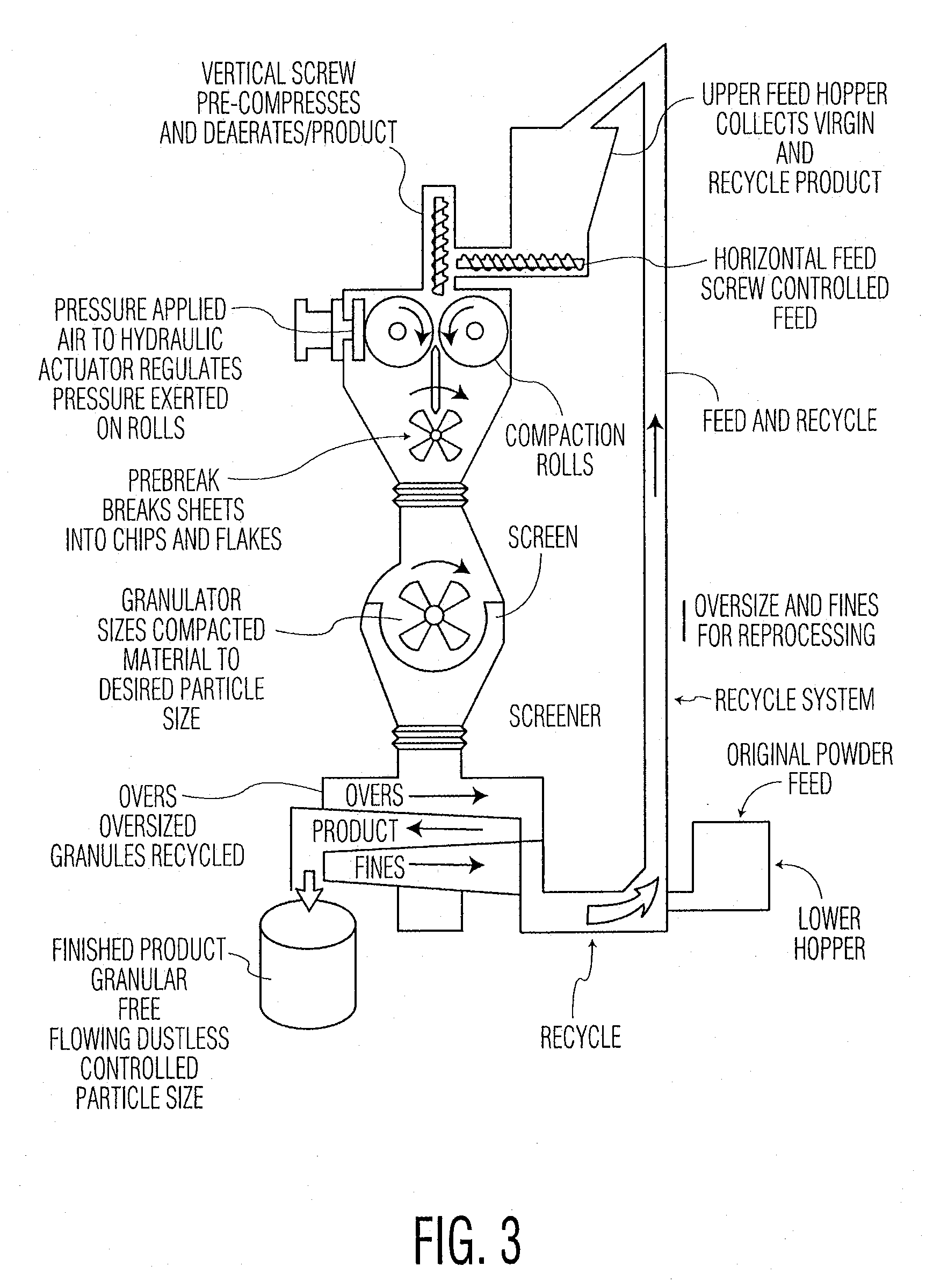
Dry granulation binders, products, and use thereof
PatentInactiveUS20080213360A1
Innovation
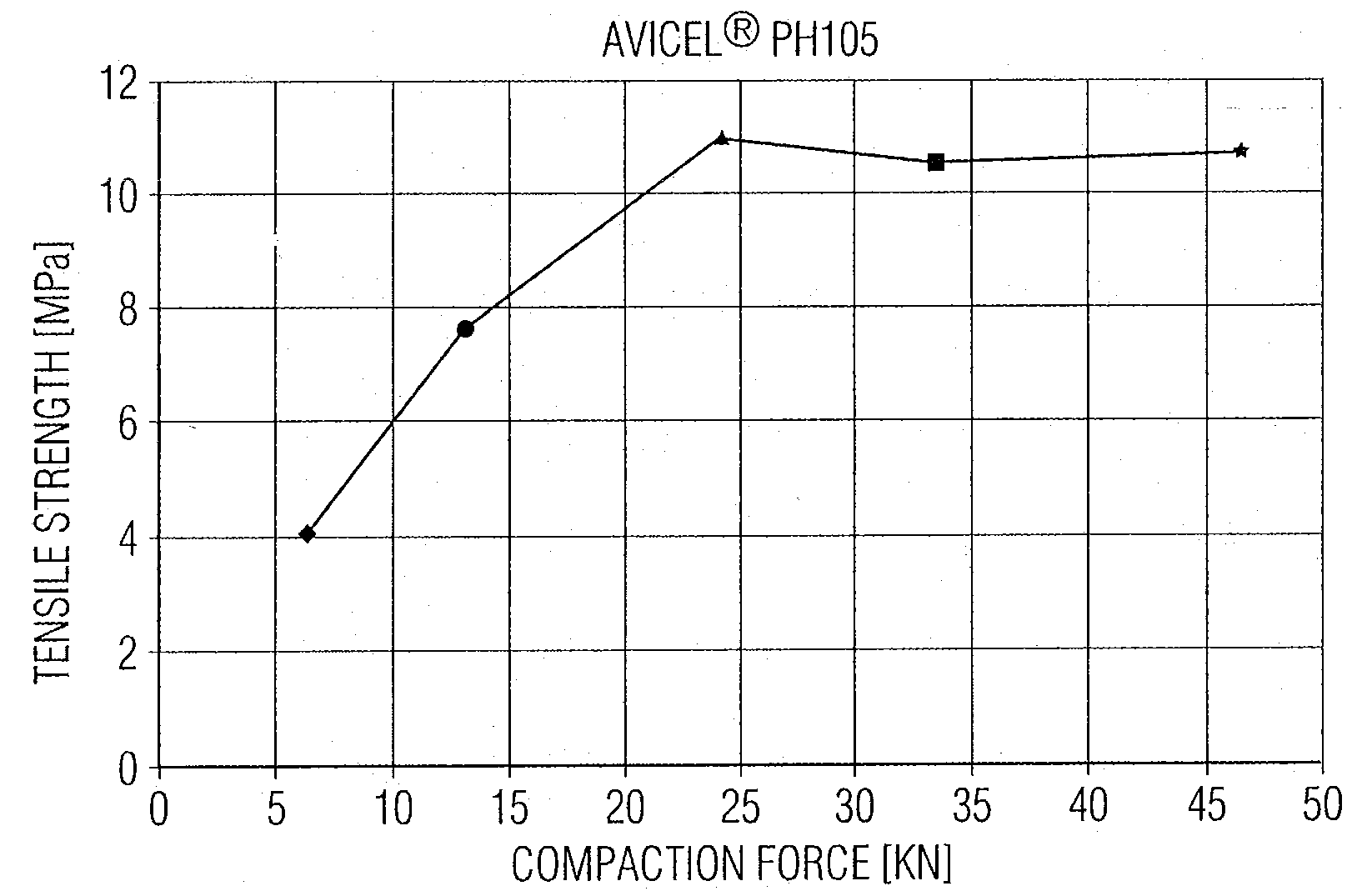
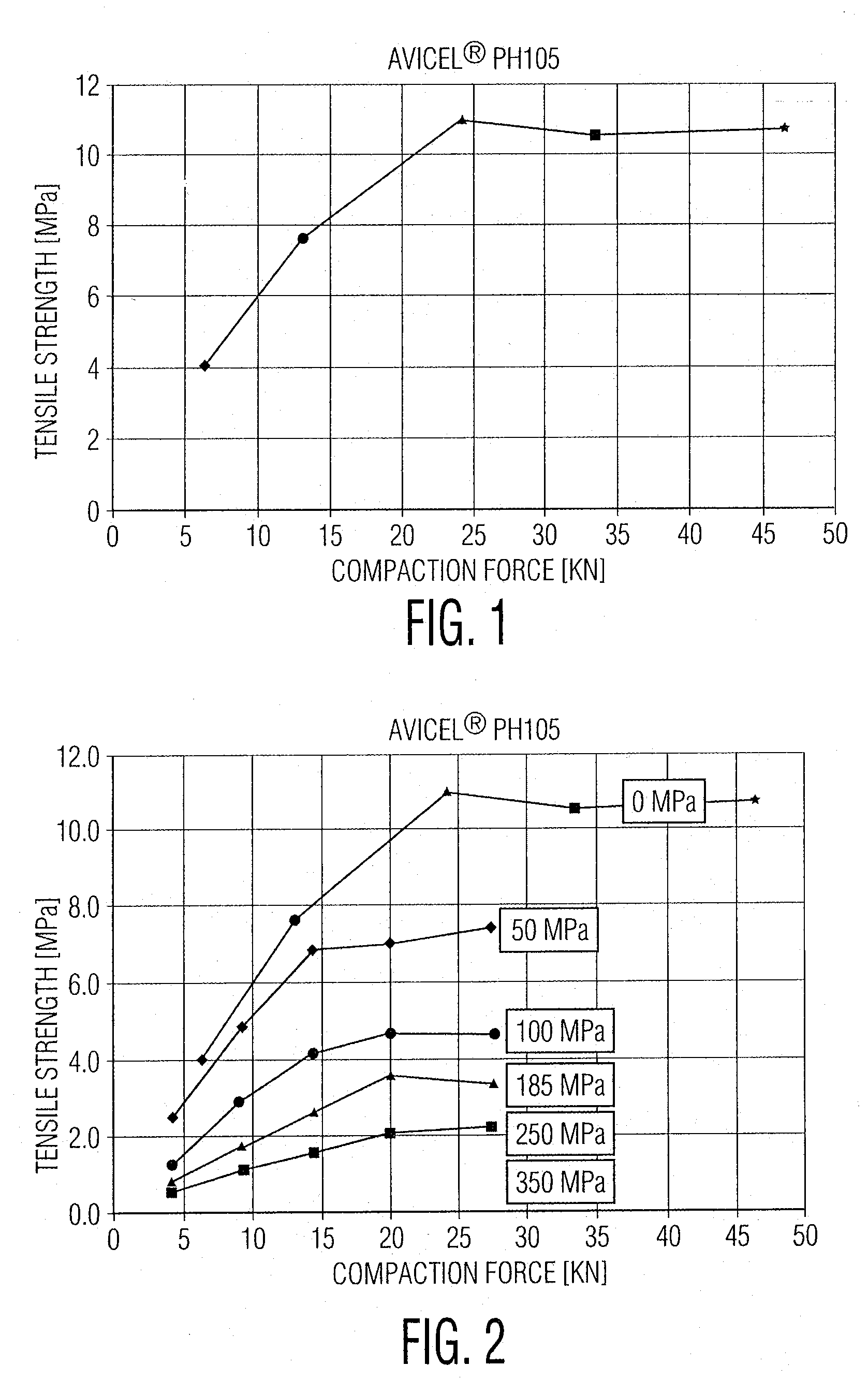
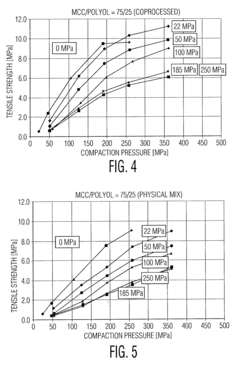
- A microcrystalline cellulose containing binder composition with at least 60 wt% microcrystalline cellulose, co-processed with sugar alcohols or carboxymethyl cellulose, which maintains high primary and secondary tensile strengths after compaction, ensuring sufficient recompactability for multiple compaction steps.
Dry granulation binders, products, and use thereof
PatentWO2008057266A2
Innovation
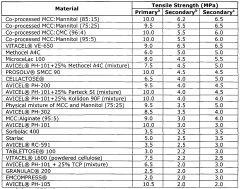
- A microcrystalline cellulose containing binder composition with at least 60 wt% microcrystalline cellulose, co-processed with sugar alcohols or carboxymethyl cellulose, achieving primary and secondary tensile strengths of at least 9.5 MPa and 5.5 MPa respectively, enhancing recompactability for multiple compaction processes.
Environmental Impact of MCC in Binders
The environmental impact of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) in binders is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating its use in various applications. MCC, derived from natural cellulose sources, is generally regarded as an environmentally friendly material due to its biodegradability and renewable nature. However, its production and use in binders can have both positive and negative environmental implications.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using MCC in binders is its potential to reduce the reliance on synthetic, petroleum-based materials. As a natural polymer, MCC can partially or fully replace synthetic binders, leading to a decrease in the carbon footprint associated with binder production. This substitution can contribute to the overall sustainability of products that incorporate these binders.
The biodegradability of MCC is another significant environmental advantage. When products containing MCC-based binders reach the end of their lifecycle, they can decompose more readily than those with synthetic binders. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental burden and aligns with circular economy principles, potentially lowering the accumulation of non-biodegradable waste in landfills and ecosystems.
However, the production of MCC does have some environmental considerations. The process of extracting and refining cellulose to produce MCC requires energy and chemical inputs. While these processes have become more efficient over time, there is still room for improvement in terms of energy consumption and chemical use. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials for MCC production is also crucial to prevent deforestation or competition with food crops.
In the context of binder erosion, the use of MCC can have mixed environmental effects. On one hand, if MCC-based binders are more resistant to erosion, they may extend the lifespan of products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby conserving resources. On the other hand, if MCC-based binders erode more quickly than synthetic alternatives, it could lead to increased material consumption and waste generation.
The water solubility of MCC is another factor to consider. While this property can be advantageous for certain applications, it may also lead to faster degradation of binders in aqueous environments. This could result in the release of cellulose particles into water systems, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. However, the natural origin of these particles generally poses less risk compared to synthetic microplastics.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of MCC in binders is multifaceted. Its use promotes sustainability through biodegradability and renewable sourcing, but careful consideration must be given to production processes, erosion characteristics, and potential effects on ecosystems. As research continues, optimizing the balance between performance and environmental benefits will be key to maximizing the positive impact of MCC in binder applications.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using MCC in binders is its potential to reduce the reliance on synthetic, petroleum-based materials. As a natural polymer, MCC can partially or fully replace synthetic binders, leading to a decrease in the carbon footprint associated with binder production. This substitution can contribute to the overall sustainability of products that incorporate these binders.
The biodegradability of MCC is another significant environmental advantage. When products containing MCC-based binders reach the end of their lifecycle, they can decompose more readily than those with synthetic binders. This characteristic reduces the long-term environmental burden and aligns with circular economy principles, potentially lowering the accumulation of non-biodegradable waste in landfills and ecosystems.
However, the production of MCC does have some environmental considerations. The process of extracting and refining cellulose to produce MCC requires energy and chemical inputs. While these processes have become more efficient over time, there is still room for improvement in terms of energy consumption and chemical use. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials for MCC production is also crucial to prevent deforestation or competition with food crops.
In the context of binder erosion, the use of MCC can have mixed environmental effects. On one hand, if MCC-based binders are more resistant to erosion, they may extend the lifespan of products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby conserving resources. On the other hand, if MCC-based binders erode more quickly than synthetic alternatives, it could lead to increased material consumption and waste generation.
The water solubility of MCC is another factor to consider. While this property can be advantageous for certain applications, it may also lead to faster degradation of binders in aqueous environments. This could result in the release of cellulose particles into water systems, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems. However, the natural origin of these particles generally poses less risk compared to synthetic microplastics.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of MCC in binders is multifaceted. Its use promotes sustainability through biodegradability and renewable sourcing, but careful consideration must be given to production processes, erosion characteristics, and potential effects on ecosystems. As research continues, optimizing the balance between performance and environmental benefits will be key to maximizing the positive impact of MCC in binder applications.
Regulatory Framework for MCC in Binder Applications
The regulatory framework for microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) in binder applications is a complex and evolving landscape that encompasses various international and regional standards. The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies MCC as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), allowing its use in food and pharmaceutical applications. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also approved MCC as a food additive, designating it with the E number E460(i).
In pharmaceutical applications, MCC is widely used as an excipient in tablet formulations. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provide detailed specifications for MCC used in pharmaceutical products. These specifications include parameters such as particle size distribution, bulk density, and moisture content, which are critical for ensuring consistent binder performance and erosion characteristics.
The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) has established guidelines for the development and manufacture of drug substances, including the use of excipients like MCC. These guidelines emphasize the importance of understanding the impact of excipients on drug product quality and performance, which is directly relevant to the study of MCC's effect on binder erosion.
Regulatory bodies also require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their formulations through rigorous testing and documentation. This includes stability studies that assess the long-term performance of binders containing MCC under various environmental conditions. Such studies are essential for understanding how MCC affects binder erosion over time and under different storage conditions.
In the context of environmental regulations, the biodegradability of MCC is an important consideration. As a cellulose-derived material, MCC is generally considered environmentally friendly. However, regulations regarding the disposal and environmental impact of pharmaceutical waste containing MCC may vary by region and should be carefully considered in formulation development.
The regulatory framework also extends to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for the production of MCC and its incorporation into binder formulations. Manufacturers must adhere to strict quality control measures to ensure consistency in MCC properties, which can significantly influence binder erosion characteristics. This includes regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities to verify compliance with GMP standards.
As research continues to elucidate the mechanisms of MCC's effect on binder erosion, regulatory guidelines may evolve to incorporate new findings. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these changes to ensure ongoing compliance and to optimize formulations for improved performance and safety.
In pharmaceutical applications, MCC is widely used as an excipient in tablet formulations. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provide detailed specifications for MCC used in pharmaceutical products. These specifications include parameters such as particle size distribution, bulk density, and moisture content, which are critical for ensuring consistent binder performance and erosion characteristics.
The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) has established guidelines for the development and manufacture of drug substances, including the use of excipients like MCC. These guidelines emphasize the importance of understanding the impact of excipients on drug product quality and performance, which is directly relevant to the study of MCC's effect on binder erosion.
Regulatory bodies also require manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their formulations through rigorous testing and documentation. This includes stability studies that assess the long-term performance of binders containing MCC under various environmental conditions. Such studies are essential for understanding how MCC affects binder erosion over time and under different storage conditions.
In the context of environmental regulations, the biodegradability of MCC is an important consideration. As a cellulose-derived material, MCC is generally considered environmentally friendly. However, regulations regarding the disposal and environmental impact of pharmaceutical waste containing MCC may vary by region and should be carefully considered in formulation development.
The regulatory framework also extends to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for the production of MCC and its incorporation into binder formulations. Manufacturers must adhere to strict quality control measures to ensure consistency in MCC properties, which can significantly influence binder erosion characteristics. This includes regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities to verify compliance with GMP standards.
As research continues to elucidate the mechanisms of MCC's effect on binder erosion, regulatory guidelines may evolve to incorporate new findings. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these changes to ensure ongoing compliance and to optimize formulations for improved performance and safety.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!